 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906144
中東和非洲生物肥料市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2026-2031 年)Middle East And Africa Biofertilizers - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
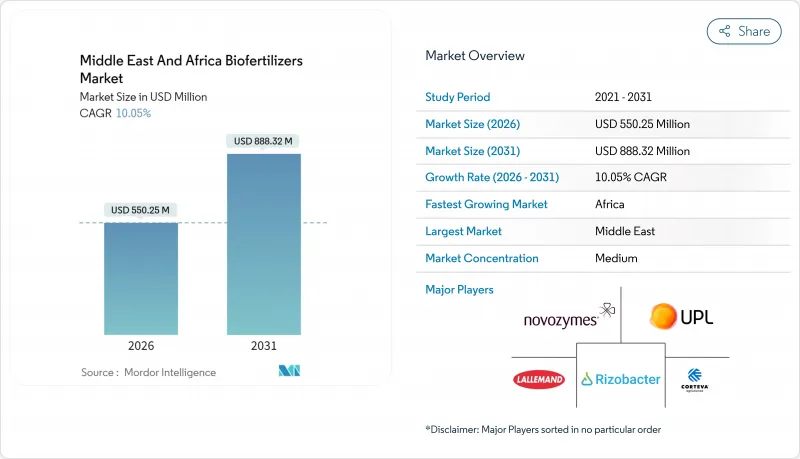
2025年中東和非洲生物肥料市場價值5億美元,預計到2031年將達到8.8832億美元,高於2026年的5.5025億美元。
預計在預測期(2026-2031 年)內,複合年成長率將達到 10.05%。
這一成長勢頭是由區域特有的挑戰所驅動的,例如水資源短缺、土壤鹽鹼化和合成肥料價格波動,這些挑戰正在加速向生物來源肥料的轉型。沙烏地阿拉伯的「2030願景」、南非的「生物投入品監管加速計畫」以及非洲聯盟的「肥料自給自足計畫」等政府舉措,透過降低監管壁壘和提供生物投入品補貼,支持生物肥料的推廣應用。跨國供應商正透過本地生產和有針對性的夥伴關係來深化其市場地位,而本土創新者則透過開發適應嚴苛農業氣候條件的微生物菌株來佔據市場利基。在與氣候智慧型農業目標一致的政策支持下,這些因素預計將推動中東和北非地區生物肥料市場的強勁成長。
中東和非洲生物肥料市場趨勢及洞察
擴大經認證的有機農田
2019年至2024年間,中東和非洲主要市場的面積將持續成長,其中埃及、肯亞和南非的普及率將領先。這一成長趨勢推動了對生物肥料的需求,因為有機認證標準要求使用生物投入物而非合成投入物。肯亞的有機農業目前涵蓋範圍積超過16.5萬公頃,主要得益於出口市場的高價以及政府透過國家有機農業政策提供的支持。這種擴張為生物肥料供應商創造了競爭激烈的市場,尤其是那些提供能夠滿足有機生產系統複雜營養需求的多菌株配方的供應商。摩洛哥的「綠色摩洛哥計畫」投入大量資源支持有機轉型,建立有利於生物投入物的法規結構,並制定品質認證途徑。
有機材料的補助和優惠政策
全部區域政府的補貼體係日益傾向生物投入品。摩洛哥的有機投入品補貼計畫使農民採用生物投入品的成本比未補貼的合成投入品降低了25%。沙烏地阿拉伯環境、水利和農業部正根據「2030願景」的永續性目標,為採用生物營養管理系統的溫室經營者提供有針對性的支援。這些政策轉變體現了對生物投入品有助於實現糧食安全目標並降低進口依賴性的戰略認知。阿拉伯聯合大公國的《2051年國家糧食安全戰略》明確優先考慮本地生產技術,包括用於可控環境農業的微生物接種劑。南非《肥料、飼料、農業化學品和畜牧化學品法》下的法規結構為生物肥料註冊提供了明確的途徑,但從3500蘭特(202.30美元)的產品註冊費到1800蘭特(104.06美元)的續期費,高昂的費用對小規模生產商構成了一定的成本障礙。
補貼化肥的主導地位
奈及利亞、埃及和其他主要農業經濟體的國家化肥補貼體系使合成肥料在價格敏感的市場領域擁有結構性優勢,從而擠壓了生物肥料的生存空間。奈及利亞的化肥補貼體系雖然有助於實現糧食安全目標,但由於人為地維持了生物肥料相對於進口合成肥料的價格優勢,無意中限制了生物肥料的推廣應用。埃及的補貼框架同樣偏向傳統肥料,但近期的政策討論表明,未來有可能將生物肥料納入補貼體系。這些體系造成了市場扭曲,迫使生物肥料供應商在性能而非成本方面競爭。維持補貼體系的財政負擔未來可能為生物肥料的推廣創造機遇,因為各國政府會尋求更具成本效益的替代方案來提高農業生產力,同時緩解預算壓力。
細分市場分析
到2025年,根瘤菌生物肥料將佔據35.85%的市場佔有率,這反映了豆類種植在該地區對糧食安全和土壤肥力管理的重要性。這項優勢源自於成熟的農藝知識和經證實有效的固氮技術,而這些技術也深受注重成本的農民青睞。跨國公司與區域研究機構之間的技術轉移協議促進了雙品牌建設,並有助於增強主要合作社之間的信任。將根瘤菌的應用與保護性耕作技術結合的培訓模組進一步鞏固了重複銷售的基礎。
菌根產品是成長最快的細分市場,預計到2031年將以12.75%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於高價值溫室栽培和乾旱地區農業系統的應用。在這些環境中,養分吸收的改善能夠帶來可觀的產量提升。全部區域的研究活動日益集中在適應當地土壤條件和氣候脅迫的本土微生物菌株,隨著市場對本地產品的接受度不斷提高,競爭格局預計將會重組。投資於菌株篩選和本地化改造的公司預計將從國際通用配方中搶佔市場佔有率。
預計到2025年,載體增強型生物肥料將維持56.80%的市場佔有率,這反映了其與小規模農戶現有施用方式的兼容性以及其成本效益。這些配方利用褐煤和木炭等當地易得的載體,降低了生產成本並支持了當地供應鏈。技術細分反映了市場兩極化的現狀:一方面是成本敏感的小農戶應用,另一方面是性能驅動的商業性營運。隨著市場日趨成熟和品質標準日益嚴格,開發能夠在高溫條件下維持活性的氣候適應型配方的公司有望獲得更大的相對價值。
液態生物肥料預計將成為成長最快的技術領域,到2031年將以15.1%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於其在海灣合作理事會(GCC)國家溫室種植和精密農業應用的廣泛應用。雖然液態生物肥料具有微生物存活率高、易於與灌溉系統整合等優勢,但低溫運輸需求限制了其在基礎設施受限市場的普及。
中東和非洲生物肥料市場按微生物類型(例如根瘤菌、固氮菌)、技術類型(例如載體增強型生物肥料、液體生物肥料)、應用(例如土壤改良)、作物類型(例如穀類)和地區(例如非洲、中東)進行細分。市場預測以價值(美元)和數量(公噸)為單位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 擴大經認證的有機農田
- 補貼和有機材料推廣政策
- 合成肥料價格波動
- 沿岸地區土壤鹽害緩解計劃
- 高科技溫室熱潮
- 土壤微生物組計劃的排碳權試點項目
- 市場限制
- 補貼化肥的主導地位
- 農民意識薄弱,推廣網路不完善
- 監管漏洞導致假冒偽劣疫苗的出現
- 液體藥品低溫運輸物流面臨的挑戰
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模和成長預測(價值和數量)
- 依微生物類型
- 根瘤菌
- 固氮菌
- 固氮螺菌
- 磷酸鹽溶解細菌
- 菌根
- 其他微生物
- 依技術類型
- 載體增強型生物肥料
- 液體生物肥料
- 封裝/微珠技術
- 其他技術
- 透過使用
- 土壤處理
- 種子處理
- 葉面噴布/根部浸泡
- 其他用途
- 按作物類型
- 糧食
- 豆子
- 經濟作物
- 水果和蔬菜
- 其他作物
- 按地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 肯亞
- 烏干達
- 坦尚尼亞
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 中東
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 埃及
- 卡達
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Novozymes A/S
- UPL Limited
- Lallemand Inc
- Corteva, Inc.
- Rizobacter Argentina SA
- FMC Corporation
- Koppert BV
- IPL Biologicals Limited
- Groundwork BioAg Ltd.
- Biobest Group NV
- Biomax Technologies Pte. Ltd.
- Mapleton Agri Biotec Pty Ltd
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Middle East and Africa biofertilizers market was valued at USD 500 million in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 550.25 million in 2026 to reach USD 888.32 million by 2031, at a CAGR of 10.05% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Momentum stems from region-specific pressures including water scarcity, soil salinity, and synthetic input price volatility, which are accelerating the shift toward biologically based options. Government programs such as Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030, South Africa's regulatory fast-track for biologicals, and the African Union's fertilizer self-sufficiency agenda reinforce adoption by lowering regulatory hurdles and subsidizing biological inputs. Multinational suppliers deepen their presence through local manufacturing and targeted partnerships, while regional innovators secure niches by tailoring microbial strains to harsh agro-climatic conditions. Collectively, these forces position the Middle East and Africa biofertilizers market for robust, policy-backed expansion that aligns with climate-smart agriculture goals.
Middle East And Africa Biofertilizers Market Trends and Insights
Expansion of Organic-Certified Farmland
Certified organic acreage across key Middle East & Africa markets expanded between 2019-2024, with Egypt, Kenya, and South Africa leading adoption rates. This growth trajectory accelerates biofertilizer demand as organic certification standards mandate biological inputs over synthetic alternatives. Kenya's organic sector now encompasses over 165,000 hectares, driven by export market premiums and government support through the National Organic Agriculture Policy. The expansion creates a captive market for biofertilizer suppliers, particularly those offering multi-strain formulations that address the complex nutrient needs of organic production systems. Morocco's Green Morocco Plan has allocated significant resources to organic transition support, creating regulatory frameworks that favor biological inputs and establish quality certification pathways.
Subsidies and Favorable Organic-Input Policies
Government subsidy schemes across the region increasingly favor biological inputs, with Morocco's organic-input subsidy program reducing farmer adoption costs by 25% compared to unsubsidized synthetic alternatives. Saudi Arabia's Ministry of Environment, Water, and Agriculture has implemented targeted support for greenhouse operators adopting biological nutrient management systems, aligning with Vision 2030 sustainability objectives. These policy shifts reflect strategic recognition that biological inputs support food security goals while reducing import dependency. The UAE's National Food Security Strategy 2051 explicitly prioritizes local production technologies, including microbial inoculants for controlled environment agriculture. South Africa's regulatory framework under the Fertilizers, Farm Feeds, Agricultural Remedies and Stock Remedies Act provides clear pathways for biofertilizer registration, though fees ranging from R 3,500 (USD 202.30) for product registration to R 1,800 (USD 104.06) for renewals create cost barriers for smaller manufacturers .
Dominance of Subsidized Synthetic Fertilizers
National fertilizer subsidy programs in Nigeria, Egypt, and other major agricultural economies create structural advantages for synthetic inputs that crowd out biological alternatives in price-sensitive market segments. Nigeria's fertilizer subsidy program, while supporting food security objectives, inadvertently limits biofertilizer adoption by maintaining artificial price advantages for imported synthetic products. Egypt's subsidy framework similarly favors conventional inputs, though recent policy discussions indicate potential inclusion of biological products in future subsidy schemes. These programs create market distortions that require biofertilizer suppliers to compete on performance differentiation rather than cost parity. The fiscal burden of maintaining subsidy programs may create future opportunities for biological inputs as governments seek cost-effective alternatives that support agricultural productivity while reducing budget pressures.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Synthetic-Fertilizer Price Volatility
- High-Tech Greenhouse Boom
- Low Farmer Awareness and Weak Extension Networks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Rhizobium-based biofertilizers command 35.85% market share in 2025, reflecting the region's substantial legume cultivation for both food security and soil fertility management. This dominance stems from well-established agronomic understanding and proven nitrogen fixation benefits that resonate with cost-conscious farmers.Technology transfer agreements between multinationals and regional labs promote dual branding, enhancing trust among progressive cooperatives. Training modules that bundle Rhizobium use with conservation agriculture practices further anchor repeat sales.
Mycorrhizal products represent the fastest-growing segment at 12.75% CAGR through 2031, driven by adoption in high-value greenhouse operations and drought-prone farming systems where enhanced nutrient uptake provides measurable yield advantages. Research initiatives across the region increasingly focus on indigenous microbial strains adapted to local soil conditions and climatic stresses, potentially reshaping competitive dynamics as locally sourced products gain market acceptance. Companies investing in strain selection and regional adaptation are positioned to capture market share from generic international formulations.
Carrier-enriched biofertilizers maintain 56.80% market share in 2025, reflecting their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with existing farmer application practices across smallholder systems. These formulations utilize locally available carriers such as lignite and charcoal, reducing production costs and supporting regional supply chains. The technology segmentation reflects broader market bifurcation between cost-focused smallholder applications and performance-oriented commercial operations. Companies developing climate-adapted formulations that maintain viability under high-temperature conditions are likely to capture disproportionate value as the market matures and quality standards tighten.
Liquid biofertilizers emerge as the fastest-growing technology segment with 15.1% CAGR through 2031, primarily driven by greenhouse adoption in GCC countries and precision agriculture applications. The liquid segment benefits from superior microbial viability and ease of integration with fertigation systems, though cold-chain requirements limit adoption in infrastructure-constrained markets.
The Middle East and Africa Biofertilizers Market is Segmented by Microorganism Type (Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and More), by Technology Type (Carrier-Enriched Biofertilizers, Liquid Biofertilizers, and More), by Application (Soil Treatment, and More), by Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, and More), and by Geography (Africa, and the Middle East). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Novozymes A/S
- UPL Limited
- Lallemand Inc
- Corteva, Inc.
- Rizobacter Argentina S.A.
- FMC Corporation
- Koppert B.V.
- IPL Biologicals Limited
- Groundwork BioAg Ltd.
- Biobest Group NV
- Biomax Technologies Pte. Ltd.
- Mapleton Agri Biotec Pty Ltd
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expansion of organic-certified farmland
- 4.2.2 Subsidies and favorable organic-input policies
- 4.2.3 Synthetic-fertilizer price volatility
- 4.2.4 Salinity-mitigation programs in Gulf soils
- 4.2.5 High-tech greenhouse boom
- 4.2.6 Carbon-credit pilots for soil microbiome projects
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Dominance of subsidized synthetic fertilizers
- 4.3.2 Low farmer awareness and weak extension networks
- 4.3.3 Counterfeit / low-quality inoculants from regulatory gaps
- 4.3.4 Cold-chain logistics hurdles for liquid formulations
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Microorganism Type
- 5.1.1 Rhizobium
- 5.1.2 Azotobacter
- 5.1.3 Azospirillum
- 5.1.4 Phosphate-solubilizing Bacteria
- 5.1.5 Mycorrhiza
- 5.1.6 Other Microorganisms
- 5.2 By Technology Type
- 5.2.1 Carrier-enriched Biofertilizers
- 5.2.2 Liquid Biofertilizers
- 5.2.3 Encapsulated / Bead Technology
- 5.2.4 Other Technologies
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Soil Treatment
- 5.3.2 Seed Treatment
- 5.3.3 Foliar / Root Dipping
- 5.3.4 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Grains
- 5.4.2 Pulses
- 5.4.3 Commercial Crops
- 5.4.4 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4.5 Other Crops
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Africa
- 5.5.1.1 South Africa
- 5.5.1.2 Kenya
- 5.5.1.3 Uganda
- 5.5.1.4 Tanzania
- 5.5.1.5 Nigeria
- 5.5.1.6 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.2 Middle East
- 5.5.2.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.2.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.2.3 Turkey
- 5.5.2.4 Egypt
- 5.5.2.5 Qatar
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.1 Africa
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Novozymes A/S
- 6.4.2 UPL Limited
- 6.4.3 Lallemand Inc
- 6.4.4 Corteva, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Rizobacter Argentina S.A.
- 6.4.6 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.7 Koppert B.V.
- 6.4.8 IPL Biologicals Limited
- 6.4.9 Groundwork BioAg Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Biobest Group NV
- 6.4.11 Biomax Technologies Pte. Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Mapleton Agri Biotec Pty Ltd
- 6.4.13 BASF SE
- 6.4.14 Bayer AG
- 6.4.15 Corteva Agriscience








