 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851644
自主配送機器人:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Autonomous Delivery Robots - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
目前,自動送貨機器人市場價值 11.1 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 28 億美元,複合年成長率為 20.33%。
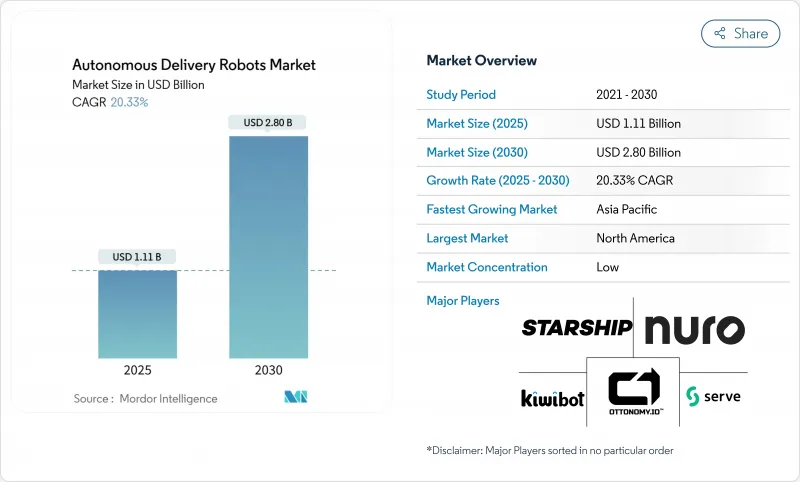
勞動力短缺加劇、技術快速成熟以及有利於人行道機器人部署的配套法規推動了市場成長。領先的物流公司仍然將這項技術視為關鍵任務。光是亞馬遜就計劃透過機器人解決方案實現自動化,從而節省2000億美元。到2024年,北美將以32.1%的市佔率引領市場,亞太地區緊隨其後,市佔率為25%,這主要得益於人口老化推動了對非接觸式醫療物流的需求。戶外人行道機器人將佔據主導地位,市場佔有率高達58%,而混合動力全地形機器人將以27.8%的複合年成長率成為成長最快的車型,這表明市場明顯偏好能夠同時適應都市區和室內路線的平台。隨著創投支持的專業公司與配送平台合作擴大車隊規模,以及傳統汽車企業積極開拓醫療保健和工業領域,市場競爭將持續激烈。儘管有效載荷限制和雷射雷達的高成本仍然是阻礙因素,但感測器價格的快速下降和新的社區參與策略預計將在預測期內擴大潛在用戶群。
全球自主配送機器人市場趨勢與洞察
按需雜貨配送的快速擴張
按需生鮮配送服務能夠為自動駕駛車隊帶來永續的單位經濟效益,因為高訂單密度可以抵消傳統司機的成本。克羅格已在其達拉斯營運中整合了無人駕駛卡車,以加快履約並降低物流成本。零售商也正在引進店內貨架掃描機器人,以減少因缺貨造成的4.5%的收入損失,例如斯巴達納許公司在60家門市部署了Simbe Robotics的機器人。總而言之,這些舉措表明,連鎖超市正在將機器人技術從試點階段推進到核心基礎設施階段,擴大了末端配送機器人可處理的訂單量。
勞動力短缺日益嚴重和工資上漲
北美地區的履約中心正面臨嚴重的員工短缺問題,迫使企業轉向自動化替代方案。預計到2030年,美國製造業將出現200萬名工人缺口,而最後一公里配送司機的離職率也加劇了成本壓力。工業機器人的價格在過去十年中下降了50%,安永會計師事務所預測價格也將進一步下降。提高都市區的配送密度將使營運商能夠達到運轉率目標,並加快自動化資產的投資回報。
LiDAR和感測器套件的前期成本很高
導航硬體通常是送貨機器人最大的投資項目。像Sonair這樣的新型超音波感測器可以將感測器成本降低高達80%,同時保持180度×180度的偵測範圍。 Kirken的無雷射雷達視覺系統已經在公共人行道上獲利運行,證明經濟高效的感測技術可以滿足可靠性閾值。這些新型感測器組合的廣泛應用仍需獲得監管部門的檢驗。
細分市場分析
到2024年,戶外機器人將佔總收入的58%,並透過人行道試驗推動自動配送機器人市場的發展。這一主導地位得益於與食品聚合平台和地方監管機構建立的可靠夥伴關係,從而實現了可擴展的城市部署。營運商不斷改進底盤,使其能夠更好地適應路緣、人行橫道和行人互動,從而持續加強在都市區的業務。
隨著零售和餐旅服務業客戶對無縫銜接的門到門服務的需求日益成長,混合動力全地形車正以27.8%的複合年成長率快速擴張。供應商們正積極響應這項需求,整合四輪轉向、模組化貨艙和重型懸吊等技術,例如Avride轉向NVIDIA驅動的四輪平台。室內服務機器人則在校園和醫院等場所佔據著一定的市場地位,因為在這些場所,即使沒有完整的街道感知能力,也能在受控的走廊中實現高度自主運作。
預計到2024年,食品配送仍將佔據42.5%的收入佔有率,證明頻繁的小批量訂單仍然是自動配送機器人市場的主要支撐。高重複性最佳化了資產利用率,簡化了路線學習,從而提升了Serve Robotics等平台的車隊盈利。
隨著零售商追求一小時內履約,食品雜貨和便利商店產業將以每年24.3%的速度成長。機器人將配備溫控托特包和送貨上門通訊協定,從而改善受購物籃大小和小費影響的經濟效益。宅配服務也在不斷發展,但目前負載容量仍受限於較重的商品種類,並且暫時仍將專注於較輕的電商訂單。
區域分析
預計到2024年,北美將維持32.1%的市場佔有率,這反映出高薪通膨和各州監管政策的差異。加州和德克薩斯州在都市區試點方面最為先進,Uber Eats旗下的Serve Robotics計劃在2025年底前部署2000台機器人。 Grubhub和Yandex計劃在250個校園部署機器人,預計將打造全球最密集的機器人網路。
亞太地區緊隨其後,持股比例為25%,主要得益於日本和韓國加速推進醫療保健和智慧城市計畫。韓國的行人友善法規將機器人的速度限制在15公里/小時,重量限制在500公斤,這為在多用戶住宅和醫院進行商業性測試打開了大門。豐田的Potaro系統旨在應用於醫院,凸顯了亞太地區對老化相關物流的關注。
歐洲嚴格的ESG(環境、社會和治理)法規對市中心的柴油貨車進行處罰,為其提供了穩固的收入基礎。 Starship Technologies公司在德國和英國營運,並獲得了監管豁免,允許低速機器人在步行街上共用。營運商仍在應對複雜的多司法管轄區核准流程,這減緩了其擴張的速度,但環境方面的利多因素意味著該技術正穩步普及。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 亞洲都市區按需生鮮宅配業務快速擴張
- 北美勞動力短缺和工資通膨上升
- 在歐盟,以環境、社會和治理(ESG)主導,推廣「最後一公里」零排放車輛
- 隨著人口老化,日本醫院分娩自動化正在推進。
- 中東豪華飯店對全天候無人服務的需求
- 5G邊緣運算提升了密集城市核心區域的機器人自主性
- 市場限制
- 美國各城市的行人道管理規定不盡相同
- 有效負載容量限制了散貨運輸的投資回報率。
- LiDAR和感測器套件的前期成本很高
- 美國都市區的故意破壞和竊盜行為
- 價值鏈分析
- 技術展望
- 宏觀趨勢分析及影響分析
- 監理展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 投資與資金籌措分析
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按機器人類型
- 室內服務機器人
- 戶外自主配送機器人
- 混合動力全地形機器人
- 透過使用
- 外賣
- 雜貨和便利配送
- 小包裹與宅配(電子商務)
- 醫療用品和藥品
- 飯店客房服務
- 工業園區物流
- 按載重能力
- 10公斤以下
- 10-25 kg
- 25-80 kg
- 超過80公斤
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 醫療機構
- 飯店及餐飲服務
- 零售與電子商務物流
- 企業和大學校園
- 機場和交通樞紐
- 智慧城市和地方政府機構
- 按組件
- 硬體
- 軟體/人工智慧堆疊
- 售後服務與車隊管理
- 依推進類型
- 電池
- 氫燃料電池
- 混合能量收集
- 依自主程度
- 半自動型(人工監控型)
- 完全自主(4級)
- 集群/集群型自治網路(第 5 級)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 中東
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 非洲
- 南非
- 肯亞
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 澳洲
- 日本
- 新加坡
- 印度
- 韓國
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Starship Technologies
- Nuro Inc.
- Kiwibot
- Serve Robotics Inc.
- Ottonomy.IO
- Relay Robotics Inc.
- Postmates Inc.(Serve by Uber)
- Aethon Inc.
- Segway Robotics Inc.
- Neolix
- Udelv Inc.
- JD Logistics(Jian Robots)
- Alibaba Cainiao(Xiaomanlv)
- Yandex Rover
- FedEx Roxo
- Amazon Scout
- Rival Robotics Inc.
- TeleRetail(Aitonomi AG)
- Daxbot
- Locus Robotics(campus variant)
- Kiwi Campus SAS
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The autonomous delivery robots market is currently valued at USD 1.11 billion and is projected to reach USD 2.8 billion by 2030, advancing at a 20.33% CAGR.

Growth is grounded in rising labor shortages, swift technological maturation, and supportive regulations that ease sidewalk deployments. Major logistics spenders continue to view the technology as mission-critical; Amazon alone targets USD 200 billion of automation savings through robotic solutions. North America leads adoption thanks to 32.1% 2024 share, while Asia-Pacific follows at 25% as aging populations increase demand for contact-free healthcare logistics. Outdoor sidewalk robots dominate with 58% share, and hybrid all-terrain units post the fastest 27.8% CAGR, signaling a clear preference for platforms that handle both urban and indoor routes. Competitive activity remains intense as venture-backed specialists scale fleets in partnership with delivery platforms, while automotive incumbents pursue healthcare and industrial niches. Headwinds tied to payload limits and high LiDAR costs persist, yet rapid sensor price declines and new community-engagement strategies point to a wider addressable base over the forecast horizon.
Global Autonomous Delivery Robots Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Expansion of On-Demand Grocery Delivery
On-demand grocery services now anchor sustainable unit economics for autonomous fleets because high order density offsets traditional driver costs. Kroger integrated driverless trucks into its Dallas operations to accelerate fulfillment and trim logistics spend. Retailers also embed in-store shelf-scanning robots to reduce the documented 4.5% revenue leakage linked to stock-outs, as shown by Simbe Robotics' rollout across 60 SpartanNash stores. Together these moves confirm that grocery chains are shifting robotics from pilot status to core infrastructure, widening order volumes available to last-mile robots.
Rising Labor Shortages and Wage Inflation
North American fulfillment centers face acute staffing gaps that push companies toward automated alternatives. The U.S. manufacturing sector projects a 2 million-worker shortage by 2030, and last-mile driver turnover amplifies cost pressure. Falling industrial robot prices-down 50% in the past decade-and further declines predicted by EY strengthen the investment case. High urban delivery density then allows operators to hit utilization targets that yield faster payback on autonomous assets.
High Upfront Cost of LiDAR and Sensor Suites
Navigation hardware often accounts for the largest capital item in a delivery robot. Emerging ultrasonic alternatives such as Sonair cut sensor spend by up to 80% while keeping a 180 X 180 degree detection envelope. Cartken's lidar-free vision stack already operates profitably on public sidewalks, proving that cost-efficient sensing can meet reliability thresholds. Even so, broad rollout waits on regulatory validation of these novel sensor mixes.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- ESG-Driven Push for Zero-Emission Last-Mile Vehicles
- Aging Population Spurring Intra-Hospital Delivery Automation
- Vandalism and Theft Incidents in South-American Metros
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Outdoor robots generated 58% of 2024 revenue, anchoring the autonomous delivery robots market through well-tested sidewalk operations. This dominance reflects reliable partnerships with food aggregators and local regulators that allow scalable city deployments. Operators continue to refine chassis for curbs, crosswalks, and pedestrian interaction, reinforcing their urban stronghold.
Hybrid all-terrain units expand rapidly at 27.8% CAGR because retail and hospitality customers ask for seamless door-to-door service that crosses thresholds. Suppliers respond by integrating four-wheel steering, modular cargo pods, and ruggedized suspension, a trend evident in Avride's pivot to NVIDIA-powered four-wheel platforms. Indoor service robots maintain niche roles in campuses and hospitals where controlled corridors permit higher autonomy without full street-grade sensing.
Food delivery retained 42.5% revenue share in 2024, proving that frequent small-ticket orders still underpin the autonomous delivery robots market. High repetition optimizes asset utilization and simplifies route learning, supporting fleet-level profitability for platforms such as Serve Robotics.
Grocery and convenience segments rise 24.3% annually as retailers chase sub-hour fulfillment. Robots accommodate temperature-controlled totes and door-step protocols that boost basket size and tip-influenced economics. Parcel courier services also advance, but payload ceilings still limit heavier SKUs, keeping focus on lightweight e-commerce orders for now.
The Autonomous Delivery Robots Market Report is Segmented by Robot Type (Indoor, Outdoor, Hybrid), Application (Food, Grocery, Parcel, and More), Load Capacity (Up To 10kg, 10-25kg, 25-80kg, Above 80kg), End-User (Healthcare, Hotels, Retail, and More), Component (Hardware, Software and More), Propulsion (Electric, Hydrogen, Hybrid), Level of Autonomy, and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 32.1% share in 2024, reflecting high wage inflation and a supportive patchwork of state-level rules. California and Texas host the largest urban pilots, with Serve Robotics targeting 2,000 units by year-end 2025 under an Uber Eats framework. College-town deployments add scale; Grubhub and Yandex plan rollouts across 250 campuses, potentially forming the world's densest robot network.
Asia-Pacific followed with a 25% stake as Japan and South Korea accelerate healthcare and smart-city programs. South Korea's sidewalk-friendly legislation caps robot speed at 15 km/h and weight at 500 kg, unlocking commercial trials in apartment complexes and hospitals. Toyota's Potaro system shows the model for intra-hospital use, highlighting APAC's focus on aging-related logistics.
Europe contributes a solid revenue base, aided by stringent ESG mandates that penalize diesel vans in city centers. Starship Technologies operates in Germany and the UK under regulatory exemptions that let slow-moving robots share pedestrian zones. Operators still navigate complex, multi-jurisdiction approval processes, slowing scale, yet the environmental tailwinds keep adoption on a steady path.
- Starship Technologies
- Nuro Inc.
- Kiwibot
- Serve Robotics Inc.
- Ottonomy.IO
- Relay Robotics Inc.
- Postmates Inc. (Serve by Uber)
- Aethon Inc.
- Segway Robotics Inc.
- Neolix
- Udelv Inc.
- JD Logistics (Jian Robots)
- Alibaba Cainiao (Xiaomanlv)
- Yandex Rover
- FedEx Roxo
- Amazon Scout
- Rival Robotics Inc.
- TeleRetail (Aitonomi AG)
- Daxbot
- Locus Robotics (campus variant)
- Kiwi Campus SAS
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid expansion of on-demand grocery delivery in urban Asia
- 4.2.2 Rising labor shortages and wage inflation in North-American fulfilment
- 4.2.3 ESG-driven push for zero-emission last-mile vehicles in the EU
- 4.2.4 Aging population spurring intra-hospital delivery automation in Japan
- 4.2.5 24/7 contact-free services demand in Middle-East luxury hotels
- 4.2.6 5G edge-compute enabling higher robot autonomy in dense city cores
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Municipal sidewalk regulation variability in US cities
- 4.3.2 Limited payload capacity restricting ROI for bulk goods
- 4.3.3 High upfront cost of LiDAR and sensor suites
- 4.3.4 Vandalism and theft incidents in S-American metros
- 4.4 Value-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Impact of Macro-Trend Analysis
- 4.7 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Investment and Funding Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Robot Type
- 5.1.1 Indoor Service Robots
- 5.1.2 Outdoor Autonomous Delivery Robots
- 5.1.3 Hybrid All-Terrain Robots
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Food Delivery
- 5.2.2 Grocery and Convenience Deliveries
- 5.2.3 Parcel and Courier (E-commerce)
- 5.2.4 Healthcare Supply and Medication
- 5.2.5 Hospitality Room-Service
- 5.2.6 Industrial Campus Logistics
- 5.3 By Load Capacity
- 5.3.1 Up to 10 kg
- 5.3.2 10 - 25 kg
- 5.3.3 25 - 80 kg
- 5.3.4 Above 80 kg
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Healthcare Facilities
- 5.4.2 Hospitality and Hotels
- 5.4.3 Retail and E-commerce Logistics
- 5.4.4 Corporates and Academic Campuses
- 5.4.5 Airports and Transportation Hubs
- 5.4.6 Smart Cities and Municipal Agencies
- 5.5 By Component
- 5.5.1 Hardware
- 5.5.2 Software / AI Stack
- 5.5.3 After-Sales Services and Fleet Management
- 5.6 By Propulsion Type
- 5.6.1 Electric Battery
- 5.6.2 Hydrogen Fuel Cell
- 5.6.3 Hybrid Energy Harvesting
- 5.7 By Level of Autonomy
- 5.7.1 Semi-Autonomous (Human-Supervised)
- 5.7.2 Fully Autonomous (Level 4)
- 5.7.3 Swarm/Clustered Autonomous Network (Level 5)
- 5.8 By Geography
- 5.8.1 North America
- 5.8.1.1 United States
- 5.8.1.2 Canada
- 5.8.1.3 Mexico
- 5.8.2 South America
- 5.8.2.1 Brazil
- 5.8.2.2 Argentina
- 5.8.2.3 Chile
- 5.8.3 Europe
- 5.8.3.1 Germany
- 5.8.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.8.3.3 France
- 5.8.3.4 Italy
- 5.8.3.5 Spain
- 5.8.4 Middle East
- 5.8.4.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.8.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.8.4.3 Turkey
- 5.8.5 Africa
- 5.8.5.1 South Africa
- 5.8.5.2 Kenya
- 5.8.6 Asia-Pacific
- 5.8.6.1 China
- 5.8.6.2 Australia
- 5.8.6.3 Japan
- 5.8.6.4 Singapore
- 5.8.6.5 India
- 5.8.6.6 South Korea
- 5.8.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Starship Technologies
- 6.4.2 Nuro Inc.
- 6.4.3 Kiwibot
- 6.4.4 Serve Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.5 Ottonomy.IO
- 6.4.6 Relay Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.7 Postmates Inc. (Serve by Uber)
- 6.4.8 Aethon Inc.
- 6.4.9 Segway Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.10 Neolix
- 6.4.11 Udelv Inc.
- 6.4.12 JD Logistics (Jian Robots)
- 6.4.13 Alibaba Cainiao (Xiaomanlv)
- 6.4.14 Yandex Rover
- 6.4.15 FedEx Roxo
- 6.4.16 Amazon Scout
- 6.4.17 Rival Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.18 TeleRetail (Aitonomi AG)
- 6.4.19 Daxbot
- 6.4.20 Locus Robotics (campus variant)
- 6.4.21 Kiwi Campus SAS
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment








