 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850114
虛擬行動服務業者(MVNO):市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
預計到 2025 年行動虛擬網路營運商 (MVNO) 市場規模將達到 753.5 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 1,044.6 億美元,複合年成長率為 6.75%。
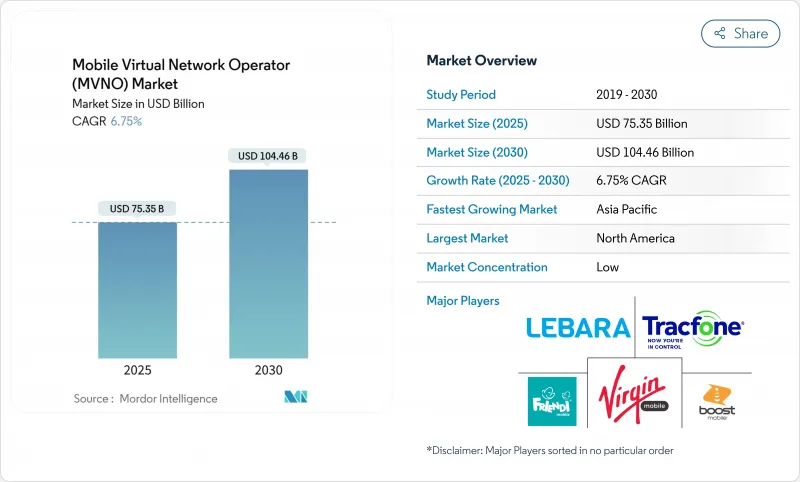
這一成長反映了該細分市場的潛力,因為金融科技和通訊業者融合、批發定價改革以及向基於 eSIM 的激活方式轉變,導致定價壓力不斷增加。 Revolut 在英國和德國推出 MVNO,以及 Nubank 在巴西推出 MVNO,夥伴關係表明銀行業務和網路連接之間的界限正在變得模糊。與此同時,韓國等市場的監管機構正在將批發費用降低高達 52%,重塑競爭經濟。雲端部署模式已佔據行動虛擬網路營運商市場的 57%,而受資本支出減少和推出週期加快的推動,雲端原生平台正以 10.6% 的複合年成長率擴張。競爭差異化將取決於 5G 網路切片、衛星到基地台鏈路以及人工智慧驅動的服務個人化。
全球虛擬行動服務業者(MVNO) 市場趨勢與洞察
行動用戶數量和智慧型手機普及率不斷上升
2023年底,亞太地區的行動連線將超過18億,人口普及率將達到63%,為該地區的GDP貢獻8,800億美元。這種快速成長為那些提供針對年輕人和移民群體客製化套餐的營運商在行動虛擬網路營運商(MVN)市場開闢了潛在的利基市場。菲律賓環球電信公司(Globe Philippines)正透過固定無線接入服務挖掘農村需求,而Telkomsel則憑藉其應用優先的「by.U」品牌瞄準數位原民。孟加拉、印度和巴基斯坦等國家仍然存在巨大的使用缺口,這為成本主導的行動虛擬網路營運商(MVNO)提供了一條擴張之路。高智慧型手機擁有率鼓勵了資料通訊密集型習慣,並強化了MVNO提供的基於使用量的典型收費系統。這些因素共同推動了行動虛擬網路營運商(MVNO)到2025年左右的普及前景。
對低成本語音和資料方案的需求
持續的通貨膨脹使消費者對價值更加敏感,並推動行動虛擬網路營運商市場中的客戶轉向廉價的供應商。在英國,現有的行動網路營運商在 2024 年下半年首次失去簽約線路,而虛擬網路營運商則增加了 170 萬用戶。 MobileX 以每月 3.48 美元起的價格出售經過人工智慧調整的套餐,客戶解約率低於 0.5%。線上銷售降低了零售開銷並允許更大的折扣,而基於應用程式的支援進一步降低了服務交付成本。主機營運商整合對獨立營運商構成威脅,但敏捷的虛擬網路營運商正在透過聯合品牌和基於社群的推薦來抵消規模劣勢並拓寬其盈利窗口。
激烈的價格競爭導致利潤壓力
轉換摩擦的降低和子品牌的豐富推高了費率方案,給整個行動虛擬網路營運商市場的 EBITDA 帶來壓力。儘管 Lycamobile 在英國擁有 170 萬條線路,但由於 5,100 萬英鎊的增值稅2022 年仍面臨 2,510 萬英鎊的虧損。託管 MNO 正在透過其自有折扣品牌加劇價格競爭,削弱獨立營運商的競爭力。 MobileX 創辦人 Peter Adderton 指出,MNO 對 TracFone 和 Mint Mobile 的收購減少了批發合作夥伴的數量並增強了他們的談判能力。 Vodafone Three 合併計劃於 2025 年完成,這將進一步增加英國的規模壓力,迫使較小的 MVNO 專業化或接受收購提案。
細分分析
到2024年,雲端部署將佔行動虛擬網路營運商市場的57%,這反映出市場正在快速轉向可擴展的基礎設施,以降低資本支出。隨著營運商尋求在流量激增期間實現彈性容量和自動化補丁管理,到2030年,雲端原生平台的複合年成長率將達到10.6%。這種轉變將加快功能部署,並推動基於人工智慧的留存工具,將客戶流失降至1%以下。 CompaxDigital與T-Mobile的聯合提案為中階虛擬網路營運商(MVNO)提供了先進的BSS/OSS堆疊,將推出時間從數月縮短至數週。像Gigs這樣的新興企業已經籌集了7300萬美元,用於銷售“MVNO-in-a-box”,凸顯了風險投資對輕資產參與企業的興趣。
由於虛擬化頻寬按需分配頻寬,雲端敏捷性進一步支援 5G 網路切片。這種靈活性使行動虛擬網路營運商 (MVNO) 能夠瞄準微細分市場,例如遊戲玩家或遠端醫療服務供應商,而無需從主機行動網路營運商 (MNO) 過度購買容量。相反,需要自主資料託管的國防和銀行客戶可能會受益於本地部署。雲端管理平面和邊緣站點使用者平面功能的混合策略使完整的行動虛擬網路營運商 (MVNO) 能夠獲得自動化的優勢,同時確保細粒度的安全性。隨著許多城市的公共雲端延遲降至 10 毫秒以下,外部部署完整核心的經濟效益可能會更加強勁。
完全行動虛擬營運商 (MVNO) 受益於直接擁有 SIM 卡、控制 HLR/HSS 以及完整的客戶生命週期數據,在 2024 年獲得了 41%的收益佔有率。它們透過捆綁內容和雲端儲存等附加價值服務來獲取更高的每用戶平均收入 (ARPU)。然而,輕量級行動虛擬業者或品牌行動虛擬業者由於其快速進入市場且領先資本投入較少,其複合年成長率高達 13.2%。零售商和應用程式公司被這種輕量級模式所吸引,因為它使他們無需具備電訊知識即可為現有生態系統添加連接。
服務業者協議是一種折衷方案,允許營運商租賃核心網路,同時擁有收費和策略控制權。經銷商協議仍然吸引沃爾瑪等大型零售商,它們利用門市客流量銷售預付套餐。德國1&1在獲得5G頻譜後,從一家成熟的行動虛擬網路營運商(MVNO)發展成為德國第四大行動網路營運商,展現了一條向上發展的行動發展之路。這樣的發展為雄心勃勃的營運商在其用戶群達到臨界點後提供了藍圖。然而,精簡模式可能會更快起飛,透過降低品牌進入門檻來啟動行動虛擬網路營運商市場。
MVNO 市場報告按部署模式(雲端、本地)、營運類型(經銷商、服務供應商、其他)、用戶類型(消費者、企業、物聯網為中心)、用例(折扣、商業、蜂窩 M2M、其他)、網路技術(2G/3G、5G、其他)、分銷管道(僅在線上/數位、實體零售、其他)和地區進行細分。
區域分析
2024年,北美以38.5%的市佔率領先行動虛擬網路營運商市場,這得益於其ARPU值是全球平均水準的四倍,以及鼓勵批發競爭的法規環境。營運商正在利用其龐大的後付費用戶群,在不蠶食高階產品線的情況下,提升銷售平價細分市場的子品牌銷售。 Verizon收購TracFone後,新增了2,000萬名預付用戶,印證了該細分市場的策略重要性。
亞太地區的複合年成長率為 10.1%,預計到 2027 年,新增用戶數將超過歐洲。這得歸功於印度、印尼和中國的智慧型手機價格下降以及頻譜競標自由化。政府對開放存取和 5G 快速部署的強制要求,為金融科技支援的行動虛擬營運商 (MVNO) 提供了肥沃的土壤,這些營運商瞄準的是銀行帳戶的人群。雲端原生參與企業也擁有豐富的開發人才,並降低了每張 SIM 卡的營運成本。
在歐洲,隨著用戶監管機構協調終端和漫遊費用,用戶成長依然強勁,對跨境虛擬網路營運商(MVNO)來說是個好兆頭。英國沃達豐三公司(Vodafone Three)計劃在未來八年投資110億英鎊,該公司必須兌現其支持至少三家獨立MVNO的承諾,從而保持激烈的競爭。隨著營運商向當地金融科技合作夥伴推出網路API,中東和非洲的新興叢集獲得了發展動力,而隨著Nubank的擴張,拉丁美洲的融合趨勢也在加速。總而言之,這些動態使區域動態成為行動虛擬網路營運商市場調整的關鍵視角。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場狀況
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 行動電話用戶和智慧型手機普及率的增加
- 對低成本語音和資料方案的需求
- 物聯網/M2M連接的興起
- 促進開放批發接取和 eSIM 接取的監管
- 金融科技與電信業者的融合催生了銀行品牌的虛擬營運商
- 衛星到行動電話的夥伴關係實現了全球MVNO覆蓋
- 市場限制
- 價格競爭激烈,利潤受到擠壓
- 網路品質和批發價格取決於主機 MNO
- 設備 OEM 控制 eSIM 所有權,繞過 MVNO 模式
- 私有頻譜共用允許公司自行提供服務
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管格局
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 投資分析
第5章市場規模及成長預測
- 按部署模型
- 雲
- 本地部署
- 按運轉方式
- 經銷商
- 服務業者
- 完整的行動虛擬營運商
- 輕量/品牌 MVNO
- 依用戶類型
- 消費者
- 公司
- 物聯網專用
- 按用途
- 折扣
- 商業
- 蜂窩 M2M
- 媒體和娛樂
- 零售
- 漫遊
- 移民
- 通訊批發
- 網路科技
- 2G/3G
- 4G/LTE
- 5G
- 衛星/NTN
- 按分銷管道
- 僅限線上/數位版
- 傳統零售店
- 開利子品牌店
- 第三方/批發
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 哥倫比亞
- 南美洲其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- ASEAN
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- TracFone Wireless(Verizon)
- Tesco Mobile
- Virgin Mobile
- Lycamobile
- Lebara Group
- Boost Mobile(T-Mobile)
- Cricket Wireless(ATandT)
- Giffgaff
- 1and1 Drillisch
- PosteMobile
- Truphone
- Kajeet
- Ting Mobile
- Google Fi
- Altice Mobile
- Asahi Net
- FreedomPop
- Airvoice Wireless
- FRiENDi Mobile
- Voiceworks
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The mobile virtual network operator market size reached USD 75.35 billion in 2025 and is on track to hit USD 104.46 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.75% CAGR.

Growth reflects the segment's ability to thrive amid price pressure, spurred by fintech-telco convergence, wholesale price reforms, and the move toward eSIM-enabled activation. Partnerships such as Revolut's MVNO roll-out in the UK and Germany and Nubank's service launch in Brazil illustrate the blurring line between banking and connectivity. At the same time, regulators in markets like South Korea are cutting wholesale fees by up to 52%, reshaping competitive economics. The cloud deployment model already commands 57% of the mobile virtual network operator market, and cloud-native platforms are expanding at 10.6% CAGR on the back of lower capex and faster launch cycles. Competitive differentiation increasingly hinges on 5G network slicing, satellite-to-cell links, and AI-driven service personalization.
Global Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) Market Trends and Insights
Rising Mobile-Subscriber Base and Smartphone Penetration
Mobile connections crossed 1.8 billion in Asia Pacific by end-2023, equal to 63% population penetration and contributing USD 880 billion to regional GDP. The surge opens addressable niches for operators that tailor plans to youth or migrant cohorts within the mobile virtual network operator market. Globe Philippines captured rural demand with fixed-wireless access, while Telkomsel's app-first "by.U" brand courts digital natives. Countries such as Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan still exhibit wide usage gaps, offering cost-led MVNOs a path to scale. High smartphone ownership propels data-heavy habits, reinforcing usage-based tariffs common to MVNO offers. These factors collectively lift adoption prospects through mid-decade.
Demand for Low-Cost Voice and Data Plans
Persistent inflation sharpens consumer sensitivity to value, pulling churn toward budget-centric providers inside the mobile virtual network operator market. In the UK, incumbent MNOs lost contract lines for the first time in late 2024, while MVNOs added 1.7 million subscribers. MobileX sells AI-tailored bundles from USD 3.48 per month and holds churn below 0.5%, an illustration of how data-driven pricing sustains loyalty. Online distribution trims retail overheads, enabling deeper discounts, and app-based support further reduces cost-to-serve. Although consolidation by host carriers threatens independents, agile MVNOs offset scale disadvantages through brand partnerships and community-based referrals, lengthening the window for profit capture.
Margin Squeeze from Intense Price Competition
Lower switching friction and plentiful sub-brands push tariffs toward cost, compressing EBITDA across the mobile virtual network operator market. Lycamobile battled £25.1 million losses in 2022 despite 1.7 million UK lines, burdened by a GBP 51 million VAT dispute and prolonged 5G service outages. Host MNOs intensify price warfare through owned discount brands, undercutting independents. MobileX founder Peter Adderton notes that MNO acquisitions of TracFone and Mint Mobile leave fewer wholesale partners, tightening negotiation leverage. The completed VodafoneThree merger in 2025 adds further scale pressure in the UK, forcing smaller MVNOs either to specialize or accept buy-out offers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of IoT/M2M Connections
- Regulatory Push for Open Wholesale Access and eSIM-Enabled Entry
- Dependence on Host MNOs for Network Quality and Wholesale Fees
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Cloud deployments accounted for 57% of the mobile virtual network operator market in 2024, reflecting rapid migration toward scalable infrastructure that lowers capex. Cloud-native platforms are posting a 10.6% CAGR through 2030 as operators seek elastic capacity during traffic spikes and automated patch management. The shift enables faster feature rollouts and facilitates AI-based retention tools that keep customer churn below 1%. CompaxDigital's joint offer with T-Mobile brings advanced BSS/OSS stacks to mid-tier MVNOs, cutting launch times from months to weeks. Start-ups like Gigs raised USD 73 million to market "MVNO-in-a-box," underscoring venture appetite for asset-light entrants.
Cloud agility further supports 5G network slicing because virtualized cores allocate bandwidth on demand. This flexibility equips MVNOs to target micro-segments such as gamers or tele-medicine providers without over-buying capacity from host MNOs. Conversely, on-premise installations remain relevant for defense or banking clients requiring sovereign data hosting. A hybrid strategy-cloud management plane paired with edge-site user-plane functions-gives full MVNOs granular security while still harvesting automation gains. As public-cloud latency falls below 10 milliseconds in many metros, the economic case for full off-premise cores will continue to strengthen.
Full MVNOs secured 41% revenue share in 2024, benefitting from direct SIM ownership, HLR/HSS control, and complete customer-life-cycle data. They capture higher ARPU by bundling value-added services such as content or cloud storage. Light or brand MVNOs, however, are expanding at 13.2% CAGR owing to quicker go-to-market and minimal upfront capital. Retailers and app firms gravitate toward this lighter model to append connectivity to existing ecosystems without deep telecom expertise.
Service-operator constructs offer a compromise, allowing ownership of billing and policy while leasing the core. Reseller agreements still attract big-box merchants like Walmart that leverage store traffic to sell prepaid bundles. Germany's 1&1 demonstrated an upward mobility pathway, evolving from full MVNO to the nation's fourth MNO after securing 5G spectrum. Such evolution provides a blueprint for ambitious operators once the subscriber base crosses critical mass. Yet light models will likely proliferate faster, energizing the mobile virtual network operator market by lowering brand-entry barriers.
The MVNO Market Report is Segmented by Deployment Model (Cloud and On-Premise), Operational Mode (Reseller, Service Operator, and More), Subscriber Type (Consumer, Enterprise, and IoT-Specific), Application (Discount, Business, Cellular M2M, and More), Network Technology (2G/3G, 5G, and More), Distribution Channel (Online/Digital-only, Traditional Retail Stores, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
North America led the mobile virtual network operator market with a 38.5% share in 2024, underpinned by ARPU levels four times the global mean and a regulatory climate that fosters wholesale competition. Operators leverage large post-paid bases to upsell value-segment sub-brands without cannibalizing premium lines. The TracFone acquisition by Verizon added 20 million prepaid users, affirming the segment's strategic weight.
Asia Pacific is advancing at a 10.1% CAGR and is set to overtake Europe in gross additions by 2027, powered by smartphone affordability and liberalized spectrum auctions in India, Indonesia, and China. Government mandates for open access plus rapid 5G rollouts make the region fertile ground for fintech-backed MVNOs targeting unbanked populations. Cloud-native entrants also find abundant developer talent, lowering operating cost per SIM.
Europe maintains steady subscriber growth as regulators harmonize termination rates and roaming fees, a boon for cross-border MVNOs. The UK's VodafoneThree entity plans GBP 11 billion investment over eight years but must honor undertakings to support at least three independent MVNOs, preserving competitive intensity. Emerging clusters in the Middle East and Africa gain traction as operators deploy network APIs to local fintech partners, while Latin America's convergence trend accelerates after Nubank's expansion. Collectively, these dynamics position geography as a critical lens for go-to-market adjustments inside the mobile virtual network operator market.
- TracFone Wireless (Verizon)
- Tesco Mobile
- Virgin Mobile
- Lycamobile
- Lebara Group
- Boost Mobile (T-Mobile)
- Cricket Wireless (ATandT)
- Giffgaff
- 1and1 Drillisch
- PosteMobile
- Truphone
- Kajeet
- Ting Mobile
- Google Fi
- Altice Mobile
- Asahi Net
- FreedomPop
- Airvoice Wireless
- FRiENDi Mobile
- Voiceworks
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising mobile-subscriber base and smartphone penetration
- 4.2.2 Demand for low-cost voice and data plans
- 4.2.3 Expansion of IoT/M2M connections
- 4.2.4 Regulatory push for open wholesale access and eSIM-enabled entry
- 4.2.5 Fintech-telco convergence spawning bank-branded MVNOs
- 4.2.6 Satellite-to-cell partnerships enabling global MVNO coverage
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Margin squeeze from intense price competition
- 4.3.2 Dependence on host MNOs for network quality and wholesale fees
- 4.3.3 Device-OEM control of eSIM ownership bypassing MVNO model
- 4.3.4 Private-spectrum sharing lets enterprises self-provision service
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment Model
- 5.1.1 Cloud
- 5.1.2 On-premise
- 5.2 By Operational Mode
- 5.2.1 Reseller
- 5.2.2 Service Operator
- 5.2.3 Full MVNO
- 5.2.4 Light / Brand MVNO
- 5.3 By Subscriber Type
- 5.3.1 Consumer
- 5.3.2 Enterprise
- 5.3.3 IoT-specific
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Discount
- 5.4.2 Business
- 5.4.3 Cellular M2M
- 5.4.4 Media and Entertainment
- 5.4.5 Retail
- 5.4.6 Roaming
- 5.4.7 Migrant
- 5.4.8 Telecom Wholesale
- 5.5 By Network Technology
- 5.5.1 2G/3G
- 5.5.2 4G/LTE
- 5.5.3 5G
- 5.5.4 Satellite/NTN
- 5.6 By Distribution Channel
- 5.6.1 Online/Digital-only
- 5.6.2 Traditional Retail Stores
- 5.6.3 Carrier Sub-brand Stores
- 5.6.4 Third-Party/Wholesale
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Mexico
- 5.7.2 South America
- 5.7.2.1 Brazil
- 5.7.2.2 Argentina
- 5.7.2.3 Colombia
- 5.7.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Italy
- 5.7.3.5 Spain
- 5.7.3.6 Russia
- 5.7.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.7.4.1 China
- 5.7.4.2 India
- 5.7.4.3 Japan
- 5.7.4.4 South Korea
- 5.7.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.7.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.7.5 Middle East
- 5.7.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.7.5.3 Turkey
- 5.7.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.7.6 Africa
- 5.7.6.1 South Africa
- 5.7.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.7.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 TracFone Wireless (Verizon)
- 6.4.2 Tesco Mobile
- 6.4.3 Virgin Mobile
- 6.4.4 Lycamobile
- 6.4.5 Lebara Group
- 6.4.6 Boost Mobile (T-Mobile)
- 6.4.7 Cricket Wireless (ATandT)
- 6.4.8 Giffgaff
- 6.4.9 1and1 Drillisch
- 6.4.10 PosteMobile
- 6.4.11 Truphone
- 6.4.12 Kajeet
- 6.4.13 Ting Mobile
- 6.4.14 Google Fi
- 6.4.15 Altice Mobile
- 6.4.16 Asahi Net
- 6.4.17 FreedomPop
- 6.4.18 Airvoice Wireless
- 6.4.19 FRiENDi Mobile
- 6.4.20 Voiceworks
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment








