 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1907329
德國貨運和物流市場:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2026-2031 年)Germany Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
德國貨運和物流市場預計將從 2025 年的 2,213.7 億美元成長到 2026 年的 2,279.9 億美元,到 2031 年達到 2,641.7 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 2.99%。
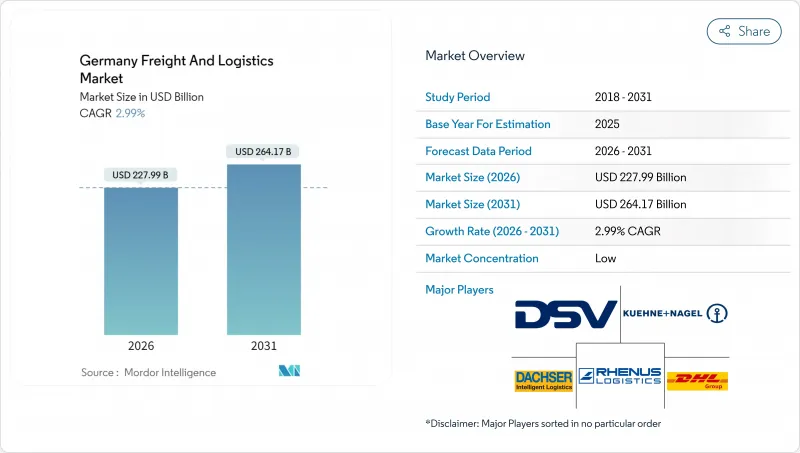
這一溫和的成長率反映了圍繞電子商務履約、出口導向製造業走廊以及提高道路運輸碳排放成本的歐洲綠色交易規則而形成的成熟生態系統的重組。到2030年,鐵路激勵措施總額將達到17億歐元(19億美元),加上每噸55歐元(60.7美元)的碳價穩步上漲,正促使托運人轉向多式聯運解決方案,同時仍依賴道路運輸進行靈活的短途運輸。同時,宅配、速遞和小包裹(CEP)產業正在蓬勃發展,這得益於87%的消費者網路購物滲透率、人均小包裹密度超過54件以及都市區倉庫自動化投資的加速成長。日益嚴重的司機短缺(到2025年將有7萬個職缺)正在加劇卡車運輸能力緊張並推高工資,促使承運人實施路線最佳化軟體並試用自動駕駛場內牽引車。在這些結構性變化中,憑藉其位於歐洲中部的位置、41000公里的高速公路網路和世界一流的港口,德國貨運和物流市場繼續支持洲際貿易流動。
德國貨運及物流市場趨勢及洞察
B2C電子商務小包裹激增
2024年,德國的電子商務滲透率將達到87%,每年處理45億個小包裹。這將形成一個密集的「最後一公里」配送網路,平均每位居民每年要接收54次配送。受亞馬遜生鮮(Amazon Fresh)和Rewe等公司當日達服務的擴張推動,生鮮平台將年增23%。為此,法蘭克福正在試行興建以路面電車為基礎的配送中心,而柏林、漢堡和慕尼黑則在試辦停車場微型配送中心。小包裹聚合商也積極回應,安裝了每小時可處理3萬個包裹的高速分揀機,並擴大了電動配送車的規模,以符合低排放區的相關規定。在「雙十一」和聖誕節等購物高峰期,都市區道路擁擠不堪,這進一步凸顯了市政當局對都市區包裹收集規劃的重視。小小包裹的持續湧入也進一步強化了機器人技術、人工智慧驅動的需求預測以及靈活的輪班安排在包裹配送網路中的戰略價值。
製造業出口的韌性
儘管全球經濟波動,但由於多元化的出口市場和關鍵原料的近岸外包,德國工廠在2024年仍實現了1.56兆歐元(1.72兆美元)的出口額。汽車製造商將其一級供應商集中在巴伐利亞州和巴登-符騰堡州組裝廠方圓500公里以內,從而縮短了運輸前置作業時間,並穩定了準時制(JIS)生產流程。機械和化學產品出口商在漢堡-慕尼黑和萊茵-魯爾走廊簽訂了長期鐵路運輸契約,使貨車周轉率提高了15%,並避免了柴油價格上漲對利潤率的影響。可預測的貨運走廊使物流供應商能夠運作高運力班次,並與碼頭營運商協商批量折扣。出口的可靠性持續支撐著德國的貨運和物流市場,維持了對溫控貨櫃、特殊計劃貨物設備和海關合規服務的需求。
司機短缺和勞動力老化
預計到2025年,德國的司機缺口將達到7萬人,其中39%的執照擁有者年齡超過55歲。這導致車輛運轉率下降,迫使德國在高峰期運作7%至10%的牽引車。雖然每年有1.8萬名新司機從培訓學校畢業,但超過2.5萬人離開這個行業,加劇了技能缺口。儘管運輸公司已將工資提高了10%並提供入職獎金,但夜班、長時間離家以及嚴格的監管等生活方式障礙仍然難以吸引人才。作為臨時解決方案,貨主們正在錯開送貨時間、包租鐵路、在倉庫內測試自動駕駛穿梭車,並將司機集中在高速公路路段。在自動化和移民政策等解決方案出現之前,這種司機短缺限制了德國貨運和物流市場的成長潛力。
細分市場分析
到2025年,製造業將佔德國貨運和物流市場佔有率的28.37%,物流支出將達到628.1億美元。該行業的韌性源自於德國在汽車、機械和加工產業的深厚專業知識,以及這些產業所依賴的有序準時制物流模式。庫存過剩和工廠正常運作的要求推動了長期、多服務合約的簽訂,涵蓋生產線旁配送、可回收包裝和子組裝等領域。同時,批發和零售業雖然目前規模較小,但預計在2026年至2031年間將以3.18%的複合年成長率成長,因為全通路模式推動了門市、暗店和直銷通路之間的快速補貨。
依賴重型卡車和預製模組現場作業順序的建築物流,雖然成長緩慢,但已形成一個穩定且持續的行業。農業、林業和漁業在收穫尖峰時段期需要低溫運輸能力和準時交付,這推動了對冷藏拖車和多式聯運生鮮產品至城市市場運輸通道的需求。由於德國的能源轉型政策導致風能和太陽能發電廠零件運輸量增加,石油、天然氣、採礦和採石業略有下降。從醫療技術到氫燃料電池組件等新興產業,形成了複雜且溫控的微型物流,為專業的第三方物流業者創造了有利的市場環境。
儘管貨運代理仍將佔據主導地位,預計到2025年將佔59.29%的市場佔有率,但宅配、速遞和小包裹業務預計將以3.44%的複合年成長率(CAGR)實現最快成長,這主要得益於電子商務習慣帶來的住宅配送量成長。此外,倉儲和儲存產業的成長也對其產生積極影響,因為企業需要消化安全庫存以應對供應商中斷的情況。貨運代理產業正在透過將數位預訂平台與多模態視覺化工具相結合進行轉型,使中小型出口商無需擁有運輸資產即可獲得優質的空運和鐵路運輸服務。
在德國貨運和物流市場,「其他」類別中附加價值服務(例如套件組裝、快速組裝、退貨處理)仍然備受重視,與製造業的精益生產實踐相輔相成。由於德國消費群龐大,國內小宅配快遞 (CEP) 服務佔了 66.56% 的市場。同時,歐洲單一市場內的跨境CEP 航線成長更為強勁,這主要得益於面向波蘭、法國和斯堪的納維亞半島消費者的營運商。貨運細分市場的表現則喜憂參半:大宗貨車運輸受到碳排放稅的嚴重衝擊,而專門針對汽車的定期配送服務則帶來了穩定的合約收入。第三方物流業者之間的機會主義整合,例如 DSV 收購 DB Schenker,正在增強其與小包裹配送代理商和港口碼頭的議價能力。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 人口統計數據
- 按經濟活動分類的GDP分配
- 按經濟活動分類的GDP成長
- 通貨膨脹
- 經濟表現及概況
- 電子商務產業的趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 運輸和倉儲業的GDP
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 卡車運輸營運成本
- 卡車運輸車隊規模(按類型)
- 主要卡車供應商
- 物流績效
- 透過交通方式分享
- 海運船隊運力
- 班輪運輸連接
- 停靠港口和演出
- 貨運費率趨勢
- 貨物噸位趨勢
- 基礎設施
- 法規結構(公路和鐵路)
- 法規結構(海事和航空)
- 價值鍊和通路分析
- 市場促進因素
- 電子商務(B2C)小包裹遞送業務快速成長
- 製造業出口的韌性
- 中小型企業 3PL 外包的擴展
- 與歐盟綠色交易相關的模式轉換促進措施
- 擴展我們的按需倉儲平台
- 由OEM廠商支持的電池物流走廊的電動車供應鏈
- 市場限制
- 駕駛人和勞動力老化
- 高速公路通行費上漲和碳定價
- 都市區缺乏收集點
- 內河水位過低造成的交通中斷
- 市場創新
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 終端用戶產業
- 農業、漁業、林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油天然氣、採礦和採石
- 批發和零售
- 其他
- 物流職能
- 宅配、速遞和小包裹(CEP)
- 按目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 按目的地
- 貨運代理
- 透過交通工具
- 航空
- 海路和內河航道
- 其他
- 透過交通工具
- 貨物運輸
- 透過交通工具
- 航空
- 管道
- 鐵路
- 路
- 海路和內河航道
- 透過交通工具
- 倉儲
- 透過溫度控制
- 非溫控型
- 溫度控制
- 透過溫度控制
- 其他服務
- 宅配、速遞和小包裹(CEP)
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 關鍵策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- A. Hartrodt
- AP Moller-Maersk
- Amazon
- BLG Logistics Group AG & Co. KG
- CMA CGM Group(Including CEVA Logistics)
- DACHSER
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- Emons Services GmbH
- FedEx
- Fiege Logistik Holding Stiftung and Co. KG
- GEODIS
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hermes Europe GmbH
- International Distributions Services(Including GLS)
- Kuehne+Nagel
- La Poste Group
- Rhenus Group
- ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Germany freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 221.37 billion in 2025 to USD 227.99 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 264.17 billion by 2031 at 2.99% CAGR over 2026-2031.

The moderate growth pace reflects an already-mature ecosystem that is repositioning around e-commerce fulfillment, export-oriented manufacturing corridors, and European Green Deal rules that raise carbon costs for road haulage. Rail incentive packages worth EUR 1.7 billion (USD 1.9 billion) through 2030, coupled with steadily climbing carbon prices of EUR 55 (USD 60.7) per tonne, are steering shippers toward intermodal solutions while still relying on road for flexible, short-haul moves. At the same time, the courier, express, and parcel (CEP) wave gains momentum from 87% consumer online-shopping penetration, pushing parcel density past 54 items per capita and accelerating automation investments in urban depots. Rising driver vacancies-70,000 open positions in 2025-tighten trucking capacity and elevate wages, motivating carriers to adopt route-optimization software and test autonomous yard tractors. Amid these structural shifts, the Germany freight and logistics market continues to leverage its central European location, 41,000 km highway grid, and world-class ports to anchor continental trade flows.
Germany Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce B2C Parcel Boom
Germany's e-commerce penetration hit 87% in 2024, translating into 4.5 billion annual parcels and driving a dense last-mile network that now averages 54 deliveries per resident. Grocery platforms grew 23% year over year as Amazon Fresh and Rewe expanded same-day services, prompting operators to pilot tram-based drop-offs in Frankfurt and micro-depots in parking structures across Berlin, Hamburg, and Munich. Parcel integrators responded by installing high-speed sorters capable of 30,000 items per hour and by adding electric delivery vans to comply with low-emission-zone rules. Seasonal peaks such as Singles' Day and Christmas overloaded city streets, making urban consolidation schemes a priority for municipalities. The sustained flow of small parcels reinforces the strategic value of robotics, AI-driven demand forecasting, and flexible shift scheduling for CEP networks.
Manufacturing Export Resilience
German factories shipped EUR 1.56 trillion (USD 1.72 trillion) worth of goods in 2024 despite global volatility, thanks to diversified destination markets and near-shoring of critical inputs. Automakers clustered tier-1 suppliers within 500 km of final-assembly plants in Bavaria and Baden-Wurttemberg, trimming transport lead times and stabilizing just-in-sequence flows. Machinery and chemical exporters locked in long-term rail contracts on the Hamburg-Munich and Rhine-Ruhr corridors, improving wagon-turnaround rates by 15% and shielding margins from diesel price spikes. The predictable freight corridors enable logistics providers to run high-capacity shuttles and negotiate volume-based discounts with terminal operators. Export reliability continues to underpin the Germany freight and logistics market, sustaining demand for temperature-controlled containers, specialized project cargo gear, and customs compliance services.
Driver Shortage and Aging Workforce
Vacancies hit 70,000 in 2025, with 39% of licensed truckers older than 55, eroding fleet utilization and forcing companies to park 7-10% of tractors during peak weeks. Training schools graduate only 18,000 new drivers annually, against retirement outflows above 25,000, widening the skills gap. Carriers raised wages 10% and offered sign-on bonuses, but lifestyle deterrents-night work, days away from home, dense regulation-limit attraction. As a stop-gap, shippers stagger delivery windows, charter rail blocks, and trial autonomous shuttles inside warehouse yards to free humans for open-road segments. The shortage constrains the Germany freight and logistics market's growth potential until automation or immigration solutions emerge.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing 3PL Outsourcing Among Mittelstand
- EU Green Deal-Linked Modal Shift Incentives
- Rising Motorway Tolls and Carbon Pricing
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing accounted for 28.37% of Germany freight and logistics market share in 2025, translating into USD 62.81 billion in logistics spend. The segment's robustness derives from Germany's deep specialization in autos, machinery, and process industries that rely on sequenced just-in-time flows. Outsized inventory values and plant uptime requirements foster long-term, multi-service contracts for line-side delivery, returnable packaging, and sub-assembly. In contrast, wholesale and retail trade, while smaller at present, registers a 3.18% CAGR (2026-2031) as omnichannel models force rapid replenishment between stores, dark stores, and direct-to-consumer channels.
Construction logistics hinges on heavy-lift trucking and on-site sequencing for prefabricated modules, creating a steady if slower-growing slice of activity. Agriculture, Fishing & Forestry calls for cold chain capacity and time-critical windows during harvest peaks, bolstering reefer trailer demand and multimodal fresh-produce corridors to urban markets. Oil, Gas, Mining & Quarrying edges downward as Germany's Energiewende moves tonnage toward components for wind and solar installations. Emerging verticals, from medical technology to hydrogen fuel-cell components, add complexity and temperature-controlled micro-flows that favor specialized 3PLs.
Freight Transport remained the cornerstone at 59.29% share in 2025; however, the Courier, Express, and Parcel arm is forecast to post the quickest expansion at 3.44% CAGR between 2026-2031, propelled by residential delivery volumes tied to the e-commerce habit. Growth also favors Warehousing & Storage, which absorbs safety stocks as firms hedge against supplier shocks. Freight Forwarding adapts by bundling digital booking portals with multimodal visibility tools, enabling smaller exporters to tap premium air and rail services without owning transportation assets.
The Germany freight and logistics market continues to prioritize value-added services such as kitting, light assembly, and returns processing under the Others banner, all of which complement manufacturers' lean-production mandates. Domestic CEP registered a 66.56% share thanks to Germany's dense consumer base, yet cross-border CEP lanes inside the European single market post stronger growth as merchants court Polish, French, and Nordic shoppers. Freight Transport sub-segments show diverging fortunes: bulk trucking feels the brunt of carbon taxes, while specialized automotive milk-runs deliver stable contract revenue. Opportunistic consolidation among 3PLs, exemplified by DSV's purchase of DB Schenker, amplifies bargaining power over parcel integrators and port terminals.
The Germany Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- A. Hartrodt
- A.P. Moller - Maersk
- Amazon
- BLG Logistics Group AG & Co. KG
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DACHSER
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- Emons Services GmbH
- FedEx
- Fiege Logistik Holding Stiftung and Co. KG
- GEODIS
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hermes Europe GmbH
- International Distributions Services (Including GLS)
- Kuehne+Nagel
- La Poste Group
- Rhenus Group
- ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 E-Commerce B2C Parcel Boom
- 4.25.2 Manufacturing Export Resilience
- 4.25.3 Growing 3PL Outsourcing Among Mittelstand
- 4.25.4 EU Green Deal-Linked Modal Shift Incentives
- 4.25.5 On-Demand Warehousing Platforms Scaling Up
- 4.25.6 OEM-Backed Battery-Logistics Corridors for EV Supply Chains
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Driver Shortage and Ageing Workforce
- 4.26.2 Rising Motorway Tolls and Carbon Pricing
- 4.26.3 Limited Urban Consolidation Hubs
- 4.26.4 Inland Waterway Low-Water Disruptions
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 A. Hartrodt
- 6.4.2 A.P. Moller - Maersk
- 6.4.3 Amazon
- 6.4.4 BLG Logistics Group AG & Co. KG
- 6.4.5 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.6 DACHSER
- 6.4.7 DHL Group
- 6.4.8 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.9 Emons Services GmbH
- 6.4.10 FedEx
- 6.4.11 Fiege Logistik Holding Stiftung and Co. KG
- 6.4.12 GEODIS
- 6.4.13 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.14 Hermes Europe GmbH
- 6.4.15 International Distributions Services (Including GLS)
- 6.4.16 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.17 La Poste Group
- 6.4.18 Rhenus Group
- 6.4.19 ROHLIG SUUS Logistics SA
- 6.4.20 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




