 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1852204
分子育種:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Molecular Breeding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
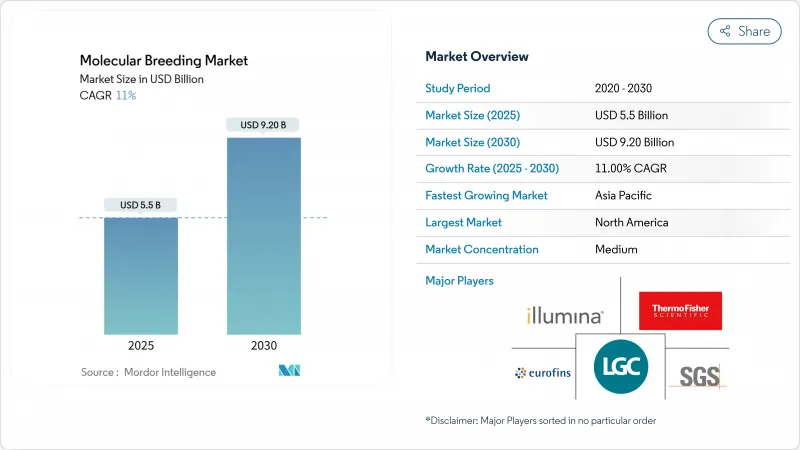
預計到 2025 年分子育種市場規模將達到 55 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 92 億美元,年複合成長率為 11.0%。
將人工智慧應用於基因組選擇,可將育種週期從數年縮短至數月,進而提高產品開發效率。美國「適應性作物與土壤願景」和印度「國家糧食安全行動計畫」等政府舉措,正在推動對氣候適應作物的需求。高通量表現型分析、定序成本降低以及基因分型服務的普及,將進一步促進市場擴張。儘管北美在研究基礎設施方面仍保持優勢,但亞太地區由於監管改革和糧食安全需求,展現出巨大的成長潛力。
全球分子育種市場趨勢與洞察
擴大生物技術研發資金
該市場的公共和私人支出正在迅速成長。賽默飛世爾科技公司在2023年投資13億美元研發,推動次世代定序儀和試劑的創新,以降低中型育種者的進入門檻。美國的數據標準化計畫正在協調基因組資料集,避免重複測試,並縮短產品上市時間。此類資本投資降低了中小企業的合規門檻,並使新型性狀的開發者能夠規避監管要求。此外,諸如國際農業研究諮詢組織(CGIAR)4億美元的營養重點項目等多邊計劃正在調動捐助資金,以加速生物強化工作。
對產量、抗氣候變遷作物的需求日益成長
在印度,一種能夠抵禦創紀錄高溫、百日成熟期的小麥品種已經上市,耐熱耐旱基因型也正從試驗階段走向商業化種植。日本的研究中心正在開發適應鹽鹼和水分脅迫條件的藜麥和大豆品種,以維持易受氣候變遷影響國家的產量水準。如今,植物育種的重點已不再局限於產量最佳化,而是擴展到多重脅迫耐受性,這就需要使用能夠整合生產力和環境適應性的多重分子標記。極端天氣事件目前每季造成的作物損失高達數十億美元,也帶來了巨大的經濟影響,因此,投資氣候適應種子組合的回報也隨之提高。
監管核准繁瑣且緩慢
每項新性狀的合規成本可能高達1,500萬美元,約佔整體研發預算的一半,限制了小型創新者的參與。歐盟對生物技術作物的限制促使企業將目光轉向監管環境較為寬鬆的市場,例如美國和巴西。儘管阿根廷、烏拉圭和泰國已於2024年更新了相關法規並簡化了核准,但監管方面的不確定性仍然會延長核准時間並增加資金籌措成本。
細分市場分析
到2024年,植物應用將佔分子育種市場63%的佔有率,這主要得益於基因組選擇技術在玉米、小麥和大豆育種計畫的應用。畜牧業正以13.1%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於基因組育種值在乳牛優於傳統評估方法,以及基於CRISPR技術的抗病豬的培育。諸如Angus SteerSELECT之類的工具,在預測重要胴體性狀方面展現出超過0.72的準確率,從而提高了育肥場的盈利並吸引了投資。
家禽業正在利用精準編輯技術對繁殖和生長基因進行編輯,以縮短世代間隔。此外,儘管目前豬育種中整合代謝組學和基因組學模型的效果有限,但在提高日均增重方面展現出潛力。這些市場發展趨勢表明,到2030年,畜牧業有望顯著提升其在分子育種市場中的佔有率。
到2024年,單核苷酸多態性(SNP)將佔分子育種市場規模的42%,並保持13.2%的複合年成長率,這主要得益於其與高通量平台的兼容性以及全基因組關聯分析(GWAS)輸出的提升。單位成本的下降正在消除先前簡單序列重複所具有的價格優勢,從而鼓勵開發中國家的專案直接採用SNP解決方案。 RNA-seq和ATAC-seq資料的功能性變異面板的引入,已使酪農蛋白性狀的育種準確率提高了3個百分點,證明了該技術的可靠性。
隨著SNP工作流程的標準化,表達序列標籤和其他傳統標記主要用於表達譜分析等特定應用。 SNP的日益普及將提升資料互通性,這對於人工智慧育種系統的發展至關重要。
區域分析
2024年,北美將佔據分子育種市場36%的佔有率,這得益於其先進的研究基礎設施和高效的法律規範。累計2024年營收將達43.3億美元的Illumina公司已與LGC Biosearch Technologies公司合作,以增強其針對作物和畜牧業的標靶基因分型定序能力。美國SECURE規則簡化了基因編輯產品的核准流程,鞏固了Illumina在該地區的市場領先地位。
亞太地區擁有最高的成長潛力,預計到2030年將以12.1%的複合年成長率成長。中國將於2024年核准抗病基因編輯小麥,印度的監管更新將簡化某些基因組編輯的核准,並加速私人育種舉措。日本分級監管體系和對作物逆境研究的重視使其成為該地區的重要樞紐。政府資金和私人創業投資的共同作用正在加強該地區的育種基礎設施,以滿足糧食安全需求。
儘管受到監管限制,歐洲仍保持著重要的市場佔有率。歐盟環境委員會於2024年底核准了新的基因組技術立法,這標誌著歐盟正朝著基於風險的評估方向發展。英國的《精準育種法案》已正式生效,該法案建立了兩級安全審查體系,旨在加速基因編輯作物的測試。瑞士也在實施類似的監管改革。市場發展將取決於政策走向,市場對符合歐洲綠色新政永續性要求的品種需求強勁。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 擴大生物技術研發資金
- 對產量、抗氣候變遷作物的需求日益成長
- 快速採用精準育種及表現型分析平台
- 政府支持的糧食安全措施
- 結合人工智慧和基因組選擇
- 低投入品種的碳權獎勵
- 市場限制
- 監管核准繁瑣且緩慢
- 定序和基因型鑒定基礎設施的高資本成本
- 育種者取得可互通資料平台的管道有限
- 社會對「分子改造」種子的擔憂
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過使用
- 植物
- 家畜
- 其他用途
- 按標記類型
- 簡單序列重複(SSR)
- 單核苷酸多態性(SNP)
- 表達序列標籤(EST)
- 其他標記
- 透過育種過程
- 標記輔助選擇(MAS)
- 數量性狀基因(QTL)定位
- 標記輔助回交
- 基因組選擇
- 按目標特徵
- 產量增加
- 抗蟲害
- 生物壓力耐受性
- 品質和營養特性
- 最終用戶
- 種子和作物保護公司
- 畜牧公司
- 學術和政府研究機構
- 獨立繁殖服務提供者
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲國家
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Illumina, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- LGC Limited(Cinven)
- Eurofins Scientific
- SGS SA
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- DanBred P/S
- LemnaTec GmbH(Nynomic AG)
- Charles River Laboratories
- Intertek Group plc
- KeyGene NV
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Bayer AG
- BASF SE
- Sequentia Biotech SL
- Hudson Alpha
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The molecular breeding market attained USD 5.5 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9.2 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 11.0%.

The incorporation of artificial intelligence with genomic selection has reduced breeding cycles from years to months, enhancing product development efficiency. Government initiatives, including the U.S. Vision for Adapted Crops and Soils and India's National Action Plan on Food Security, are driving demand for climate-resilient crop varieties. Market expansion is facilitated by high-throughput phenotyping, decreased sequencing costs, and accessible genotyping services. While North America retains its advantage in research infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates substantial growth potential due to regulatory reforms and food security requirements.
Global Molecular Breeding Market Trends and Insights
Expanding Biotechnology Research and Development Funding
Private and public spending in the market is increasing rapidly. Thermo Fisher invested USD 1.3 billion in research and development in 2023 to advance next-generation sequencing and reagent innovation, reducing entry costs for midsized breeders. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's data-standards programs are harmonizing genomic datasets, preventing redundant trials, and reducing time-to-market. These capital investments have decreased compliance barriers for smaller firms, enabling novel trait developers to navigate regulatory requirements. Additionally, multilateral initiatives, such as CGIAR's USD 400 million nutrition-focused portfolio, are attracting donor funds and accelerating biofortification outcomes.
Growing Demand for High-Yield, Climate-Resilient Crops
India's release of 100-day wheat varieties capable of withstanding record temperatures has enabled heat- and drought-tolerant genotypes to advance from pilot to commercial scale. Japanese research centers are developing quinoa and soybean varieties adapted to saline and water-stress conditions to maintain production levels in climate-vulnerable countries. Plant breeding priorities now extend beyond yield optimization to include multistress tolerance, necessitating the use of multiplexed molecular markers that integrate productivity with environmental resilience. The financial implications are significant, as extreme weather events currently cause crop losses worth billions of USD per season, increasing the return on investment for climate-resilient seed portfolios.
Stringent, Slow-Moving Regulatory Approvals
The compliance cost per new trait can reach USD 15 million, consuming approximately half of the total development budgets and deterring smaller innovators. The European Union's regulation of gene-edited crops under GMO legislation drives companies to focus on markets with favorable regulations, such as the United States and Brazil. While Argentina, Uruguay, and Thailand updated their regulations in 2024 to simplify approvals, regulatory uncertainty continues to extend timelines and increase financing costs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Adoption of Precision Breeding and Phenotyping Platforms
- Government-Backed Food Security Initiatives
- High Capital Cost of Sequencing and Genotyping Infrastructure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Plant applications accounted for 63% of the molecular breeding market in 2024, primarily through genomic selection implementation in maize, wheat, and soybean breeding programs. The livestock segment is experiencing growth at a 13.1% CAGR, driven by genomic breeding values that demonstrate superior performance compared to traditional estimates in dairy cattle and CRISPR-based disease-resistant pig development. Tools such as Angus SteerSELECT have demonstrated prediction accuracies exceeding 0.72 for critical carcass traits, enhancing feedlot profitability and attracting investment.
The poultry sector is implementing precision editing of fertility and growth genes to reduce generation intervals. Furthermore, integrated metabolomic and genomic models in swine breeding demonstrate potential for improving average daily gain, despite current modest outcomes. These developments indicate that the livestock segment may substantially increase its contribution to the molecular breeding market by 2030.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) accounted for 42% of the molecular breeding market size in 2024 and maintain a 13.2% CAGR due to their compatibility with high-throughput platforms and enhanced genome-wide association outputs. The reduction in unit costs has diminished the price advantage previously held by simple sequence repeats, prompting developing-country programs to adopt SNP solutions directly. The implementation of functional-variant panels from RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data has improved breeding accuracies by 3 percentage points in dairy-protein traits, demonstrating the technology's reliability.
The standardization of SNP workflows has positioned express sequence tags and other traditional markers primarily in specialized applications such as expression profiling. The increased adoption of SNPs enhances data interoperability, which is fundamental for developing AI-enabled breeding systems.
The Molecular Breeding Market Report is Segmented by Application (Plant, Livestock, and More), by Marker Type (Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR), and More), by Breeding Process (Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), and More), by Trait Target (Yield Enhancement, and More), by End-User (Seed and Crop-Protection Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America holds 36% of the molecular breeding market share in 2024, supported by advanced research infrastructure and efficient regulatory frameworks. Illumina reported USD 4.33 billion revenue in 2024 and has partnered with LGC Biosearch Technologies to increase targeted genotyping-by-sequencing capabilities for row-crop and livestock segments. The USDA's SECURE rule streamlines the approval process for gene-edited products, maintaining the region's market leadership.
Asia-Pacific demonstrates the highest growth potential with a projected 12.1% CAGR through 2030. China approved disease-resistant gene-edited wheat in 2024, while India's regulatory updates streamline approvals for specific genome edits, accelerating private breeding initiatives. Japan's tiered regulatory system and focus on crop-stress research establishes it as a key regional hub. The combination of government funding and private venture capital is strengthening the region's breeding infrastructure to address food security needs.
Europe maintains significant market presence despite regulatory constraints. The EU Environment Committee's approval of new genomic technology legislation in late 2024 indicates movement toward risk-based assessment. The UK implemented the Precision Breeding Act, establishing a two-tier safety review system to expedite gene-edited crop trials. Switzerland is implementing similar regulatory changes. Market growth depends on policy developments, with substantial demand for varieties meeting European Green Deal sustainability requirements.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- LGC Limited (Cinven)
- Eurofins Scientific
- SGS SA
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- DanBred P/S
- LemnaTec GmbH (Nynomic AG)
- Charles River Laboratories
- Intertek Group plc
- KeyGene NV
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Bayer AG
- BASF SE
- Sequentia Biotech SL
- Hudson Alpha
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expanding Biotechnology Research and Development Funding
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand for High-Yield, Climate-Resilient Crops
- 4.2.3 Rapid Adoption of Precision Breeding and Phenotyping Platforms
- 4.2.4 Government-Backed Food Security Initiatives
- 4.2.5 Convergence of AI and Genomic Selection
- 4.2.6 Carbon-Credit Incentives for Low-Input Cultivars
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent, Slow-Moving Regulatory Approvals
- 4.3.2 High Capital Cost of Sequencing and Genotyping Infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Limited Breeder Access to Interoperable Data Platforms
- 4.3.4 Public Perception Concerns Over "Molecular-Modified" Seeds
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Plant
- 5.1.2 Livestock
- 5.1.3 Other Application
- 5.2 By Marker Type
- 5.2.1 Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR)
- 5.2.2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP)
- 5.2.3 Expressed Sequence Tags (EST)
- 5.2.4 Other Markers
- 5.3 By Breeding Process
- 5.3.1 Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS)
- 5.3.2 Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping
- 5.3.3 Marker-Assisted Back-Crossing
- 5.3.4 Genomic Selection
- 5.4 By Trait Target
- 5.4.1 Yield Enhancement
- 5.4.2 Disease and Pest Resistance
- 5.4.3 Abiotic Stress Tolerance
- 5.4.4 Quality and Nutritional Traits
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Seed and Crop-Protection Companies
- 5.5.2 Livestock Breeding Firms
- 5.5.3 Academic and Government Research Institutes
- 5.5.4 Independent Breeding Service Providers
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Russia
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Illumina, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.3 LGC Limited (Cinven)
- 6.4.4 Eurofins Scientific
- 6.4.5 SGS SA
- 6.4.6 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.7 DanBred P/S
- 6.4.8 LemnaTec GmbH (Nynomic AG)
- 6.4.9 Charles River Laboratories
- 6.4.10 Intertek Group plc
- 6.4.11 KeyGene NV
- 6.4.12 Syngenta AG
- 6.4.13 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.14 Bayer AG
- 6.4.15 BASF SE
- 6.4.16 Sequentia Biotech SL
- 6.4.17 Hudson Alpha








