 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906232
印尼電子商務物流市場:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
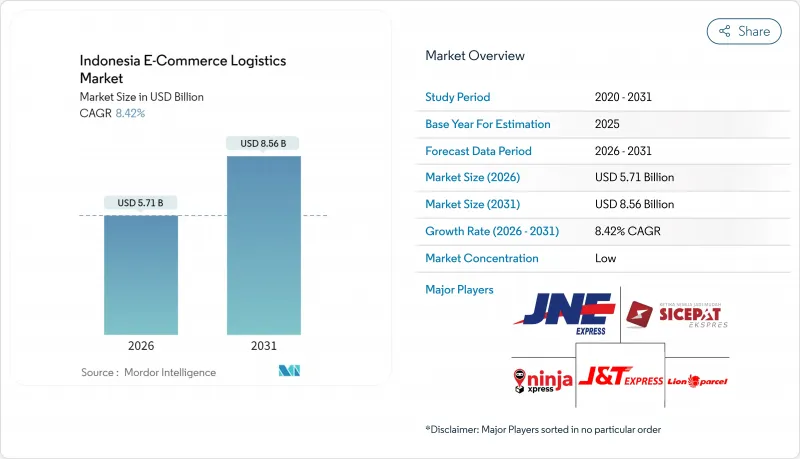
預計到 2026 年,印尼電子商務物流市場規模將達到 57.1 億美元,高於 2025 年的 52.7 億美元,預計到 2031 年將達到 85.6 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 8.42%。
預計到2024年,數位訂單量將成長35%,這得益於政府專案不斷推進,將各州物流樞紐與國家平台連結起來,進而持續提升網路整合效率。對公路、港口和自動化分類中心的投資正在縮短配送週期,而都市區消費者則要求供應商加快當日達和隔天達服務的提供。分散式競爭雖然抑制了價格上漲,但也對利潤率造成了壓力,促使承運商升級人工智慧驅動的路線規劃和倉儲機器人技術。同時,針對價值低於1500美元小包裹的監管改革正在簡化跨境規流程,並為小規模出口商開闢新的收入管道。
印尼電子商務物流市場趨勢及洞察
區域城市小包裹處理量迅速成長
4G網路的擴展和智慧型手機的普及推動了主要城市以外網路購物的擴張,導致三寶壟和瑪瑯等區域性城市的小包裹量激增。營運商被迫重新設計網路,透過將區域自提點與都市區微型倉配中心相結合,在人口密度較低的地區提供更具成本效益的服務。像Tokopedia Now這樣的電商平台正擴大在附近區域設立多個自提點,迫使物流公司協調更大範圍內的快速收貨、包裝和配送流程。國家物流生態系統計畫正在建構連接區域倉庫和國家物流公司的通用資料基礎設施,從而降低中小企業的進入門檻。
政府計劃將物流成本降低至國內生產毛額的8%。
印尼2025-2029年國家中期發展計畫(RPJMN)將物流效率認定為經濟韌性的支柱之一。各部會正在協調公路、港口和資訊通訊技術(ICT)的發展,以減少空駛返程和行政延誤。新的《國家物流局法案》旨在集中政策,防止2024年發生的港口堵塞事件再次發生,當時有26415個貨櫃滯留。資訊通訊部(Kominfo)已被指定為中立的數據整合機構,鼓勵承運商提供API介面,以實現貨物可視性和動態艙位預訂。
群島國家的區域特徵推高了島際「最後一公里」運輸成本。
為17500個島嶼提供服務,為承運商帶來了額外的航程、天氣風險和回程貨物短缺問題,導致運輸成本比爪哇島的標準高出40%至60%。由於港口水深較淺和海事法規重疊,近海航運仍然服務不足,季風季節也會擾亂船期和庫存預測。雖然「海運費」補貼提供了一些支持,但商業航運公司仍需承擔前往馬魯古群島和巴布亞可靠航線的額外成本。
細分市場分析
至2025年,運輸業將佔印尼電子商務物流市場規模的76.35%。這主要得益於爪哇島內發達的公路網路以及連接整個群島的海運。然而,以貼標和套件組裝為代表的附加價值服務預計將以6.98%的複合年成長率成長,從而滿足品牌對客製化包裝的需求。營運商正積極採用機械臂和RFID閘機來提高準確性並縮短停留時間。卡車運輸、倉儲和客製化系統的整合正在贏得大型電商平台的訂單。
儘管基礎設施建設的持續推進提高了道路可靠性,但不斷上漲的燃油價格和日益嚴格的環保目標正迫使運輸公司最佳化路線並試用電動貨車。倉儲需求主要集中在雅加達和泗水港口附近,客製化建造的自動化物流中心租賃業務激增。能夠靈活調整運能以應對諸如雙十一和齋月等季節性高峰的履約運營商,已在各大平台獲得了高收益的倉儲時段。
預計到2025年,B2C將在印尼電子商務物流市場佔據73.40%的佔有率,這主要得益於電商平台的規模和都市區較高的客戶密度。消費者對價格的高度敏感迫使物流公司降低成本,導致大量配送和群眾外包配送人員在最終配送環節的使用率上升。 B2B領域預計將以6.59%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於製造商採購流程的數位化以及對即時補貨需求的不斷成長。工廠管線服務供應商正在增加庫存審核、品質檢驗和供應商管理庫存(VMS)等服務,以提高客戶留存率。
C2C市場目前仍屬於小眾市場,但隨著二手時尚和手工藝品社交電商平台的興起,預計該市場將持續成長。在這些平台中,產品認證和低成本退貨機制是其服務提案。由市場平台管理的網路可以部署混合模式,整合B2C和B2B長途貨運,從而提高卡車運轉率,並可能擠壓獨立貨運代理商的利潤空間。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 來自區域城市(二、三線城市)的小包裹處理量迅速成長
- 政府計劃將物流成本降低至國內生產毛額的8%。
- 當日達和隔日達配送選項快速成長
- 印尼400兆印尼幣的基礎建設投資將推動電子商務配送網路的擴張
- 基礎設施投資(新收費公路、港口、機場)正在縮短交貨時間,並開啟二、三線市場。
- 由於資本轉移到努沙登加拉群島,需要對履約基地進行重組。
- 市場限制
- 群島地區增加了島際「最後一公里」運輸成本
- 分散的CEP定價競爭降低了提供者的利潤率
- 印尼的島嶼地區推高了最後一公里配送成本。
- 現代甲級倉庫技術純熟勞工短缺
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 供需分析
- 產業吸引力—五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 逆向/退貨貨物流洞察
- 地緣政治事件如何影響供應鏈轉型
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過服務
- 運輸
- 路
- 鐵路
- 航空郵件
- 海上運輸
- 倉儲和履約
- 附加價值服務(貼標籤、包裝、套件組裝)
- 運輸
- 按經營模式
- B2C
- B2B
- C2C
- 按目的地
- 國內的
- 跨境(國際)
- 按配送速度
- 當日送達(24小時內)
- 隔日送達(24-48小時)
- 標準(3-5天)
- 其他(5天或以上)
- 按產品類型
- 食品/飲料
- 個人護理及家居用品
- 時尚與生活方式(配件、服裝、鞋履)
- 家具
- 家用電器/電器產品
- 其他產品
- 按城市級別
- 第一大都會區
- 第二層
- 三級及以下
- 按州
- 中爪哇
- 東爪哇
- 西爪哇
- 雅加達
- 萬丹省
- 其他州
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- JNE Express
- J&T Express
- SiCepat Ekspres
- Ninja Xpress
- Lion Parcel
- Wahana Express
- TIKI
- Pos Indonesia
- Paxel
- DHL Express
- UPS
- FedEx
- GoSend(Gojek)
- Grab Express
- Shipper
- Shopee Express
- Lazada eLogistics
- Kuehne+Nagel
- DSV
- Kerry Logistics
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 5.71 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 5.27 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 8.56 billion, growing at 8.42% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Digital ordering volumes climbed 35% in 2024, and government programs that connect provincial logistics hubs with national platforms continue to streamline network integration. Investments in roads, ports, and automated sortation centers shorten delivery cycles, while urban consumers push providers to accelerate same-day and next-day options. Fragmented competition keeps prices low but pressures profit margins, prompting carriers to upgrade AI-driven route planning and warehouse robotics. Meanwhile, regulatory reforms for parcels below USD 1,500 ease cross-border compliance, opening new revenue channels for small exporters.
Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Explosive Parcel-Volume Surge from Tier-2/3 Cities
Improved 4G coverage and smartphone affordability are propelling online shopping outside metropolitan cores, lifting parcel counts in Semarang, Malang, and other secondary markets. Providers must redesign networks to serve lower-density zones cost-effectively, blending regional depots with city-level micro-fulfillment points. Quick-commerce operators such as Tokopedia Now increasingly stock multiple pick points nearby, forcing carriers to orchestrate rapid pick-pack-ship flows across a wider geography. The National Logistics Ecosystem program supplies common data rails that link provincial warehouses to national carriers, lowering onboarding barriers for smaller players.
Government Push to Cut Logistics Cost-to-GDP to 8%
Indonesia's RPJMN 2025-2029 embeds logistics efficiency as a pillar of economic resilience. Ministries coordinate road, port, and ICT upgrades to shrink empty backhauls and administrative delays. A new National Logistics Agency bill aims to centralize policy, preventing port congestion episodes such as the 2024 container backlog that stranded 26,415 boxes. Kominfo has been assigned as a neutral data integrator, incentivizing carriers to expose API feeds that enable shipment visibility and dynamic slot booking.
Archipelagic Geography Inflates Inter-Island Last-Mile Costs
Serving 17,500 islands saddles carriers with extra sea legs, weather risks, and scarce return loads that push delivery costs 40-60% above Java norms. Short sea shipping remains underserved due to shallow ports and overlapping maritime rules, while monsoon seasons upend schedules and inventory forecasts. The Sea Toll subsidy helps, yet commercial providers still shoulder cost premiums for reliable sailings to Maluku or Papua.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Uptake of Same-Day/Next-Day Delivery Options
- IDR 400 Trillion Infrastructure Investment
- Fragmented CEP Price War Eroding Provider Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Transportation captured 76.35% of the Indonesia e-commerce logistics market size in 2025 as road networks carry bulk intra-Java traffic and sea freight stitches together the archipelago. Yet value-added services, led by labeling and kitting, are projected to grow 6.98% CAGR, feeding brands' need for curated packaging. Operators increasingly embed robotic arms and RFID gates to elevate accuracy and shrink dwell times. Integrated setups that blend trucking, storage, and customization win large marketplace contracts.
Ongoing infrastructure upgrades enhance road reliability, but rising fuel prices and environmental targets nudge carriers to optimize routing and test electric vans. Warehousing demand clusters near Jakarta and Surabaya ports, prompting a surge in build-to-suit leases for automated hubs. Fulfillment players that can flex capacity around seasonal peaks, such as Singles Day or Ramadan, secure higher-margin slots with leading platforms.
B2C retained 73.40% of Indonesia e-commerce logistics market share in 2025 on the back of marketplace scale and urban customer density. Price sensitivity compels carriers to strip costs, spurring batch deliveries and crowdsourced riders for the final mile. B2B, forecast to rise 6.59% CAGR, benefits from manufacturers' digitizing procurement and demanding just-in-time replenishment. Providers targeting factory lines add inventory audit, quality checks, and vendor-managed stock to deepen client stickiness.
C2C stays niche but receives lift from social-commerce platforms that trade preloved fashion and crafts. Here, authentication and low-cost return loops differentiate service propositions. Marketplace-controlled networks could roll out hybrid models that pool B2C and B2B line-haul to boost truck utilization, compressing independent forwarders' margins.
The Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market Report is Segmented by Service (Transportation, Warehousing & Fulfilment, and Value-Added Services), Business Model (B2C, B2B, and C2C), Destination (Domestic and Cross-Border), Delivery Speed (Same-Day, and More), Product Category (Foods & Beverages, and More), City Tier (Tier 1, 2, and More), and Province (Jakarta, and More). Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- JNE Express
- J&T Express
- SiCepat Ekspres
- Ninja Xpress
- Lion Parcel
- Wahana Express
- TIKI
- Pos Indonesia
- Paxel
- DHL Express
- UPS
- FedEx
- GoSend (Gojek)
- Grab Express
- Shipper
- Shopee Express
- Lazada eLogistics
- Kuehne + Nagel
- DSV
- Kerry Logistics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Explosive parcel-volume surge from tier-2/3 cities
- 4.2.2 Government push to cut logistics cost-to-GDP to 8 %
- 4.2.3 Rapid uptake of same-day / next-day delivery options
- 4.2.4 Indonesia's IDR 400 Trillion Infrastructure Investment Set to Boost E-Commerce Delivery Reach
- 4.2.5 Infrastructure Investments (new toll roads, ports, airports) is shrinking delivery transit times and opening tier-2/3 markets
- 4.2.6 National-capital move to Nusantara redrawing fulfilment hubs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Archipelagic geography inflates inter-island last-mile costs
- 4.3.2 Fragmented CEP price war eroding provider margins
- 4.3.3 Indonesia's Island Geography Drives Up Last-Mile Delivery Costs
- 4.3.4 Skilled-labour gap in modern Grade-A warehouses
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Demand & Supply Analysis
- 4.8 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Reverse / Return Logistics Insights
- 4.10 Impact of Geo-Political Events on Supply Chain Shifts
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.1.1 Road
- 5.1.1.2 Rail
- 5.1.1.3 Air
- 5.1.1.4 Sea
- 5.1.2 Warehousing & Fulfilment
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Services (Labelling, Packaging, Kitting)
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.2 By Business Model
- 5.2.1 B2C
- 5.2.2 B2B
- 5.2.3 C2C
- 5.3 By Destination
- 5.3.1 Domestic
- 5.3.2 Cross-border (international)
- 5.4 By Delivery Speed
- 5.4.1 Same-day (less than 24 h)
- 5.4.2 Next-day (24-48 h)
- 5.4.3 Standard (3-5 days)
- 5.4.4 Others (more than 5 days)
- 5.5 By Product Category
- 5.5.1 Foods & Beverages
- 5.5.2 Personal & Household Care
- 5.5.3 Fashion & Lifestyle (accessories, apparel, footwear)
- 5.5.4 Furniture
- 5.5.5 Consumer Electronics & Household Appliances
- 5.5.6 Other Products
- 5.6 By City Tier
- 5.6.1 Tier 1
- 5.6.2 Tier 2
- 5.6.3 Tier 3 and Below
- 5.7 By Provinces
- 5.7.1 Central Java
- 5.7.2 East Java
- 5.7.3 West Java
- 5.7.4 Jakarta
- 5.7.5 Banten
- 5.7.6 Rest of Provinces
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 JNE Express
- 6.4.2 J&T Express
- 6.4.3 SiCepat Ekspres
- 6.4.4 Ninja Xpress
- 6.4.5 Lion Parcel
- 6.4.6 Wahana Express
- 6.4.7 TIKI
- 6.4.8 Pos Indonesia
- 6.4.9 Paxel
- 6.4.10 DHL Express
- 6.4.11 UPS
- 6.4.12 FedEx
- 6.4.13 GoSend (Gojek)
- 6.4.14 Grab Express
- 6.4.15 Shipper
- 6.4.16 Shopee Express
- 6.4.17 Lazada eLogistics
- 6.4.18 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.19 DSV
- 6.4.20 Kerry Logistics
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment









