 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906217
馬來西亞網路安全市場:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Malaysia Cybersecurity - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
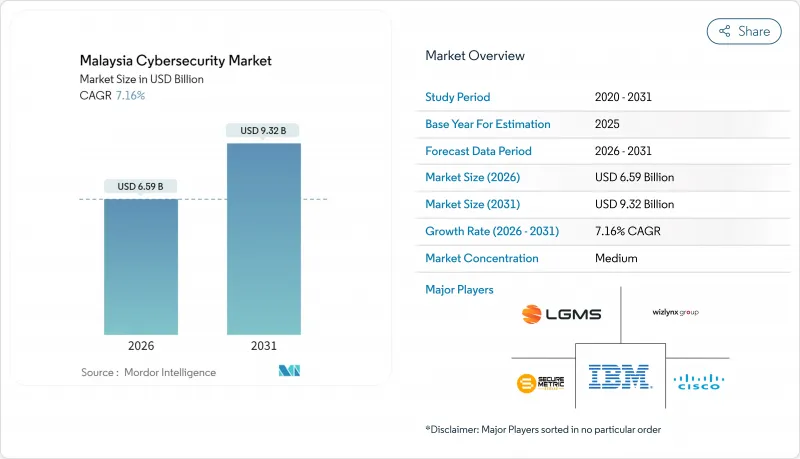
預計馬來西亞網路安全市場將從 2025 年的 61.5 億美元成長到 2026 年的 65.9 億美元,並預計到 2031 年將達到 93.2 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 7.16%。
馬來西亞網路安全市場保持兩位數的低成長勢頭,使其成為該國更廣泛的ICT生態系統中成長最快的數位基礎設施領域之一。雲端優先戰略、2024年《網路安全法》下嚴格的許可製度以及資料外洩造成的經濟損失,都在推動市場的持續成長。大型企業正在將其現有的控制措施擴展到零信任計劃,而中小企業則開始透過訂閱服務進行初步部署,這些服務提供較低的前期成本。對5G邊緣網路、超大規模資料中心和操作技術(OT)現代化改造的同步投資,進一步鞏固了馬來西亞網路安全市場長期成長的基礎。
馬來西亞網路安全市場趨勢與洞察
馬來西亞快速部署「雲端優先」策略,推動公共部門雲端安全支出成長
馬來西亞加速推進的「雲端優先」策略正促使政府支出轉向雲端原生防禦,例如雲端雲端存取安全仲介)和工作負載保護平台(WPP)。各部會和機構目前正將分類、加密和持續監控納入所有應用程式遷移計劃,從而推動了對諮詢和託管服務的基本需求。公共部門早期成功的案例正鼓勵金融機構和電信業者採用類似的架構,並在馬來西亞網路安全市場產生連鎖反應。系統整合商正圍繞責任共擔模式重新設計其產品組合,在單一合約下提供諮詢、實施和託管檢測服務。這些變化正帶來支出結構性的針對性的改進,而非短暫的成長。
2024 年網路安全法案:許可強制令和 NCII 合規要求推動供應商需求
2024 年網路安全法案強制要求對穿透測試和保全行動等核心服務進行許可,並要求關鍵基礎設施營運商遵守行業特定的行為準則。各組織機構正積極回應,將合規性提升至經營團隊層面的優先事項,並聘請外部審核以滿足新的法律標準。由於企業優先選擇經過預先審核的合作夥伴以避免違規,早期獲得許可的供應商已獲得明顯的銷售優勢。該法案還明確了事件報告時限,從而推動了對即時偵測工具和威脅情報整合的需求。這些變化共同推動了馬來西亞網路安全市場規模的持續成長,因為持續的合規義務已納入 IT 預算。
高階安全架構師嚴重短缺,導致計劃工期延長,成本上升。
經驗豐富的架構師持續短缺,導致複雜的雲端遷移專案停滯不前,計劃工期延長37%,人事費用上升超過25%。這種人才短缺推高了大型轉型合約的競標價格,加劇了企業預算壓力,並延誤了關鍵里程碑的完成。企業正透過將架構工作外包給託管安全服務提供者 (MSSP) 或從區域中心引入專家來應對這項挑戰,但簽證核准時間限制了短期內的改進。儘管供應商的藍圖包含低程式碼策略引擎和參考架構以縮短設計時間,但對於受監管的工作負載,實際操作的監督仍然至關重要。因此,人才短缺持續拖累馬來西亞網路安全市場的複合年成長率 (CAGR)。
細分市場分析
預計到2025年,解決方案將佔據馬來西亞網路安全市場52.20%的佔有率,其中以保護混合環境的網路和雲端安全套件為主導。然而,隨著企業尋求運作的專業技術支持,預計到2031年,服務將以7.42%的複合年成長率超越解決方案。高偵測準確率、全天候監控和內建合規性儀表板使託管安全服務提供者 (MSSP) 成為策略合作夥伴,而非戰術性供應商。基於每月活躍資產的定價模式降低了中型企業的進入門檻。本地供應商利用其對監管法規的熟悉程度來贏得與網路安全法律相關的合約。同時,全球供應商提供能夠整合來自不同工具的警報的編配平台。諮詢、實施和託管偵測與回應 (MDR) 服務的整合,提供了超越技術轉售的價值提案,鞏固了馬來西亞網路安全市場以服務主導的成長模式。
然而,對於擁有嚴格資料居住規則的組織而言,解決方案組合仍然至關重要。銀行、金融和保險 (BFSI) 以及公共產業行業的設備更新週期為防火牆、入侵防禦系統和安全郵件閘道提供了持續的收入來源。下一代安全資訊和事件管理 (SIEM) 平台整合了行為分析和自動化功能,以彌補人才短缺,並將產品創新與國家技能發展目標相契合。供應商將永久許可證與雲端交付的分析功能捆綁銷售,以彌合本地控制和 SaaS 可視性之間的差距。與本地整合商的聯合產品能夠加快價值實現速度,並體現馬來西亞網路安全市場的協作特性。
到2025年,本地部署系統將佔馬來西亞網路安全市場規模的52.85%,這主要受傳統工作負載和資料權限要求的驅動,而這些需求在銀行業和公共服務業仍然佔據主導地位。這些產業的硬體更新換代為設備供應商提供了穩定的基礎。然而,雲端採用率預計將超過本地部署更新,到2031年將以8.05%的複合年成長率成長。付費使用制、持續的功能發布以及人工智慧驅動的分析,使得雲端控制對奉行數位化優先策略的機構極具吸引力。責任共擔框架鼓勵企業將維護工作外包給專業供應商,從而支持雲端技術在馬來西亞網路安全市場的長期應用。
供應商藍圖包括在馬來西亞境內設立資料本地化節點,以增強受監管客戶的信心。雖然未來對自主雲端平台的改進可能會降低剩餘的阻力,但與工業控制網路相關的硬體更新換代可能會繼續支撐本地部署設備的市場。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 市場定義與研究假設
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 馬來西亞快速部署「雲端優先」策略,推動公共部門雲端安全支出成長
- 根據2024年《網路安全法案》頒發的許可證以及強制遵守國家網路資訊基礎設施(NCII)的要求將推動供應商需求。
- 新山資料中心激增推動了周邊安全和營運技術安全的投資
- 超過97%的5G覆蓋率將推動行動核心網路和邊緣安全升級。
- 資料外洩造成的122億美元經濟損失促使各董事會增加預算
- 國家製定培養25000名網路防禦人員的目標推動了諮詢和培訓支出。
- 市場限制
- 高階安全架構師嚴重短缺,導致計劃工期延長,成本上升。
- 由於傳統IT基礎設施主要依賴資本支出(CAPEX),中小企業面臨預算限制。
- 跨境資料主權規則的碎片化正在減緩雲端遷移進程。
- 金融服務業以外領域多因子認證普及率低會增加剩餘風險
- 價值鏈分析
- 重要法規結構評估
- 關鍵相關人員影響評估
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 宏觀經濟因素的影響
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 報價
- 解決方案
- 應用程式安全
- 雲端安全
- 資料安全
- 身分和存取管理
- 基礎設施保護
- 綜合風險管理
- 網路安全
- 端點安全
- 服務
- 專業服務
- 託管服務
- 解決方案
- 透過部署模式
- 雲
- 本地部署
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- BFSI
- 衛生保健
- 資訊科技和電信
- 工業與國防
- 零售與電子商務
- 能源與公共產業
- 製造業
- 其他
- 按最終用戶公司規模分類
- 主要企業
- 中小企業
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- LGMS Berhad
- IBM Corporation
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Securemetric Bhd
- Wizlynx Group
- Akati Sekurity
- Palo Alto Networks
- Fortinet Inc.
- Check Point Software Tech.
- Trend Micro Inc.
- Kaspersky Lab
- Nexagate Sdn Bhd
- Ishan Tech Sdn Bhd
- Capgemini SE
- Microsoft Corp.
- AVG Technologies(Gen Digital)
- ATandT Cybersecurity
- NTT Data Security
- BAE Systems AI Malaysia
- Darktrace plc
- CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
- 評估差距和未滿足的需求
The Malaysia cybersecurity market is expected to grow from USD 6.15 billion in 2025 to USD 6.59 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 9.32 billion by 2031 at 7.16% CAGR over 2026-2031.

This low-double-digit trajectory positions the Malaysia cybersecurity market among the faster-growing digital-infrastructure segments within the country's wider ICT ecosystem. Cloud-first mandates, strict licensing under the Cyber Security Act 2024, and the monetized cost of data breaches are each propelling sustained demand. Large enterprises are broadening existing controls into zero-trust programs, while small and medium enterprises are starting first-time deployments through subscription services that lower upfront costs. Parallel investments in 5G edge networks, hyperscale data centers, and operational-technology modernization further anchor a long runway for the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
Malaysia Cybersecurity Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Roll-out of Malaysia's Cloud-First Strategy Propelling Public-Sector Cloud Security Spending
Malaysia's accelerated cloud-first strategy is redirecting government spending toward cloud-native defenses such as cloud access security brokers and workload-protection platforms. Ministries now integrate classification, encryption, and continuous monitoring into every application-migration plan, lifting baseline demand for advisory and managed services. Public-sector visibility into early success stories is encouraging financial institutions and telecom carriers to adopt similar architectures, creating a multiplier effect across the Malaysia cybersecurity market. System integrators have redesigned portfolios around shared-responsibility models, bundling consulting, deployment, and managed detection under single contracts. Collectively, these changes translate to a structural uplift in addressable spending rather than a one-time spike.
Cyber Security Act 2024 Licensing and Mandatory NCII Compliance Fuelling Vendor Demand
The Cyber Security Act 2024 enforces mandatory licensing for penetration testing, security-operations, and other core services, while critical-infrastructure operators must observe sector-specific codes of practice. Organizations have responded by elevating compliance to board-level priority and retaining external auditors to align controls with the new legal baseline. Providers that secured early licences gained a measurable sales advantage because enterprises prefer pre-qualified partners to avoid regulatory missteps. The act also formalized incident-reporting timelines, spurring demand for real-time detection tools and threat-intelligence integrations. Together, these shifts embed recurring compliance obligations into IT budgets, sustaining momentum in the Malaysia cybersecurity market size.
Acute Shortage of Senior Security Architects Inflating Project Timelines and Costs
Complex cloud migrations stall because experienced architects remain scarce, extending project timelines by 37% and boosting labor costs by more than one-quarter . The scarcity inflates bids for large transformation contracts, squeezing corporate budgets and delaying key milestones. Organizations counter by outsourcing architecture to MSSPs or importing expertise from regional hubs, but long visa lead times cap near-term relief. Vendor roadmaps now include low-code policy engines and reference architectures that cut design hours, yet hands-on oversight remains indispensable for regulated workloads. Talent constraints therefore act as a persistent drag on the Malaysia cybersecurity market CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Data-Centre Boom in Johor Bahru Elevating Perimeter and OT Security Investments
- 5G Coverage >= 97 % Driving Mobile Core and Edge Security Upgrades
- SME Budget Constraints Owing to Legacy CAPEX-heavy IT Footprints
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solutions maintained 52.20% share of the Malaysia cybersecurity market in 2025, led by network and cloud-security suites that protect hybrid environments. However, services are forecast to outpace solutions at a 7.42% CAGR through 2031 as enterprises look for always-on expertise. Higher detection accuracy, round-the-clock monitoring, and built-in compliance dashboards position MSSPs as strategic partners rather than tactical suppliers. Pricing models based on monthly active assets lower entry barriers for mid-tier firms. Local providers leverage regulatory familiarity to capture contracts tied to the Cyber Security Act, while global vendors package orchestration platforms that unify alerts across point tools. Convergence of advisory, deployment, and MDR services brings value propositions beyond technology resale, solidifying service-led growth in the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
The solutions portfolio nevertheless remains critical for organizations with strict data-residency rules. Appliance refresh cycles in BFSI and utilities sustain revenue for firewall, intrusion-prevention, and secure-email gateways. New-generation SIEM platforms incorporate behavioral analytics and automation to offset talent scarcity, aligning product innovation with national skills-development goals. Vendors bundle perpetual licenses with cloud-delivered analytics to bridge on-premise controls and SaaS visibility. Co-delivery with local integrators accelerates time to value, reflecting the collaborative nature of the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
On-premise systems accounted for 52.85% of the Malaysia cybersecurity market size in 2025 because legacy workloads and data-sovereignty mandates still dominate in banking and public service. Hardware refreshes in these sectors provide a stable base for appliance vendors. Yet cloud deployments are expanding at an 8.05% CAGR through 2031, outstripping on-premise upgrades. Consumption-based pricing, continuous feature releases, and AI-driven analytics make cloud controls appealing for institutions pursuing digital-first strategies. Shared-responsibility frameworks encourage enterprises to off-load maintenance to specialized providers, supporting long-term adoption in the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
Vendor roadmaps include data-localization nodes within Malaysia to reassure regulated customers. Over time, improvements in sovereign-cloud platforms may erode the remaining resistance, but hardware refreshes tied to industrial-control networks ensure a continuing market for on-premise gear.
The Malaysia Cybersecurity Market Report is Segmented by Offering (Solutions [Application Security, Cloud Security, and More], Services [Professional Services, and More]), Deployment Mode (Cloud, On-Premise), End-User Industry (BFSI, Healthcare, IT and Telecom, Industrial and Defense, Retail and E-Commerce, and More), End-User Enterprise Size (Large Enterprises, Smes). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- LGMS Berhad
- IBM Corporation
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Securemetric Bhd
- Wizlynx Group
- Akati Sekurity
- Palo Alto Networks
- Fortinet Inc.
- Check Point Software Tech.
- Trend Micro Inc.
- Kaspersky Lab
- Nexagate Sdn Bhd
- Ishan Tech Sdn Bhd
- Capgemini SE
- Microsoft Corp.
- AVG Technologies (Gen Digital)
- ATandT Cybersecurity
- NTT Data Security
- BAE Systems AI Malaysia
- Darktrace plc
- CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Market Definition and Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid Roll-out of Malaysia's Cloud-First Strategy Propelling Public-Sector Cloud Security Spending
- 4.2.2 Cyber Security Act 2024 Licensing and Mandatory NCII Compliance Fuelling Vendor Demand
- 4.2.3 Data-Centre Boom in Johor Bahru Elevating Perimeter and OT Security Investments
- 4.2.4 5G Coverage >= 97 % Driving Mobile Core and Edge Security Upgrades
- 4.2.5 USD 12.2 bn Economic Losses From Breaches Raising Boardroom Budgets
- 4.2.6 National Goal of 25 000 Cyber Defenders Boosting Consulting and Training Spend
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Acute Shortage of Senior Security Architects Inflating Project Timelines and Costs
- 4.3.2 SME Budget Constraints Owing to Legacy CAPEX-heavy IT Footprints
- 4.3.3 Fragmented Cross-border Data-Sovereignty Rules Slowing Cloud Migrations
- 4.3.4 Low Multi-factor-Auth Adoption Outside BFSI Heightening Residual Risk
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Evaluation of Critical Regulatory Framework
- 4.6 Impact Assessment of Key Stakeholders
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Impact of Macro-economic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Offering
- 5.1.1 Solutions
- 5.1.1.1 Application Security
- 5.1.1.2 Cloud Security
- 5.1.1.3 Data Security
- 5.1.1.4 Identity and Access Management
- 5.1.1.5 Infrastructure Protection
- 5.1.1.6 Integrated Risk Management
- 5.1.1.7 Network Security
- 5.1.1.8 End-point Security
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.1.2.1 Professional Services
- 5.1.2.2 Managed Services
- 5.1.1 Solutions
- 5.2 By Deployment Mode
- 5.2.1 Cloud
- 5.2.2 On-Premise
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 BFSI
- 5.3.2 Healthcare
- 5.3.3 IT and Telecom
- 5.3.4 Industrial and Defense
- 5.3.5 Retail and E-commerce
- 5.3.6 Energy and Utilities
- 5.3.7 Manufacturing
- 5.3.8 Others
- 5.4 By End-user Enterprise Size
- 5.4.1 Large Enterprises
- 5.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 LGMS Berhad
- 6.4.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.3 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.4 Securemetric Bhd
- 6.4.5 Wizlynx Group
- 6.4.6 Akati Sekurity
- 6.4.7 Palo Alto Networks
- 6.4.8 Fortinet Inc.
- 6.4.9 Check Point Software Tech.
- 6.4.10 Trend Micro Inc.
- 6.4.11 Kaspersky Lab
- 6.4.12 Nexagate Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.13 Ishan Tech Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.14 Capgemini SE
- 6.4.15 Microsoft Corp.
- 6.4.16 AVG Technologies (Gen Digital)
- 6.4.17 ATandT Cybersecurity
- 6.4.18 NTT Data Security
- 6.4.19 BAE Systems AI Malaysia
- 6.4.20 Darktrace plc
- 6.4.21 CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment







