 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910942
海運:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Maritime Freight Transport - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
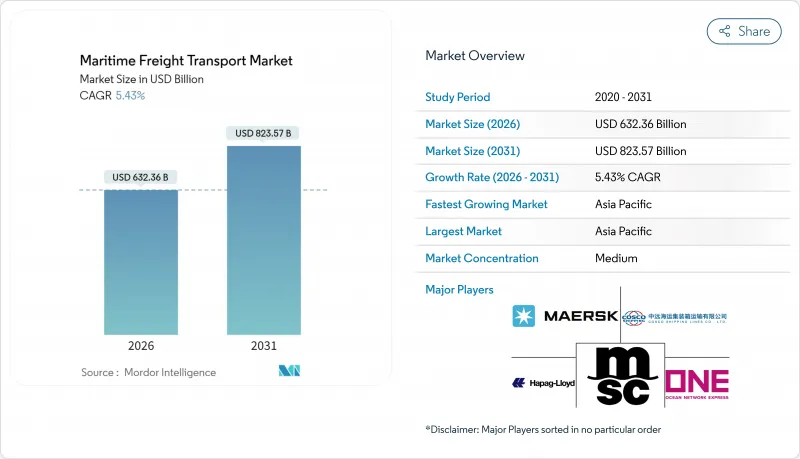
預計到 2025 年,海運市場規模將達到 5997.8 億美元,預計在預測期(2026-2031 年)內將以 5.43% 的複合年成長率成長,從 2026 年的 6323.6 億美元成長到 2031 年的 8235.7 億美元。
持續成長的驅動力來自強勁的全球貿易量、船舶為避開擁塞區和衝突地區而改道導致的噸英里需求增加,以及貨物運輸加速向南南走廊轉移,從而活性化了亞洲內部貿易。遵守歐盟排放權交易體系(EU ETS)將使營運成本在2025年增加206美元/噸,但同時,這將加速船隊更新換代,使其達到低碳水平,並增強長期競爭力。重組合作夥伴關係,例如馬士基和赫伯羅特之間的「雙子座」合作,正在重新調整東西向航線的艙位分配,將班次可靠性目標提高到90%,並增強服務差異化。目前佔貨櫃貿易80%以上的數位化貨運平台,正在幫助實現即時運力平衡,將平均停留時間縮短12%,並實現空船航段的商業化。
全球海運市場趨勢及展望
南亞內部貿易走廊的快速發展
2023年,東協將超越歐盟,成為中國最大的貿易夥伴,貿易額將達4,688億美元。 10.5%的成長標誌著亞洲內部貨運環線已成為新的成長引擎。亞太自由貿易協定(ACFTA)逐步取消關稅將使物流繞過西方轉運樞紐,從而簡化運輸流程。預計2026年完工的平陸運河全長84英里,預計每年可運輸8,900萬噸貨物,並降低供應鏈成本7.25億美元。製造業向東南亞的轉移將加強港口附近的產業叢集,並擴大對二級門戶港口的支線運輸需求。由此帶來的貨物密度將支援對15000標準箱旗艦船舶的大規模投資,這些船舶專為短途運輸和高周轉率而設計。預計這些趨勢將在預測期內為海運市場貢獻約1.2個百分點的複合年成長率。
近岸外包推動了對短程支線的需求
2024年,美國和墨西哥之間的跨境卡車運輸量創下歷史新高,凸顯了近岸外包對墨西哥灣沿岸和加勒比海地區支線運輸的影響。大型航運公司現在繞過墨西哥灣沿岸小規模的港口,轉而與區域性專業公司簽訂契約,運營樞紐輻射式短途運輸服務,從而將門到門運輸週期縮短兩到四天。 X-Press Feeders與六個歐洲港口簽署的「綠色走廊協議」就是一個很好的例子,它展示了營運商如何在實現範圍3排放目標的同時,抓住短途遠洋運輸的成長機會。經營團隊表示,降低物流成本是他們最主要的驅動力,其中41%的人優先考慮接近性而非全球規模。不斷成長的需求推高了1500-2000標準箱船舶的運轉率和日租費率,使海運市場成長率提高了0.8個百分點。
港口基礎設施長期存在瓶頸
2025年,隨著新加坡和科倫坡港接收大量開往好望角的船舶,壅塞達到頂峰,堆場運轉率超過90%,平均泊位等待時間增加三倍。在美國關稅生效前,上海港在2025年1月處理了創紀錄的500萬標準箱,即使新增了18個全自動碼頭,堆場設施仍然不堪重負。洛杉磯港和長灘港的底盤短缺問題日益嚴重,而麻六甲海峽則因地緣政治動盪和氣候變遷而面臨吃水限制。閘口自動化和內陸鐵路連接投資不足阻礙了貨物運輸速度,使海運市場的長期複合年成長率下降了1.1個百分點。
細分市場分析
乾散貨運輸將主導市場,預計2025年將佔海運市場佔有率的28.65%,這主要得益於中國鐵礦石和煤炭的需求,其庫存量高達1.65億噸。然而,儘管噸位需求強勁成長,但2025年計畫交付的3,600萬載重噸新船仍可能導致實際運價(TCE)疲軟。為降低下行風險,業者正轉向與指數掛鉤的租船合約。運力過剩的擔憂可能會促使小型船舶提前報廢,從而限制特定航線的供應,並緩解運價下行壓力。
液散貨運輸是一股特別顯著的成長引擎,預計2031年將維持4.02%的複合年成長率,主要得益於液化天然氣(LNG)產量的不斷成長和化學品貿易的多元化發展。預計到2025年,現貨超大型油輪(VLCC)的每日租金收入將達到51,600美元,將刺激大型能源公司對定期租船的需求。油輪船東正在部署雙燃料運輸能力以獲取綠色高價貨物,港口營運商也正在投資低溫出口設備,以適應使用氨燃料的船舶。液散貨運輸的強勁成長動能為海運市場增添了必要的多元化,並能有效緩衝其他貨物運輸的波動。
區域分析
預計到2025年,亞太地區將佔海運市場的37.65%,並在2031年之前以5.02%的複合年成長率持續成長。這主要得益於亞太地區57%的區域內貿易依賴度以及成長來源擺脫對歐美需求週期的依賴。上海的「18個全無人碼頭」自動化計畫將減少起重機作業的波動,並為泊位效率樹立新的標竿。預計到2026年,中國的平陸運河年吞吐能力將達到8,900萬噸,將消除內陸運輸瓶頸,每年節省7.25億美元。
北美貨櫃吞吐量將面臨前所未有的1%的萎縮,原因是關稅調整和2025年10月起實施的301條款課稅增加了中國製造船舶的成本。然而,墨西哥的貿易復甦帶來了一些抵銷效應,近岸外包也促進了墨西哥灣支線服務和內陸鐵路的改善。在歐洲,每年100億歐元(110.3億美元)的排放權交易體系(ETS)合規成本迫使航運公司重新調整航線優先順序並重新思考燃料策略。同時,「綠色走廊」試點計畫正使歐洲港口成為替代燃料燃料庫的先驅。
中東將利用沙烏地阿拉伯45億美元的港口投資,力爭2026年將區域物流收入提升至388億美元。伊拉克-美索不達米亞走廊(IMEC)將透過鐵路和港口一體化,把亞歐之間的運輸時間縮短40%,凸顯該地區在多極貿易流量中的重要性。南美洲正利用其中立地位,在供應鏈中斷的情況下,促進巴西大豆對華出口。隨著連接俄羅斯和奈及利亞的航線開闢了通往金磚國家(BRICS)的農業走廊,非洲的佔有率也逐漸成長。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 南亞內部貿易走廊的快速發展
- 近岸外包推動了對近岸支線的需求
- 歐盟排放交易體系(EU-ETS)航運排放法規將重塑船隊經濟格局
- 透過數位化貨運平台實現即時運輸能力匹配
- 替代燃料可降低長期營運成本。
- 由於蘇伊士運河繞行工程和巴拿馬運河擴建工程,運輸噸英里數增加。
- 市場限制
- 港口基礎設施長期存在瓶頸
- 2023-2026年貨櫃訂單積壓訂單創歷史新高,或將導致供應過剩
- 日益嚴重的海上網路安全威脅
- 通貨膨脹導致燃油價格波動
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 新冠疫情與地緣政治事件的影響
- 波特五力模型
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按貨物類型
- 貨櫃貨物
- 乾燥
- 冷藏
- 乾散貨
- 液體散貨
- 普通貨物
- 滾裝貨物
- 貨櫃貨物
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 電子裝置和半導體
- 化學品/石油化工產品
- 食品/飲料
- 製藥和醫療保健
- 零售與電子商務
- 其他
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 秘魯
- 智利
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 亞太地區
- 印度
- 中國
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 東南亞(新加坡、馬來西亞、泰國、印尼、越南、菲律賓)
- 亞太其他地區
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 義大利
- 比荷盧經濟聯盟(比利時、荷蘭、盧森堡)
- 北歐國家(丹麥、芬蘭、冰島、挪威、瑞典)
- 其他歐洲地區
- 中東和非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Mediterranean Shipping Company(MSC)
- AP Moller-Maersk
- COSCO Shipping Lines
- Hapag-Lloyd
- Ocean Network Express(ONE)
- Evergreen Marine Corp.
- HMM Co., Ltd.
- Yang Ming Marine Transport
- ZIM Integrated Shipping
- Pacific International Lines(PIL)
- SITC International
- X-Press Feeders
- Matson Inc.
- Swire Shipping
- NYK Line
- K Line
- MOL Logistics
- CMA CGM
- Wan Hai Lines
- Emirates Shipping Line
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Maritime Freight Transport Market was valued at USD 599.78 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 632.36 billion in 2026 to reach USD 823.57 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.43% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Sustained expansion springs from resilient global trade volumes, the rerouting of vessels around congestion and conflict zones that inflates ton-mile demand, and the accelerating shift of cargo toward South-South corridors that intensify intra-Asian flows. Compliance with the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) adds USD 206 per metric ton to operating costs in 2025 but simultaneously accelerates fleet renewal toward low-carbon tonnage, supporting long-run competitiveness. Alliance realignments such as the Gemini Cooperation between Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd recalibrate slot allocation across East-West lanes, raising schedule reliability targets to 90% and sharpening service differentiation. Digital freight platforms that now govern more than 80% of container transactions provide real-time capacity balancing, cut average dwell time by 12%, and help carriers monetize empty repositioning legs.
Global Maritime Freight Transport Market Trends and Insights
Surge in South-South Intra-Asian Trade Corridors
ASEAN surpassed the European Union as China's top trading partner in 2023 at USD 468.8 billion, a 10.5% jump that cements intra-Asian cargo loops as the new growth engine. Progressive tariff eliminations under ACFTA streamline flows that bypass Western transshipment hubs, while China's 84-mile Pinglu Canal slated for 2026 will move 89 million tons annually and slice USD 725 million from supply-chain costs. Manufacturing migration toward Southeast Asia reinforces near-port industrial clusters, amplifying feeder demand to secondary gateways. The resulting cargo density underpins scale investments in 15,000 TEU workhorses optimized for shorter hauls yet higher turn-round frequencies. Collectively, these dynamics contribute an estimated 1.2 percentage-points to the Maritime freight transport market CAGR forecast period.
Near-shoring Drives Short-Sea Feeder Demand
U.S.-Mexico truck crossings hit record levels in 2024, validating near-shoring's spillover into Gulf and Caribbean feeder loops. Mainline carriers now skip smaller Gulf ports, contracting regional specialists for hub-and-spoke shuttles that compress door-to-door cycles by two to four days. X-Press Feeders' pact with six European ports to create green corridors exemplifies operators capturing rising short-sea volumes while satisfying Scope 3 emission objectives. Executives cite logistics cost reduction as the single largest incentive, with 41% prioritizing proximity over global scale. Elevated demand lifts vessel utilization and daily charter rates for 1,500-2,000 TEU ships, translating into a 0.8 percentage-point uptick in the Maritime freight transport market growth trajectory.
Chronic Port-Side Infrastructure Bottlenecks
Congestion peaked in 2025 as Singapore and Colombo absorbed Cape-routed vessels, causing yard utilization to exceed 90% and average berth wait times to triple. Shanghai processed a record 5 million TEU in January 2025 ahead of U.S. tariff enactments, stressing yard equipment even after adding 18 fully automated terminals. Los Angeles and Long Beach struggle with chassis shortages, while the Malacca Strait faces geopolitical disruptions and climate-driven draft limitations. Investment lags in gate automation and hinterland rail links hamper cargo velocity, subtracting 1.1 percentage-points from the Maritime freight transport market's long-run CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- EU-ETS on Maritime Emissions Reshapes Fleet Economics
- Digital Freight Platforms Enable Real-Time Capacity Matching
- Oversupply Risk from Record Container-Ship Orderbook 2023-26
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Dry bulk holds the lion's share, accounting for 28.65% of Maritime freight transport market size in 2025 on the back of China's 165 million-ton iron-ore and coal restocking drive. However, a 36 million dwt delivery slate scheduled for 2025 risks dampening TCE rates despite robust tonnage demand growth. Operators therefore pivot to index-linked charters to mitigate downside exposure. Overcapacity fears spur early scrapping of Handysize vessels, constraining supply in niche routes and moderating rate compression.
Liquid bulk is the standout growth engine, posting a 4.02% CAGR through 2031 as LNG liquefaction volumes scale and chemicals trades diversify. Spot VLCC earnings are forecast at USD 51,600 per day for 2025, stimulating time-charter interest among energy majors. Tanker owners install dual-fuel capability to capture green-premium cargoes, while port operators invest in cryogenic export arms to service ammonia-ready tonnage. The strengthening liquid bulk trajectory adds needed diversity to the Maritime freight transport market, cushioning volatility in other cargo streams.
The Maritime Freight Transport Market Report is Segmented by Cargo Type (Containerized Cargo, Dry Bulk Cargo, Liquid Bulk Cargo, General Cargo, Roll-On/Roll-Off Cargo), End-User Industry (Electronics & Semiconductors, Chemicals & Petrochemicals, Food & Beverage, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commands 37.65% of Maritime freight transport market share in 2025 and is set to expand at a 5.02% CAGR to 2031, buoyed by 57% intra-regional trade dependence that diversifies growth away from Western demand cycles. Shanghai's automation blueprint-18 fully unmanned terminals-cuts crane moves per hour variance and sets new benchmarks for berth productivity. China's Pinglu Canal, capable of handling 89 million tons a year by 2026, will reduce inland transit bottlenecks and save USD 725 million annually.
North America confronts a rare 1% contraction in container throughput as tariff realignments and Section 301 levies raise costs on Chinese-built vessels beginning October 2025. Yet Mexico's trade renaissance offers partial offset, with near-shoring catalyzing Gulf feeder services and inland rail upgrades. Europe faces EUR 10 billion (USD 11.03 billion) annual ETS compliance costs that reprioritize corridor routing and bunker strategies. Simultaneously, green-corridor pilots position European ports as early-adoption nodes for alternative-fuel bunkering.
The Middle East leverages USD 4.5 billion in Saudi port investments to lift regional logistics revenue to USD 38.8 billion by 2026. IMEC promises to shorten Asia-Europe transit times by 40% via integrated rail-port linkages, underscoring the region's role in multipolar trade flows. South America capitalizes on its neutral stance; Brazilian soybean exports to China expand under disrupted supply chains. Africa's share gradually rises as Russia-Nigeria services unlock agricultural corridors for BRICS members.
- Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC)
- A.P. Moller-Maersk
- COSCO Shipping Lines
- Hapag-Lloyd
- Ocean Network Express (ONE)
- Evergreen Marine Corp.
- HMM Co., Ltd.
- Yang Ming Marine Transport
- ZIM Integrated Shipping
- Pacific International Lines (PIL)
- SITC International
- X-Press Feeders
- Matson Inc.
- Swire Shipping
- NYK Line
- K Line
- MOL Logistics
- CMA CGM
- Wan Hai Lines
- Emirates Shipping Line
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in South-South intra-Asian trade corridors
- 4.2.2 Near-shoring drives short-sea feeder demand
- 4.2.3 EU-ETS on maritime emissions reshapes fleet economics
- 4.2.4 Digital freight platforms enable real-time capacity matching
- 4.2.5 Alternative fuels adoption lowers long-term OPEX
- 4.2.6 Suez diversions & Panama expansion boost ton-miles
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Chronic port-side infrastructure bottlenecks
- 4.3.2 Oversupply risk from record container-ship orderbook 2023-26
- 4.3.3 Escalating maritime cyber-security threats
- 4.3.4 Inflation-driven bunker price volatility
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Impact of COVID-19 and Geo-Political Events
- 4.8 Porters Five Forces
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Cargo Type
- 5.1.1 Containerized Cargo
- 5.1.1.1 Dry
- 5.1.1.2 Reefer
- 5.1.2 Dry Bulk Cargo
- 5.1.3 Liquid Bulk Cargo
- 5.1.4 General Cargo
- 5.1.5 Roll-On/Roll-Off Cargo
- 5.1.1 Containerized Cargo
- 5.2 By End-User Industry
- 5.2.1 Electronics & Semiconductors
- 5.2.2 Chemicals & Petrochemicals
- 5.2.3 Food & Beverage
- 5.2.4 Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Retail & E-commerce
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.2 South America
- 5.3.2.1 Brazil
- 5.3.2.2 Peru
- 5.3.2.3 Chile
- 5.3.2.4 Argentina
- 5.3.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 India
- 5.3.3.2 China
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 Australia
- 5.3.3.5 South Korea
- 5.3.3.6 South East Asia (Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Philippines)
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 Europe
- 5.3.4.1 United Kingdom
- 5.3.4.2 Germany
- 5.3.4.3 France
- 5.3.4.4 Spain
- 5.3.4.5 Italy
- 5.3.4.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.3.4.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.3.4.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 United Arab of Emirates
- 5.3.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.3.5.5 Rest of Middle East And Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC)
- 6.4.2 A.P. Moller-Maersk
- 6.4.3 COSCO Shipping Lines
- 6.4.4 Hapag-Lloyd
- 6.4.5 Ocean Network Express (ONE)
- 6.4.6 Evergreen Marine Corp.
- 6.4.7 HMM Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Yang Ming Marine Transport
- 6.4.9 ZIM Integrated Shipping
- 6.4.10 Pacific International Lines (PIL)
- 6.4.11 SITC International
- 6.4.12 X-Press Feeders
- 6.4.13 Matson Inc.
- 6.4.14 Swire Shipping
- 6.4.15 NYK Line
- 6.4.16 K Line
- 6.4.17 MOL Logistics
- 6.4.18 CMA CGM
- 6.4.19 Wan Hai Lines
- 6.4.20 Emirates Shipping Line
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment









