 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910550
新加坡第三方物流(3PL) 市場:佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測 (2026-2031)Singapore 3PL - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
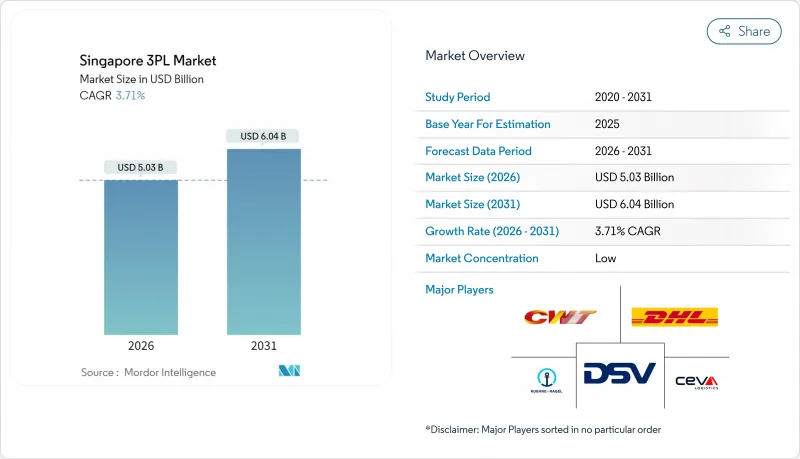
新加坡第三方物流(3PL) 市場在 2025 年的價值為 48.5 億美元,預計到 2031 年將達到 60.4 億美元,高於 2026 年的 50.3 億美元。
預計在預測期(2026-2031 年)內,複合年成長率將達到 3.71%。
新加坡物流業的穩定擴張得益於其無與倫比的多模態能力、65項自由貿易協定網路以及一系列大型基礎設施大型企劃,這些因素共同鞏固了新加坡作為東南亞主要交通和配送中心的地位。電子商務的快速發展推動了生命科學生產對低溫運輸的需求,而倉儲自動化技術的日益普及也擴大了外包物流的目標客戶群。同時,混合資產模式降低了服務創新的進入門檻。然而,結構性成本壓力——例如土地和人事費用上漲、港口堵塞加劇以及新的碳排放報告要求——正在加劇,這使得規模化、自動化程度高且監管能力強的營運商更具優勢。全球物流巨頭的策略性收購表明,在新加坡擁有高階業務佈局對於建立亞太地區的端到端供應鏈至關重要。
新加坡第三方物流(3PL) 市場趨勢與洞察
國內和跨境電子商務的爆炸性成長
東南亞線上零售的快速成長正在改變人們對履約速度、逆向物流服務和最後一公里配送效率的需求。新加坡佔據了相當大的流量,零售商將庫存集中在該國,從而能夠為該地區6.8億消費者提供兩到三天的配送服務。物流供應商正在擴建小包裹分類線並整合海關API,以更好地處理日益複雜的SKU和退貨流程。新加坡郵政投資2,220萬美元對其區域電商物流中心進行設施升級,使其處理能力翻了兩番,達到每天40萬件包裹,凸顯了應對措施的資本密集特徵。社群經銷商和大件商品類別進一步擴大了第三方物流服務商的收入基礎。同時,東協內部監管協調的加強正在減少跨境摩擦,從而提升經由新加坡口岸處理的貨物量。
政府主導的大型企劃(大士大型港口、樟宜貨運樞紐)
耗資200億美元的圖阿斯超級港計畫於2040年全面完工,年吞吐能力將達到6,500萬個標準箱。該港口將配備全自動岸邊起重機、無人駕駛車輛和基於人工智慧的泊位調度系統。這些設施將縮短船舶週轉時間,並降低物流用戶的營運成本。配合樟宜機場的貨運基礎設施擴建(包括第二個航空貨運物流園區),年吞吐能力將從300萬噸提升至540萬噸。自由貿易區模式,以加快轉運週期。這些長期計劃,加上地緣政治動盪導致供應鏈改道需求日益成長,將使新加坡在吸引改道貨物方面佔據先機,因為鄰近港口正面臨土地和水深限制。
房地產和人事費用上漲
土地稀缺導致工業用地租金上漲,預計到2025年將達到每平方公尺每月11.8至31.1美元。同時,儘管GDP成長放緩,名目工資仍上漲了5.2%。根據漸進式工資模式,保全人員目前的最低月薪為1,961美元,而零工經濟宅配員的強制性退休金繳款則使其總收入增加17%至20%。這些結構性成本因素正在擠壓依賴勞力密集倉儲營運和末端配送業務的企業的利潤空間,加速了自動化技術的普及和部分非核心職能的境外外包。
細分市場分析
截至2025年,國內運輸管理將佔新加坡第三方物流(3PL)市場的32.65%,反映出在人口稠密、多式聯運網路支撐的新加坡島嶼上協調最後一公里配送路線的複雜性。隨著零售商對交貨期限和即時可視性的需求日益成長,這一細分市場持續穩步發展。加值倉儲和配送服務雖然收入基數較小,但預計到2031年將以7.02%的複合年成長率成長,因為營運商希望透過外包套件組裝、貼標和退貨管理來降低營運資本。高盈利和合約穩定性吸引新進入者,但中級自動化所需的資本投資使現有企業保持了優勢。
邊緣運算感測器和人工智慧驅動的貨架陳列軟體將揀貨到出貨週期縮短了20%,提高了客戶的期望值。這推動了對整合運輸、倉儲和清關的編配平台的需求,這些平台將整合到一個統一的服務等級協定(SLA)中。新加坡、馬來西亞和泰國之間跨境卡車運輸路線的增加提高了路線密度,這對國際運輸管理服務提供者來說是一個好消息。隨著混合動力卡車的日益普及,在其倉庫網路中整合電池更換設施的公司有望獲得更多客戶佔有率,從而鞏固新加坡第三方物流(3PL)市場從純粹運輸向綜合物流解決方案的結構性轉變。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 國內和跨境電子商務的爆炸性成長
- 大型政府主導計劃(大士港、樟宜貨運樞紐)
- 生命科學和精準醫療領域的低溫運輸需求
- 東協貿易一體化與新加坡自由貿易網路
- 倉儲自動化與機器人競賽
- 電池換流基礎設施能夠支援大規模電動車隊。
- 市場限制
- 房地產和勞動成本飆升
- 由於需求突然增加,港口和機場出現擁擠
- 第三方物流(3PL) IT 基礎架構的網路安全回應成本
- 強制性碳排放報告給中小企業帶來的負擔
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 新加坡作為東協轉運樞紐的角色
- 電子商務產業概況(國內和跨境)
- 新冠疫情及地緣政治事件的影響檢驗
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過服務
- 國內運輸管理(DTM)
- 路
- 鐵路
- 海路
- 水道
- 國際運輸管理(ITM)
- 路
- 鐵路
- 海路
- 水道
- 加值倉儲及配送服務 (VAWD)
- 國內運輸管理(DTM)
- 最終用戶
- 車
- 能源與公共產業
- 製造業
- 生命科學與醫療保健
- 科技與電子
- 電子商務
- 消費品和日用必需品(快速消費品)
- 食品/飲料
- 其他
- 透過物流模型
- 輕資產(管理型)
- 資產密集型(擁有車輛和倉庫)
- 混合
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度分析
- 戰略舉措和投資
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- DHL Group
- DSV
- CEVA Logistics
- CWT Ltd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Toll Group
- Nippon Express
- UPS Inc.
- FedEx
- Singapore Post Ltd(SingPost)
- CJ Logistics Asia
- Rhenus Logistics Pte Ltd
- Yang Kee Logistics Pte Ltd
- Ninja Van
- Uparcel
- Kintetsu World Express
- Yusen Logistics
- Nippon Express
- Geodis
- Kerry Logistics
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Singapore 3PL Market was valued at USD 4.85 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 5.03 billion in 2026 to reach USD 6.04 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

The steady expansion stems from Singapore's unrivaled multimodal connectivity, its network of 65 free-trade agreements, and a pipeline of infrastructure megaprojects that collectively deepen the city-state's role as Southeast Asia's principal transshipment and distribution hub. Rapid e-commerce penetration accelerated cold-chain demand from life-sciences production, and rising adoption of warehouse automation increases the addressable base for outsourced logistics, while hybrid asset models lower entry barriers for service innovation. At the same time, escalating land and labor costs, acute port congestion, and new carbon-reporting mandates add structural cost pressure that rewards operators with scale, automation, and strong regulatory compliance capabilities. Strategic acquisitions by global logistics majors highlight how ownership of premium Singapore footprints is becoming essential for end-to-end Asia-Pacific supply-chain orchestration.
Singapore 3PL Market Trends and Insights
Explosive Growth of Domestic & Cross-Border E-commerce
Southeast Asia's online retail boom is transforming demand profiles for fulfillment speed, reverse-logistics services, and last-mile routing efficiency. Singapore captures outsized volumes because merchants consolidate inventory in the republic to reach 680 million regional consumers in two-to-three-day delivery windows. Logistics providers are scaling parcel-sortation lines and integrating customs-clearance APIs to handle higher SKU complexity and return flows. Singapore Post quadrupled processing capacity to 400,000 parcels daily at its Regional eCommerce Logistics Hub after a USD 22.2 million upgrade, illustrating the capital intensity of this response. Social-commerce sellers and bulky-item categories further broaden the revenue pool for third-party specialists, while regulatory harmonization across ASEAN lowers cross-border friction and boosts volumes handled through Singapore gateways.
Government Megaprojects (Tuas Mega-Port, Changi Cargo Hub)
The USD 20 billion Tuas Mega-Port, slated for full completion by 2040 with 65 million TEU annual capacity, introduces fully automated quay cranes, driverless vehicles, and AI-driven berth scheduling that together compress vessel turnaround times and trim operating costs for logistics users. Parallel expansion of Changi Airport's cargo infrastructure, including a second air-freight logistics park, will lift capacity from 3 million to 5.4 million tons yearly and embed a free-trade zone model that accelerates transshipment cycle times. These long-horizon projects dovetail with supply-chain rerouting caused by geopolitical disruptions, giving Singapore a first-mover advantage in capturing diverted traffic as neighboring gateways confront land and depth constraints.
Escalating Real Estate & Labor Costs
Industrial rents climbed to USD 11.8-31.1 per m2 monthly in 2025 amid land scarcity, while nominal wages advanced 5.2% even as GDP growth lagged. Security officers now earn at least USD 1,961 per month under the Progressive Wage Model, and compulsory pension contributions for gig couriers add a 17-20% payroll burden. These structural cost inflators compress margins for providers relying on labor-intensive warehousing and last-mile fleets, prompting accelerated automation rollouts and selective offshoring of non-core activities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cold-chain Demand from Life-sciences & Precision Medicine
- ASEAN Trade Integration & Singapore's Free-trade Network
- Port & Airport Congestion from Demand Surges
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Domestic Transportation Management accounted for 32.65% of the Singapore third-party logistics market in 2025, reflecting the complexity of orchestrating final-mile routes across a densely populated island supported by multimodal links. The segment continues to grow steadily as retailers push tighter cut-off times and real-time visibility expectations. Value-Added Warehousing & Distribution, while representing a smaller revenue base, is forecast to deliver a 7.02% CAGR through 2031 as merchants outsource kitting, labeling, and returns management to trim working capital. Higher margin profiles and sticky contracts attract new entrants, but the capital spend required for mezzanine-floor automation preserves an edge for incumbents.
Edge-computing sensors and AI-powered slot-assignment software have cut pick-to-ship cycles by 20%, heightening customer expectations and boosting demand for orchestration platforms that bundle transport, warehousing, and customs clearance into a single SLA. Cross-border trucking lanes linking Singapore to Malaysia and Thailand add route density that benefits international transportation management providers. As hybrid electric trucks gain mileage, firms integrating battery-swap nodes within their depot networks stand to capture incremental wallet share, reinforcing the structural shift from pure haulage toward integrated logistics solutions within the Singapore third-party logistics market.
The Singapore Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Report is Segmented by Service (Domestic Transportation Management, International Transportation Management, and More), by End User (Automotive, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing, Life Sciences & Healthcare, Technology & Electronics, E-Commerce, and More), and by Logistics Model (Asset-Light, Asset-Heavy, Hybrid). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- DSV
- CEVA Logistics
- CWT Ltd
- Kuehne + Nagel
- Toll Group
- Nippon Express
- UPS Inc.
- FedEx
- Singapore Post Ltd (SingPost)
- CJ Logistics Asia
- Rhenus Logistics Pte Ltd
- Yang Kee Logistics Pte Ltd
- Ninja Van
- Uparcel
- Kintetsu World Express
- Yusen Logistics
- Nippon Express
- Geodis
- Kerry Logistics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Explosive growth of domestic & cross-border e-commerce
- 4.2.2 Government megaprojects (Tuas Mega-Port, Changi Cargo Hub)
- 4.2.3 Cold-chain demand from life-sciences & precision medicine
- 4.2.4 ASEAN trade integration & Singapore's free-trade network
- 4.2.5 Warehouse-automation & robotics adoption race
- 4.2.6 Battery-swap infrastructure enabling heavy-EV fleets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Escalating real-estate & labour costs
- 4.3.2 Port & airport congestion from demand surges
- 4.3.3 Cyber-security compliance costs for 3PL IT stacks
- 4.3.4 Mandatory carbon-reporting burdens on SMEs
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Singapore as ASEAN Trans-shipment Hub
- 4.9 E-commerce Sector Snapshot (Domestic & Cross-border)
- 4.10 Covid-19 Impact Review and Geo-Political Events
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management (DTM)
- 5.1.1.1 Roadways
- 5.1.1.2 Railways
- 5.1.1.3 Airways
- 5.1.1.4 Waterways
- 5.1.2 International Transportation Management (ITM)
- 5.1.2.1 Roadways
- 5.1.2.2 Railways
- 5.1.2.3 Airways
- 5.1.2.4 Waterways
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Warehousing & Distribution (VAWD)
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management (DTM)
- 5.2 By End User
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.2 Energy & Utilities
- 5.2.3 Manufacturing
- 5.2.4 Life Sciences & Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Technology & Electronics
- 5.2.6 E-commerce
- 5.2.7 Consumer Goods & FMCG
- 5.2.8 Food & Beverages
- 5.2.9 Others
- 5.3 By Logistics Model
- 5.3.1 Asset-Light (Management-Based)
- 5.3.2 Asset-Heavy (Own Fleet & Warehouses)
- 5.3.3 Hybrid
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration Analysis
- 6.2 Strategic Moves & Investments
- 6.3 Market-Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 DSV
- 6.4.3 CEVA Logistics
- 6.4.4 CWT Ltd
- 6.4.5 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.6 Toll Group
- 6.4.7 Nippon Express
- 6.4.8 UPS Inc.
- 6.4.9 FedEx
- 6.4.10 Singapore Post Ltd (SingPost)
- 6.4.11 CJ Logistics Asia
- 6.4.12 Rhenus Logistics Pte Ltd
- 6.4.13 Yang Kee Logistics Pte Ltd
- 6.4.14 Ninja Van
- 6.4.15 Uparcel
- 6.4.16 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.4.17 Yusen Logistics
- 6.4.18 Nippon Express
- 6.4.19 Geodis
- 6.4.20 Kerry Logistics









