 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906035
中東和非洲貨運物流市場:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2026-2031 年)Middle East And Africa Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
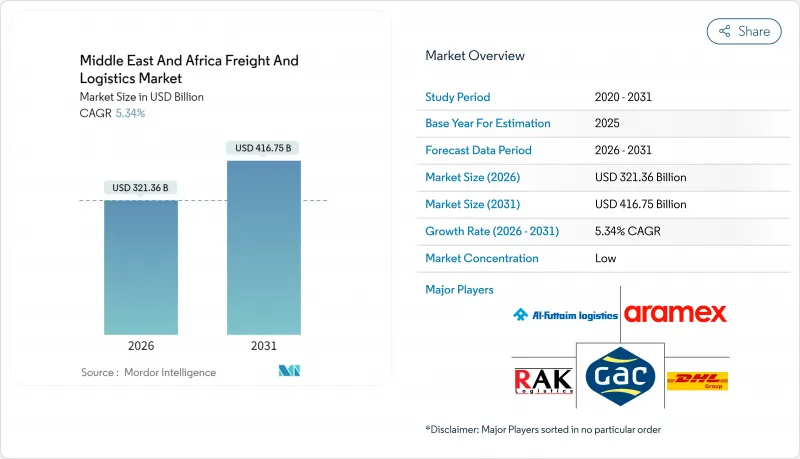
預計到 2026 年,中東和非洲的貨運和物流市場規模將達到 3,213.6 億美元。
這意味著從 2025 年的 3,050.7 億美元成長到 2031 年的 4,167.5 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的年複合成長率(CAGR)為 5.34%。
這一成長前景得益於該地區連接亞洲、歐洲和非洲的戰略位置,以及因紅海航道中斷而推動的大規模基礎設施投資和永久性運力擴張。電子商務的擴張、新型多模態走廊的開發以及低溫運輸需求的激增,正在提升基準和單次貨運收入。主權財富基金、自由貿易協定和數位化貨運平台在緩解地緣政治波動的同時,也加劇了競爭。那些能夠最大限度地提高網路密度、採用先進技術並實踐永續的營運商,將有望獲得豐厚的回報。
中東及非洲貨運物流市場趨勢及洞察
電子商務和跨境零售的快速成長
跨境電商正在提升最後一公里配送的頻率,其中國內宅配(CEP)佔貨運量的67.88%,而國際包裹遞送預計到2030年將以5.77%的複合年成長率成長。物流業者正在擴展自動化分類中心和多承運商API,這些設施連接傑貝阿里港和阿勒馬克圖姆國際機場。沿岸地區的營運商正在實施人工智慧路線規劃,並與當地大學合作,以應對數位人才短缺的問題。全通路零售商要求整合履約,並將物流量轉移到快遞網路。
對多模態物流基礎設施的巨額投資
沙烏地阿拉伯計劃在2030年投資1,333億美元用於港口、機場和鐵路建設,其中包括在NEOM港建設首批全自動起重機的計劃,該項目預計將於2026年投入運作。杜拜環球港務集團(DP World)2024年25億美元的營運規模和創紀錄的200億美元收入,顯示了私人資本的大力投入。自動化和可再生能源的整合正在縮短船舶停留時間,改善成本曲線,並重塑轉運競爭力。
公路、鐵路和港口基礎設施不平衡
由於內陸非洲國家依賴沿海門戶,基礎設施不平衡推高了物流成本。非洲開發銀行指出,道路密度不均和通用海上資產資金不足是長期存在的瓶頸問題。公私合營走廊和收費公路融資框架在礦業走廊以外地區吸引的私人資本有限。運輸能力集中在少數幾個樞紐,增加了其受天氣和勞工動盪影響的風險,阻礙了其向內陸市場的滲透。
細分市場分析
2025年,批發和零售貿易佔總收入的33.92%,而製造業由於本地化和工業園區的擴張,在2031年之前將以5.58%的複合年成長率實現最快成長。石油、天然氣和礦業物流依然規模龐大,這得益於大宗商品分銷和能源安全支出。建築物流受益於大型基礎設施計劃,而農業和食品運輸則在糧食安全戰略的推動下不斷擴張。
奈及利亞耗資200億美元的奧吉迪格本工業園區凸顯了對專業重型起重和計劃貨物運輸服務的需求。準時制生產需要同步的物料流入,這推動了對即時追蹤和預測性庫存分析的需求。
截至2025年,貨運代理將佔中東和非洲貨運物流市場59.21%的佔有率,而宅配、速遞和小包裹運輸將推動市場成長,到2031年複合年成長率將達到5.57%。公路散裝運輸將保持其市場地位,而受電子商務的推動,限時小包裹運輸將有所成長。貨運代理和倉儲業將持續穩定成長,其中溫控倉儲利潤率較高。歸類於「其他活動」的技術主導附加價值服務將快速擴張,從而推動對端到端數位化整合的需求。
國際貨運代理商正投入數十億美元資金建設其樞紐,而 Aramex 將藉助 ADQ 的支持鞏固其區域市場佔有率。機器人技術和人工智慧庫存管理工具將進一步拉動沿岸地區倉庫的生產力差距,打造一個集包裹遞送、交叉轉運和貨運代理於一體的平台。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 電子商務和跨境零售的快速成長
- 對多模態物流基礎設施的大規模投資
- 自由貿易協定(FTA)的擴展和新興貿易走廊的成長
- 藥品和生鮮食品的低溫運輸需求
- 利用倉庫自動化彌補勞力短缺
- 快速採用數位貨運平台和即時視覺化工具
- 市場限制
- 道路、鐵路和港口基礎設施不完善
- 複雜的海關規定和邊境延誤
- 紅海/蘇伊士運河瓶頸造成的交通中斷
- 促進要素短缺和本地化政策
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 地緣政治與疫情的影響
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過物流功能
- 宅配、特快和小包裹 (CEP)
- 按目的地類型
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 按目的地類型
- 貨運代理
- 透過交通工具
- 航空
- 海路和內河航道
- 其他
- 透過交通工具
- 貨物運輸
- 透過交通工具
- 航空
- 鐵路
- 路
- 海路和內河航道
- 管道
- 透過交通工具
- 倉儲和存儲
- 透過溫度控制
- 非溫控型
- 溫度控制
- 透過溫度控制
- 其他服務
- 宅配、特快和小包裹 (CEP)
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 農業、漁業、林業
- 建造
- 製造業
- 石油天然氣、採礦和採石
- 批發和零售
- 其他
- 按地區
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 卡達
- 阿曼
- 科威特
- 奈及利亞
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- DHL
- Aramex
- Gulf Agency Company(GAC)
- RAK Logistics
- Al-Futtaim Logistics
- Almajdouie Group
- Gulf Warehousing Company
- RSA Global
- Saudi Transport & Investment Co.(Mubarrad)
- City Logistics
- BLG Logistics
- Kuehne+Nagel
- CEVA Logistics
- DSV
- Rhenus Logistics
- ATC Allied Transport
- Barloworld Logistics
- Unitrans Supply Chain Solutions(Pty)Ltd
- Cargo Carriers(Pty)Limited
- Compass Logistics International
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Middle East And Africa Freight And Logistics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 321.36 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 305.07 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 416.75 billion, growing at 5.34% CAGR over 2026-2031.

The growth outlook flows from the region's pivotal position linking Asia, Europe, and Africa, combined with heavy infrastructure spending and permanent capacity upgrades triggered by Red Sea shipping disruptions. E-commerce expansion, the rollout of new multimodal corridors, and a surge in cold-chain demand strengthen baseline tonnage and yield per shipment. Sovereign wealth funds, free trade agreements, and digital freight platforms reinforce competitive intensity while mitigating geopolitical volatility. Operators that maximize network density, technology adoption, and sustainable practices are positioned to capture outsized returns.
Middle East And Africa Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce boom and cross-border retail
Cross-border e-commerce lifts last-mile shipment frequency, with domestic CEP covering 67.88% of traffic while international CEP advances at a 5.77% CAGR through 2030. Logistics providers are scaling automated sortation hubs and multi-carrier APIs that link Jebel Ali Port to Al Maktoum International Airport. Gulf operators deploy AI routing and collaborate with local universities to fill digital talent gaps. Omnichannel retailers demand integrated fulfillment that merges warehousing, click-and-collect, and door delivery, shifting volume toward express networks.
Mega-investments in multimodal logistics infrastructure
Saudi Arabia earmarked USD 133.3 billion for ports, airports, and railways through 2030, including Port of NEOM's first fully automated cranes slated for 2026 launch. DP World's USD 2.5 billion program and record USD 20 billion 2024 revenue signal deep private capital engagement. Automation and renewable energy integration compress dwell times and improve cost curves, reshaping transshipment competitiveness.
Uneven road, rail, and port infrastructure
Infrastructure gaps raise logistics costs for landlocked African economies relying on coastal gateways. The African Development Bank cites road density disparities and underfunded common-user marine assets as persistent bottlenecks. PPP corridors and toll finance frameworks attract limited private capital outside mining routes. Concentrated capacity in a handful of hubs heightens vulnerability to weather or labor stoppages, stalling hinterland market penetration.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cold-chain demand for pharma and perishables
- Rapid adoption of digital freight platforms and real-time visibility tools
- Red Sea/Suez chokepoint disruptions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Wholesale and retail trade contributed 33.92% of 2025 revenue, while manufacturing posts the fastest 5.58% CAGR through 2031 as localization and industrial parks proliferate. Oil, gas, and mining logistics remain sizable, supported by commodity flows and energy security spending. Construction logistics taps infrastructure mega-projects, and agri-food shipments expand under food-security strategies.
Nigeria's USD 20 billion Ogidigben industrial park underscores demand for specialized heavy-lift and project cargo services. Just-in-time production requires synchronized inbound material flows, elevating demand for real-time tracking and predictive inventory analytics
Freight transport retained 59.21% of the Middle East and Africa freight and logistics market in 2025, while courier, express, and parcel leads growth at 5.57% CAGR to 2031. Road-based bulk remains foundational, yet time-definite parcels capture e-commerce tailwinds. Freight forwarding and warehousing post steady gains, and temperature-controlled storage earns premium margins. Technology-driven value-added services under "other" activities scale quickly, feeding demand for end-to-end digital orchestration.
International integrators pledge nine-figure capex for hubs, whereas Aramex leverages ADQ backing to consolidate regional share. Robotics and AI inventory tools widen productivity differentials in Gulf warehouses, creating platforms that fuse parcel delivery, cross-dock, and forwarding under a single interface.
The Middle East and Africa Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by Logistics Function (Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, and More), End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others), Geography (United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, and More). Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL
- Aramex
- Gulf Agency Company (GAC)
- RAK Logistics
- Al-Futtaim Logistics
- Almajdouie Group
- Gulf Warehousing Company
- RSA Global
- Saudi Transport & Investment Co. (Mubarrad)
- City Logistics
- BLG Logistics
- Kuehne + Nagel
- CEVA Logistics
- DSV
- Rhenus Logistics
- ATC Allied Transport
- Barloworld Logistics
- Unitrans Supply Chain Solutions (Pty) Ltd
- Cargo Carriers (Pty) Limited
- Compass Logistics International
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 E-Commerce Boom and Cross-Border Retail
- 4.2.2 Mega-Investments in Multimodal Logistics Infrastructure
- 4.2.3 Growth of FTAs and Emerging Trade Corridors
- 4.2.4 Cold-Chain Demand for Pharma and Perishables
- 4.2.5 Warehouse Automation to Offset Labour Shortages
- 4.2.6 Rapid Adoption of Digital Freight Platforms and Real-Time Visibility Tools
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Uneven Road, Rail and Port Infrastructure
- 4.3.2 Complex Customs Rules and Border Delays
- 4.3.3 Red-Sea/Suez Chokepoint Disruptions
- 4.3.4 Driver Shortages and Localisation Policies
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Geopolitics & Pandemics
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Logistics Function
- 5.1.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.1.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.1.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.1.1.2 International
- 5.1.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.1.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.1.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.1.2.1.1 Air
- 5.1.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.1.2.1.3 Others
- 5.1.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.1.3 Freight Transport
- 5.1.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.1.3.1.1 Air
- 5.1.3.1.2 Rail
- 5.1.3.1.3 Road
- 5.1.3.1.4 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.1.3.1.5 Pipelines
- 5.1.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.1.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.1.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.1.4.1.1 Non-Temperatured Control
- 5.1.4.1.2 Temperatured Control
- 5.1.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.1.5 Other Services
- 5.1.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2 By End User Industry
- 5.2.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.2.2 Construction
- 5.2.3 Manufacturing
- 5.2.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.2.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.3 Qatar
- 5.3.4 Oman
- 5.3.5 Kuwait
- 5.3.6 Nigeria
- 5.3.7 South Africa
- 5.3.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL
- 6.4.2 Aramex
- 6.4.3 Gulf Agency Company (GAC)
- 6.4.4 RAK Logistics
- 6.4.5 Al-Futtaim Logistics
- 6.4.6 Almajdouie Group
- 6.4.7 Gulf Warehousing Company
- 6.4.8 RSA Global
- 6.4.9 Saudi Transport & Investment Co. (Mubarrad)
- 6.4.10 City Logistics
- 6.4.11 BLG Logistics
- 6.4.12 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.13 CEVA Logistics
- 6.4.14 DSV
- 6.4.15 Rhenus Logistics
- 6.4.16 ATC Allied Transport
- 6.4.17 Barloworld Logistics
- 6.4.18 Unitrans Supply Chain Solutions (Pty) Ltd
- 6.4.19 Cargo Carriers (Pty) Limited
- 6.4.20 Compass Logistics International
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment








