 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910555
冶金焦:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Metallurgical Coke - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
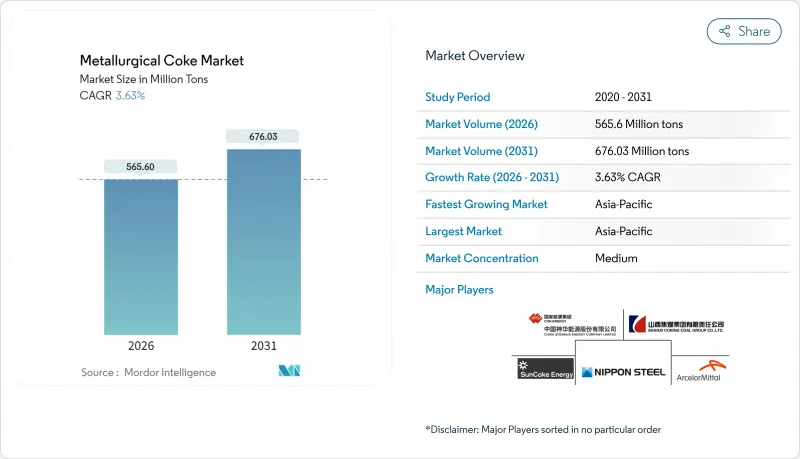
2025年冶金焦市場價值為5.4578億噸,預計從2026年的5.656億噸成長到2031年的6.7603億噸,在預測期(2026-2031年)內複合年成長率為3.63%。
亞太地區鋼鐵產量的成長、北美穩定的公共基礎設施投資以及保護綜合鋼鐵美國。供應鏈韌性正變得日益重要,垂直整合的鋼鐵企業正努力確保專屬焦炭產能,並優先選擇擁有地理分散資產的供應商。
全球冶金焦市場趨勢及展望
公共基礎設施對鋼鐵的需求不斷成長
大規模公共工程項目確保了多年期鋼鐵承購協議的簽訂,直接轉化為冶金焦市場穩定的需求。政府合約保證了訂單的可預測性,幫助焦炭生產商最佳化爐窯運轉率和物流規劃。即使在景氣衰退時期,公共工程項目通常也會持續進行,從而緩解需求波動,保障供應商的長期收益。像美國和印度這樣基礎建設與國內鋼鐵政策緊密結合的地區,供應鏈韌性更強。這種契合度促使鋼鐵廠續簽長期採購協議,從而確保優質低灰焦的供應。
擴大汽車產能
汽車產量的成長,主要集中在中國、印度、墨西哥和東南亞地區,推動了精密鑄造用焦炭的需求,並促進了先進高強度鋼種的高溫加工。電動車平台需要輕量化且堅固的電池外殼,這對焦炭原料的碳含量穩定性提出了更高的品質要求。汽車工廠的地理集中催生了區域性焦炭供應基地,為擁有多式聯運網路的本地生產商帶來了成本優勢。隨著汽車製造商擴大將零件生產在地化以降低供應鏈風險,附近焦炭廠的需求模式也變得更加可預測。然而,汽車需求的周期性仍然要求焦炭供應商在月度合約配額和現貨市場之間保持靈活的產能。
焦化廠需遵守嚴格的環境法規
在美國,國家有害空氣污染物排放標準(NEPS)最終確定了更低的洩漏限值,並強制要求對廠區進行連續的苯監測,以及採用先進的洩漏檢測通訊協定。歐盟強制要求在整個煤炭價值鏈中進行甲烷測量和報告,並為焦化設施增加了新的合規要求。脫硫裝置、苯萃取裝置和除塵器的資本投資可能超過每噸產能100美元,使得小規模獨立生產商難以資金籌措。因此,監管負擔正在加速產業整合,並提高進入門檻,從而限制了冶金焦市場的成長。
細分市場分析
高爐焦佔冶金焦市場的63.74%。穩定的生鐵產量目標帶來了穩定的年訂單量,而更先進的製程控制則提高了鋼鐵廠所需的冷強度和碳含量(CSR)指標。儘管塊狀焦產量較低,但其複合年成長率(CAGR)為4.05%,高於整體市場成長率,這主要得益於其在鑄造和非鐵金屬的應用,這些行業對10-25毫米的精確尺寸要求較高。
一體化生產商透過多年合約鎖定產量,以確保爐窯效率;而運作餘熱回收爐的供應商則因其可預測的品質而獲得溢價。儘管環保法規日益嚴格,但該領域的持續成長仍支撐著冶金焦市場的整體發展,確保產能擴張仍將圍繞傳統的滾筒式沖壓爐。
預計到 2025 年,低灰分(8-12% 灰分)產品將佔冶金焦市場的 70.25%,到 2031 年將以 4.38% 的複合年成長率成長,這反映了爐渣法規和排放上限的收緊。
印度對低灰焦的進口限制(每半年進口量上限為140萬噸)凸顯了此等級焦炭對供應安全的戰略重要性。投資於先進洗煤和配煤技術的生產商能夠更好地掌握這一高階市場,並與大型鋼鐵廠簽訂長期供應契約,從而加深其在冶金焦行業的滲透率。
冶金焦炭報告按焦炭類型(高爐焦炭、鑄造焦炭等)、等級(低灰分 8-12%,高灰分 15% 及以上)、應用(鋼鐵製造、鑄造、製糖等)、最終用戶行業(綜合鋼鐵製造商、小型鋼廠/電弧爐 (EAF) 運營商等)和北美地區(歐洲亞省)、中東地區和中東地區進行細分、中東地區和中東地區。
區域分析
到2025年,亞太地區將佔全球整體的69.10%,並在2031年之前保持3.98%的複合年成長率,這主要得益於印度產能的積極擴張以及東南亞基礎設施計劃的持續需求。中國暫停核准新建燃煤鋼鐵廠的政策抑制了新計畫的推進,但由於檢修停產和效率維修,現有鋼鐵廠仍在消耗高品質焦炭。
在北美,長期基礎設施投資正在穩定鋼鐵訂單。墨西哥的汽車產業叢集和加拿大的自然資源管道正在增加需求,並支持北美大陸的焦炭分銷。
歐洲仍然是一個重要的市場,在氫氣直接還原鐵產能普及之前,瑞典、德國和法國對優質焦炭的需求仍然至關重要。歐盟甲烷法規2024/1787將增加新的監測成本,並可能導致一些獲利能力的焦爐關閉。這將加劇區域供應緊張,並維持進口依賴。以巴西一體化鋼鐵廠為基礎的南美洲,以及以新興綠色鋼鐵中心為支撐的中東和非洲,為那些尋求企業發展傳統高爐煉鋼核心業務的生產商提供了新的多元化發展前景。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 公共基礎設施對鋼鐵的需求不斷成長
- 擴大汽車產能
- 提高亞太地區綜合鋼鐵廠產能
- 新興經濟體的都市建設熱潮
- 擴大餘熱回收焦爐的商業化應用
- 市場限制
- 冶金焦價格波動
- 焦化廠需遵守嚴格的環境法規
- 轉向氫基直接還原鐵?
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
第5章 市場規模及成長預測(銷售)
- 按可樂類型
- 高爐焦炭
- 鑄造焦炭
- 堅果可樂
- 可口可樂的微風
- 按年級
- 灰分含量低(灰分含量8-12%)
- 高灰分含量(灰分含量15%或以上)
- 透過使用
- 鋼鐵製造
- 鑄件
- 糖加工
- 玻璃製造
- 其他方法(化學還原法及其他方法)
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 綜合鋼鐵製造商
- 小型軋機/電弧爐 (EAF) 操作員
- 鑄造廠
- 非鐵金屬產業
- 其他
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 東南亞國協
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 義大利
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- ArcelorMittal
- BlueScope Steel Ltd.
- China Baowu Steel Group
- China Shenhua Energy Co. Ltd.
- Drummond Company Inc.
- Gujarat NRE Coke Ltd.(GNCL)
- Hickman-Williams & Company
- Jiangsu Surung High-Carbon Co. Ltd.
- JSW Steel Ltd.
- Mahalaxmi Ennore Coke Pvt Ltd
- Mechel PAO
- Nippon Steel Corporation
- OKK Koksovny as
- POSCO
- Shanxi Coking Coal Group
- SunCoke Energy Inc.
- Tata Steel Ltd.
- United States Steel Corporation
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Metallurgical Coke Market was valued at 545.78 Million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 565.6 Million tons in 2026 to reach 676.03 Million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.63% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Escalating steel production in Asia Pacific, steady public-infrastructure investment in North America, and long-term contracts that shield integrated mills from short-term price swings underpin this expansion. Blast-furnace operations retain economic advantages over alternative ironmaking routes, so demand for premium low-ash coke remains firm despite decarbonization headwinds. Environmental regulation is tightening across the United States and the European Union, yet heat-recovery coke ovens help large operators contain compliance costs and safeguard margins. Supply-chain resilience is rising in strategic importance, pushing vertically integrated steel producers to secure captive coke capacity and favor suppliers with geographically diversified assets.
Global Metallurgical Coke Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Steel in Public Infrastructure
Large public-works programs have locked in multi-year steel offtake commitments that translate directly into steady metallurgical coke market demand. Government contracts provide predictable order books, helping coke producers optimize oven utilization rates and logistics planning. Because public projects often proceed even in downturns, they soften demand volatility and protect long-term supplier revenues. Regions with synchronized infrastructure and domestic steel policy, such as the United States and India, enjoy superior supply-chain resilience. This alignment encourages mills to renew long-term offtake agreements that secure premium low-ash coke supplies.
Expanding Automotive Production Capacity
Vehicle output growth, particularly in China, India, Mexico, and Southeast Asia, lifts foundry coke requirements for precision castings and heats advanced high-strength steel grades. Electric-vehicle platforms demand lightweight yet rigid battery housings that intensify quality requirements for consistent carbon levels in coke feedstock. Geographic clustering of automotive plants fosters localized coke-supply hubs, giving regional producers with multimodal transport access a cost edge. As automakers localize components to mitigate supply-chain risk, demand patterns become more predictable for nearby coke plants. Nevertheless, cyclical vehicle demand still obliges coke suppliers to keep flexible capacity that can swing between monthly contract allocations and spot markets.
Stringent Environmental Regulations on Coking Plants
The United States finalized lower leak limits under the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants, mandating continuous benzene monitoring at fencelines and advanced leak-detection protocols. The European Union now requires methane measurement and reporting across the coal value chain, adding compliance layers for coke facilities. Capital expenditure for desulfurization, benzene extraction, and dust-capture equipment can exceed USD 100 per-ton of capacity, costs that smaller independent producers struggle to finance. Consequently, the regulatory burden accelerates industry consolidation and raises barriers to entry, moderating metallurgical coke market growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Urban Construction Boom in Emerging Economies
- Increasing Commercialization of Heat-Recovery Coke Ovens
- Shift Toward Hydrogen-Based Direct Reduced Iron
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Blast-furnace varieties hold a 63.74% slice of the metallurgical coke market. Stable hot-metal production targets keep annual call-offs steady, while process-control upgrades raise the cold-strength and CSR specifications mills expect. Nut coke, though a lower-volume grade, is eclipsing aggregate growth at a 4.05% CAGR due to foundry and non-ferrous use cases that require precise 10-25 mm sizing.
Integrated producers contract multi-year volumes to safeguard furnace efficiency, so suppliers running heat-recovery ovens capture premiums for predictable quality. The segment's incremental growth continues to anchor the broader metallurgical coke market, ensuring that capacity expansions still centre on traditional drum-stamp batteries despite mounting environmental scrutiny.
Low-ash (8-12% ash) product occupied 70.25% of the metallurgical coke market in 2025 and is forecast to record a 4.38% CAGR through 2031, reflecting tighter furnace slag limits and emission caps.
Import restrictions in India that cap low-ash cargoes at 1.4 million tons per half-year underscore the grade's strategic importance for supply security. Producers investing in advanced coal washing and blending technology are best positioned to seize this premium segment and secure long-term supply agreements with large mills, thereby deepening penetration within the metallurgical coke industry.
The Metallurgical Coke Report is Segmented by Coke Type (Blast-Furnace Coke, Foundry Coke, and More), Grade (Low Ash 8 To 12% Ash and High Ash More Than 15% Ash), Application (Iron and Steel Making, Foundry Castings, Sugar Processing, and More), End-User Industry (Integrated Steel Producers, Mini-mills/EAF Operators, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific delivered 69.10% of global volume in 2025 and will maintain a 3.98% CAGR through 2031 owing to India's vigorous capacity build-out and ongoing demand from Southeast Asian infrastructure projects. China's moratorium on new coal-based steel permits curbs greenfield projects, yet existing furnaces still consume high-quality coke for maintenance outages and efficiency upgrades.
North America is driven by long-life infrastructure spending that stabilized steel orders. Mexico's automotive clusters and Canada's natural-resource pipelines add incremental volume and sustain intracontinental coke flows.
Europe remains significant because high-grade coke is indispensable for Sweden, Germany, and France until hydrogen DRI facilities scale. The EU Methane Regulation 2024/1787 ushers in new monitoring costs that could shutter sub-economic batteries, tightening internal supply and sustaining import dependence. South America, underpinned by Brazilian integrated mills, and the Middle-East and Africa, buoyed by emerging green-steel hubs, collectively form a diversification frontier for producers seeking exposure beyond traditional blast-furnace heartlands.
- ArcelorMittal
- BlueScope Steel Ltd.
- China Baowu Steel Group
- China Shenhua Energy Co. Ltd.
- Drummond Company Inc.
- Gujarat NRE Coke Ltd. (GNCL)
- Hickman-Williams & Company
- Jiangsu Surung High-Carbon Co. Ltd.
- JSW Steel Ltd.
- Mahalaxmi Ennore Coke Pvt Ltd
- Mechel PAO
- Nippon Steel Corporation
- OKK Koksovny a.s.
- POSCO
- Shanxi Coking Coal Group
- SunCoke Energy Inc.
- Tata Steel Ltd.
- United States Steel Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Demand for Steel in Public Infrastructure
- 4.2.2 Expanding Automotive Production Capacity
- 4.2.3 Increasing Capacity Additions in Integrated Steel Mills in Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 Urban Construction Boom in Emerging Economies
- 4.2.5 Increasing Commercialisation of Heat-Recovery Coke Ovens
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Metallurgical Coke Price Volatility
- 4.3.2 Stringent Environmental Regulations on Coking Plants
- 4.3.3 Shift Toward Hydrogen?Based Direct Reduced Iron
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts ( Volume)
- 5.1 By Coke Type
- 5.1.1 Blast-Furnace Coke
- 5.1.2 Foundry Coke
- 5.1.3 Nut Coke
- 5.1.4 Coke Breeze
- 5.2 By Grade
- 5.2.1 Low Ash (8 to 12% Ash)
- 5.2.2 High Ash (more than 15% Ash)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Iron and Steel Making
- 5.3.2 Foundry Castings
- 5.3.3 Sugar Processing
- 5.3.4 Glass Manufacturing
- 5.3.5 Others (Chemical Reduction and Others)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Integrated Steel Producers
- 5.4.2 Mini-mills/EAF Operators
- 5.4.3 Foundries
- 5.4.4 Non-ferrous Metallurgy
- 5.4.5 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.5.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 Italy
- 5.5.3.4 France
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ArcelorMittal
- 6.4.2 BlueScope Steel Ltd.
- 6.4.3 China Baowu Steel Group
- 6.4.4 China Shenhua Energy Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Drummond Company Inc.
- 6.4.6 Gujarat NRE Coke Ltd. (GNCL)
- 6.4.7 Hickman-Williams & Company
- 6.4.8 Jiangsu Surung High-Carbon Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 JSW Steel Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Mahalaxmi Ennore Coke Pvt Ltd
- 6.4.11 Mechel PAO
- 6.4.12 Nippon Steel Corporation
- 6.4.13 OKK Koksovny a.s.
- 6.4.14 POSCO
- 6.4.15 Shanxi Coking Coal Group
- 6.4.16 SunCoke Energy Inc.
- 6.4.17 Tata Steel Ltd.
- 6.4.18 United States Steel Corporation
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











