 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1692507
英國區域供熱 -市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢和統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)UK District Heating - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
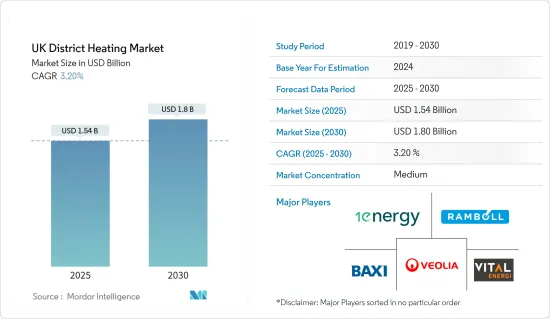
英國區域供熱市場規模預計在 2025 年為 15.4 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 18 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 3.2%。
主要亮點
- 根據永續發展情境(SDS),區域供熱、熱泵、可再生能源供熱和氫氣等清潔供熱技術預計將促進區域供熱網路的銷售並對市場需求產生積極影響。
- 對節能供暖解決方案的需求不斷成長,推動了新技術的採用。根據英國政府的一項研究,預計到2030年,英國14-20%的供暖需求將由熱力網路滿足,到2050年這一比例將達到43%。英國消耗的能源中約有一半用於供熱。商業、住宅和公共部門佔最終能源消耗的三分之二。熱量主要用於住宅/家庭和商業建築的熱水和空間供暖。
- 第五代區域供熱系統正成為現有第四代區域供熱系統的新替代方案。第五代區域供熱製冷系統是一種雙向、分散、近地面溫度網路,透過利用冷儲存和熱回流直接交換來完美平衡熱量需求。
- 政府也主導了多項擴大該國熱力網路的舉措,為所研究市場的成長創造了良好的前景。例如,2022 年底,英國政府宣布從政府 3.2 億英鎊(3.99 億美元)的熱力網路投資計劃(HNIP) 中撥款 1,910 萬英鎊(2,380 萬美元),旨在支持英格蘭和威爾斯的熱力網路。
- 然而,與市場替代方案相比,區域供熱系統屬於資本密集系統。 DHC 系統需要溝渠網路以及泵浦和系統的持續維護。這些因素阻礙了對 DHC 系統的需求。
- 此外,在現有城市和建築物中安裝區域供熱水管非常困難且成本高昂,使安裝過程變得複雜,因此繼續對所研究市場的成長構成重大挑戰。
英國區域供熱市場趨勢
都市化和工業化進程不斷加快,推動市場
- 英國和世界各地的快速都市化正在推動需求並支持向再生能源來源的轉變,以實現中央供暖和製冷。這有助於減少二氧化碳排放,提高效率並滿足都市區日益成長的能源需求,並提供具有成本效益的溫度控制。例如,在英國,都市化導致北部地區集中式系統的使用迅速增加。
- 根據世界銀行預測,到2022年英國都市化將達到84.39%,比過去十年提高了近三個百分點。儘管成長緩慢,但趨勢始終是正面的,對市場成長產生了重大影響。
- 鑑於寒冷天氣條件的普遍性,英國在全球 DHC 解決方案需求中所佔佔有率過大,大部分配電網路位於該地區的都市區。該地區在 20 世紀下半葉發展了廣泛的供熱基礎設施。它們仍然是都市區供暖和熱水的主要能量。
- 區域能源系統受益於並支持這樣的環境,並且本質上適合城市景觀。由於該技術與環境條件和勞動力需求協同效應,因此非常適合城市人口。城市中心的發展促進了區域網路的建立。英國、倫敦、威爾斯和諾丁漢就是典型的例子。除了需要一定規模的開發外,熱管網的高資本成本還要求在盡可能小的空間內提供能源服務,以最大限度地增加最終用戶的數量。因此,密集的城市發展非常適合分散供暖。
住宅和家庭領域佔據了很大的市場佔有率
- 家庭供暖佔英國總排放的近 14%(根據政府研究所的數據),需要緊急解決,以符合政府實現碳減排目標的雄心。區域供熱是向英國各地家庭提供低碳熱能的有效解決方案。目前,英國僅有 2% 多一點的住宅接入區域供熱網路(根據能源節約信託基金的數據),但隨著英國在未來幾十年內逐步實現淨零排放,預計會有更多住宅接入區域供熱網路。
- 英國目前安裝的大多數區域供熱系統都採用燃氣熱電聯產 (CHP) 系統。公寓大樓或多用戶住宅中的單一熱電聯產裝置通常效率較高,並且比每個家庭中的燃氣鍋爐所需的維護更少。英國政府氣候變遷委員會 (CCC) 預測,到 2050 年,約有 12% 的家庭供暖將由區域供熱提供。
- 英國有超過 17,000 個供熱網路,連接約 50 萬人。在人口密集的都市區,熱力網路被視為特別有吸引力的選擇。熱網是解決燃料貧窮問題並降低住宅管理成本的有效方法。
- 熱力網路可以是任意規模,並且可以隨著時間的推移添加更便宜、低碳的熱源,而無需進行挖掘道路或重建住宅等重大變化。因此,住宅領域減少碳排放的力道不斷加大將支持研究市場的成長。例如,根據英國商業、能源和產業戰略部等消息來源,預計2040年英國住宅房地產領域的二氧化碳排放將達到6,800萬噸。
- 此外,英國計劃於2025年實施的未來住宅標準將要求新建住宅的二氧化碳排放量比按照現行標準建造的住宅減少75%至80%。為了從電網脫碳和供暖電氣化中受益,住宅需要「零碳準備」並且不需要進行任何維修。新建住宅可能會禁止使用石化燃料供暖,從而轉向熱網等低碳供暖技術。
英國區域供熱產業概況。
英國區域供熱市場競爭適中,主要參與者包括 Vital Energi、1 Energy Group Limited、Baxi Heating UK、Ramboll UK Limited 和 Veolia Environnement SA。市場上的公司正在採取聯盟和收購等策略來增強其產品供應並獲得永續的競爭優勢。
2023年5月,英國政府向英格蘭各地七個尖端熱力網路計劃提供政府資助。其中包括英國首個地下熱能提取系統,該系統有可能為約 4,000 戶家庭提供低成本暖氣。英國政府表示,這些已確定的計劃將從政府的綠色熱能網路基金中獲得 9,100 萬英鎊(1.136 億美元)的資助。
2023 年 4 月,電力公司 Pinnacle Power 與 DIF Capital Partners 簽署協議,在英國各地建造和部署價值 10 億英鎊(12.5 億美元)的低碳熱力網路。兩家公司之間的新夥伴關係將加速「城鎮規模熱力網路」的推出,這可能有助於英國各地多個住宅和建築的脫碳。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概覽
- 技術分析
- 宏觀經濟情勢如何影響市場
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
- 替代品的威脅
- 產業供應鏈分析
- 政府措施和計劃
- 區域供熱合約/現場競標
第5章市場動態
- 市場促進因素
- 對節能、經濟的暖氣系統的需求不斷增加
- 都市化和工業化進程
- 市場挑戰
- 基礎設施成本高
第6章市場區隔
- 按最終用戶
- 住宅/家庭用途
- 非家庭用途
- 熱網能源結構現況及未來趨勢
- 按行業和客戶分類的熱網連接數量
- 熱能儲存的使用與未來的可能性
- 基於區域的熱網密度
- 消費者對熱力網路的態度
- 熱網機會
第7章競爭格局
- 公司簡介
- Vital Energi Utilities Ltd.
- 1Energy Group Limited
- Baxi Heating UK
- Ramboll UK Limited
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Sweco UK(AWECO AB)
- Vanttenfall(Vattenfall AB)
- Equans Services Limited
- E.ON PLC
第8章投資分析
第9章:市場的未來
The UK District Heating Market size is estimated at USD 1.54 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.80 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- To meet the Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS), clean heating technologies, such as district heating, heat pumps, and renewable and hydrogen-based heating, are expected to increase the sales of district heating networks, positively influencing market demand.
- The rising demand for energy-efficient heating solutions is pushing for the adoption of new technologies. As per the UK government's research, 14-20 percent of the heat demand in the United Kingdom is expected to be met by heat networks by 2030 and 43 percent by 2050. Around half of the energy consumed in the United Kingdom is used as heat. The commercial, domestic, and public sectors accounted for two-thirds of the final energy consumption. Heat is primarily used for water and space heating in residential/domestic and commercial buildings.
- The fifth generation is emerging as a new system to replace the existing fourth-generation district heating system. 5th generation district heating & cooling systems are bi-directional, decentralized, close-to-ground temperature networks that use the direct exchange of cold and warm thermal storage and return flows to balance the thermal demand in full measure.
- Several government-led initiatives to expand the heat networks in the country also create a favorable outlook for the growth of the studied market. For instance, in late 2022, the UK Government announced GBP19.1 million (USD 23.8 million) funding that came from the government's GBP320 million (USD 399 million) Heat Networks Investment Project (HNIP), aimed at supporting heat networks across England and Wales.
- However, district heating systems are more capital-intensive as compared to alternatives in the market. The DHC system requires a network of trenches and continuous maintenance of pumps and systems. These factors hinder the demand for DHC systems.
- Furthermore, it becomes difficult and costly to install distribution pipes for district heating in pre-existing cities/buildings that were not planned for such features, thereby adding complexity to the installation process, which continues to remain among the major challenging factors for the growth of the studied market.
UK District Heating Market Trends
Rising Urbanization and Industrialization to Drive the Market
- Rapid urbanization across the world, including in the UK, is driving the demand and pushing the switch to renewable energy sources for centralized heating & cooling, which can help reduce CO2 emissions, improve efficiency, increase urban energy needs, and provide cost-effective temperature control. For instance, driven by urbanization, the United Kingdom has rapidly increased its use of centralized systems in its northern regions.
- In the United Kingdom, urbanization amounted to 84.39% in 2022, as per the World Bank. This presents almost a three percentage point increase over the past decade. Though slow, the upward trend has been consistently positive, significantly influencing the market growth.
- Considering the prominence of cold weather conditions, the UK commands a prominent share of the global demand for DHC solutions, and a major share of the distribution network is situated in urban areas in the region. Large heat distribution infrastructures were developed during the second half of the 20th century in the region. These remain the principal ways to provide energy for space and water heating in urban areas.
- District energy systems benefit from and support this environment and are inherently appropriate to urban landscapes. The technology's synergy with the environmental conditions and the working population's needs are well suited for urban demographics. The growth of urban centers facilitates the construction of district networks. England, London, Wales, and Nottingham are some of the best examples in the market. In addition to requiring a particular scale of development, the high capital costs of heat networks demand energy services be delivered in the tightest space possible to maximize the number of end users. Thus, dense urban developments are highly suitable for distributed heat provision.
Residential and Domestic Segment Holds Significant Market Share
- Domestic heating accounts for nearly 14 percent of all emissions in the United Kingdom (according to the Institute for Government) and needs to be tackled urgently in line with the government's aim to meet its carbon reduction targets. District heating offers an effective solution for the supply of low-carbon heat to homes across the United Kingdom. While just over 2 percent of residences in the United Kingdom are currently connected to a district heating network (as per Energy Saving Trust), more are expected to come online as the country transitions to net zero over the coming decades.
- Most district heating systems currently installed in the United Kingdom use a gas-powered combined heat and power system (CHP), which generates electricity. A single CHP is usually more efficient in a housing estate or block of flats and requires less maintenance than a gas-powered boiler in every flat or house. The UK government's Committee for Climate Change (CCC) estimates that around 12 percent of domestic heat will be supplied by district heating by 2050.
- There are over 17,000 heat networks in place in the United Kingdom, and around half a million connections to them, most of them being domestic customers (as per Energy Saving Trust). They are perceived as a particularly attractive option in dense urban areas. They are an effective way of dealing with fuel poverty while reducing housing management costs.
- The establishment of heat networks, which can vary widely in size, implies that cheaper, lower-carbon sources of heat generation can be added over time without abrupt changes, such as digging up roads or changing people's homes. Hence, the growing efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of the residential sector will support the studied market's growth. For instance, according to sources like the UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, carbon dioxide emission from the residential real estate sector in the United Kingdom is anticipated to reach 68 million metric tons by 2040.
- Furthermore, the Future Homes Standard, expected to be introduced in the United Kingdom in 2025, requires carbon emissions produced by new homes to be around 75-80 percent lower than those built to current standards. Houses will have to be 'zero carbon ready,' with no retrofit work needed to benefit from the electricity grid's decarbonization and the heating's electrification. Fossil fuel heating may be banned in new houses, with an expected shift toward low-carbon heating technologies, such as heat networks.
UK District Heating Industry Overview
The UK district heating market is moderately competitive, with the presence of major players like Vital Energi, 1 Energy Group Limited, Baxi Heating UK, Ramboll UK Limited, and Veolia Environnement SA. Players in the market are adopting strategies such as partnerships and acquisitions to enhance their product offerings and gain sustainable competitive advantage.
In May 2023, the UK Government awarded government funding to 7 state-of-the-art heat network projects across England, which includes the UK's first system drawing heat from underground, with the potential of providing low-cost heating for nearly 4,000 homes. According to the government, the identified projects will receive a share of GBP 91 million (USD 113.6 million) from the government's Green Heat Network Fund.
In April 2023, Utility company Pinnacle Power entered an agreement with DIF Capital Partners to build and deploy GBP 1 billion (USD 1.25 billion) worth of low-carbon heat networks across the UK. The new partnership between the companies will accelerate the deployment of "town-and-city-scale heat networks" that will likely help to decarbonize several homes and buildings across the country.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Technological Analysis
- 4.3 Impact of Macroeconomic Scenarios on the Market
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4.5 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5 Industry Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Government Initiatives and Programs
- 4.7 District Heating Contracts/Live Tenders
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Augmented Demand for Energy-efficient and Cost-effective Heating Systems
- 5.1.2 Rising Urbanization and Industrialization
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 High Infrastructure Cost
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By End User
- 6.1.1 Residential/Domestic
- 6.1.2 Non-domestic
- 6.2 Current Energy Mix of Heat Networks and Future Trends
- 6.3 Heat Network Connections by Sectors and Customers
- 6.4 Thermal Storage Usage and Future Potential
- 6.5 Heat Networks Density Based on Regions
- 6.6 Consumer Attitudes to Heat Networks
- 6.7 Opportunities for Heat Network
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Vital Energi Utilities Ltd.
- 7.1.2 1Energy Group Limited
- 7.1.3 Baxi Heating UK
- 7.1.4 Ramboll UK Limited
- 7.1.5 Veolia Environnement SA
- 7.1.6 Sweco UK (AWECO AB)
- 7.1.7 Vanttenfall (Vattenfall AB)
- 7.1.8 Equans Services Limited
- 7.1.9 E.ON PLC











