 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1934855
綠色氨:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Green Ammonia - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
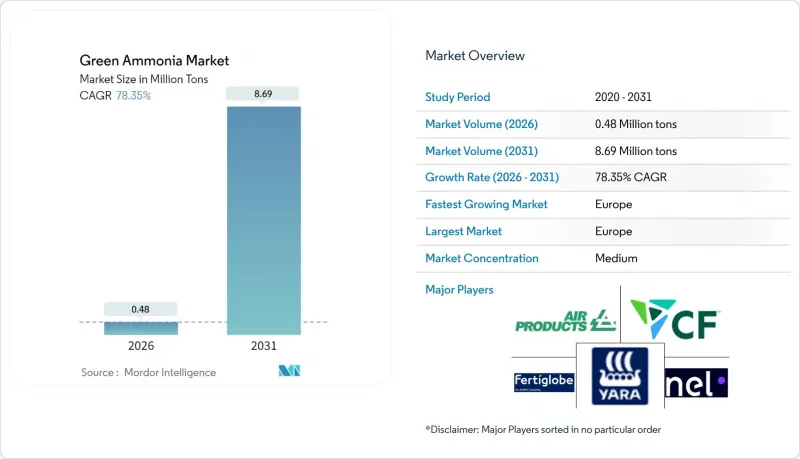
預計到 2026 年,綠色氨市場規模將達到 48 萬噸,高於 2025 年的 27 萬噸。
預計到 2031 年將達到 869 萬噸,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 78.35%。
歐洲、日本和印度的政策支持力度加大,資源豐富地區再生能源成本降至0.02美元/度左右,以及綠色氨作為肥料和無碳燃料的雙重效用,都在加速其普及應用。航運業的脫碳需求,特別是歐盟計畫從2024年起將航運業納入排放交易體系(ETS),正催生對氨動力船舶的早期需求。同時,德國、日本和韓國的氫能策略已將綠色氨定位為關鍵的氫載體。在計劃層面,整合可再生能源發電、大規模電解和氨合成的工廠正在實現規模經濟。儘管來自藍氨的競爭仍然存在,但綠色氨市場具有許多優勢,包括不受天然氣價格波動的影響以及未來可能獲得碳價溢價。
全球綠色氨市場趨勢及展望
糧食不安全國家對化肥的需求不斷成長
開發中國家正優先發展綠色氨的國內生產,以減少對化肥進口的依賴,並加強糧食安全。俄烏衝突暴露了傳統化肥貿易的脆弱性,此後,肯亞和奈及利亞等國宣布了吉瓦級可再生能源製氨計劃,以穩定供應鏈。非洲聯盟2063年碳中和目標鼓勵公私合營,將風能和太陽能資源與小規模農戶合作社連結起來。多邊金融機構已撥款23億美元用於永續化肥項目,並為電解設施提供優惠融資。擁有強大太陽能和風能潛力的國家能夠以低於進口灰色氨的成本生產綠色氨,從而改變競爭格局。不斷上漲的糧食進口成本促使各國農業部將化肥政策與能源獨立目標結合,鼓勵簽署承購協議,以支持新工廠的資金籌措。這一勢頭正顯著推動非洲和南亞綠色氨市場的擴張。
脫碳政策促進航運業使用綠色燃料。
國際海事組織(IMO)提出的2050年排放減半目標以及歐盟碳定價機制的擴大,正推動氨燃料的普及應用。包括馬士基和日本郵船在內的航運公司已訂購了可使用氨燃料的船舶,並計劃在2030年前投入商業營運。日本經濟產業省(METI)正在為氨引擎提供聯合資助,並強制要求發電廠使用20%的氨燃料進行混燒,這造成了燃料需求的重複。 IMO將於2025年發布的臨時指南將明確安全通訊協定,並鼓勵在鹿特丹和新加坡建造加註中心。將回程傳輸與可再生氫回程運輸相結合的港口當局將獲得先發優勢,並加強區域叢集。
電解和哈伯-博世製程改造需要大量資金
電解組件的成本佔總安裝成本的一半,鹼性電解槽的成本為每千瓦800至1200美元。一個年產100萬噸的綠色氨生產綜合體需要500至1000兆瓦的電解產能,投資額為4000至12億美元,這還不包括哈伯-博世合成裝置或可再生能源發電設施的成本。連續生產氨需要穩定的再生能源或電池緩衝系統,這將使資本支出增加10%至15%。企劃案融資依賴15至25年的購電協議和產品銷售協議,而這些協議在新興市場仍然不常見。儘管有美國《通貨膨脹控制法案》和歐洲創新基金等激勵措施,但不斷上漲的技術風險溢價已顯著增加了平準化成本。這些不斷上漲的成本正在推遲最終的投資決策,並對綠色氨市場構成重大挑戰。
細分市場分析
至2025年,農業部門將佔綠色氨市場87.25%的佔有率,並在2031年之前以84.1%的複合年成長率成長。這項數據表明,即使新的能源應用不斷湧現,化肥需求仍將主導。糧食安全情勢嚴峻的地區正在尋求能源獨立的營養解決方案,而一系列補貼計畫正在縮短當地生產設施的投資回收期。
儘管目前船用燃料的需求基數仍然不高,但穩定的造船訂單和燃料加註碼頭的公告表明,到2028年,船用燃料市場將迎來一個轉折點。日本正在火力發電廠進行氨混燒試驗(混燒比例高達20%),這表明存在交叉需求,可以提高電廠的運轉率並降低單位成本。在德國和韓國進口策略的支持下,氫載體產業為可再生能源供應中心和工業消費中心之間的長距離運輸提供了支持。化學原料和鋼鐵脫碳創造了利基性、高附加價值的銷售管道,實現了收入來源多元化,並保護了綠色氨產業免受大宗商品週期波動的影響。
綠氨市場報告按應用領域(農業、船舶燃料、發電、氫載體及其他應用)和地區(亞太、北美、歐洲、南美以及中東和非洲)進行細分。市場預測以噸為單位。
區域分析
歐洲憑藉全面的政策協調,將碳定價機制內部化並鼓勵可再生能源應用,在綠色氨市場佔據主導地位,預計到2025年市場佔有率將達到35.35%,年複合成長率高達84.9%。挪威的SkiGA離岸風力發電氨計劃每年將供應10萬噸氨,為區域整合價值鏈樹立標竿。德國正在鹿特丹建造一個專用進口碼頭,以配合其國內電解能的擴張,確保工業用戶的氨供應冗餘。
亞太地區作為區域貢獻者發揮關鍵作用。日本的目標是到2050年實現3000萬噸的氨需求量,其中包括航運和發電廠的需求。同時,中國正在省級獎勵策略下,試辦一座數吉瓦的可再生能源氨廠。韓國的公私合營聯盟將13家公司和5個機構連接起來,負責生產和進口物流;而印度每年55萬噸的補貼計劃正在推動諸如AM Green在安得拉邦建設的100萬噸級綜合體等大型企劃。這些努力正在促進全部區域的強勁成長,亞太地區的工廠正在為滿足國內需求和出口做好準備。北美地區正受惠於《通膨控制法案》下的生產稅額扣抵,CF Industries在路易斯安那州的合資企業設定的年產量目標為140萬噸,便是最好的例證。中東和非洲地區正崛起為出口導向樞紐,阿拉伯聯合大公國成功向德國交付了首批H2Global試點產品,展現了長途貿易的經濟效益。南美洲正在巴西塞阿拉州開展多個計劃,充分利用陸上風電和港口接近性,不斷擴大其在全球綠色氨市場的佔有率。在這些大洲,比較優勢將取決於可再生資源禀賦、政策獎勵以及與需求中心的運輸距離,這些因素將影響未來的投資配置。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 糧食不安全國家對化肥的需求不斷成長
- 脫碳政策加速航運業綠色燃料的發展。
- 對綠色氨作為氫載體的需求日益成長
- 增加綠色低碳肥料的採購
- 在發電和電力系統穩定領域不斷擴大應用
- 市場限制
- 改造電解和哈伯-博世製程需要大量資金投入。
- 船舶加油中的安全和毒性挑戰
- 藍氨競爭(如果天然氣和碳捕獲與儲存(CCS)成本低)
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過使用
- 農業
- 船用燃料
- 發電
- 氫載體
- 其他用途(工業原料等)
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 東南亞國協
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 北歐國家
- 其他歐洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- ACME Group
- Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
- AM Green
- Casale SA
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- Engie SA
- ENOWA
- Fertiglobe
- Fortescue
- Greenko Group
- Iberdrola, SA
- ITM Power plc
- KAPSOM plc
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Nel
- Ocior
- Orsted AS
- Proton Ventures
- Siemens Energy
- Technip Energies NV
- thyssenkrupp Uhde GmbH
- Yara
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Green Ammonia market size in 2026 is estimated at 0.48 million tons, growing from 2025 value of 0.27 million tons with 2031 projections showing 8.69 million tons, growing at 78.35% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Intensifying policy support in Europe, Japan and India, falling renewable electricity costs toward USD 0.02 per kWh in resource-rich regions, and the dual utility of green ammonia as fertilizer and carbon-free fuel collectively accelerate adoption. Maritime decarbonization mandates, particularly the European Union's inclusion of shipping in its Emissions Trading System from 2024, create early demand for ammonia-powered vessels, while hydrogen strategies in Germany, Japan and South Korea position green ammonia as a key hydrogen carrier. At the project level, integrated plants that combine renewable generation, large-scale electrolysis and ammonia synthesis are unlocking economies of scale. Meanwhile, competition from blue ammonia continues, yet the green ammonia market benefits from independence from natural-gas volatility and the prospect of future carbon-pricing premiums.
Global Green Ammonia Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Fertilizer Demand from Food-Insecure Nations
Developing economies are prioritizing domestic production of green ammonia to reduce fertilizer import dependence and strengthen food security. The Russia-Ukraine conflict exposed vulnerabilities in conventional fertilizer trade, prompting Kenya, Nigeria, and similar nations to announce gigawatt-scale renewable-to-ammonia projects to stabilize supply chains. The African Union's 2063 neutrality goals foster public-private ventures that link wind and solar resources to smallholder cooperatives. Multilateral lenders have allocated USD 2.3 billion to sustainable fertilizer programs, channeling concessional finance into electrolysis capacity. Countries with high solar and wind potential can achieve delivered costs that undercut imported gray ammonia, shifting the competitive balance. As food-import bills rise, agricultural ministries increasingly bundle fertilizer policy with energy-independence targets, accelerating offtake agreements that underpin financial close for new plants. This momentum contributes strongly to green ammonia market expansion across Africa and South Asia.
Decarbonization Policies Accelerating Green Fuels in Shipping
The International Maritime Organization's target to halve emissions by 2050 and the EU carbon-pricing extension are catalyzing ammonia fuel adoption. Maersk, NYK Line, and other carriers have placed orders for ammonia-ready vessels, planning commercial operation before 2030. Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry co-funds ammonia engines and mandates 20% ammonia co-firing in power plants, creating overlapping fuel demand. Interim IMO guidelines issued in 2025 clarify safety protocols, triggering investment in bunkering hubs at Rotterdam and Singapore. Port authorities that integrate bunkering infrastructure with renewable-hydrogen backhaul capture early-mover advantages, reinforcing regional clusters.
High Capital Requirements for Electrolysis and Haber-Bosch Retrofits
Electrolyzer packages account for up to half of the total installed cost, at USD 800-1,200 per kW for alkaline units. A 1 million-ton-per-year green ammonia complex demands 500-1,000 MW of electrolyzers, translating to USD 400-1,200 million before adding Haber-Bosch synthesis and renewable generation assets. Continuous ammonia output requires firm renewable power or battery buffer systems, adding 10-15% to capital expenditure. Project finance hinges on 15-25-year power-purchase and offtake contracts-structures still uncommon in emerging markets. Despite incentives like the US Inflation Reduction Act and Europe's Innovation Fund, higher technology risk premiums are significantly increasing the levelized costs. This rise is causing delays in final investment decisions, highlighting a significant challenge for the green ammonia market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Demand for Green Ammonia as a Hydrogen Carrier
- Increasing Procurement of Green and Low-Carbon Fertilizers
- Safety and Toxicity Hurdles for Maritime Bunkering
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Agriculture commanded 87.25% of the green ammonia market share in 2025, and the segment is expanding at an 84.1% CAGR through 2031. The statistic underscores the continued primacy of fertilizer demand even as new energy applications emerge. Food-insecure regions seek energy-independent nutrient solutions, and bundled subsidy schemes shorten payback periods on local production assets.
Marine fuel holds a modest baseline today, yet confirmed shipbuilding orders and bunkering terminal announcements indicate an inflection by 2028. Power generation trials in Japan, co-firing up to 20% ammonia in thermal plants, illustrate crossover demand that raises plant load factors and cuts per-unit costs. The hydrogen-carrier segment, backed by import strategies in Germany and South Korea, offers long-haul linkage between renewable hot-spots and industrial consumption centers. Chemical feedstock and steel decarbonization add niche but premium-valued outlets, broadening the revenue mix and cushioning the green ammonia industry against commodity-cycle volatility.
The Green Ammonia Market Report is Segmented by Application (Agriculture, Marine Fuel, Power Generation, Hydrogen Carrier, Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (tons).
Geography Analysis
Europe's leadership, with a 35.35% green ammonia market share in 2025 and an 84.9% CAGR, rests on comprehensive policy alignment that internalizes carbon prices and rewards renewable content. Norway's SkiGA offshore-wind-to-ammonia project will supply 100,000 tons per year, setting a regional benchmark for integrated value chains. Germany's dedicated import terminal at Rotterdam complements domestic electrolysis build-out, ensuring redundancy in supply for industrial users.
Asia-Pacific plays a significant role as a regional contributor. Japan targets 30 million tons of ammonia demand by 2050, combining maritime and power-station offtake, while China pilots multi-GW renewable ammonia plants under provincial stimulus packages. South Korea's public-private coalition aligns 13 firms and five institutes around production and import logistics, and India's 550,000-ton annual subsidy scheme catalyzes megaprojects such as AM Green's 1 million-ton complex in Andhra Pradesh. These initiatives collectively underpin strong regional growth, with Asia-Pacific facilities positioned both for domestic uptake and exports. North America benefits from the Inflation Reduction Act's production tax credits, evidenced by CF Industries' Louisiana joint venture targeting 1.4 million tons annual capacity. The Middle East and Africa are emerging as export-oriented hubs; the UAE secured the first H2Global pilot shipment to Germany, validating long-distance trade economics. Brazil's Ceara state aggregates several projects leveraging onshore wind and port proximity, broadening South America's stake in the global green ammonia market. Across these continents, comparative advantage hinges on renewable resource endowment, policy incentives and shipping distances to demand centers, factors that will shape future investment allocation.
- ACME Group
- Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
- AM Green
- Casale SA
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- Engie SA
- ENOWA
- Fertiglobe
- Fortescue
- Greenko Group
- Iberdrola, S.A.
- ITM Power plc
- KAPSOM plc
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Nel
- Ocior
- Orsted AS
- Proton Ventures
- Siemens Energy
- Technip Energies N.V.
- thyssenkrupp Uhde GmbH
- Yara
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing fertilizer demand from food-insecure nations
- 4.2.2 Decarbonization policies accelerating green fuels in shipping
- 4.2.3 Growing demand for green ammonia as a hydrogen carrier
- 4.2.4 Increasing procurement of green and low-carbon fertilizers
- 4.2.5 Increasing usage in power generation and grid stability
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capital requirements for electrolysis and Haber-Bosch retrofits
- 4.3.2 Safety and toxicity hurdles for maritime bunkering
- 4.3.3 Blue-ammonia cost competition where gas and carbon capture storage (CCS) are cheap
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Agriculture
- 5.1.2 Marine Fuel
- 5.1.3 Power Generation
- 5.1.4 Hydrogen Carrier
- 5.1.5 Other Applications (Industrial Feedstock, etc.)
- 5.2 By Geography
- 5.2.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.1.1 China
- 5.2.1.2 Japan
- 5.2.1.3 India
- 5.2.1.4 South Korea
- 5.2.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.2.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.2 North America
- 5.2.2.1 United States
- 5.2.2.2 Canada
- 5.2.2.3 Mexico
- 5.2.3 Europe
- 5.2.3.1 Germany
- 5.2.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.2.3.3 France
- 5.2.3.4 Italy
- 5.2.3.5 Spain
- 5.2.3.6 Russia
- 5.2.3.7 NORDIC Countries
- 5.2.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.2.4 South America
- 5.2.4.1 Brazil
- 5.2.4.2 Argentina
- 5.2.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.2.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.2.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.2.5.2 South Africa
- 5.2.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.2.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ACME Group
- 6.4.2 Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
- 6.4.3 AM Green
- 6.4.4 Casale SA
- 6.4.5 CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.6 Engie SA
- 6.4.7 ENOWA
- 6.4.8 Fertiglobe
- 6.4.9 Fortescue
- 6.4.10 Greenko Group
- 6.4.11 Iberdrola, S.A.
- 6.4.12 ITM Power plc
- 6.4.13 KAPSOM plc
- 6.4.14 MAN Energy Solutions
- 6.4.15 Nel
- 6.4.16 Ocior
- 6.4.17 Orsted AS
- 6.4.18 Proton Ventures
- 6.4.19 Siemens Energy
- 6.4.20 Technip Energies N.V.
- 6.4.21 thyssenkrupp Uhde GmbH
- 6.4.22 Yara
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Growing research on affordable production of green ammonia









