 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910870
日本低溫運輸物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Japan Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
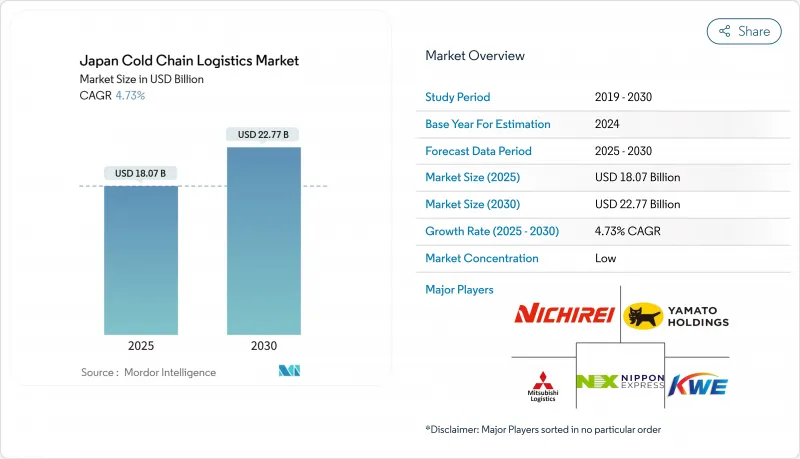
據估計,日本低溫運輸物流市場規模在 2026 年將達到 189.2 億美元,高於 2025 年的 180.7 億美元,預計到 2031 年將達到 237.8 億美元。
預計2026年至2031年年複合成長率(CAGR)為4.68%。
短期內,對溫度敏感的電商食品配送、超精準的藥品分銷以及創紀錄的水產品出口正在匯聚,形成一波需求浪潮,加速設施升級、車輛電氣化以及數位化可視化平台的普及。零售商正將微型倉配中心改造為多區域樞紐,以應對當日達訂單的激增;生物製藥企業則在2-8°C的低溫環境下儲備冗餘儲存容量,以保護高價值庫存。政府資助的疫苗儲備將確保超低溫設施的持續運作,而區域全面經濟夥伴關係協定(RCEP)帶來的貿易擴張也將促進長期成長,重振海運冷藏運輸路線。為此,大型物流業者正在加速併購、自動化以及替代燃料車輛的測試,以提高獲利能力並降低碳排放風險。
日本低溫運輸物流市場趨勢與洞察
需要溫度控制的電子商務食品配送
線上生鮮購物的快速普及正在重新定義倉儲設施的規模和位置。樂天瑪特目前在東京和關西地區每天處理7萬份冷藏和冷凍訂單,其微型倉配中心配備了產品運輸機器人和三區儲存模組。便利商店連鎖企業也在採用類似的模式:7-Eleven的7NOW服務計劃在全國2萬家門市擴展,建造一個高密度的「最後一公里」配送網路,該網路依賴於零下低溫儲物櫃和保溫托特包。零售商還推出了移動餐車,為郊區的老年人提供服務,並將配送車輛用作移動冷藏室。這些變化有利於能夠小規模靈活擴展的第三方業者。同時,現有倉庫業主正在投資高層倉庫的自動化改造,以在訂單量下降的情況下維持利潤率。最終形成了一個生態系統,在這個系統中,與消費者接近性與托盤搬運的準確性同等重要。
生物製藥、細胞和基因治療產品線(2-8°C)
日本生物製藥產業正在擴展精準物流,以減少GLP-1供應鏈審核中發現的480億美元溫度偏差損失。可在4°C下維持穩定的新型mRNA製劑顯著降低了對-80°C低溫儲存的依賴,新建設施也開始採用雙溫區策略。筑波醫療物流中心二期工程設有15-25°C、2-8°C和-20°C三個溫度隔離區以及三重冗餘電源,充分體現了滿足PMDA檢驗標準所需的巨額資本投入。小規模物流公司難以資金籌措如此複雜的設施建設成本,因此加速將業務外包給擁有檢驗的資料記錄器、全天候監控系統以及符合GDP標準的標準作業程式(SOP)的公司。茨城縣和埼玉縣周邊地區的集中佈局造成了供需失衡,促使九州和北海道地區計劃區域配送中心(DC)。
持證冷藏車司機短缺
司機數量持續下降,平均年齡超過50歲,年工作時長受加班限制。由於操作冷凍系統需要高級認證,低溫運輸營運商受到的影響比常溫運輸業者更大。日本通運正透過投資Gatik AI來應對這項挑戰,以偵測和營運資料中心之間的自動駕駛中間運輸路線。一項由政府支持的東京至大阪試點計畫旨在2027年獲得編隊行駛認證。在自動駕駛普及之前,業者正將長途運輸業務轉移到鐵路和滾裝船運輸,將寶貴的司機資源集中在複雜的「最後一公里」配送上。如果工資獎勵措施未能吸引新的持牌業者,區域路線將面臨服務缺口和全國覆蓋範圍縮小的風險。
細分市場分析
截至2025年,冷藏倉庫將佔日本低溫運輸物流市場收入的41.30%,反映出食品和製藥業庫存緩衝策略的建立。多溫控設施正在採用穿梭起重機和移動貨架,以在不擴大用地面積的情況下容納不斷增加的SKU。 LOGI FLAG TECH越谷i大樓展示了私人業者如何透過安裝太陽能板和天然冷媒,在降低公用事業成本的同時,實現-25°C的設定溫度。雖然公共倉庫對尋求靈活條款的中小型企業仍然具有吸引力,但高附加價值藥品佔有率的不斷成長正促使大型托運人轉向使用能夠確保符合GDP標準的專用自有設施。
預計到2031年,附加價值服務將以每年4.72%的速度成長,主要受銷售點附近套件組裝、重新貼標和後處理服務需求成長的推動。營運商正透過整合品質保證實驗室和快速組裝區,並將托盤儲存轉化為收入來源,來彌補吞吐量放緩的局面。冷藏運輸需求保持穩定,Konoike Transport公司為永旺集團的都市區配送引入了續航里程達120公里的電動卡車。模式轉換也不斷擴大:栗林海雲公司在其仙台至大阪的冷凍麵條航線上,從100%的卡車運輸轉向滾裝船運輸,二氧化碳排放減少了74%,並將港到港的運輸時間縮短至3小時。空運在臨床試驗和緊急召回方面仍然佔據著一定的市場佔有率,但隨著JR Freight公司引入更多冷藏貨櫃,其市場佔有率正被溫控鐵路運輸蠶食。
其他福利
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 電子商務生鮮配送的成長,需要溫度控制
- 不斷擴展的生物製藥、細胞和基因治療產品線需要2-8°C的物流。
- 政府補貼的疫苗儲備措施
- 受RCEP關稅減讓影響,水產品出口快速成長。
- 透過自動化和物聯網降低托盤級搬運成本
- 透過引入氫燃料冷藏卡車來減少對柴油的依賴
- 市場限制
- 由於勞動力老化,持有執照的冷藏車駕駛人短缺。
- 都市區不斷上漲的房地產價格限制了新建冷庫的建設。
- 夏季高峰尖峰時段超低溫冷凍庫可能導致電網不穩定
- 嚴格的氟碳化合物淘汰法規正在推動對維修設施的投資增加。
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 排放標準和ESG目標的影響
- 地緣政治與疫情的影響
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按服務類型
- 冷藏保管
- 公共倉庫
- 私人倉庫
- 冷藏運輸
- 路
- 鐵路
- 海路
- 航空郵件
- 附加價值服務
- 冷藏保管
- 按溫度類型
- 冷藏(0-5°C)
- 冷凍(-18 至 0°C)
- 室溫
- 超低溫冷凍(約20度C或更低)
- 透過使用
- 水果和蔬菜
- 肉類/家禽
- 魚貝類
- 乳製品和冷凍甜點
- 麵包糖果甜點
- 即食餐
- 藥品和生技藥品
- 疫苗和臨床試驗材料
- 化學品/特殊材料
- 其他
- 按地區(國內)
- 關東
- 關西
- 中部
- 九州、沖繩
- 北海道和東北地區
- 其他中東和非洲地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Nichirei Logistics Group
- Mitsubishi Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- Itochu Logistics
- Sagawa Express
- Konoike Transport Co., Ltd
- K-Line Logistics
- DHL Supply Chain
- Kuehne+Nagel
- CEVA Logistics
- Mitsui-Soko Group
- SENKO Co., Ltd.
- Suzuyo & Co.
- SF Express
- 郵船物流(日本郵船株式會社旗下部門)
- MOL Logistics
- Matsuoka Co., Ltd.
- YOKOREI Co., Ltd
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 18.92 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 18.07 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 23.78 billion, growing at 4.68% CAGR over 2026-2031.

In the near term, temperature-sensitive e-commerce grocery delivery, ultra-precision pharmaceutical distribution, and record seafood exports form a synchronized demand wave that accelerates facility upgrades, fleet electrification, and digital visibility platforms. Retailers convert micro-fulfillment centers into multi-zone hubs to handle surging same-day orders, while biologics producers secure redundant 2-8 °C capacity to protect high-value inventory. Long-term growth also benefits from government-funded vaccine stockpiles that ensure continuous utilization of ultra-low-temperature assets and from expanded Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) trade flows that stimulate maritime reefer lanes. In response, major logistics providers pursue mergers, automation rollouts, and alternative-fuel vehicle pilots to improve margins and reduce carbon exposure.
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Temperature-sensitive e-commerce grocery delivery
Rapid online grocery adoption is redefining facility scale and location. Rakuten Mart now processes 70,000 chilled and frozen orders daily across Tokyo and Kansai, supported by micro-fulfillment centers equipped with goods-to-person robots and three-zone storage modules. Convenience chains replicate this model: 7-Eleven's 7NOW service plans nationwide coverage through 20,000 stores, creating dense last-mile networks that rely on sub-zero lockers and insulated totes. Retailers also deploy mobile shops to reach suburban seniors, turning delivery vans into rolling cold rooms. These shifts favor agile third-party operators able to add capacity in smaller increments, while legacy warehouse owners invest in high-bay automation to protect margins as order sizes decline. The result is an ecosystem where proximity to the consumer is valued as highly as pallet throughput accuracy.
Biologics & cell-gene therapy pipeline (2-8 °C)
Japan's biopharma sector is scaling precision logistics to curb USD 48 billion in global temperature excursion losses revealed by GLP-1 supply chain audits. New mRNA formulations that remain stable at 4 °C slash dependence on -80 °C storage, prompting a dual-temperature strategy in new builds. Tsukuba Medical Logistics Center Phase 2 offers segregated 15-25 °C, 2-8 °C, and -20 °C zones with triple-redundant power, underscoring the capital intensity required to meet PMDA validation rules. Smaller carriers struggle to finance such complexity, accelerating contract outsourcing to firms with validated data-loggers, 24/7 monitoring, and GDP-compliant SOPs. Geographic concentration around Ibaraki and Saitama generates supply-demand imbalances that spur regional DC projects in Kyushu and Hokkaido.
Shortage of licensed reefer-truck drivers
Driver numbers continue to decline as the median age tops 50 and overtime caps limit annual hours. Cold chain fleets feel the pinch more than ambient carriers because advanced endorsements are required to handle refrigerant systems. Nippon Express addressed the gap by investing in Gatik AI to test autonomous middle-mile routes between DCs. Government-backed pilots linking Tokyo and Osaka aim to certify platooning by 2027. Until autonomy scales, operators shift long-haul volumes onto rail and RORO vessels, preserving scarce drivers for intricate last-mile drops. Rural routes risk service gaps that could weaken national coverage if wage premiums fail to attract new licensees.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government-subsidized vaccine stockpiling
- Surge in seafood exports via RCEP corridors
- High urban real-estate prices for cold warehouses
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Refrigerated storage controlled 41.30% of 2025 revenue within the Japan cold chain logistics market, reflecting entrenched inventory-buffer strategies across food and pharma sectors. Multi-temperature facilities deploy shuttle cranes and mobile racks to handle SKU proliferation without expanding footprints. The LOGI FLAG TECH Koshigaya I build demonstrates how private operators embed solar panels and natural refrigerants to curb utility bills while achieving -25 °C setpoints. Public warehouses remain attractive to SMEs seeking flexible terms, yet the growing share of high-value pharmaceuticals steers larger shippers toward dedicated in-house sites that guarantee GDP compliance.
Value-added services are set to grow 4.72% annually through 2031 as customers demand kitting, re-labeling, and post-processing near point-of-sale. Providers integrate QA labs and light assembly zones, converting pallet storage into fee-earning activities that offset slower throughput. Refrigerated transportation keeps stable demand as Konoike Transport deploys electric trucks with 120-kilometer range for Aeon Group urban deliveries. Modal shifts expand: Kuribayashi Shipping's switch from 100% trucking to RORO ships on Sendai-Osaka frozen noodle lanes cut CO2 74% while trimming transit to 3 hours dock-to-dock. Airfreight retains a niche for clinical trials and urgent recalls but yields share to temperature-controlled rail as JR Freight adds reefer containers.
The Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market Report is Segmented by Service Type (Refrigerated Storage, Refrigerated Transportation, Value-Added Services), Temperature Type (Chilled, Frozen, Ambient, Deep-Frozen/Ultra-Low), Application (Fruits & Vegetables, Meat & Poultry, Fish & Seafood, Dairy & Frozen Desserts, Bakery & Confectionery, and More), and Geography (Kanto, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Nichirei Logistics Group
- Mitsubishi Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- Itochu Logistics
- Sagawa Express
- Konoike Transport Co., Ltd
- K-Line Logistics
- DHL Supply Chain
- Kuehne + Nagel
- CEVA Logistics
- Mitsui-Soko Group
- SENKO Co., Ltd.
- Suzuyo & Co.
- SF Express
- Yusen Logistics (Part of NYK Line)
- MOL Logistics
- Matsuoka Co., Ltd.
- YOKOREI Co., Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expansion of temperature-sensitive e-commerce grocery delivery
- 4.2.2 Growing biologics and cell-gene therapy pipeline requiring 2-8 °C logistics
- 4.2.3 Government-subsidised vaccine stockpiling initiatives
- 4.2.4 Surge in seafood exports driven by RCEP tariff reductions
- 4.2.5 Automation and IoT lowering per-pallet handling costs
- 4.2.6 Hydrogen-powered reefer truck pilots lowering diesel dependency
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Shortage of licensed reefer-truck drivers amid ageing workforce
- 4.3.2 High urban real-estate prices limiting new cold-warehouse builds
- 4.3.3 Grid-instability risk for ultra-low-temp freezers during summer peaks
- 4.3.4 Stringent fluorocarbon phase-out rules increasing retrofit CAPEX
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Emission Standards and ESG Targets
- 4.9 Impact of Geopolitics and Pandemic
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Service Type
- 5.1.1 Refrigerated Storage
- 5.1.1.1 Public Warehousing
- 5.1.1.2 Private Warehousing
- 5.1.2 Refrigerated Transportation
- 5.1.2.1 Road
- 5.1.2.2 Rail
- 5.1.2.3 Sea
- 5.1.2.4 Air
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Services
- 5.1.1 Refrigerated Storage
- 5.2 By Temperature Type
- 5.2.1 Chilled (0-5 °C)
- 5.2.2 Frozen (-18-0 °C)
- 5.2.3 Ambient
- 5.2.4 Deep-Frozen / Ultra-Low (less than-20 °C)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.2 Meat and Poultry
- 5.3.3 Fish and Seafood
- 5.3.4 Dairy and Frozen Desserts
- 5.3.5 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.3.6 Ready-to-Eat Meals
- 5.3.7 Pharmaceuticals and Biologics
- 5.3.8 Vaccines and Clinical Trial Materials
- 5.3.9 Chemicals and Specialty Materials
- 5.3.10 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Region (Domestic)
- 5.4.1 Kanto
- 5.4.2 Kansai
- 5.4.3 Chubu
- 5.4.4 Kyushu and Okinawa
- 5.4.5 Hokkaido and Tohoku
- 5.4.6 Rest of Japan
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nippon Express
- 6.4.2 Yamato Holdings
- 6.4.3 Nichirei Logistics Group
- 6.4.4 Mitsubishi Logistics
- 6.4.5 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.4.6 Itochu Logistics
- 6.4.7 Sagawa Express
- 6.4.8 Konoike Transport Co., Ltd
- 6.4.9 K-Line Logistics
- 6.4.10 DHL Supply Chain
- 6.4.11 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.12 CEVA Logistics
- 6.4.13 Mitsui-Soko Group
- 6.4.14 SENKO Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Suzuyo & Co.
- 6.4.16 SF Express
- 6.4.17 Yusen Logistics (Part of NYK Line)
- 6.4.18 MOL Logistics
- 6.4.19 Matsuoka Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.20 YOKOREI Co., Ltd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment








