 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910869
日本第三方物流(3PL)市場:佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2026-2031)Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
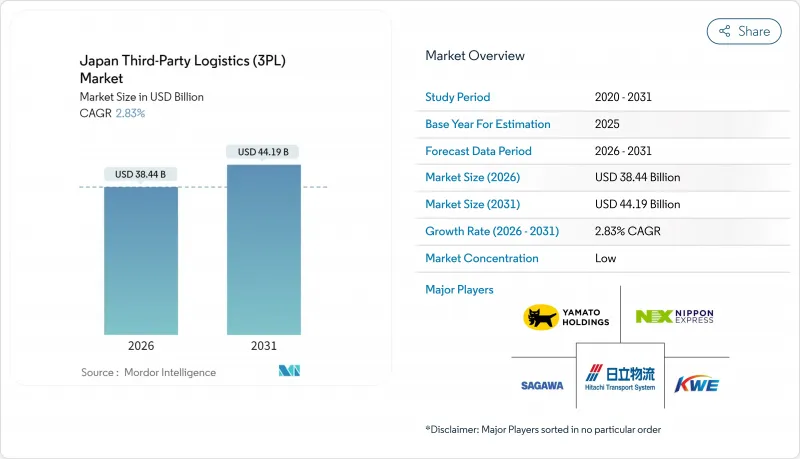
預計到 2026 年,日本第三方物流市場規模將達到 384.4 億美元,從 2025 年的 373.8 億美元成長到 2031 年的 441.9 億美元。
預計2026年至2031年年複合成長率(CAGR)為2.83%。
新的駕駛人加班限制、旨在促進數位化的全面補貼以及日益嚴格的脫碳目標,正迫使所有物流業者重新思考其網路設計。資產密集型業者需要在自動化預算和不斷上漲的租金之間尋求平衡,而利用數位平台的輕參與企業則無需擁有自有車輛也能蓬勃發展。零售商、醫療保健公司和半導體製造商都在尋求全國範圍的覆蓋和即時可視性,這推動了對能夠縮短前置作業時間和減少碳排放的整合解決方案的需求。因此,日本的第三方物流市場正悄悄從單一功能的運輸模式轉型為數據驅動的編配,即使在勞動力和土地資源嚴重受限的情況下,也能確保貨物的順暢流通。
日本第三方物流(3PL)市場趨勢與洞察
基於當日達和隔天達的電子商務文化正迫使零售商建立覆蓋全國的第三方物流網路。
消費者對快速配送的需求日益成長,迫使零售商與在日本第三方物流 (3PL) 市場經營分散式履約中心的第三方物流合作夥伴攜手。繼大和運輸退出亞馬遜當日達服務後,丸和運輸等新興企業宣布引進 1 萬輛新型輕型卡車以搶佔新業務,凸顯了靈活敏捷的企業所面臨的機遇。零售商正從單一庫存模式轉向多配送中心策略,以縮短最終配送距離,並在司機工時受限的情況下維持服務水準。在人口密集的都會區,第三方物流業者正在部署微型倉配中心並整合即時調度軟體,以應對激增的需求。這些趨勢使得建立全國性網路成為贏得大規模電商合約的先決條件,鞏固了快速反應能力在日本第三方物流市場的戰略重要性。
國家供應鏈數位化指令(綠色物流法案和開放API舉措)
日本的《綠色物流法》和開放API指令正在加速推動該國第三方物流市場的數位轉型。國土交通省已投入880億日圓公共資金,用於建造貨運匹配平台、通用數據標準和碳排放追蹤工具。一項聯合交付試點計畫能夠衡量二氧化碳減排量並將其轉化為可交易的碳權額度,從而為早期採用者共用運力和數據提供切實的獎勵。大型供應商正在部署以API為先導的運輸管理系統,而中型業者則加入聯盟平台以取得數位化貨運代理服務。中期來看,標準化的資料流可望提高平均整車運輸價格,部分抵銷新勞動法規導致的運力下降。
長期卡車駕駛人短缺
新的加班限制減少了每週的駕駛時間,而貨運量卻持續成長。即使薪資上漲,五分之四的運輸公司仍面臨駕駛人空缺。機器人正在倉庫中搬運托盤,使駕駛人能夠騰出精力專注於道路運輸,一些公司也開始透過體育特長生招募來吸引年輕員工。儘管有這些巧妙的解決方案,人才短缺仍然是限制成長的最迫切障礙。
細分市場分析
倉儲和分類領域目前是成長最快的收入板塊,年複合成長率達4.35%。需求主要來自全通路零售商和疫苗經銷商,他們需要配備溫控隔間、自動化穿梭車和單品掃描功能的設施。國內運輸管理業務量仍然最大,但營運時間限制和燃油價格波動限制了其成長。能夠將運輸和智慧倉儲管理相結合的供應商正在贏得更高的客戶佔有率和長期合約。
機器人貨物搬運、夾層揀貨模組和語音控制收貨站的投資正在增加。日本通運公司開設了一座配備自動推車的通用設計倉庫,使員工能夠專注於增值工作。這些資本投資透過提高每平方公尺的運轉率,幫助企業克服人手不足並降低當地租金。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 以當日達和隔日達為特徵的電子商務文化,正促使零售商建立覆蓋全國的第三方物流網路。
- 數位化(綠色物流法案與開放API舉措)
- 碳中和計畫和排放交易試點推動綠色第三方物流模式轉換
- 供應鏈韌性補貼和「中國+1」產業回流推動國內工廠物流需求
- 消費者群體老化;不斷擴大的宅配和醫療配送通路需要溫控第三方物流網路
- 5G 和物聯網的引入推動了人們對即時可視性的期望,從而推動了對技術密集型第三方物流(3PL) 的投資。
- 市場限制
- 駕駛人和勞動力老化問題日益嚴重。
- 倉儲空間短缺和租金上漲
- 競爭激烈的最後一公里包裹遞送市場正在擠壓利潤空間,並阻礙創新投資。
- 中型製造企業內部物流的文化偏好
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 主要政府法規和政策
- 技術趨勢與自動化
- 倉儲市場的整體趨勢
- 來自快遞、最後一公里配送和低溫運輸產業的需求
- 電子商務業務洞察
- 地緣政治事件如何影響市場
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方和消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過服務
- 國內運輸管理
- 路
- 鐵路
- 航空
- 內河航道
- 國際運輸管理
- 航空
- 海上運輸
- 其他
- 加值倉儲及配送服務 (VAWD)
- 國內運輸管理
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 車
- 能源與公共產業
- 製造業
- 生命科學與醫療保健
- 科技與電子
- 零售與電子商務
- 消費品/日用必需品
- 食品/飲料
- 其他
- 透過物流模型
- 輕資產(管理基礎)
- 資產密集型(擁有車輛和倉庫)
- 混合
- 按地區(日本)
- 關東
- 關西
- 中部
- 九州、沖繩
- 中國
- 四國
- 北海道
- 東北
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Nippon Express Co., Ltd.
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Kintetsu World Express, Inc.
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- LOGISTEED, Ltd.
- NYK Line(Including Yusen Logistics)
- Mitsui-Soko Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sankyu Inc.
- Nichirei Corporation
- Marubeni Logistics Corporation
- Kokusai Express Co., Ltd.
- Toyotsu Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
- Senko Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sumitomo Corporation
- Meitetsu Group
- DHL Group
- SBS Holdings, Inc.
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Samsung SDS
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Japan Third-Party Logistics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 38.44 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 37.38 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 44.19 billion, growing at 2.83% CAGR over 2026-2031.

New driver-overtime limits, sweeping digitalization grants, and rising decarbonization targets are forcing every logistics provider to rethink network design. Asset-heavy operators now balance automation budgets against rent inflation, while digital platforms let asset-light newcomers grow without owning fleets. Retailers, healthcare firms, and semiconductor manufacturers are asking for nationwide coverage and real-time visibility, lifting demand for integrated solutions that cut lead times and carbon footprints. As a result, the Japan 3PL market is quietly shifting from single-function transport toward data-enabled orchestration that keeps shipments moving despite deep labor and land constraints.
Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Trends and Insights
Same-Day/Next-Day E-commerce Culture Forcing Retailers Toward Nationwide 3PL Networks
Accelerating consumer demand for rapid delivery is compelling retailers to engage 3PL partners that operate distributed fulfillment nodes across the Japan 3PL market. After Yamato Transport exited Amazon's same-day service, challengers such as Maruwa Transport committed to 10,000 new light trucks to capture the business, underscoring the opportunity for agile players. Retailers are shifting away from single-site inventory models toward multi-DC strategies that shorten final-mile distances and protect service standards despite driver-hour caps. Within densely populated metros, 3PLs now deploy micro-fulfillment centers and integrate real-time routing software to absorb demand spikes. As a result, nationwide network coverage has become a prerequisite for winning large e-commerce contracts, solidifying the strategic importance of fast-response capabilities across the Japan 3PL market.
National Supply-Chain Digitalization Mandates (Green Logistics Act & Open-API Initiatives)
Japan's Green Logistics Act and Open-API directives are accelerating digital adoption throughout the Japan 3PL market. Public funding totaling USD 88 billion supports load-matching platforms, common data standards, and carbon-tracking tools overseen by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism. Collaborative delivery pilots measure CO2 savings that can translate into tradable credits, giving early movers a tangible incentive to share capacity and data. Leading providers are rolling out API-first transport management systems, while midsize operators join consortium platforms to access digital freight brokerage. Over the medium term, standardized data flows are expected to lift average truck load factors and partially offset the capacity loss triggered by new labor rules.
Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage
New overtime caps slice weekly driving hours, yet delivery counts keep climbing. Four out of five carriers report open seats even after pay bumps. Robots now shuttle pallets inside depots, letting scarce drivers focus on road miles, while some firms target younger recruits through sports-based hiring drives. Despite creative fixes, the talent gap remains the single most immediate brake on growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Carbon-Neutral Commitments & Emissions-Trading Pilots Driving Modal Shift to Green 3PLs
- Reshoring & Supply-Chain Resilience Subsidies
- Warehouse Land Scarcity & Rent Inflation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Warehousing Space that stores and sorts now accounts for the fastest revenue line, expanding at 4.35% CAGR. Demand comes from omnichannel retailers and vaccine distributors that need temperature-zoned rooms, automated shuttles, and item-level scanning. Domestic transportation management still carries the largest volume, yet driver-hour rules and fuel volatility cap its growth. Providers that blend both-transport plus smart storage-capture higher wallet share and longer contract tenures.
Investments flow into goods-to-person robots, mezzanine pick modules, and voice-directed receiving stations. Nippon Express opened a universal design warehouse where autonomous carts free staff to handle value-adding tasks. These upgrades help operators overcome labor shortages and keep regional rents under control by squeezing more turns from every square meter.
The Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Report is Segmented by Service (Domestic Transportation Management, International Transportation Management, and More), by End User (Automotive, Energy and Utilities, and More), by Logistics Model (Asset-Light, Asset-Heavy, and Hybrid), by Region (Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Kyushu and Okinawa, Chugoku, Shikoku, Hokkaido, Tohoku). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Nippon Express Co., Ltd.
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Kintetsu World Express, Inc.
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- LOGISTEED, Ltd.
- NYK Line (Including Yusen Logistics)
- Mitsui-Soko Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sankyu Inc.
- Nichirei Corporation
- Marubeni Logistics Corporation
- Kokusai Express Co., Ltd.
- Toyotsu Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
- Senko Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sumitomo Corporation
- Meitetsu Group
- DHL Group
- SBS Holdings, Inc.
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Samsung SDS
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Same-Day / Next-Day E-commerce Culture Forcing Retailers Toward Nationwide 3PL Networks
- 4.2.2 National Supply-Chain Digitalization Mandates (Green Logistics Act and Open-API Initiatives)
- 4.2.3 Carbon-Neutral Commitments and Emissions-Trading Pilots Driving Modal Shift to Green 3PLs
- 4.2.4 Supply-Chain Resilience Subsidies and China-plus-One Reshoring Fueling Domestic Plant Logistics Demand
- 4.2.5 Ageing Consumer Base Expanding Home-Delivery Grocery and Healthcare Channels Requiring Temperature-Stable 3PL Networks
- 4.2.6 5G & IoT Roll-Out Elevating Real-Time Visibility Expectations and Forcing Tech-Heavy 3PL Investments
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage and Aging Workforce
- 4.3.2 Warehouse Land Scarcity and Rent Inflation
- 4.3.3 Hyper-Competitive Last-Mile Parcel Market Compressing Margins and Discouraging Innovation Investment
- 4.3.4 Cultural Preference for In-House Logistics among Mid-Size Manufacturers
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Key Government Regulations & Initiatives
- 4.6 Technological Trends and Automation
- 4.7 General Trends in Warehousing Market
- 4.8 Demand from CEP, Last-Mile Delivery and Cold-Chain Segments
- 4.9 Insights on E-Commerce Business
- 4.10 Impact of Geopolitical Events on the Market
- 4.11 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.11.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.11.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.11.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.11.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.11.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management
- 5.1.1.1 Road
- 5.1.1.2 Rail
- 5.1.1.3 Air
- 5.1.1.4 Inland Waterway
- 5.1.2 International Transportation Management
- 5.1.2.1 Air
- 5.1.2.2 Sea
- 5.1.2.3 Others
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Warehousing and Distribution (VAWD)
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management
- 5.2 By End-User Industry
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.2 Energy and Utilities
- 5.2.3 Manufacturing
- 5.2.4 Life Sciences and Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Technology and Electronics
- 5.2.6 Retail and E-commerce
- 5.2.7 Consumer Goods and FMCG
- 5.2.8 Food and Beverages
- 5.2.9 Others
- 5.3 By Logistics Model
- 5.3.1 Asset-Light (Management-Based)
- 5.3.2 Asset-Heavy (Own Fleet and Warehouses)
- 5.3.3 Hybrid
- 5.4 By Region (Japan)
- 5.4.1 Kanto
- 5.4.2 Kansai
- 5.4.3 Chubu
- 5.4.4 Kyushu and Okinawa
- 5.4.5 Chugoku
- 5.4.6 Shikoku
- 5.4.7 Hokkaido
- 5.4.8 Tohoku
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Nippon Express Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Kintetsu World Express, Inc.
- 6.4.4 SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 LOGISTEED, Ltd.
- 6.4.6 NYK Line (Including Yusen Logistics)
- 6.4.7 Mitsui-Soko Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Sankyu Inc.
- 6.4.9 Nichirei Corporation
- 6.4.10 Marubeni Logistics Corporation
- 6.4.11 Kokusai Express Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Toyotsu Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Senko Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Sumitomo Corporation
- 6.4.16 Meitetsu Group
- 6.4.17 DHL Group
- 6.4.18 SBS Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.19 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.20 Samsung SDS









