|
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851529
太陽能逆變器:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Solar PV Inverters - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
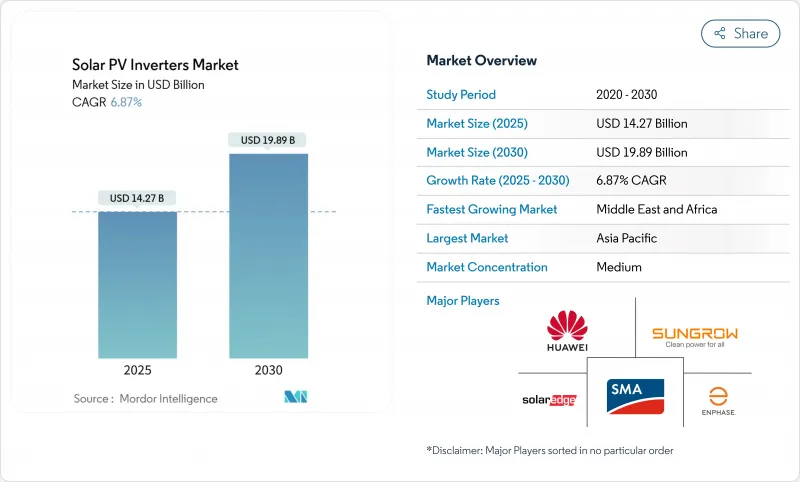
預計到 2025 年,太陽能逆變器市場規模將達到 142.7 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 198.9 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)複合年成長率為 6.87%。
市場擴張得益於從簡單的直流轉交流轉換到智慧電網塑形解決方案的轉變,這些解決方案能夠保護電能品質並為業主開闢新的收入來源。亞太地區支撐著全球需求,而中東地區由於大型公共產業計劃和電網現代化挑戰的交匯,目前是成長最快的地區。日本強勁的更換週期、印度的屋頂安裝強制令以及美國和歐洲的高壓設計正在推動近期銷量成長,而持續的SiC/IGBT短缺以及中國日益嚴重的限流措施則減緩了市場擴張的步伐。儘管存在這些不利因素,但由於先進電網支援功能的溢價,太陽能逆變器市場總收入仍在持續成長。
全球太陽能逆變器市場趨勢與洞察
公共產業規模計劃中高壓 1500V串列型逆變器的快速應用(美國、西班牙)
為了降低系統平衡成本並提高功率密度,電力開發人員擴大採用 1500V 直流架構,並試行 2000V 直流架構。 GE Vernova 的 2000V 平台實現了 30% 的功率輸出提升,從而降低了平準化能源成本。這種電壓轉型使得 1000V 陣列在新建設項目中經濟效益下降,尤其是在土地和電網餘量允許更大容量模組的情況下,從而推動了維修計劃的發展。半導體需求的成長導致碳化矽 (SiC) 裝置供應趨緊,並提升了知名品牌熱設計專業知識的策略重要性。
印度強製商業建築安裝屋頂太陽能光電發電系統將提振對100kW以下逆變器的需求。
印度政策強制要求在新舊商業建築上安裝屋頂光電陣列,從而持續推動對100kW以下逆變器的需求。 2024會計年度計畫新增裝機量將達到創紀錄的4GW,凸顯了市場機會的巨大潛力。國內製造商正受惠於2026年建成110GW電池和組件的進口替代目標,從而加強國內價值鏈。 </p><p></p><h4>高電流SiC/IGBT功率組件持續短缺和價格波動</h4><p>SiC晶圓供不應求持續限制著高效逆變器的生產,並推高了材料成本。晶圓供應困難加劇了市場風險,但英飛凌已表示,將透過轉向成本效益更高的200mm SiC晶圓來緩解2026年後的供應壓力。 </p> </p><h3><u>細分市場分析</u></h3><p>儘管集中式逆變器在2024年仍保持55%的營收領先優勢,但隨著組件級電子技術不再局限於早期採用者,微型逆變器預計將以8.1%的複合年成長率成長。 Enphase在2025年向美國市場交付了超過650萬台微型逆變器,符合美國在地化標準,並展現了該領域的商業規模。太陽能逆變器市場正在獎勵那些將ASIC設計、無線數據和熱工程整合到小型設備中的公司。雖然由於中國電力限制,集中式架構目前面臨需求放緩,但在其他地區,尤其是在那些工廠級控制和具有競爭力的資本投資是首要考慮因素的公用事業計劃中,集中式架構正在獲得市場佔有率。 </p>
微電子領域的競爭尤其激烈,其競爭障礙並非硬體成本,而是韌體的複雜性和安全認證。因此,低成本的參與企業難以跟上快速推出的新功能,例如快速關斷和電池介面模式。儘管微型逆變器的銷售成長強勁,但在未來十年內,它們不太可能取代組串式逆變器平台。
2024年,公用事業公司將佔總出貨量的63%,反映出大量計劃已簽訂長期購電協議(PPA)。儘管如此,隨著電網服務和淨收費機制改善家庭經濟狀況,住宅太陽能系統仍將以每年7.6%的速度成長。印度的「總理陽光之家」(Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar)計畫目標是在2027年3月前安裝30吉瓦的屋頂太陽能陣列,而澳洲的儲能電池加裝附加元件正在推動安裝速度。商業屋頂太陽能系統正受益於印度的屋頂太陽能強制令,但在其他地區,它們面臨融資條件較為謹慎、投資回收期較長的問題。
使用者越來越重視雙向功能和孤島運作穩定性,這促使逆變器廠商將電池控制邏輯整合到產品中。這推高了平均售價,抵銷了宏觀層面太陽能逆變器整體銷售成長放緩的影響。同時,電力公司正專注於1500V和2000V平台,並整合類似STATCOM的功能,以滿足更嚴格的電網規範。
太陽能逆變器市場報告按逆變器類型(中型逆變器、組串式逆變器、微型逆變器、混合/電池就緒型逆變器)、相數(單相、三相)、連接類型(併網、離網)、應用(住宅、商業/工業、公用事業規模)和地區(北美、歐洲、亞太、南美、中東和非洲)進行細分。
區域分析
亞太地區佔2024年全球出貨量的55%,主要得益於中國垂直整合的供應鏈和印度政策主導的綠色屋頂推廣。中國新的市場化關稅機制可能會減緩待開發區項目的步伐,但儲能和高壓組串等維修。預計到2026年,印度的製造能力將達到110吉瓦,這將加強國內採購鏈,並保護國內太陽能逆變器市場免受進口波動的影響,但監管執行方面的區域差異將限制短期內的成長。
到2030年,中東地區將以9.4%的複合年成長率實現最快增速,這將使吉瓦級計劃符合其經濟多元化發展藍圖。嚴酷的沙漠環境將推動對高散熱設計的需求,為專注於封閉式配電櫃解決方案的歐洲原始設備製造商(OEM)創造市場機會。沙烏地阿拉伯和阿拉伯聯合大公國的電網強化措施提高了對低電壓穿越和無功功率管理的要求,迫使供應商根據更嚴格的公共產業標準對其產品進行認證。
北美和歐洲的安裝基礎已相當成熟,更換和維修週期主導著不斷成長的需求。在美國,《通貨膨脹控制法案》的國內能源信貸政策正在加速本地能源生產,德克薩斯州、南卡羅來納州和亞利桑那州的設施目標是到2026年實現年發電量遠超過30吉瓦。在歐洲,德國和西班牙等市場的可再生能源滲透率超過50%,這提升了電網調節能力的價值,並使供應商即使在新建設成長停滯的情況下也能提供更高的平均售價。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 公用事業規模計劃中高壓1500V組串式逆變器的快速應用(美國、西班牙)
- 印度強製商業建築安裝屋頂太陽能的政策將提振對100kW逆變器的需求。
- 2012年至2016年日本上網電價補貼政策(FIT)實施期間安裝的逆變器採取了積極的更換週期。
- 整合先進的電網支援功能以支援歐洲應用服務供應商
- 混合太陽能和儲能解決方案的成長推動了澳洲雙向逆變器的發展
- 巴西政府將推出在地化獎勵,鼓勵國內生產中央逆變器。
- 市場限制
- 高電流SiC/IGBT功率模組持續短缺和價格波動
- 中國西北地區限電措施升級,導致集中式逆變器訂單減少
- 美國互聯互通監管法規碎片化,推高了認證成本。
- 德國對屋頂直流電路的消防安全隱患阻礙了微型逆變器的普及。
- 供應鏈分析
- 監理展望
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按逆變器類型
- 中央逆變器
- 組串式逆變器
- 微型逆變器
- 混合動力/電池相容型逆變器
- 按階段
- 單相
- 三相
- 按連線類型
- 併網
- 離網
- 透過使用
- 住宅
- 商業和工業
- 實用規模
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 北歐國家
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 馬來西亞
- 泰國
- 印尼
- 越南
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 哥倫比亞
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略性舉措(併購、夥伴關係、購電協議)
- 市場佔有率分析(主要企業的市場排名/佔有率)
- 公司簡介
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- Enphase Energy Inc.
- FIMER SpA
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Growatt New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ginlong(Solis)Technologies
- TMEIC Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Omron Corporation
- Power Electronics Espana SL
- Chint Power Systems Co., Ltd.
- GoodWe Technologies Co., Ltd.
- GE Vernova
- Canadian Solar Inc.(CSI Solar)
- Toshiba Mitsubishi-Electric Industrial Systems Corp.(TMEIC)
- Kepco KPS(South Korea)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Solar PV Inverters Market size is estimated at USD 14.27 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 19.89 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.87% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The market's expansion is underpinned by a move from simple DC-to-AC conversion toward smart, grid-forming solutions that safeguard power quality and unlock new revenue streams for owners. Asia-Pacific anchors global demand, yet the Middle East is now the fastest-growing territory as large utility projects intersect with grid-modernization agendas. Robust replacement cycles in Japan, rooftop mandates in India, and higher-voltage designs across the United States and Europe amplify near-term unit volumes, while persistent SiC/IGBT shortages and rising curtailment in China temper the pace of expansion. Despite those headwinds, premium pricing for advanced grid-support functions keeps aggregate revenue upward in the solar PV inverter market .
Global Solar PV Inverters Market Trends and Insights
Rapid adoption of high-voltage 1 500 V string inverters in utility-scale projects (US, Spain)
Utility developers increasingly specify 1,500 V-and pilot 2,000 V-DC architectures to lower balance-of-system costs and boost power density. GE Vernova's 2,000 V platform showcases a 30% output gain that decreases levelized energy costs. This voltage migration renders 1,000 V arrays economically obsolete on new-build sites and spurs retrofit projects, especially where land and grid headroom allow bigger block sizes. Heightened semiconductor demand follows, tightening the supply of SiC devices and elevating the strategic importance of thermal design expertise among leading brands.
Mandatory rooftop-solar mandates in India's commercial buildings boosting <=100 kW inverter demand
India's policy obliges new and existing commercial structures to install rooftop arrays, driving the sustained need for <=100 kW inverters. Record additions of 4 GW in fiscal 2024 signal the scale of the opportunity . Domestic manufacturers benefit from import-substitution targets embedded in the country's 110 GW cell-and-module build-out by 2026, reinforcing the local value chain. While implementation gaps remain across several states, standardized installation practices create a template for broader residential uptake.
Persistent shortages & price volatility of high-current SiC / IGBT power modules
SiC wafer supply tightness continues to constrain high-efficiency inverters and amplify bill-of-material costs. Wolfspeed's financial distress heightens risk perceptions, whereas Infineon's switch to cost-effective 200 mm SiC wafers signals relief from 2026 onward . European and North American producers, dependent on advanced semiconductors for grid-forming functionality, experience sharper margin compression than vertically integrated Chinese peers able to fall back on silicon alternatives.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Aggressive replacement cycle of inverters installed during Japan's 2012-2016 FIT boom
- Integration of advanced grid-support functions lifting ASPs in Europe
- Rising curtailment in China's northwest dampening central-inverter orders
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Central units retained a 55% revenue lead in 2024, yet microinverters are forecast to grow at an 8.1% CAGR as module-level electronics move beyond the early-adopter niche. Enphase shipped more than 6.5 million domestic microinverters in 2025, satisfying US localization criteria and underlining the segment's commercial scale . The solar PV inverter market rewards firms that combine ASIC design, wireless data, and thermal engineering in a miniature footprint. Central architectures now confront flattish demand in China due to curtailment but remain anchored in utility projects elsewhere, especially where plant-level controls and competitive capex remain priorities.
Competitive intensity is pronounced in microelectronics; barriers arise from firmware sophistication and safety certifications rather than raw hardware cost. Consequently, low-price entrants struggle to keep pace with rapid feature rollouts such as rapid shutdown and battery interface modes. Despite robust volume growth, microinverters are not likely to eclipse string platforms before the next decade, keeping the solar PV inverter market diversified by architecture.
Utility plants captured 63% of 2024 shipments, reflecting large project pipelines locked under long-term PPAs. Even so, residential systems should expand by 7.6% annually as grid services and net-billing frameworks enhance household economics. India's Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar program targets 30 GW of rooftop arrays by March 2027, while Australia's battery add-on trend lifts attachment rates. Commercial rooftops ride India's rooftop mandate wave but face cautious finance terms in other regions that stretch payback timelines.
Prosumers increasingly value bidirectional capability and island-mode resilience, prompting inverter OEMs to integrate battery control logic. The resulting ASP uplift compensates for slower macro installation growth, supporting aggregate revenue progression inside the solar PV inverter market. Utility developers, meanwhile, focus on 1,500 V and 2,000 V platforms, coupling them with STATCOM-like functionalities to meet stricter grid-code compliance.
The Solar PV Inverter Market Report is Segmented by Inverter Type (Central Inverters, String Inverters, Micro Inverters, and Hybrid/Battery-Ready Inverters), Phase (Single-Phase and Three-Phase), Connection Type (On-Grid and Off-Grid), Application (Residential, Commercial and Industrial, and Utility-Scale), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific generated 55% of 2024 shipments, underpinned by China's vertically integrated supply chain and India's policy-driven rooftop push. While China's new market-based tariff regime may slow greenfield installations, volume resilience stems from retrofits that embed storage and higher-voltage strings. India's manufacturing capacity, set to reach 110 GW by 2026, tightens domestic procurement loops and shields the local solar PV inverter market from import volatility, although regional disparities in regulatory execution temper immediate gains.
The Middle East, clocking the quickest 9.4% CAGR through 2030, aligns gigawatt-scale projects with economic diversification blueprints. Harsh desert conditions drive demand for high-derating-temperature designs, opening niches for European OEMs specializing in sealed cubicle solutions. Grid-reinforcement efforts in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates elevate low-voltage ride-through and reactive-power management specifications, pressing vendors to certify products against stricter utility benchmarks.
North America and Europe operate in a mature install base where replacement and retrofit cycles dominate incremental demand. The US Inflation Reduction Act's domestic content credits accelerate localized production, with Texas, South Carolina, and Arizona facilities targeting annual output well above 30 GW by 2026. Europe's renewable penetration surpassing 50% in markets such as Germany and Spain raises the value of grid-forming features, allowing vendors to pass through higher ASPs even as new-build volumes plateau.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- Enphase Energy Inc.
- FIMER SpA
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Growatt New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ginlong (Solis) Technologies
- TMEIC Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Omron Corporation
- Power Electronics Espana S.L.
- Chint Power Systems Co., Ltd.
- GoodWe Technologies Co., Ltd.
- GE Vernova
- Canadian Solar Inc. (CSI Solar)
- Toshiba Mitsubishi-Electric Industrial Systems Corp. (TMEIC)
- Kepco KPS (South Korea)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid adoption of high-voltage 1 500 V string inverters in utility-scale projects (US, Spain)
- 4.2.2 Mandatory rooftop-solar mandates in India's commercial buildings boosting ?100 kW inverter demand
- 4.2.3 Aggressive replacement cycle of inverters installed during Japan's 2012-2016 FIT boom
- 4.2.4 Integration of advanced grid-support functions lifting ASPs in Europe
- 4.2.5 Growth of hybrid PV-storage solutions driving bidirectional inverters in Australia
- 4.2.6 Localization incentives in Brazil encouraging domestic manufacture of central inverters
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Persistent shortages & price volatility of high-current SiC / IGBT power modules
- 4.3.2 Rising curtailment in China's northwest dampening central-inverter orders
- 4.3.3 Fragmented US interconnection codes inflating certification costs
- 4.3.4 Fire-safety concerns on rooftop DC circuits slowing microinverter uptake in Germany
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Inverter Type
- 5.1.1 Central Inverters
- 5.1.2 String Inverters
- 5.1.3 Microinverters
- 5.1.4 Hybrid/Battery-Ready Inverters
- 5.2 By Phase
- 5.2.1 Single-Phase
- 5.2.2 Three-Phase
- 5.3 By Connection Type
- 5.3.1 On-Grid
- 5.3.2 Off-Grid
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Residential
- 5.4.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 5.4.3 Utility-Scale
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Nordic Countries
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Malaysia
- 5.5.3.6 Thailand
- 5.5.3.7 Indonesia
- 5.5.3.8 Vietnam
- 5.5.3.9 Australia
- 5.5.3.10 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Colombia
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Egypt
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.3 SMA Solar Technology AG
- 6.4.4 SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.5 Enphase Energy Inc.
- 6.4.6 FIMER SpA
- 6.4.7 Delta Electronics, Inc.
- 6.4.8 Growatt New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Ginlong (Solis) Technologies
- 6.4.10 TMEIC Corporation
- 6.4.11 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.12 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.13 Siemens AG
- 6.4.14 Eaton Corporation plc
- 6.4.15 Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.17 Power Electronics Espana S.L.
- 6.4.18 Chint Power Systems Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 GoodWe Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.20 GE Vernova
- 6.4.21 Canadian Solar Inc. (CSI Solar)
- 6.4.22 Toshiba Mitsubishi-Electric Industrial Systems Corp. (TMEIC)
- 6.4.23 Kepco KPS (South Korea)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment