 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1911343
印尼潤滑油市場:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2026-2031年)Indonesia Lubricants - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
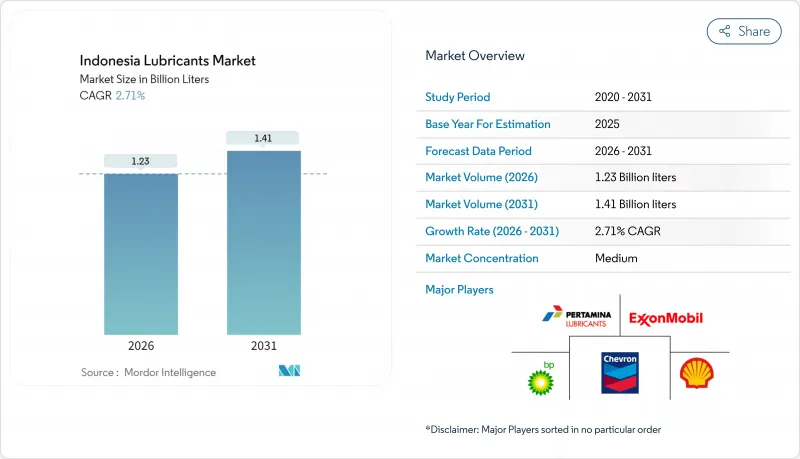
2025年印尼潤滑油市場價值為12億公升,預計到2031年將達到14.1億公升,而2026年為12.3億公升,預測期(2026-2031年)複合年成長率為2.71%。
即便電動車政策即將訂定,印尼市場對潤滑油的需求依然強勁,這反映了印尼工業的穩定擴張、完善的基礎設施規劃以及龐大的汽車保有量。雖然礦物油產品仍佔總銷售量的三分之二,但隨著車隊營運商尋求更低的生命週期營運成本,延長換油週期的趨勢日益明顯,高階合成油的市場需求也加速成長。從殼牌新建的潤滑脂工廠到埃克森美孚的現場MACHINEXT服務,跨國公司的產能擴張充分展現了技術、在地化生產和分銷網路如何塑造競爭優勢。同時,強制性的SNI認證、B40生物柴油的引入以及原油價格的波動加劇了成本壓力,促使企業升級產品系列,轉向防腐蝕添加劑和生物基混合油。印尼擁有17,000個島嶼,供應鏈的複雜性帶來了物流方面的挑戰,尤其是在為偏遠地區的高價值採礦和工業應用提供潤滑油方面。
印尼潤滑油市場趨勢及洞察
汽車擁有量不斷增加
印尼汽車產業的蓬勃發展正推動潤滑油消費,這主要得益於乘用車數量的成長以及物流網路中商用車輛車隊的現代化。根據國際汽車製造商協會(OICA)預測,印尼2024年的汽車產量將達到119萬輛。自動擋摩托車的普及催生了對專用於自動擋應用的潤滑油配方的需求。電子商務的擴張和「最後一公里」配送的盛行提高了車輛運轉率,導致潤滑油更換頻率高於傳統消費模式。政府大力推廣電動車,並計劃在2040年前逐步淘汰內燃機,這在一定程度上限制了汽車潤滑油需求的成長。區域分銷網路難以有效服務印尼的離島島嶼,造成供應瓶頸,阻礙了新興汽車叢集的市場滲透。
工業和製造業的快速成長
印尼製造業的蓬勃發展與金屬加工、發電和重型機械應用領域工業潤滑油消費量的成長直接相關。作為全球最大的鎳生產國,印尼進一步擴大了冶煉過程中對特殊金屬加工液和液壓系統潤滑油的需求。製造業投資催生了新的工業基礎設施,需要初始潤滑油加註和持續的維護保養。埃克森美孚於2024年6月推出的MACHINEXT原位潤滑管理技術,展示了數位化最佳化如何延長設備使用壽命並降低整體擁有成本。雖然製造業集中在爪哇島帶來了物流優勢,但也限制了資源豐富的周邊地區的成長潛力,這些地區的基礎建設落後於工業投資。
宏觀經濟和商品價格波動抑制了產能運轉率。
受宏觀經濟不確定性和商品價格波動的影響,印尼潤滑油產業面臨產能運轉率挑戰,抑制了工業活動和消費支出。目前,印尼國內潤滑油產業的運轉率約為60%。全球供應鏈中斷和匯率波動影響基礎油進口成本,迫使製造商調整定價策略並考慮其對需求彈性的影響。棕櫚油和採礦等出口依賴型產業會經歷週期性衰退,導致商品價格疲軟時期工業潤滑油消費量下降。製造業產能集中在爪哇島,造成區域發展不平衡,外島企業在經濟動盪時期難以確保供應鏈的可靠性。強制性SNI標準下的監管合規成本增加了中小企業在利潤率壓縮時期難以承受的營運成本。
細分市場分析
到2025年,汽車機油將佔印尼潤滑油市場佔有率的35.80%,這反映了印尼以車輛為中心的潤滑油消費模式以及內燃機在乘用車和商用車領域的主導地位。液壓油將成為成長最快的產品類型,2026年至2031年的複合年成長率將達到3.51%,這主要得益於基礎建設和採礦設備的發展,這些領域對高性能液壓系統的需求日益成長。工業機油應用於發電和船舶領域,而變速箱油則受益於摩托車行業自動變速箱的日益普及。齒輪油為印尼的重型和工業機械提供支持,尤其是在加里曼丹和蘇拉威西的採礦作業中。
加工處理油,包括橡膠加工油和白油,供應印尼的輪胎製造和石化業;金屬加工油則支持該國不斷擴張的製造業。渦輪機油和變壓器油用於發電基礎設施,而潤滑脂則廣泛應用於各種領域,從汽車底盤潤滑到工業軸承系統。產品組合正朝著專業配方方向發展,這反映了印尼工業日益複雜化以及原始設備製造商(OEM)規格的影響力不斷增強,這些規格要求使用符合API、JASO和ACEA等國際標準的高性能潤滑油。
印尼潤滑油市場報告按產品類型(汽車引擎油、工業引擎油、變速箱油、齒輪油、煞車油、液壓油、潤滑脂等)、終端用戶產業(汽車、船舶、航太、重型機械、工業)和基礎油類型(礦物油、合成油、半合成油、生物基油)進行細分。市場預測以公升為單位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 汽車擁有量不斷成長的趨勢
- 工業和製造業的快速成長
- 全國基礎設施建設和蓬勃發展的採礦活動
- 船舶和漁船隊的現代化
- 生物柴油相關潤滑油污染推動了對優質添加劑的需求
- 市場限制
- 宏觀經濟和商品價格波動限制了產能運轉率。
- 延長合成機油更換週期可降低每輛車的機油消耗量。
- 油價波動正在擠壓利潤空間,並影響對價格敏感的買家。
- 價值鏈分析
- 法律規範
- 終端用戶趨勢
- 汽車產業
- 製造業
- 發電業
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依產品類型
- 汽車引擎油
- 工業機油
- 變速箱油
- 齒輪油
- 煞車油
- 油壓
- 潤滑脂
- 加工油(包括橡膠加工油和白油)
- 金屬加工油
- 渦輪機油
- 變壓器油
- 其他產品類型
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 車
- 搭乘用車
- 商用車輛
- 摩托車
- 船
- 航太
- 重型機械
- 建造
- 礦業
- 農業
- 工業的
- 發電
- 冶金/金屬加工
- 紡織業
- 石油和天然氣
- 其他終端用戶產業
- 車
- 依基礎油類型
- 礦物油性潤滑劑
- 合成潤滑油
- 半合成潤滑油
- 生物性潤滑劑
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- BP Plc(Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Gulf Oil International Ltd
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- PETRONAS Lubricants International
- PT Pertamina Lubricants
- PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- Shell plc
- The Lubrizol Corporation
- TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- TotalEnergies
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
第8章:執行長面臨的關鍵策略挑戰
The Indonesian Lubricants Market was valued at 1.20 billion liters in 2025 and estimated to grow from 1.23 billion liters in 2026 to reach 1.41 billion liters by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Demand continues to track Indonesia's steady industrial expansion, resolute infrastructure pipeline, and resilient vehicle parc, even as electric-mobility policies loom. Mineral-oil products still account for two-thirds of volume, yet the premium shift to synthetics accelerates because extended drain intervals appeal to fleet operators seeking lower lifetime operating costs. Capacity additions by multinationals-from Shell's new grease plant to ExxonMobil's on-site MACHINEXT service-underline how technology, localized production, and distribution reach shape competitive advantage. Meanwhile, mandatory SNI certification, B40 biodiesel adoption, and volatile crude prices intensify cost pressures, prompting portfolio upgrades toward anti-corrosion additives and bio-based blends. Supply-chain complexity across 17,000 islands creates logistical challenges, particularly for reaching high-value mining and industrial applications in outer regions.
Indonesia Lubricants Market Trends and Insights
Growing Automotive Parc Expansion
Indonesia's expanding automotive sector drives lubricant consumption through both passenger vehicle growth and commercial fleet modernization across the archipelago's logistics networks. According to the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), the country produced 1.19 million vehicles in 2024. The shift toward automatic transmission motorcycles creates demand for specialized lubricant formulations for matic applications. E-commerce expansion and the proliferation of last-mile delivery increase vehicle utilization rates, leading to a higher frequency of lubricant replacement beyond traditional consumer patterns. The government's push for electric vehicles and its planned phase-out of internal combustion engines by 2040 creates a structural ceiling for growth in automotive lubricant volumes. Regional distribution networks struggle to efficiently serve Indonesia's outer islands, creating supply bottlenecks that limit market penetration in emerging automotive clusters.
Rapid Industrial and Manufacturing Growth
Indonesia's manufacturing sector momentum directly translates to heightened industrial lubricant consumption across metalworking, power generation, and heavy equipment applications. The country's position as the world's largest nickel producer amplifies demand for specialized metalworking fluids and hydraulic systems lubricants in smelting operations. Manufacturing investment creates new industrial capacity requiring initial lubricant fills and ongoing maintenance programs. ExxonMobil's MACHINEXT on-site lubrication management technology, launched in June 2024, demonstrates how digital optimization reduces the total cost of ownership while extending equipment life cycles. The concentration of manufacturing on Java Island creates logistical advantages but limits growth potential in resource-rich outer regions where infrastructure development lags behind industrial investment.
Macroeconomic and Commodity-Price Volatility Dampening Cap-Utilization
Indonesia's lubricant industry faces capacity utilization challenges due to macroeconomic uncertainty and fluctuations in commodity prices, which dampen industrial activity and consumer spending patterns. The domestic industry operates at approximately 60% capacity utilization. Global supply chain disruptions and currency volatility impact base oil import costs, forcing manufacturers to adjust their pricing strategies and consider the effect on demand elasticity. Export-dependent sectors, such as palm oil and mining, experience cyclical downturns that reduce industrial lubricant consumption during commodity price slumps. The concentration of manufacturing capacity on Java island creates regional imbalances, while outer island operations struggle with supply chain reliability during economic turbulence. Regulatory compliance costs under mandatory SNI standards add operational overhead that smaller players cannot easily absorb during periods of margin compression.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Nation-wide Infrastructure and Mining Activity Boom
- Marine and Fisheries Fleet Modernization
- Longer Drain-Interval Synthetic Formulations Lowering Volume/Vehicle
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Automotive engine oil commands 35.80% Indonesia's lubricant market share in 2025, reflecting Indonesia's vehicle-centric lubricant consumption patterns and the dominance of internal combustion engines across passenger and commercial segments. Hydraulic fluids represent the fastest-growing product category, with a 3.51% CAGR for 2026-2031, driven by infrastructure construction and the expansion of mining equipment, which require high-performance hydraulic systems. Industrial engine oil serves power generation and marine applications, while transmission fluids benefit from the automatic transmission boom in the motorcycle industry. Gear oils support Indonesia's heavy equipment and industrial machinery base, particularly in mining operations across Kalimantan and Sulawesi.
Process oils, including rubber process oil and white oil, serve the tire manufacturing and petrochemical industries in Indonesia, while metalworking fluids support the country's expanding manufacturing sector. Turbine oils and transformer oils cater to the power generation infrastructure, while greases serve a diverse range of applications, from automotive chassis lubrication to industrial bearing systems. The evolution of the product mix toward specialized formulations reflects Indonesia's increasing industrial sophistication and the growing influence of OEM specifications, which demand performance lubricants that meet international standards, such as API, JASO, and ACEA certifications.
The Indonesia Lubricants Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Automotive Engine Oil, Industrial Engine Oil, Transmission Fluids, Gear Oil, Brake Fluids, Hydraulic Fluids, Greases, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive, Marine, Aerospace, Heavy Equipment, and Industrial), and Base Stock Type (Mineral Oil-Based, Synthetic, Semi-Synthetic, and Bio-Based). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Liters).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- BP Plc (Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Gulf Oil International Ltd
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- PETRONAS Lubricants International
- PT Pertamina Lubricants
- PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- Shell plc
- The Lubrizol Corporation
- TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- TotalEnergies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing automotive parc expansion
- 4.2.2 Rapid industrial and manufacturing growth
- 4.2.3 Nation-wide infrastructure and mining activity boom
- 4.2.4 Marine and fisheries fleet modernization
- 4.2.5 Biodiesel-linked lubricant contamination driving premium additives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Macroeconomic and commodity-price volatility dampening cap-utilization
- 4.3.2 Longer drain-interval synthetic formulations lowering volume/vehicle
- 4.3.3 Crude-oil price swings squeezing margins and price-sensitive buyers
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Framework
- 4.6 End-User Trends
- 4.6.1 Automotive Industry
- 4.6.2 Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6.3 Power Generation Industry
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Automotive Engine Oil
- 5.1.2 Industrial Engine Oil
- 5.1.3 Transmission Fluids
- 5.1.4 Gear Oil
- 5.1.5 Brake Fluids
- 5.1.6 Hydraulic Fluids
- 5.1.7 Greases
- 5.1.8 Process Oil (Including Rubber Process Oil and White Oil)
- 5.1.9 Metalworking Fluids
- 5.1.10 Turbine Oil
- 5.1.11 Transformer Oil
- 5.1.12 Other Product Types
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.1.1 Passenger Vehicles
- 5.2.1.2 Commercial Vehicles
- 5.2.1.3 Two-Wheelers
- 5.2.2 Marine
- 5.2.3 Aerospace
- 5.2.4 Heavy Equipment
- 5.2.4.1 Construction
- 5.2.4.2 Mining
- 5.2.4.3 Agriculture
- 5.2.5 Industrial
- 5.2.5.1 Power Generation
- 5.2.5.2 Metallurgy and Metalworking
- 5.2.5.3 Textiles
- 5.2.5.4 Oil and Gas
- 5.2.5.5 Other End-Use Industries
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.3 By Base Stock Type
- 5.3.1 Mineral Oil-Based Lubricants
- 5.3.2 Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.3 Semi-Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.4 Bio-Based Lubricants
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BP Plc (Castrol)
- 6.4.2 Chevron Corporation
- 6.4.3 Exxon Mobil Corporation
- 6.4.4 FUCHS
- 6.4.5 Gulf Oil International Ltd
- 6.4.6 Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 PETRONAS Lubricants International
- 6.4.8 PT Pertamina Lubricants
- 6.4.9 PT Wiraswasta Gemilang Indonesia
- 6.4.10 Shell plc
- 6.4.11 The Lubrizol Corporation
- 6.4.12 TOP 1 Oil Products Company
- 6.4.13 TotalEnergies
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment







