 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1844491
中東和非洲接近感測器:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Middle East And Africa Proximity Sensors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
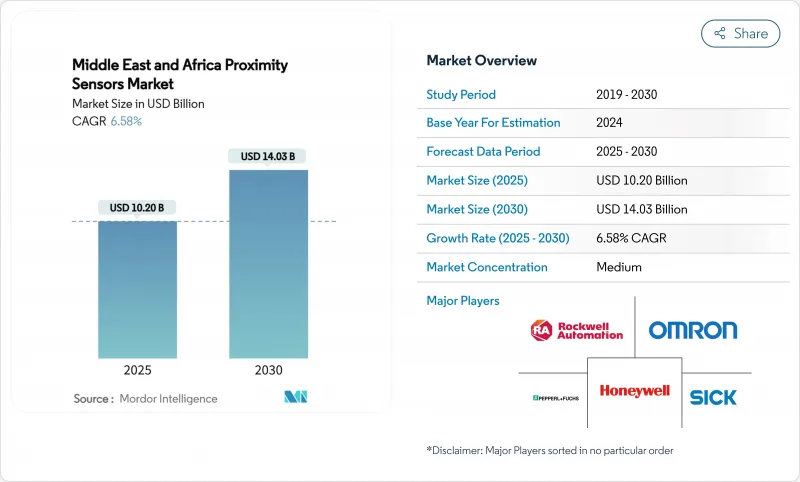
中東和非洲接近感測器市場預計到 2025 年將達到 102 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 140.3 億美元,複合年成長率為 6.58%。
該地區的多元化發展、大規模可再生能源部署以及不斷成長的汽車樞紐正在創造對非接觸式感測設備的持續需求。雖然沙烏地阿拉伯、阿拉伯聯合大公國 (UAE) 和南非繼續集中大部分工業自動化計劃,但埃及的風能走廊和摩洛哥的出口導向汽車廠正在推動最快的成長。海灣合作理事會國家的進口替代激勵措施有利於能夠本地化最終組裝的供應商,而 IO-Link 的穩定採用正在使偏好傾向於數位輸出設備。在惡劣的沙漠和採礦環境中,傳統光電感測器的限制正在推動人們採用遠距超音波和堅固的電感感測器。歐洲和日本供應商之間的合作標誌著策略轉向共用區域生產和服務網路,以滿足當地的認證需求。
中東和非洲接近感測器市場趨勢和洞察
GCC離散製造業的工業自動化投資
海灣合作理事會(GCC)各國政府正根據其國家工業戰略,要求提高新建工廠的自動化程度,推動工廠營運商採用能夠承受高溫和細塵的感測器網路。整合式 IO-Link 連接現已成為沙烏地阿拉伯和阿拉伯聯合大公國主要待開發區計劃的實際規範,可實現設備級診斷,從而減少非計劃性停機時間。在海灣合作理事會自由區內完成的接近感測器次組件受本地內容規則和降低的關稅約束,這鼓勵全球供應商與本地分銷商共同生產。這些政策與能源補貼相結合,使中東和北非地區的接近感測器市場保持穩定上升的趨勢。
擴大摩洛哥和南非的汽車組裝
摩洛哥預計到2024年將生產61.4萬輛汽車,成為歐盟最大的外部汽車供應商。丹吉爾自由區的一級供應商正在指定使用遠距雷射和超音波感測器進行電池組定位,使每條生產線的感測器數量增加高達20%。儘管南非面臨整體產量下滑的局面,但為了保持全球競爭力,南非正在推進電池組裝環節的自動化,這進一步刺激了中東和北非地區的接近感測器市場。
沙漠塵埃條件下光電感測器性能劣化
嚴重的沙塵暴會使光學感測器的可靠性降低 80% 以上,造成傳送帶和包裝線的計劃外停機,迫使操作員依賴每月的清潔週期和保護性空氣吹掃系統,從而增加總體擁有成本並抑制中東和北非地區接近感測器市場對光電模型的廣泛採用。
細分分析
2024年,超音波式感測器將佔中東和北非地區接近感測器接近感測器的41.3%,市場規模達42億美元。其密封設計消除了容易積聚灰塵的光學窗口,從而延長了礦山和鋼廠的平均故障間隔時間。超音波感測器僅佔銷售額的14%,但隨著風電場逐步實現遠距檢測的標準化,其複合年成長率可望達到9.8%。光電式感測器的採用受限於灰塵導致的誤觸發,而電容式感測器在食品和飲料生產線中仍佔有一席之地,其非接觸式液位感測技術可防止污染。磁霍爾效應感測器適用於汽車和船舶等細分應用,而新型渦流感測器則有助於航太工業的複合材料檢測。原生IO-Link支援正成為所有類型感測器的關鍵採購標準,這進一步強化了中東和北非地區接近感測器市場的數位化主題。
第二代電感式平台整合了片上溫度補償和自癒演算法,可隔離部分線圈故障。供應商強調符合IECEx標準,以確保在石化區安裝,而此監管障礙有利於老牌歐洲製造商。同時,日本和韓國供應商正在擴大其區域庫存,以縮短前置作業時間,這在政府資金籌措里程碑壓縮計劃工期的情況下,是一個關鍵的差異化因素。
受裝配線大規模生產和拾放機器人的推動,10 毫米以下的短距離感測器佔據了 48.7% 的市場佔有率。然而,預計 40 毫米以上的遠距感測器的複合年成長率將達到 8.9%,隨著組裝機和公用事業規模的太陽能發電廠對探測範圍的要求越來越高,這一差距正在縮小。光是沙烏地阿拉伯 2.9 吉瓦的風發電工程就預計在 2025 年至 2027 年間就需要 5 萬個遠距感測器。中距離感測器(10-40 毫米)在自動化倉庫和不同輸送機寬度的包裝系統中保持均衡的佔有率。
感測器製造商目前正在將微功率雷達整合到遠距槽中,這增加了傳統超音波線的競爭壓力。在超高頻探頭中,高頻電容式探頭在半導體後端組裝越來越受到關注。這類應用在該地區尚處於起步階段,但在海灣合作理事會的技術藍圖中卻是一個突出的特徵。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- GCC離散製造業的工業自動化投資
- 擴大摩洛哥和南非的汽車組裝
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國清真食品智慧包裝生產線激增
- 沙烏地阿拉伯和埃及的風力發電機建設推動遠距感測器的發展
- 惡劣採礦環境中的免維護電感式感測器(南非、奈米比亞)
- 市場限制
- 沙漠塵埃環境中光電感測器性能的劣化
- 撒哈拉以南地區二級汽車供應商的資本支出週期波動
- 奈及利亞和肯亞的本地附加價值低=進口關稅高
- 假冒低價感測器(非官方貿易)降低品牌溢價
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監理展望(IEC Ex、SASO、GSO)
- 技術展望(IO-Link、ASIC小型化)
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 依技術
- 電感式
- 電容式
- 光電式
- 超音波
- 磁性(霍爾效應)
- 其他(渦流、光學)
- 按檢測範圍
- 短距離(小於10毫米)
- 中距離(10-40mm)
- 遠距(40mm以上)
- 依輸出類型
- 數字(NPN、PNP)
- 模擬(電流、電壓)
- 按最終用戶產業
- 車
- 工業製造與自動化
- 消費性電子產品
- 飲食
- 航太/國防
- 包裝/物流
- 可再生能源
- 其他
- 按國家
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 南非
- 埃及
- 奈及利亞
- 其他中東和非洲地區
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略舉措
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- SICK AG
- Omron Corporation
- Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Datalogic SpA
- IFM Electronic gmbh
- Balluff gmbh
- Keyence Corporation
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Panasonic Industry
- Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- Baumer Holding AG
- Contrinex SA
- Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- Autonics Co. Ltd.
- Riko Opto-electronics
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market stood at USD 10.2 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 14.03 billion by 2030, registering a 6.58% CAGR.

The region's diversification push, large-scale renewable-energy roll-outs and growing automotive hubs are creating sustained demand for non-contact sensing devices. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and South Africa continue to concentrate the bulk of industrial automation projects, while Egypt's wind corridors and Morocco's export-oriented vehicle plants are driving the fastest incremental volumes. Import-substitution incentives in GCC states favour suppliers that can localise final assembly, and the steady adoption of IO-Link is tilting preference toward digital-output devices. Long-range ultrasonic and ruggedised inductive types are gaining visibility as harsh desert and mining environments expose the limits of legacy photoelectric alternatives. Cooperative ventures among European and Japanese vendors signal a strategic shift toward shared regional production and service networks that can meet local certification demands.
Middle East And Africa Proximity Sensors Market Trends and Insights
Industrial-automation investments in GCC discrete manufacturing
GCC governments are mandating higher automation ratios in new factories under national industrial strategies, pushing plant operators toward sensor networks that can withstand high ambient temperatures and fine dust. Integrated IO-Link connectivity is now a de-facto specification in major Saudi and Emirati green-field projects, enabling device-level diagnostics that cut unscheduled downtime. Local content rules grant tariff relief for proximity-sensor sub-assemblies finished within GCC free zones, steering global suppliers toward joint manufacturing with regional distributors. These policies, coupled with subsidised energy, keep the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market on a steady uptrend.
Automotive assembly expansion across Morocco and South Africa
Morocco produced 614,000 vehicles in 2024 and has become the European Union's largest external vehicle supplier, a status that necessitates near-zero defect tolerances on body-in-white lines. Tier-1 suppliers in Tangier's free zone are specifying long-range laser and ultrasonic sensors for battery-pack positioning, raising per-line sensor counts by up to 20%. South Africa, while contending with lower overall volumes, is automating battery-assembly stages to stay globally competitive, further stimulating the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Photonic-sensor performance degradation in desert dust conditions
Severe sandstorms can slash optical-sensor reliability by more than 80%, triggering unplanned stoppages on conveyor and packaging lines. Operators resort to monthly cleaning cycles and protective air-purge systems, lifting the total cost of ownership and restraining wider adoption of photoelectric models within the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in UAE smart-packaging lines for halal foods
- Wind-turbine build-out in Saudi Arabia and Egypt
- Volatile capex cycles in Sub-Saharan automotive Tier-2 suppliers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Inductive devices contributed 41.3% to the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market in 2024, valued at a Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market size of USD 4.2 billion. Their sealed construction eliminates optical windows that accumulate dust, extending mean-time-between-failure in mines and steel mills. Ultrasonic units, though only 14% of revenue, are on track for the fastest 9.8% CAGR as wind-energy operators standardise on long-range detection. Photoelectric adoption is restricted by dust-induced false triggers, while capacitive variants retain a foothold in food-and-beverage lines where non-contact level sensing prevents contamination. Magnetic Hall-effect sensors meet niche automotive and marine applications, and emerging eddy-current models serve aerospace composites inspection. Across all formats, native IO-Link support is becoming a decisive purchase criterion, reinforcing the digitalisation theme in the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Second-generation inductive platforms now bundle on-chip temperature compensation and self-healing algorithms that isolate partial coil faults. Suppliers emphasise conformity to IECEx standards to secure placement in petrochemical zones, a regulatory hurdle that favours established European manufacturers. Meanwhile, Japanese and Korean vendors are expanding regional stockholding to shorten lead times, a key differentiator where project schedules are compressed by government funding milestones.
Short-range models below 10 mm dominated at 48.7% share thanks to high unit volumes on assembly lines and pick-and-place robots. Yet long-range units above 40 mm are forecast to chart an 8.9% CAGR, closing the gap as turbine and utility-scale solar plants specify wider detection envelopes. A 2.9 GW tranche of Saudi wind projects alone will require an incremental 50,000 long-range sensors during 2025-2027. Medium-range devices (10-40 mm) keep a balanced presence in automated storage and packaging systems where conveyor widths vary.
Sensor makers now incorporate micro-power radar for long-range slots, raising competitive pressure on legacy ultrasonic lines. At the ultra-short end, high-frequency capacitive probes are gaining interest for semiconductor backend assembly, an application cluster still nascent in the region but flagged in GCC technology roadmaps.
The Middle East and Africa Proximity Sensors Market is Segmented by Technology (Inductive, Capacitive), Sensing Range (Short, Medium, Long), Output Type (Digital, Analog), End-User Industry (Automotive, Industrial Manufacturing and Automation), and Country (Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, and Rest of Middle East and Africa). The Market Size and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- SICK AG
- Omron Corporation
- Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Datalogic S.p.A.
- IFM Electronic gmbh
- Balluff gmbh
- Keyence Corporation
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Panasonic Industry
- Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- Baumer Holding AG
- Contrinex SA
- Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- Autonics Co. Ltd.
- Riko Opto-electronics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Industrial-Automation Investments in GCC Discrete Manufacturing
- 4.2.2 Automotive Assembly Expansion across Morocco and South Africa
- 4.2.3 Surge in UAE Smart-Packaging Lines for Halal Foods
- 4.2.4 Wind-Turbine Build-Out in Saudi Arabia and Egypt Driving Long-Range Sensors
- 4.2.5 Maintenance-Free Inductive Sensors in Harsh Mining Sites (RSA, Namibia)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Photonic-Sensor Performance Degradation in Desert Dust Conditions
- 4.3.2 Volatile Capex Cycles in Sub-Saharan Automotive Tier-2 Suppliers
- 4.3.3 Low Local Value-Add = High Import Tariffs in Nigeria and Kenya
- 4.3.4 Counterfeit Low-Cost Sensors Diluting Brand Premiums (informal trade)
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook (IEC Ex, SASO, GSO)
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (IO-Link, ASIC miniaturization)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Inductive
- 5.1.2 Capacitive
- 5.1.3 Photoelectric
- 5.1.4 Ultrasonic
- 5.1.5 Magnetic (Hall-Effect)
- 5.1.6 Others (Eddy-Current, Optical)
- 5.2 By Sensing Range
- 5.2.1 Short Range (less than 10 mm)
- 5.2.2 Medium Range (10-40 mm)
- 5.2.3 Long Range (greater than 40 mm)
- 5.3 By Output Type
- 5.3.1 Digital (NPN, PNP)
- 5.3.2 Analog (Current, Voltage)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive
- 5.4.2 Industrial Manufacturing and Automation
- 5.4.3 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.4 Food and Beverage
- 5.4.5 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.6 Packaging and Logistics
- 5.4.7 Renewable Energy
- 5.4.8 Others
- 5.5 By Country
- 5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.4 Egypt
- 5.5.5 Nigeria
- 5.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 SICK AG
- 6.4.2 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.3 Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- 6.4.4 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.5 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.6 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.7 Datalogic S.p.A.
- 6.4.8 IFM Electronic gmbh
- 6.4.9 Balluff gmbh
- 6.4.10 Keyence Corporation
- 6.4.11 Delta Electronics Inc.
- 6.4.12 Banner Engineering Corp.
- 6.4.13 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.14 Panasonic Industry
- 6.4.15 Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- 6.4.16 Baumer Holding AG
- 6.4.17 Contrinex SA
- 6.4.18 Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- 6.4.19 Autonics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Riko Opto-electronics
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment








