 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910825
歐洲電動卡車市場-佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Europe Electric Truck - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
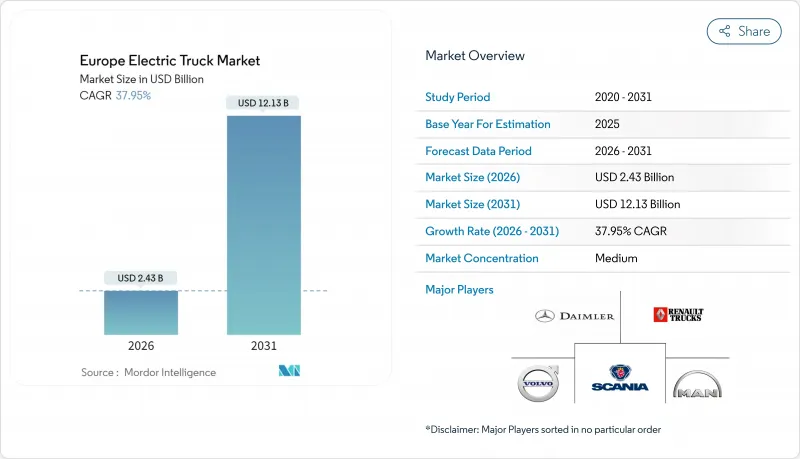
歐洲電動卡車市場預計將從 2025 年的 17.6 億美元成長到 2026 年的 24.3 億美元,預計到 2031 年將達到 121.3 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 37.95%。
歐盟具有約束力的二氧化碳減排目標、電池組價格的下降以及兆瓦級充電走廊的快速發展,共同推動了這一快速成長。這些因素正匯聚一堂,推動電動卡車從試點計劃走向主流車隊,尤其是在繁忙的物流路線上。監管期限迫使製造商擴大生產規模,而企業永續性措施則轉化為穩定的訂單,從而穩定需求並促進規模經濟。同時,電池能量密度的提高、可再生能源的日益普及以及創新的資金籌措模式正在縮小電動卡車與柴油卡車的總擁有成本 (TCO) 差距,進一步加速了電動卡車在區域和長途貨運領域的應用。因此,歐洲電動卡車市場正從早期採用者邁向覆蓋整個歐洲大陸主要貨運路線的廣泛商業性部署階段。
歐洲電動卡車市場趨勢與洞察
歐盟二氧化碳排放標準及2040年零排放車輛銷售義務
具有約束力的二氧化碳減排目標使零排放卡車成為一項法律要求,而非可永續性。 2030 年和 2035 年的中期目標提供了明確的銷售指標,為製造商數十億美元的電氣化投資提供了基礎。車隊營運商若不遵守規定將面臨嚴厲處罰,這推動了電池式電動車和燃料電池車型的大規模採購。德國的「零排放城市」政策等國家政策進一步收緊了合規標準,確保歐洲電動卡車市場在 2040 年截止日期前實現強勁成長。
電池組成本迅速下降
到2024年,電池組價格將下降20%,穩定在每度電115美元。年行駛里程超過8萬公里的高里程物流車隊將率先實現與柴油車成本持平,因為燃料節省將抵消資本成本溢價。磷酸鐵鋰電池技術的廣泛應用降低了原料風險,並將充放電循環壽命延長至4000次以上,進一步降低了總擁有成本。歐洲超級工廠的建設將縮短供應鏈,增加本地採購,並增強規模經濟效益,以應對快速的學習曲線。
與柴油車相比,車輛初始成本更優
與柴油卡車相比,電動卡車的價格仍然高出40%至60%,這對中歐和南歐對價格敏感的業者來說是一個障礙。這項溢價反映了電池成本、低產量和技術複雜性,但預計到2027-2028年,成本的快速下降將顯著緩解此限制。低利率融資管道有限進一步加劇了小規模車隊面臨的這個問題。然而,卡車即服務(TaaS)模式和政府獎勵正在加速推動透過將資本支出轉變為更符合現金流模式的營運支出結構來抵消這一劣勢。
細分市場分析
到2025年,純電動卡車將佔歐洲電動卡車市場規模的76.12%,而燃料電池卡車預計到2031年將以42.75%的複合年成長率(CAGR)實現最高成長。燃料電池卡車的初期優勢在於充電站密度高、在小批量和區域貨運中久經考驗的可靠性,以及對於經常長途運輸的車隊而言營運成本低。在預測期內,氫氣加註網路將在斯堪地那維亞和德國不斷擴展,從而促進燃料電池在重型和溫控貨物運輸領域的應用,這些領域對車輛的運轉率和周轉速度要求較高。隨著零排放區法規逐步取消內燃機備用模式,插電式混合動力卡車的市佔率將逐漸縮小。
由於車隊使用場景的趨同,純電動車將繼續主導都市區和短途區域線路,因為在這些線路中,夜間在倉庫充電是最方便的基礎設施模式。燃料電池驅動在每日行駛里程超過 600 公里的線路上將特別強勁,因為大型電池組帶來的負載容量損失可能會降低單次運輸的收入。隨著電池能量密度的提高和充電曲線的陡峭化,目前相當一部分燃料電池候選線路可能會轉變為純電動車方案,凸顯了歐洲電動卡車市場競爭的動態性。
到2025年,12噸以上的重型剛性卡車將佔歐洲電動卡車市場規模的47.05%。可預測的樞紐輻射式物流循環最大限度地提高了電池利用率,因此投資建造充電站設施是合理的。從2026年起,牽引車-半拖車細分市場將呈現最快成長,複合年成長率將達到39.05%,這得益於兆瓦級充電樁在歐洲貨運網路中的部署,以及先進的溫度控管技術在長途行駛循環下對電池組壽命的保障。 3.5噸以下的輕型卡車在排放氣體法規適用的密集都市區持續維持穩定的市場需求。中型專用車輛,例如垃圾壓縮車和配備起重機的底盤,正受到市政當局的日益關注,但年銷量仍然較低。
重型牽引車領域的競爭日益激烈,Start-Ups紛紛新興企業軟硬體提案解決方案,試圖降低總成本。現有廠商則以模組化平台應對,這些平台針對本地和跨境應用進行了最佳化,並力求保持其服務網路優勢。因此,歐洲電動卡車市場牽引車細分市場的價格預計將迅速下降,並為整個產品組合樹立新的標竿。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 歐盟二氧化碳排放標準與2040年零排放汽車銷售義務
- 電池組成本迅速下降
- 商業車隊脫碳計劃
- 購屋獎勵和道路通行費豁免
- 透過兆瓦級充電走廊開闢長途運輸路線
- 卡車即服務 (TaaS) 融資模式
- 市場限制
- 與柴油車相比,車輛初始成本更高
- 重型電動車公共充電基礎設施不足
- 倉庫層面的電力容量限制
- 電動卡車維修技能和零件短缺
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模及成長預測(價值(美元)及銷售量(單位))
- 依推進類型
- 電池式電動車
- 燃料電池電動車
- 插電式混合動力
- 按卡車類型
- 小型卡車(3.5噸以下)
- 中型卡車(3.6至12噸)
- 大型卡車(超過12噸)
- 聯結車
- 依電池類型
- 鋰鎳錳鈷氧化物(NMC)
- 磷酸鋰鐵(LFP)
- 其他(NCA、LTO、固體原型)
- 按電池容量
- 少於50度
- 50至250千瓦時
- 250度或以上
- 按範圍
- 最遠可達 200 公里(都市區)
- 201-400公里(區域配送)
- 超過400公里(長途)
- 透過使用
- 物流/小型配送
- 市政服務(廢棄物、道路清潔)
- 建築和採礦
- 零售和消費品分銷
- 公共產業及其他行業
- 按國家/地區
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 荷蘭
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 挪威
- 丹麥
- 比利時
- 波蘭
- 其他歐洲地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- AB Volvo
- Daimler Truck AG(Mercedes-Benz Trucks)
- Scania AB
- MAN Truck and Bus(SE)
- DAF Trucks NV
- Renault Trucks
- IVECO Group NV
- BYD Co. Ltd.
- Tesla Inc.
- Einride AB
- Tevva Motors Ltd.
- E-Force One AG
- Quantron AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Nikola Motor Europe
- Hyundai Motor Company
- E-Trucks Europe BV
- Lion Electric(EU operations)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The European electric truck market is expected to grow from USD 1.76 billion in 2025 to USD 2.43 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 12.13 billion by 2031 at 37.95% CAGR over 2026-2031.

This steep growth path is driven by the European Union's binding CO2-reduction targets, falling battery pack prices, and the rapid build-out of megawatt-class charging corridors. Together, these forces shift electric trucks from pilot projects to mainstream fleet assets, especially in high-utilization logistics routes. Regulatory deadlines compel manufacturers to ramp output, while corporate sustainability pledges translate into firm purchase orders that stabilize demand and spur scale economies. At the same time, improvements in battery energy density, rising renewable-power penetration, and innovative financing models narrow the remaining total-cost-of-ownership premium versus diesel, further accelerating adoption across regional and long-haul applications. As a result, the European electric truck market is moving from early-adopter clusters to a broad commercial footprint that touches every major freight corridor on the continent.
Europe Electric Truck Market Trends and Insights
EU CO2 Emission Standards and 2040 ZEV Sales Mandate
Binding CO2 reduction targets make zero-emission trucks a legal requirement rather than a voluntary sustainability choice. Interim 2030 and 2035 benchmarks provide a clear volume signal that enables manufacturers to justify multi-billion-dollar electrification investments. Fleet operators face steep non-compliance penalties, propelling procurement toward battery-electric and fuel-cell models at scale. National policies such as Germany's emission-free urban zones tighten the compliance net further, ensuring that the European electric truck market gains momentum well before the 2040 deadline.
Rapid Battery-Pack Cost Declines
In 2024, battery pack prices dropped by 20%, settling at USD 115 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Cost parity with diesel emerges first in high-mileage logistics fleets that cover more than 80,000 km annually, where fuel savings offset capital premiums. Wider adoption of LFP chemistry cuts raw-material exposure, boosts cycle life beyond 4,000 charges, and further lowers total ownership cost. European gigafactory build-outs shorten supply chains and anchor regional content, reinforcing the scale economies that sustain the steep learning curve.
High Upfront Vehicle Cost Versus Diesel
Electric trucks still carry a 40-60% sticker premium compared with diesel, a barrier for price-sensitive operators in Central and Southern Europe. The premium reflects battery costs, low production volumes, and technology complexity, though rapid cost declines suggest this restraint will diminish significantly by 2027-2028. Limited access to cheap financing amplifies the issue for small fleets. However, truck-as-a-service models and government incentives increasingly neutralize this disadvantage by converting capital expenditure into operational expense structures that better align with cash flow patterns.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate Fleet-Decarbonization Commitments
- Purchase Incentives and Road-Toll Exemptions
- Sparse Public HDV-Ready Charging Infrastructure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Battery-electric trucks held 76.12% of the European electric truck market size in 2025, while fuel-cell models track the steepest 42.75% CAGR through 2031. The initial dominance arises from a dense charging-station footprint, proven reliability in parcel delivery and regional freight, and lower operating costs for fleets that rack up daily mileage. Over the forecast period, hydrogen refueling networks extend across Scandinavia and Germany, catalyzing fuel-cell uptake in heavy haul and temperature-sensitive commodities that demand high uptime and quick turnarounds. Plug-in hybrids occupy a narrowing transition niche as zero-emission zoning rules begin to exclude combustion back-up modes entirely.
Fleet use-case alignment will continue to favor battery-electric formats in city and short regional corridors because overnight depot charging remains the simplest infrastructure model. Fuel-cell traction intensifies in routes exceeding 600 km per day, especially where payload penalties from large battery packs would otherwise erode revenue per trip. As battery-energy density improves and charging curves steepen, a measurable share of current fuel-cell prospect routes may flip to pure battery solutions, underscoring the dynamic nature of competition inside the Europe electric truck market.
Heavy-duty rigid trucks over 12 tons currently deliver 47.05% of Europe's electric truck market size in 2025. Their predictable hub-and-spoke logistics cycles maximize battery utilization and justify depot-charging investment. From 2026 onward, the tractor-trailer segment shows the fastest ramp, with a 39.05% CAGR as megawatt chargers roll out on the pan-European freight network and advanced thermal management maintains pack longevity under long-haul duty cycles. Light trucks up to 3.5 tons continue experiencing steady adoption in dense urban zones governed by emission-free mandates. Medium-duty specials such as garbage compactors or crane-equipped chassis see growing municipal interest, but at lower annual volume.
The competitive theater is intensifying around heavy-duty tractors, where newcomers from China and emerging European startups pitch integrated hardware-plus-software stacks that promise lower total cost. Legacy OEMs respond with modular platforms optimized for both regional and cross-border applications, aiming to protect service-network advantages. As a result, the European electric truck market will witness fast price discovery in the tractor segment, setting reference points for the rest of the portfolio.
The Europe Electric Truck Market Report is Segmented by Propulsion (Battery-Electric and More), Truck Type (Light Truck, Medium-Duty Truck, and More), Battery (NMC, LFP, and Others), Capacity (Below 50kWh, 50-250kWh, and More), Range (Up To 200km, 201-400km, and More), Application (Logistics and Parcel, Municipal Services, and More), and Country (Germany, UK, and More). Market Forecasts in Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- AB Volvo
- Daimler Truck AG (Mercedes-Benz Trucks)
- Scania AB
- MAN Truck and Bus (SE)
- DAF Trucks N.V.
- Renault Trucks
- IVECO Group N.V.
- BYD Co. Ltd.
- Tesla Inc.
- Einride AB
- Tevva Motors Ltd.
- E-Force One AG
- Quantron AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Nikola Motor Europe
- Hyundai Motor Company
- E-Trucks Europe BV
- Lion Electric (EU operations)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 EU CO2 Emission Standards and 2040 ZEV Sales Mandate
- 4.2.2 Rapid Battery-Pack Cost Declines
- 4.2.3 Corporate Fleet-Decarbonisation Commitments
- 4.2.4 Purchase Incentives and Road-Toll Exemptions
- 4.2.5 Megawatt-Charging Corridors Unlocking Long-Haul Routes
- 4.2.6 Truck-As-A-Service Financing Models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Upfront Vehicle Cost Vs. Diesel
- 4.3.2 Sparse Public HDV-Ready Charging Infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Depot-Level Grid-Capacity Constraints
- 4.3.4 Shortage of E-Truck Maintenance Skills and Parts
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Propulsion Type
- 5.1.1 Battery-Electric
- 5.1.2 Fuel-Cell Electric
- 5.1.3 Plug-in Hybrid
- 5.2 By Truck Type
- 5.2.1 Light Truck (Up to 3.5 t)
- 5.2.2 Medium-Duty Truck (3.6 to 12 t)
- 5.2.3 Heavy-Duty Truck (Above 12 t)
- 5.2.4 Tractor-Trailer
- 5.3 By Battery Type
- 5.3.1 Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
- 5.3.2 Lithium-Iron-Phosphate (LFP)
- 5.3.3 Others (NCA, LTO, solid-state prototypes)
- 5.4 By Battery Capacity
- 5.4.1 Less Than 50 kWh
- 5.4.2 50 to 250 kWh
- 5.4.3 Above 250 kWh
- 5.5 By Range
- 5.5.1 Up to 200 km (urban)
- 5.5.2 201 to 400 km (regional)
- 5.5.3 Above 400 km (long-haul)
- 5.6 By Application
- 5.6.1 Logistics and Parcel
- 5.6.2 Municipal Services (Waste, Street-sweep)
- 5.6.3 Construction and Mining
- 5.6.4 Retail and FMCG Delivery
- 5.6.5 Utility and Other Industrial
- 5.7 By Country
- 5.7.1 Germany
- 5.7.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3 France
- 5.7.4 Italy
- 5.7.5 Netherlands
- 5.7.6 Spain
- 5.7.7 Sweden
- 5.7.8 Norway
- 5.7.9 Denmark
- 5.7.10 Belgium
- 5.7.11 Poland
- 5.7.12 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AB Volvo
- 6.4.2 Daimler Truck AG (Mercedes-Benz Trucks)
- 6.4.3 Scania AB
- 6.4.4 MAN Truck and Bus (SE)
- 6.4.5 DAF Trucks N.V.
- 6.4.6 Renault Trucks
- 6.4.7 IVECO Group N.V.
- 6.4.8 BYD Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Tesla Inc.
- 6.4.10 Einride AB
- 6.4.11 Tevva Motors Ltd.
- 6.4.12 E-Force One AG
- 6.4.13 Quantron AG
- 6.4.14 Ford Motor Company
- 6.4.15 Nikola Motor Europe
- 6.4.16 Hyundai Motor Company
- 6.4.17 E-Trucks Europe BV
- 6.4.18 Lion Electric (EU operations)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment









