 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1911316
歐洲廂型車市場-佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Europe Van - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
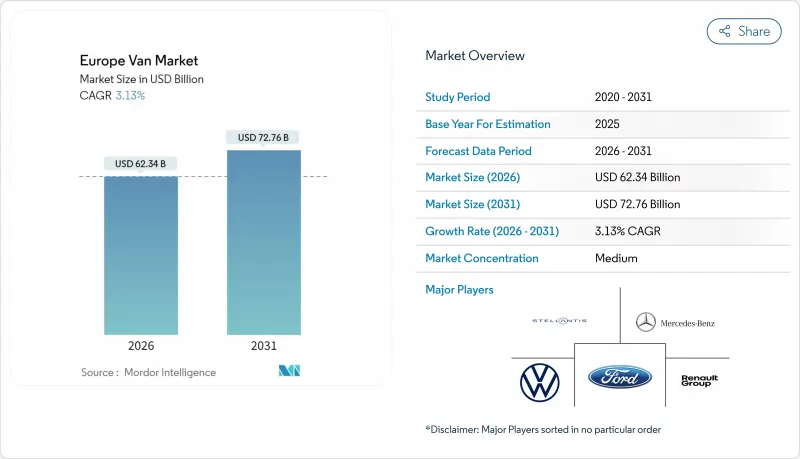
預計到 2026 年,歐洲廂型車市場規模將達到 623.4 億美元,高於 2025 年的 604.5 億美元。預計到 2031 年,該市場規模將達到 727.6 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 3.13%。
這一成長勢頭得益於歐盟日益嚴格的排放法規、電子商務物流的快速發展以及電池價格的快速下降。同時,柴油動力系統仍是長途運輸能力的基礎。德國車隊營運商繼續引領市場,他們將大規模批量採購與自有充電基礎設施的投資相結合。此外,Stellantis 和梅賽德斯-奔馳的平台策略,以及比亞迪和上汽大通等注重價格的新興參與企業的崛起,正在重塑競爭格局,因為整合充電服務、軟體和融資已成為交易的標配。儘管半導體短缺和缺乏場內快速充電基礎設施限制了短期生產,但總擁有成本 (TCO) 的平衡以及替代燃料法規的趨同正在推動歐洲廂式貨車市場向電動化車隊不可逆轉地轉變。
歐洲廂型車市場趨勢與洞察
電動貨車銷量上升
在歐盟27個市場中的21個市場,電動貨車的總擁有成本已經超過了柴油車,因此,電動貨車的採購決策正從政策合規轉向成本主導。 DHL訂購2400輛福特E-Transit的合約表明,批量訂單和工資扣除可以如何加速規模化發展。 B類駕照的適用範圍擴大到4.25噸,取消了駕照限制。預測顯示,到2026年,輕型商用電池式電動車(BEV)的價格將與柴油車持平,從而鎖定長期需求。車隊管理人員也重視電動貨車更安靜的駕駛體驗和即時扭力反應,這些優勢可以提高都市區生產力,即使在充電網路不發達的地區,電動貨車的普及也推動了其市場成長。
電子商務最後一公里需求快速成長
快速成長的電子商務推動了配送車輛密度的增加和配送路線的縮短,從而最佳化了都市區配送中心對靜音、零排放純電動車(BEV)的需求。巴塞隆納的微型配送中心計畫減少了30%的配送車輛里程,並採用了緊湊型純電動車(具有瞬時扭力和低噪音特性),這些車輛不會限制都市區的通行。暗店和定時配送模式將需求分散到季節性高峰之外,確保全年運轉率。路線最佳化軟體與交通系統協同工作,在提高配送效率的同時降低能耗。這些營運優勢,加上不受限制的都市區通行,使得電動貨車成為西歐各地最後一公里配送的首選車輛。
電池高成本,車輛資本投資較高
儘管營運成本有所降低,電動貨車的初始價格仍比柴油車高出40%至60%,而且在大型場所建造充電設施需要超過100萬歐元(約117萬美元)的投資,這給中小運輸業者帶來了沉重的融資壓力。租賃公司缺乏殘值數據加劇了資金籌措障礙,投資回收期往往超出正常的預算週期。利率上升進一步加重了資本負擔,而各國公共補貼差異巨大,降低了規劃的確定性。這些成本障礙減緩了區域營運商和中小企業採用電動貨車的步伐,他們通常會推遲電動化進程,直到二手純電動車的供應改善或出現能夠承擔初始成本的「卡車即服務」承包解決方案。
細分市場分析
預計到2025年,N1類I型廂型車將佔歐洲廂型車市場的48.76%,並在2031年之前以3.52%的複合年成長率成長。這反映了零排放車輛駕駛執照要求的放寬,B類駕照的適用範圍已擴大至4.25噸。 N1類I型廂型車尺寸緊湊,非常適合低排放區、狹窄的裝卸貨平台和快速路邊配送,而其在實際駕駛中250-300公里的續航里程足以滿足整個都市區工作週期,無需在工作途中充電。
二類和三類輕型商用車對於冷藏食品運輸、施工機械和區域配送仍然至關重要,但它們仍需等待高密度充電器和續航里程達400公里的電池(例如福特新款89kWh E-Transit所搭載的電池)的到來。車隊管理人員正在密切關注每千瓦時有效載荷效率(kg/kWh),以確保增加的電池重量不會影響生產效率。隨著新一代磷酸鋰鐵鋰電池組在重量和成本方面的進步,較重的車型有望加入早期採用浪潮,從而鞏固輕型商用車作為電氣化橋頭堡的地位。
到2025年,容積超過5立方公尺的車型將佔歐洲廂型車市場62.78%的佔有率,這主要得益於經銷商為實現高有效載荷率而最大化每公里收入。汽車製造商正透過模組化平台來滿足這一核心市場的需求,這些平台結合了高車頂、多種軸距和2噸的有效載荷限制,例如雷諾Master的11-22立方公尺配置。
然而,容積小於5立方公尺的車型正在崛起,年複合成長率達4.67%。這主要得益於生鮮和藥品配送公司對車輛在街道上的操控性、便利停車以及低容量電池的需求,這些因素都有助於降低成本。緊湊型純電動車由於配備了容量小於50千瓦時的電池組,降低了購置成本和充電時間,因此能夠更快地實現總擁有成本(TCO)的損益平衡。這種兩極化的市場格局迫使汽車製造商(OEM)採取兩種不同的藍圖:一種是針對托盤貨物運輸最佳化的高負載容量車型,另一種是專為密集都市區環線配送而設計的小型、軟體驅動型微型貨車。後者在等待時間和通行費會削弱柴油車經濟性的環境中更具優勢。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 電動貨車銷量成長
- 電子商務最後一公里配送快速成長
- 歐盟低排放區法規
- 都市區微型倉配中心的採用
- OEM滑板電動車平台
- 電池即服務 (BaaS) 車隊模式
- 市場限制
- 電池和車輛資本投資高成本
- 半導體供應受限
- 倉庫內缺乏快速充電設施
- 駕駛人及駕照發放規定
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模及成長預測(價值(美元)及銷售量(單位))
- 按車輛總重量
- N1 一級(總重量低於 2 噸)
- N1 II 類(總重量 2-2.5 噸)
- N1 III級(總重量2.5-3.5噸)
- 透過貨艙
- 5立方米或以下
- 5立方米或以上
- 最終用戶
- 商用車輛車隊
- 對於政府和地方政府
- 租賃公司
- 按驅動類型
- 內燃機 - 汽油
- 內燃機 - 柴油
- 電池電動車
- 油電混合車
- 燃料電池電動車
- 替代燃料(壓縮天然氣/液化石油氣)
- 按銷售管道
- 廠商直銷車隊
- 授權經銷商
- 線上/數位平台
- 按國家/地區
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 荷蘭
- 瑞典
- 挪威
- 其他歐洲地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Stellantis NV
- Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- Volkswagen AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Renault Group
- Iveco Group NV
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- BYD Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Company
- SAIC Maxus Automotive
- MAN Truck & Bus SE
- Opel Automobile GmbH
- London Electric Vehicle Company(LEVC)
- B-ON GmbH(StreetScooter GmbH)
- Rivian Automotive LLC
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The European van market market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 62.34 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 60.45 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 72.76 billion, growing at 3.13% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Momentum stems from tightening EU emission limits, the boom in e-commerce logistics, and fast-falling battery prices, while diesel powertrains still underpin long-haul capacity. Market leadership continues to rest with German fleets that have the scale to combine large procurement orders and in-house charging investments. At the same time, platform strategies from Stellantis and Mercedes-Benz, along with price-focused entrants BYD and SAIC Maxus, are redefining competitive dynamics as integrated charging, software, and financing services become part of every deal. Although semiconductor bottlenecks and depot fast-charging gaps curb near-term output, the convergence of total cost of ownership (TCO) parity and alternative-fuels rules indicates the European van market is approaching an irreversible switch toward electrified fleets.
Europe Van Market Trends and Insights
Rise in Sales of Electric Vans
Electric-van purchases are moving from policy compliance to cost-driven decisions as the total cost of ownership now beats diesel in 21 of 27 EU markets. DHL's 2,400-unit Ford E-Transit deal shows how bulk orders and salary-sacrifice programs accelerate scale, while B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t erase licensing limits. Projections indicate price parity for light commercial BEVs by 2026, locking in long-term demand. Fleet managers also value silent operation and instant torque that improve urban productivity, reinforcing momentum even where charging networks remain incomplete.
E-commerce Last-Mile Boom
Rapid e-commerce growth drives higher van density and shorter delivery routes, making quiet, zero-emission BEVs ideal for city nodes. Barcelona's micro-hub program trimmed van miles 30%, favoring compact BEVs with instant torque and low noise that face no urban access bans . Dark stores and subscription delivery models spread demand beyond seasonal peaks, ensuring year-round utilization. Route-optimization software integrates with traffic systems, boosting drop rates while lowering energy use. These operational gains combine with unrestricted urban access to make electric vans the preferred workhorse for last-mile fleets across Western Europe.
High Battery and Vehicle CAPEX
Up-front prices for electric vans remain 40-60% above diesel, while depot chargers can push investment above EUR 1 million (~USD 1.17 million) for large sites, straining the cash flow of small haulers despite lower running costs . Financing hurdles grow as leasing firms lack residual-value data, lengthening payback periods beyond typical budget cycles. Rising interest rates add to capital pressure, and public subsidies vary widely by country, creating planning uncertainty. These cost barriers slow adoption among regional operators and SMEs, who often defer electrification until second-hand BEV supply improves or turnkey Truck-as-a-Service packages absorb initial outlays.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- EU Low-Emission-Zone Mandates
- Urban Micro-fulfilment Hub Adoption
- Semiconductor Supply Constraints
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
N1 Class I vans claimed 48.76% of the European van market share in 2025 and will expand at a 3.52% CAGR through 2031, reflecting how B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t remove driver-license barriers for zero-emission vehicles. Their compact footprints suit low-emission zones, narrow loading bays, and quick curbside drop-offs, while real-world battery ranges of 250-300 km now cover full urban duty cycles without mid-shift charging.
Class II and III models remain indispensable for refrigerated food, construction tools, and regional parcel runs but await denser chargers and 400 km batteries such as Ford's 89 kWh E-Transit update. Fleet managers compare kilograms delivered per kilowatt-hour payload efficiency to ensure that added battery mass never dilutes productivity. As next-generation lithium-iron-phosphate packs cut weight and cost, heavier classes are positioned to join the early adoption curve, reinforcing the light-duty segment's role as an electrification beachhead.
Vans above 5 m3 dominated the European van market, with 62.78% of the share in 2025, powered by wholesale distributors that maximize revenue kilometers via higher cube utilization. OEMs serve this core with modular platforms such as the Renault Master's 11-22 m3 configurations, which blend tall roofs, multiple wheelbases, and two-tonne payload ceilings.
Yet, less than/equal to 5 m3 models are rising at a 4.67% CAGR, underpinned by grocery quick-commerce and pharmacy delivery firms that prize alley maneuverability, easy parking, and lower battery capacities that keep sticker prices in check. Compact BEVs reach total cost-of-ownership breakeven faster because sub-50 kWh packs trim purchase costs and charge times. The bifurcation pushes OEMs toward dual roadmaps: high-cube variants optimized for palletized freight and smaller, software-enabled micro-vans engineered for dense urban loops where idle time and access fees erode diesel economics.
The Europe Van Market Report is Segmented by Gross Vehicle Weight (N1 Class I, N1 Class II, and N1 Class III), Cargo Space (Less Than/Equals 5 M3 and Above 5 M3), End User (Commercial Fleets, Government and Municipal, and More), Drive Type (IC Engine - Petrol, IC Engine - Diesel, and More), Sales Channel (Direct OEM Fleet Sales, and More), and Country. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Stellantis N.V.
- Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- Volkswagen AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Renault Group
- Iveco Group N.V.
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- BYD Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Company
- SAIC Maxus Automotive
- MAN Truck & Bus SE
- Opel Automobile GmbH
- London Electric Vehicle Company (LEVC)
- B-ON GmbH (StreetScooter GmbH)
- Rivian Automotive LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise in Sales of Electric Vans
- 4.2.2 E-commerce Last-Mile Boom
- 4.2.3 EU Low-Emission-Zone Mandates
- 4.2.4 Urban Micro-fulfilment Hub Adoption
- 4.2.5 OEM Skateboard EV Platforms
- 4.2.6 Battery-as-a-Service Fleet Models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Battery and Vehicle CAPEX
- 4.3.2 Semiconductor Supply Constraints
- 4.3.3 Limited Depot Fast-Charging Sites
- 4.3.4 Driver Shortage and License Rules
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Gross Vehicle Weight
- 5.1.1 N1 Class I (Less than/Equals 2 t GVW)
- 5.1.2 N1 Class II (2-2.5 t GVW)
- 5.1.3 N1 Class III (2.5-3.5 t GVW)
- 5.2 By Cargo Space
- 5.2.1 Less than/Equals 5 m3
- 5.2.2 Above 5 m3
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial Fleets
- 5.3.2 Government and Municipal
- 5.3.3 Rental and Leasing Operators
- 5.4 By Drive Type
- 5.4.1 IC Engine - Petrol
- 5.4.2 IC Engine - Diesel
- 5.4.3 Battery Electric
- 5.4.4 Hybrid Electric
- 5.4.5 Fuel-Cell Electric
- 5.4.6 Alternative Fuel (CNG/LPG)
- 5.5 By Sales Channel
- 5.5.1 Direct OEM Fleet Sales
- 5.5.2 Authorised Dealerships
- 5.5.3 Online / Digital Platforms
- 5.6 By Country
- 5.6.1 Germany
- 5.6.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3 France
- 5.6.4 Italy
- 5.6.5 Spain
- 5.6.6 Netherlands
- 5.6.7 Sweden
- 5.6.8 Norway
- 5.6.9 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Stellantis N.V.
- 6.4.2 Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- 6.4.3 Volkswagen AG
- 6.4.4 Ford Motor Company
- 6.4.5 Renault Group
- 6.4.6 Iveco Group N.V.
- 6.4.7 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 6.4.8 Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- 6.4.9 BYD Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Hyundai Motor Company
- 6.4.11 SAIC Maxus Automotive
- 6.4.12 MAN Truck & Bus SE
- 6.4.13 Opel Automobile GmbH
- 6.4.14 London Electric Vehicle Company (LEVC)
- 6.4.15 B-ON GmbH (StreetScooter GmbH)
- 6.4.16 Rivian Automotive LLC
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment








