|
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1842717
6G通訊的光和光電的機會:市場·技術 (2026-2046年)6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046 |
||||||
光學和光電子學是6G通訊成功的關鍵組成部分,本報告將提供相關指導。本報告針對6G價值鏈上的所有利害關係人,包括投資者、營運商、光學和光電子材料供應商以及整合商。雖然6G的部署主要透過改進現有5G硬體和頻率來實現,但預計物理層之外也將有顯著的改進。光學和光電子學對於實現顛覆性的新服務和高盈利能力至關重要。
關鍵新硬體
6G有望在效能方面實現數量級的提升,從而實現廣泛應用,並有可能催生全新的客戶端設備和商業模式。這需要引入光無線通訊(OWC)、光訊號處理(OSP)、自供電太陽能光伏技術、利用日光輻射冷卻的被動冷卻(PDRC)以及改進的光纖和中間介質。大部分基礎設施需要具備光學透明性,以便能夠作為 "社會融合通訊網路" 廣泛應用。
實現卓越效能的關鍵路徑
只有融合這些光學和光電技術,6G 才能真正達到其承諾的性能水準。 6G 超越了簡單的 GHz 頻段衛星通訊和室內 Wi-Fi;它涵蓋了全新的光學技術,包括雷射和雷射二極體、可重構光電智慧表面 (RIS)、光子晶片、多結太陽能電池薄膜、平流層太陽能無人機基地台、光電傳輸線、光學全像術以及用於智慧窗戶的多功能結構光電材料。
一份內容全面、極具實用價值的452頁產業報告
這份452頁的報告匯集了博士級的專業知識,對2025年之前的產業發展趨勢進行了深入分析。報告會持續更新,以確保內容與時俱進,涵蓋所有機遇,而不僅僅是OWC。
目錄
第1章 摘要整理和結論
- 本報告的目的和焦點
- 調查手法
- 關於 6G 通訊系統和硬體的 17 個結論和 10 個資訊圖
- 11SWOT評估
- 6G系統·材料·標準化藍圖
- 6G材料·硬體設備市場預測
第2章 簡介
- 概述:6G 硬體設計理念與經驗教訓
- 6G 成功的關鍵光學與光電技術
- 創新潛力6G材料發展
- 學術研究實例及最新市場研究介紹
第3章 6G光無線通訊 (OWC) 基礎設施及客戶設備
- OWC及2025年研究趨勢
- OWC範圍及2025年研究進展
- 星間及機載星間光通訊網絡
- 地面光通訊站(空中巴士案例研究)
- OWC在6G通信中的重要性(2025-2026年研究展望)
- 6G光通訊:包含2025年研究展望
- 總結
- 資訊圖表:光/光電通訊硬體在6G的重要性
- 資訊圖表:Tbps級光纖OWC網路遠紅外線 (THz)、近紅外線和可見光
- 2025 年重點研究
- 6G 非地面網路應用:6G-NTN 活動
- 6G 用戶端設備:利用更多光學技術
- 人機介面:智慧型手機及其他設備
- 2026 年至 2046 年進展預測
- 智慧型手機可見光通訊 (VLC) 研究 (2025)
- 下一代光無線通訊 (OWC) 的光子技術:雷射、雷射二極體、光電探測器等(2025-2026 年研究)
- 雷射
- 未來 6G 光無線通訊 (OWC) 的 LED、雷射二極體、光接收器及其他裝置和材料
第四章:光學面向 6G 的可重構智慧表面 (ORIS) 與光調諧技術(包括 2025 年的進展)
- 概述
- 光 RIS (ORIS) 的 SWOT 分析和最新進展
- 概述
- ORIS 和分散式 RIS (DRIS) 方案的優勢
- ORIS 的挑戰
- 6G OWC 的 RIS SWOT 評估
- 可見光通訊的 SWOT 評估
- ORIS 實施流程
- 用於遠端、地下、水下和太空應用的 RIS 技術
- 概述
- 用於車載通訊網路和行動環境的 RIS 增強型 OWC
- 混合射頻-自由空間光 RIS
- 水下光無線通訊 (UOWC) 系統
- 地下通訊所需的 RIS
- 雷射利用RIS技術實現平流層與空間通信
- 短距離室內光無線通訊及其RIS:2025年研究展望
- 室內和機載短距離通信
- 利用RIS技術增強其他室內和短距離室外系統,例如LiFi
- 用於6G的超透鏡技術
- 鏡陣列ORIS的設計與應用
第五章:用於6G基礎設施和客戶端設備的其他光/光電支援技術(固態輻射冷卻、PDRC、透明硬體、智慧窗戶)
- 概述
- 6G概述
- 支援6G RIS的冷卻窗戶範例
- 背景:熱學、介電和超寬頻隙(UWBG)材料6G 優先分析-基於最新研究論文數量
- 適用於 6G 基礎設施的固態冷卻和溫度控制技術
- 6G 需求涵蓋多種光熱解決方案
- 領先候選材料和結構的比較
- 可實現 5-20°C 溫度降低的光學被動固態冷卻技術
- 日間輻射冷卻 (PDRC) 的基本原理、10 家公司舉措、2025 年研究的領先材料以及 SWOT 分析
- 2024 年至 2025 年與 6G 相關的光學冷卻研究進展(材料和細節)
- 用於 6G 的先進輻射冷卻,包括 Janus 效應和反斯托克斯螢光(含 SWOT 分析和 2025 年研究分析)
- 自冷卻的可行性利用反斯托克斯螢光和雅努斯效應實現雷射和其他 6G 設備
第六章:光訊號處理 (OSP)、光伏、遠紅外線和太赫茲 (THz),包括多功能 6G 基礎設施和客戶端設備、波導和光纖電纜、光纖以及光電感測器
- 概述
- 用於 6G 的光訊號處理 (OSP)
- 光學和光電技術在 6G 能量採集的應用
- 13 種能量採集技術,包括光學和光電技術
- 適用於 6G 個人設備、主動 RIS 和大規模 MIMO 基地台的能量收集方案
- 以頻率和太陽能功率定位劃分的電磁能量擷取工具包
- 能量採集策略和 SWOT 分析能量採集系統,包括與無質量能量的光子相容性
- 6G 通訊基礎架構和用戶端設備中的零能耗元件 (ZED):裝置架構的重要性
- 裝置架構
- 光伏及其衍生技術為何對 6G 至關重要
- 經驗曲線顯示成本下降最快的路徑 未來發電量將顯著成長 利用光電子學和光學技術提高單位體積和單位面積的光伏輸出 到 2025 年光伏研究效率最高的趨勢 6G 各種形式的演變和高通用性 pn 結光伏與其他方法的比較 重點關注鈣鈦礦光伏——原因和 2025 年的研究進展 用於 6G 基礎設施的熱光伏
- SWOT 分析:6G 波導與電纜設計與材料
- 應用與選擇
- 太赫茲石墨烯、聚四氟乙烯 (PTFE)、聚溴乙烯 (PBVE)、聚丙烯 (PP)、聚乙烯/聚丙烯 (PE/PP)、鈮酸鋰 (LiNb)、砷化銦 (InAs)、磷化鎵 (GaP):兩項 SWOT 分析,以及截至 2025 年的研究進展
- 未來 6G 光纖中間材料(二氧化矽、藍寶石、聚溴丙烯/聚乙烯 (PBTP)、聚乙烯 (PE)、聚醯亞胺 (PI)、纖維增強塑膠 (FRP)):SWOT 分析
- 光子定義的無線電到電纜整合,用於太赫茲 6G 的光子整合
- 6G 系統設計中光纖的 SWOT 分析
- 光電感測器:光子感測器、紅外線感測器、雷射雷達 (LiDAR)、光電薄膜電晶體、光電感測器、太陽能感測器
第七章:參與 6G 相關資料和硬體的 40 家公司:產品、計畫、專利和 Zhar Research評估
- 摘要:預期 6G 硬體配置、廠商案例和專利趨勢(蘋果、英特爾、思科等)
- AGC Japan
- Airbus Europe
- Alcan Systems Germany
- Alibaba China
- Alphacore USA
- China Telecom China Mobile, China Unicom, Huawei, ZTE, Lenovo, CICT China collaboration
- Ericsson Sweden
- Fractal Antenna Systems USA
- Greenerwave France
- Huawei China
- ITOCHU Japan
- Kymeta Corp. USA
- Kyocera Japan
- Metacept Systems USA
- Metawave USA
- NEC Japan
- Nokia Finland with LG Uplus South Korea
- NTT DoCoMo and NTTJapan
- Orange France
- Panasonic Japan
- Pivotal Commware USA
- Qualcomm USA
- Samsung Electronic South Korea
- Sekisui Japan
- SensorMetrix USA
- SK Telecom South Korea
- Sony Japan
- Teraview USA
- Vivo Mobile Communications China
- VTT Finland
- ZTE China
Summary
6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046
Your optics and optronics are essential for 6G Communications to succeed. The new report, "6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046" shows the way. It serves those entering the 6G value chain from investors to operators and particularly suppliers and integrators of those vital optical and optronic materials. Yes, 6G will launch mostly with modified 5G hardware and 5G frequency use but strong improvements above the physical layer. However, urgently, that must be followed by adding the optics and optronics that galvanises disruptive services and paybacks.
Essential new hardware
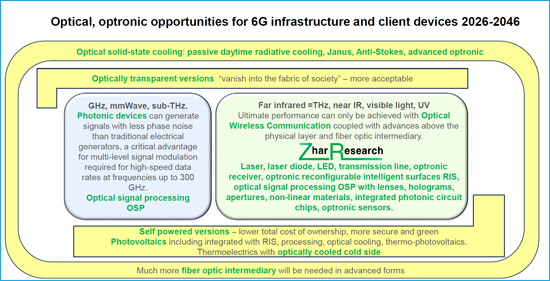
6G promises the widely available performance improved by magnitudes that can lead to radically new client devices and business propositions. For this, it must add Optical Wireless Communications OWC, Optical Signal Processing OSP, photovoltaics for self-powering, Passive Daylight Radiative Cooling PDRC, extra, improved fiber optics intermediary and more. Much infrastructure will need to become optically transparent to, "vanish into the fabric of society" - acceptable in far more places.
Essential route to widespread superlative performance
Only with these and other forms of optics and optronics can 6G approach the promised magnitudes of improvement in parameters during widespread deployment. Think beyond ubiquity from mere GHz satcoms and defaulting to WiFi indoors. 6G must embrace a world of lasers, laser diodes, optronic reconfigurable intelligent surfaces and receivers, photonic chips, multijunction solar film, solar drone "towers in the sky", optronic transmission lines, optical holography and multifunctional structural optronic material including in smart windows.
Uniquely thorough and broad-ranging report
The commercially-oriented 452-page report, "6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046" is uniquely useful. It deeply examines the remarkable advances through 2025 with PhD level insights. It is constantly updated so you only get the latest. It covers all your opportunities not just OWC.
New initiatives, advances, comparisons, possibilities
The 71-page "Executive Summary and Conclusions" is easy reading with graphics presenting 11 of the SWOT appraisals, the materials and component toolkits and prioritisation by new research success and appraised usefulness. Scan the 48 forecast lines and graphs with explanations. See 16 key conclusions. The 35-page Chapter 2. "Introduction" gives the lessons though wireless communications generations and need for two phases of 6G. Here are candidate optical and optronic materials and components and the trend from components-in-a-box to smart materials and metasurfaces. See examples of optical transparency developed for 6G. In all chapters, there are many references to research papers and assessment of them. They are mostly through 2025, with some that will publish in 2026.
Chapter 3. "Optical Wireless Communications involving infrastructure and client devices for 6G" (30 pages) gives the basics. Then see such things as Optical Satellite Networks between satellites and aircraft-to-satellite and optical ground stations with Airbus embracing 6G proposing a formidable toolkit. There are infograms on "Importance of optical/ optronic communication hardware in 6G" and "OWC with fiber optics in a potential Tbps 6G network adding far IR (THz), near IR and visible light". Read application in 6G of Non-Terrestrial Networks NTN including the work of 6G-NTN. See 6G client devices will incorporating more optical and optronic technology. What future OWC lasers, laser diodes, photodetectors and other OWC photonics are revealed in 2025 and planned 2026 research? Infograms and comparisons tables are used throughout, not rambling text.
Chapter 4. "Optical Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces ORIS and optical tuning for 6G including advances in 2025" (67 pages) goes deeply into latest advances, the potential and the objectives in these areas. What ORIS benefits, challenges, materials? Why does optical tuning control attract even for the opening non-optical frequencies of 6G? What materials?
Chapter 5. "Other optical and optronic support for 6G infrastructure and client devices : solid-state radiative cooling, PDRC, transparent hardware, smart windows" (93 pages) covers a large number of opportunities beyond OWC. Many are yet to be widely considered for 6G but, being important, they are your opportunity to fill gaps in the market. For example, every wireless generation uses infrastructure needing much more electricity and therefore needing much more cooling. PDRC does not cause local heating unlike conventional vapor compression cooling.
Dr. Peter Harrop, the primary author and CEO of Zhar Research advises, "PDRC converts heat to the infrared atmospheric window of frequency that emits into outer space and it reflects radiative heat arriving, sometimes doing even more. As 6G infrastructure increasingly merges into such things as high-rise buildings and solar drones loitering in the stratosphere, its cooling, energy harvesting and other services tend to become solid-state, optically transparent and shared with the host. 6G smart windows are one example covered. Learn which materials and technologies are winning in the 2025 research pipeline and in other work and planning."
Chapter 6. "Optical Signal Processing OSP, photovoltaics including as multifunctional 6G infrastructure and client devices, Far IR THz waveguides and cable, fiber optics, optronic sensors" (92 pages) is a deep dive into these aspects. What OSP advances are relevant to 6G? Materials? How will photovoltaics retain the fastest cost reduction and double output for a given area? Relevance to 6G infrastructure and client devices? PDRC cooling of the challenging cold side of thermoelectric harvesters needed? Photovoltaics handling data? Thermovoltaics? What are the many optronic sensors needed for 6G? Next THz waveguides and possibility of cable? Fiber optics reinvented? Materials winning in 2025 research?
Company profiles: 6G relevance and progress
The report then ends with 51 pages covering Chapter 7. "40 companies involved in "6G materials and hardware: products, plans, patents, Zhar Research appraisals: 2025-6", including 6G-related patents, achievements, intentions, and commentary.
The report, "6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046" is your essential guide.
CAPTION: Optical, optronic opportunities for 6G infrastructure and client devices 2026-2046. Source, "6G Communications Optical and Optronic Opportunities: Markets, Technologies 2026-2046".

Table of Contents
1. Executive summary and conclusions
- 1.1. Purpose and focus of this report
- 1.1.1. General
- 1.1.2. Infogram: 6G optical, optronic opportunities with infrastructure and client devices 2026-2046
- 1.1.3. Infogram: increasing adoption of optics/ optronics for 6G - nine candidates
- 1.1.4. Lessons from analysis of 245 latest researches and recommendations
- 1.2. Methodology of this analysis
- 1.3. 17 conclusions for 6G Communications systems and hardware with 10 infograms
- 1.4. 11 SWOT appraisals
- 1.4.1. SWOT appraisal of 6G adding sub-THz, THz, near infrared and visible frequencies
- 1.4.2. SWOT appraisal of Optical Wireless Communications for 6G
- 1.4.3. SWOT appraisal of visible light communication VLC
- 1.4.4. SWOT appraisal of 6G RIS
- 1.4.5. SWOT appraisal Simultaneous Transmission And Reflection STAR-RIS
- 1.4.6. SWOT appraisal of 6G RIS for Optical Wireless Communication OWC
- 1.4.7. SWOT appraisal of Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling PDRC and materials prioritisation analysis
- 1.4.8. SWOT appraisal of Optical Signal Processing for 6G
- 1.4.9. SWOT appraisal of photovoltaics for 6G Zero Emission Devices ZED
- 1.4.10. SWOT appraisal of terahertz far infrared cable waveguides in 6G system design
- 1.4.11. SWOT appraisal of fiber optics in 6G system design
- 1.5. 6G systems, materials and standards roadmaps in six lines 2026-2046
- 1.6. Market forecasts for 6G materials, hardware, context 2026-2046 in 45 lines, graphs, explanation
- 1.6.1. Overview
- 1.6.2. Optical and optronic 6G materials and device market 2026-2046
- 1.6.3. 6G fully passive metamaterial reflect-array market OWC and total $ billion 2029-2046
- 1.6.4. Other forecasts 2026-2046 including 6G optronic RIS
2. Introduction
- 2.1. Overview: lessons and planned 6G hardware anatomy
- 2.1.1. Lessons from the evolution of wireless communication
- 2.1.2. The 1G to 6G journey seeking higher performance
- 2.1.3. Why 6G must come in two phases
- 2.1.4. Situation with primary 6G infrastructure and client devices by type
- 2.1.5. Detail on 6G Phase One
- 2.1.6. Progressing to 6G Phase Two: spectrum, objectives, SWOT
- 2.2. How many optical and optronic technologies are essential for 6G success
- 2.2.1. Overview
- 2.2.2. Increasing adoption of optics/ optronics for 6G - eight candidates
- 2.2.3. OWC with fiber optics in a potential Tbps 6G network adding far IR (THz), near IR and visible light
- 2.2.4. Mismatch of planned and researched 6G frequencies may invite usurpers
- 2.2.5. SWOT appraisal of Optical Wireless Communications for 6G
- 2.2.6. SWOT appraisal of Visible Light Communication VLC
- 2.3. Likely radical advances in 6G materials
- 2.3.1. Strong 6G trend from components-in-a-box to smart materials and metasurfaces with SWOT
- 2.3.2. The place of metamaterials in 6G including optical
- 2.3.3. SWOT appraisal for metamaterials and metasurfaces generally
- 2.3.4. Electrically-functionalised transparent glass for 6G OTA, T-RIS
- 2.4. Further reading - academic research examples through 2025 and new market research
3. Optical Wireless Communication infrastructure and client devices for 6G
- 3.1. Optical Wireless Communication OWC including 2025 research
- 3.1.1. OWC scope and potential with research advances through 2025
- 3.1.2. Optical Satellite Networks between satellites and aircraft to satellite
- 3.1.3. Optical ground stations: Airbus examples
- 3.1.4. OWC relevance to 6G Communications: studies through 2025-6
- 3.2. Optical 6G Communications including 2025 research
- 3.2.1. General
- 3.2.2. Infogram: Importance of optical/ optronic communication hardware in 6G
- 3.2.3. Infogram: OWC with fiber optics in a potential Tbps 6G network adding far IR (THz), near IR and visible light
- 3.2.4. Relevant 2025 research
- 3.2.5. Application in 6G Non-Terrestrial Networks: activity of 6G-NTN
- 3.3. Client devices for 6G gain more optical technology
- 3.3.1. Human interfaced: smartphones, other
- 3.3.2. Progress expected 2026-2046
- 3.3.3. Research in 2025 on VLC to a smartphone and VLC processing
- 3.4. Future OWC lasers, laser diodes, photodetectors and other OWC photonics revealed in 2025 and 2026 research
- 3.4.1. Lasers
- 3.4.2. Future 6G OWC LED, laser diode, photonic receiver and other devices and materials
4. Optical Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces ORIS and optical tuning for 6G including advances in 2025
- 4.1. Overview
- 4.1.1. Definitions, terminology, basics
- 4.1.2. Optical tuning for GHz, mmWave and subTHz RIS with 2025 advances
- 4.2. Optical Communication RIS called ORIS with SWOTs and 2025 advances
- 4.2.1. Overview
- 4.2.2. ORIS benefits and the Distributed RIS DRIS option
- 4.2.3. ORIS challenges
- 4.2.4. SWOT appraisal of 6G RIS for OWC
- 4.2.5. SWOT appraisal of visible light communication
- 4.3. ORIS implementation procedures
- 4.4. Long range, underground, underwater and space OWC: RIS: research advances 2025 and earlier
- 4.4.1. General
- 4.4.2. RIS enhanced OWC vehicular networks and mobile environments
- 4.4.3. Hybrid RF-FSO RIS
- 4.4.4. Underwater UOWC systems
- 4.4.5. Underground OWC needing RIS
- 4.4.6. Laser stratospheric and space communications with RIS technology
- 4.5. Short range and indoor OWC and its RIS: research advances through 2025 and earlier
- 4.5.1. Indoors and short range in air
- 4.5.2. Leveraging other indoor and short-range outdoor systems such as LiFi with RIS
- 4.6. Metalenses for 6G including advances through 2025
- 4.7. Mirror array ORIS design and application with 2025 advances
5. Other optical and optronic support for 6G infrastructure and client devices : solid-state radiative cooling, PDRC, transparent hardware, smart windows
- 5.1. Overview
- 5.1.1. General 6G situation
- 5.1.2. Example of cooling windows that can also be 6G RIS
- 5.1.3. Context: Thermal, dielectric, UWBG materials for 6G prioritised by number of latest research announcements
- 5.2. Solid state cooling and temperature control suitable for 6G infrastructure
- 5.2.1. 6G requirements involve many optical thermal solutions
- 5.2.2. Leading candidate materials and structures compared
- 5.2.3. Leading optical passive solid-state cooling for 5C to 20C drop 2026-2046
- 5.2.4. PDRC basics, 10 companies' activity, winning materials in 2025 research, SWOT
- 5.2.5. Specific optical cooling research advances in 2024 and 2025 relevant to 6G: materials, details
- 5.2.6. Advanced Radiative Cooling for 6G including Janus and Anti-Stokes with SWOTs, analysis of 2025 research
- 5.2.7. Potential for self-cooling lasers and other 6G by optical anti-Stokes fluorescence and Janus effect
6. Optical Signal Processing OSP, photovoltaics including as multifunctional 6G infrastructure and client devices, Far IR THz waveguides and cable, fiber optics, optronic sensors
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Optical Signal Processing OSP for 6G
- 6.2.1. Definition
- 6.2.2. Devices involved
- 6.2.3. SWOT appraisal of Optical Signal Processing for 6G
- 6.2.4. OSP and allied advances through 2025 relevant to 6G
- 6.3. Place of optics and optronics in 6G energy harvesting
- 6.3.1. 13 energy harvesting technologies with place of optics, optronics for 6G
- 6.3.2. 6G personal device, active RIS and UM MIMO base station power demands matched to energy harvesting options
- 6.3.3. Electromagnetic energy harvesting toolkit by frequency: place of photovoltaics
- 6.3.4. Energy harvesting system improvement strategies including photonics compatibility with "massless energy" with SWOT
- 6.3.5. Significance of Zero Energy Devices ZED in 6G Communications infrastructure and client devices
- 6.3.6. Device architecture
- 6.4. How photovoltaics and variants are very important for 6G
- 6.4.1. Experience curve of fastest cost reduction
- 6.4.2. Massive power increases ahead
- 6.4.3. Increasing 6G photovoltaic output per unit volume and area 2026-2046 with optronics, optical, other approaches
- 6.4.4. Best photovoltaic research efficiencies trend to 2025
- 6.4.5. Format options evolving 2026-2046 make it exceptionally versatile for 6G
- 6.4.6. Photovoltaics by pn junction compared to other options 2026-2046
- 6.4.7. Strong focus on perovskite photovoltaics - reasons and research progress 2025
- 6.4.8. Thermoradiative photovoltaics for 6G infrastructure
- 6.5. Design and materials of 6G waveguides and cables with SWOTs and 2025 research advances
- 6.5.1. Uses and options
- 6.5.2. THz graphene, PTFE, PBVE, PP, PE/PP, LiNb, InAs, GaP with two SWOTs and research advances through 2025
- 6.5.3. Future fiber optic intermediary for 6G with SWOT: silica, sapphire, PBTP, PE, PI, FRP
- 6.5.4. Photonics defined radio to cable and photonic integration for THz 6G
- 6.5.5. SWOT appraisal of fiber optics in 6G system design
- 6.6. Optronic sensors: photonic, infrared, LIDAR, optoelectronic memtransistors, photoelectric, photovoltaic
7. 40 companies involved in 6G materials and hardware: products, plans, patents, Zhar Research appraisals: 2025-6
- 7.1. Overview: Likely 6G hardware landscape with examples of manufacturers and patenting trends, Apple, Intel, Cisco
- 7.1.1. Rapidly changing situation 2025-6
- 7.1.2. Examples of material patenting and literature trends
- 7.2. AGC Japan
- 7.3. Airbus Europe
- 7.4. Alcan Systems Germany
- 7.5. Alibaba China
- 7.6. Alphacore USA
- 7.7. China Telecom China Mobile, China Unicom, Huawei, ZTE, Lenovo, CICT China collaboration
- 7.8. Ericsson Sweden
- 7.9. Fractal Antenna Systems USA
- 7.10. Greenerwave France
- 7.11. Huawei China
- 7.12. ITOCHU Japan
- 7.13. Kymeta Corp. USA
- 7.14. Kyocera Japan
- 7.15. Metacept Systems USA
- 7.16. Metawave USA
- 7.17. NEC Japan
- 7.18. Nokia Finland with LG Uplus South Korea
- 7.19. NTT DoCoMo and NTTJapan
- 7.20. Orange France
- 7.21. Panasonic Japan
- 7.22. Pivotal Commware USA
- 7.23. Qualcomm USA
- 7.24. Samsung Electronic South Korea
- 7.25. Sekisui Japan
- 7.26. SensorMetrix USA
- 7.27. SK Telecom South Korea
- 7.28. Sony Japan
- 7.29. Teraview USA
- 7.30. Vivo Mobile Communications China
- 7.31. VTT Finland
- 7.32. ZTE China