 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851174
變數施肥技術:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Variable Rate Technology - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
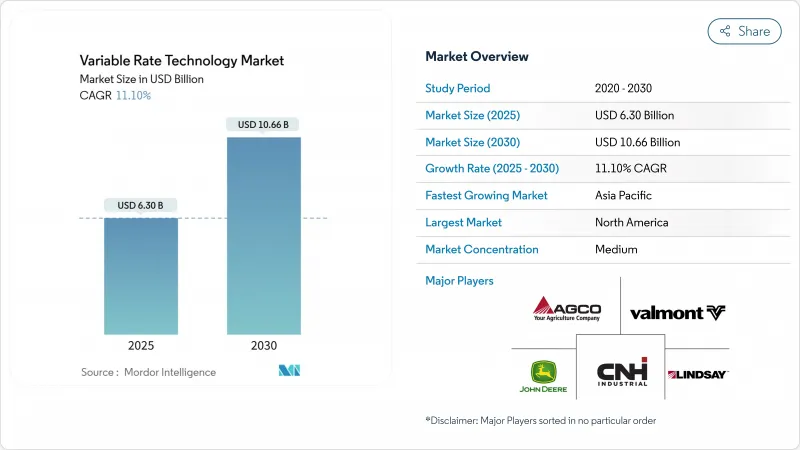
預計到 2025 年,可變施肥技術市場規模將達到 63 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 106.6 億美元,預測期內複合年成長率為 11.10%。
在資源日益匱乏的情況下生產更多糧食的壓力不斷增加,加上對化肥和農藥使用的監管審查日益嚴格,使得可變施肥技術市場成為精準投入管理的關鍵推動因素。農業數位化、人工智慧在設備中的應用以及優惠的補貼政策提升了該技術的吸引力,而設備製造商的整合則加速了平台創新。北美仍然是收入的主要驅動力,但隨著現代化計畫的擴展,亞太地區對成長的貢獻最大。價值創造仍然主要依賴硬體銷售,但以服務為中心的經營模式正在迅速發展,這預示著行業正在向以結果為導向的模式轉變。
全球變速施肥技術市場趨勢與洞察
農場快速數位化
美國已有61%的農場依賴精準農業硬體,將即時農藝數據傳輸到雲端平台。設備製造商正投入數十億美元研發自動化解決方案,以減少勞動力投入並提高施肥精度,約翰迪爾公司推出的十年200億美元國內製造計劃便體現了這一點。歐洲的政策也同樣優先考慮農業的未來數位化策略,並確保對連網型設備的持續投入。人工智慧主導的封閉式創造了閉迴路回饋系統,不斷調整處方箋,推動可變施肥技術市場從靜態地圖轉向自學習系統。然而,大型農場和小型農場之間日益擴大的數位落差威脅著科技的公平普及。
政府補貼和激勵措施
政策制定者正透過補貼、退稅和生態計畫來承擔實施成本。美國農業部的「氣候智慧型商品計劃」承諾投入31億美元,用於需要精細化生產數據並最終實現精準投入工具的計劃。澳洲的「農場互聯互通計畫」承擔了智慧灌溉設備一半的成本,而印度的「數位農業使命」已累計600億盧比(約7.2289億美元)用於互聯基礎建設。歐洲通用農業政策將至少25%的直接支付用於獎勵可變施肥的生態計畫。這些補貼降低了准入門檻,尤其對那些先前因高科技支出而現金流受限的中型農場而言更是如此。
具備VRT功能的機器需要高額的資本支出。
通常情況下,當農場經濟規模超過10萬歐元(約114,923.51美元)時,才能達到盈利平衡點,這使得規模較小的農場無力負擔設備購置費用。雖然像AgDirect這樣的貸款機構提供針對特定行業的貸款,但對於資產負債表薄弱的家庭農場來說,抵押品往往難以獲得。為了解決這個問題,出現了設備即服務(EaaS)契約,這種合約將成本分攤到所服務的農田上,而不是分攤到擁有的設備上。
細分市場分析
2024年,穀物和穀類將佔總收入的37.60%,鞏固其作為可變施肥技術市場基礎的地位。這些大面積種植的作物受惠於數十年的配方測繪,能夠精準地調整大片土地上的氮、磷和播種密度。棉花、烟草和特种纤维等经济作物预计将以14.80%的复合年增长率快速增长,因为更高的淨利率使其能够负担得起高階传感器和设备端人工智慧。隨著與品質掛鉤的定價機制的實施,商業作物可變施肥技術市場規模預計將會擴大,該機制獎勵精準的馬克隆值或葉片等級。利用頻譜相機對植物壓力進行持續監測,並將數據輸入即時模型,在幾分鐘內啟動鉀肥或葉面施肥干預措施。這種快速響應能力使種植者能夠獲得合約獎金並減少因等級問題導致的降級。雖然穀類預計將保持其現有裝機量,但特種作物領域將在採用先進技術方面引領潮流。
第二代土壤光譜技術現在可以測量養分釋放曲線,從而支持油籽和豆類輪作中的微量施肥。這項技術在巴西和印度的應用尤其廣泛,因為這兩個國家的蛋白質和油脂含量直接影響農產品價格。隨著水果出口商對糖度和顏色容差要求越來越高,可變施肥技術市場正進一步滲透到果園和葡萄園的運作中。供應商將樹液分析和灌溉控制打包成訂閱服務,使即使是小面積果園也能獲得高階分析服務,而無需購買必要的設備。
2024年,化肥市場佔有率將達到31.70%,因為氮肥利用效率的提昇在大多數氣候帶都能帶來快速的投資回報。預計到2030年,變數灌溉將以17.20%的複合年成長率成長,這反映了日益嚴重的水資源短缺以及對季節性取水量的監管限制。在加州的一項試驗中,精準中心支軸式噴灌在不損失產量的情況下減少了25%的用水量,證明了其在杏仁和開心果種植中的經濟效益。預計到2030年,灌溉設備中變數施肥技術的市場銷售額將增加10億美元,主要得益於一項旨在補償低壓噴嘴維修的補助計劃。作物保護噴灑技術也備受關注,因為基於電腦視覺的雜草辨識技術可減少高達80%的除草劑用量。除了這些優勢之外,產量監測應用還有助於改進未來的配方,並完善數據回饋循環,從而支援分析軟體的續訂。
無線土壤探針和雲端儀錶板的整合,使得灌溉決策能夠將蒸散量預測和未來降雨機率納入考慮。這種預測能力延長了水泵壽命,降低了能源需求,並提升了資源利用效率的提案。肥料施用方面,可攜式實驗室套件可與施肥速率控制器同步,利用即時組織檢測技術,將靜態地圖轉換為動態的季內施肥計畫。生物作物保護投入品的創新進一步凸顯了精準微量施肥的需求,而精準微量施肥依賴於感測器驅動的變數施肥演算法。
區域分析
2024年,北美佔據了可變施肥技術市場39%的佔有率。強勁的設備普及、優惠的融資政策以及美國農業部氣候智慧型採購規則支撐了市場需求。補貼機制獎勵有據可查的養分減量,促進了能夠採集噴嘴級數據的智慧型裝置的普及。中西部和草原地區的部分農村寬頻網路覆蓋落後,但預計到2026年,衛星鏈路的部署將擴大覆蓋範圍。俄亥俄州的一項試驗表明,當可變氮肥施用和無人機植株數量相結合時,作物產量提高了6%。經銷商體系提供經過認證的技術人員來維護設備並解讀數據,凸顯了服務業的成長動能。
亞太地區經濟成長最快,預計2030年年均複合成長率將達14.1%。中國最新的五年計畫倡導低碳高效農業,並輔以精準的投入品供應。印度的農民登記系統與Aadhaar(印度居民身分識別系統)關聯,簡化了感測器套件補貼的發放流程;日本食品農業省聯合資助了一項針對水稻田的變數播種試驗。該地區的小塊農地結構催生了許多創新解決方案,例如由鄉村創業家營運的共享無人機服務。澳洲和中國北方地區的水資源短缺正在加速推廣可變水量灌溉技術,並促進跨境知識轉移和硬體進口。
在歐洲,可變施肥技術的應用將被納入全面的氣候變遷政策。 2023-2027年通用農業政策撥款2,695億歐元(3,124億美元),其中近一半將用於應對氣候變遷的措施,例如減少化肥徑流和農藥漂移。每個成員國必須將至少25%的直接支付用於生態計畫。像荷蘭這樣的國家正在透過資助數位化津貼來加速推廣,這些補助金可以報銷高達40%的感測器安裝費用。資料主權規則提高了平台遵守《一般資料保護規則)義務的合規成本。儘管如此,像德國5G農業試驗平台這樣的聯盟計劃正在提高安全連接的可靠性,而歐洲範圍內的碳排放舉措也依賴收費管理機構產生的可追溯的投入數據。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 農場快速數位化
- 政府補貼和獎勵
- 農業勞動力短缺日益嚴重
- 利用衛星窄帶物聯網技術進行亞英畝級施肥
- 碳權貨幣化需要投入可追溯性。
- 用於離線VRT分析的設備端AI晶片
- 市場限制
- VRT相容機器的高額資本投入
- 農村地區網路連接基礎設施薄弱
- 資料所有權和共用模糊不清
- 缺乏VRT熟練農藝服務提供者
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按作物類型
- 穀物和穀類
- 水果和蔬菜
- 油籽和豆類
- 經濟作物
- 透過使用
- 肥料
- 作物保護化學品
- 土壤感
- 產量監測
- 灌溉
- 其他(可變施肥播種/種植、可變施用石灰和土壤改良劑)
- 報價
- 硬體
- 軟體
- 服務
- 透過實施方法
- 基於地圖的VRT
- 基於感測器的VRT
- 按農場規模
- 大型農場(超過1000公頃)
- 中型農場(200-1000公頃)
- 小型農場(小於200公頃)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 英國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東
- 土耳其
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation
- CNH Industrial NV
- Valmont Industries, Inc.
- Lindsay Corporation
- EarthOptics
- Hexagon AB
- CropX Technologies
- TeeJet Technologies(Spraying Systems)
- DJI
- DroneDeploy
- The Climate Corporation(Bayer AG)
- EOS Data Analytics,Inc
- SoilOptix
- Frontier Agriculture Ltd
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Variable Rate Technology Market size is estimated at USD 6.30 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 10.66 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.10% during the forecast period.

Rising pressure to produce more food with fewer resources, combined with regulatory scrutiny over fertilizer and pesticide use, positions the variable rate technology market as a pivotal enabler of precision input management. Wider farm digitalization, embedded on-equipment AI, and favorable subsidy programs strengthen technology appeal, while consolidation among equipment makers accelerates platform innovation. North America remains the revenue anchor, yet Asia-Pacific contributes the most incremental growth as modernization schemes expand. Hardware sales still dominate value creation, but service-centric business models scale quickly, signaling an industry shift toward outcome-based offerings.
Global Variable Rate Technology Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Digitalization of Farms
Sixty-one percent of United States farms already rely on precision hardware that feeds real-time agronomic data into cloud platforms. Equipment makers allocate multibillion-dollar budgets to autonomous solutions that lower labor needs and refine application accuracy, illustrated by John Deere's decade-long USD 20 billion domestic manufacturing plan. European policy likewise prioritizes an upcoming digital strategy for agriculture, ensuring sustained funding for connected devices. Closed feedback loops created by AI-driven algorithms continuously adjust prescriptions, moving the variable rate technology market beyond static maps toward self-learning systems. Yet a widening digital divide between large and small farms threatens equitable technology uptake.
Government Subsidies and Incentive Schemes
Policymakers use grants, rebates, and eco-schemes to underwrite adoption costs. The USDA Climate-Smart Commodities initiative channels USD 3.1 billion into projects that necessitate granular production data and, by extension, precision input tools. Australia's On-Farm Connectivity Program covers half the cost of smart irrigation devices, while India's Digital Agriculture Mission earmarks INR 6,000 crore (USD 722.89 million) for connected infrastructure. Europe's Common Agricultural Policy directs at least 25% of direct payments toward eco-schemes that reward variable-rate fertilization. These subsidies lower entry barriers, especially for mid-size farms whose cash flows were once restricted by high-tech spending.
High Capital Expenditure of VRT-Ready Machinery
Profitability breakeven often starts at economic farm sizes above EUR 100,000 (USD 114,923.51), leaving smaller operations priced out of equipment purchases. Lenders such as AgDirect offer sector-specific loans, yet collateral hurdles persist for family farms with thin balance sheets. As a workaround, equipment-as-a-service contracts spread costs across acres serviced rather than units owned.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Agricultural Labor Shortage
- Satellite NB-IoT-Enabled Sub-Acre Prescriptions
- Patchy Rural Connectivity Infrastructure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, cereals and grains represented 37.60% of revenues, cementing their role as the foundation of the variable rate technology market. These broad-acre crops benefit from decades of prescription mapping that fine-tunes nitrogen, phosphorus, and seeding density across large tracts. Commercial crops such as cotton, tobacco, and specialty fibers deliver the fastest gains with a 14.80% CAGR outlook, as higher margins justify premium sensors and on-equipment AI. Variable rate technology market size for commercial crops is anticipated to climb in tandem with quality-linked pricing schemes that reward precise micronaire or leaf grade. Continuous monitoring of plant stress via multispectral cameras feeds real-time models that initiate potassium or foliar-feed interventions within minutes. This responsiveness helps producers capture contract bonuses and reduce grade-related downgrades. Cereals will keep anchoring installed base volumes, yet specialty segments set the pace for advanced feature uptake.
Second-generation soil spectroscopy now measures nutrient release curves that underpin fertilizer micro-dosing in oilseed and pulse rotations. Adoption is especially strong in Brazil and India, where protein and oil content directly influence farm-gate prices. The variable rate technology market further penetrates orchard and vineyard operations as fruit exporters demand tighter Brix and color tolerances. Providers bundle sap analysis and irrigation rate control into subscription services so smaller acreage fruit farms can access high-end analytics without outright equipment purchases.
Fertilizers held a 31.70% market share in 2024 because nitrogen efficiency improvements deliver quick paybacks in most climatic zones. Variable-rate irrigation is poised for a 17.20% CAGR by 2030, reflecting escalating water scarcity and regulatory caps on seasonal withdrawals. In California trials, precision pivots cut water use by 25% with no yield penalty, validating the economics for almond and pistachio groves. The variable rate technology market size for irrigation equipment is forecast to add USD 1 billion in incremental sales by 2030, buoyed by subsidy programs that reimburse low-pressure nozzle retrofits. Crop-protection spraying follows close behind as computer-vision weed identification slashes herbicide volumes by up to 80%. Added to these gains, yield monitoring applications complete the data feedback loop that refines future prescriptions and anchors subscription renewals for analytics software.
Integration of wireless soil probes with cloud dashboards enables irrigation decisions that account for evapotranspiration forecasts and future rainfall probability. This predictive capability extends pump life and trims energy demand, reinforcing the resource-efficiency value proposition. Fertilizer applications now leverage real-time tissue testing via portable lab kits that sync to rate controllers, converting static maps into season-long dynamic schedules. Product innovation in biological crop-protection inputs further amplifies the need for precise micro-dosing that hinges on sensor-driven variable rate algorithms.
The Variable Rate Technology Market Report is Segmented by Crop Type (Cereals and Grains and More), by Application (Fertilizers, Crop-Protection Chemicals, and More), by Offering (Hardware and More), by Implementation Method (Map-Based VRT and More), by Farm Size (Large Farms and More) and by Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 39% of 2024 revenue for the variable rate technology market. Strong machinery penetration, supportive financing, and USDA climate-smart procurement rules anchor demand. Subsidy frameworks reward documented nutrient reductions, spurring the adoption of smart implements that capture nozzle-level logs. Rural broadband lags in parts of the Midwest and Prairie provinces, yet satellite link rollouts promise coverage boosts by 2026. Ohio State trials show a 6% yield lift when VR nitrogen intersects with drone stand counts, proof points that validate ongoing investment. Dealer ecosystems supply certified technicians who maintain fleets and interpret data, underscoring the service growth narrative.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest climber, tracking a 14.1% CAGR to 2030 as governments attach digital farming clauses to modernization spending. China's latest Five-Year Plan promotes low-carbon, high-efficiency agriculture that dovetails with targeted input delivery. India's Aadhaar-linked Farmer Registry simplifies subsidy disbursement for sensor kits, while Japan's Food and Agriculture Ministry co-funds paddy-specific variable rate seeding trials. The region's small-plot structure sparks creative solutions, including shared-service drones operated by village entrepreneurs. Water scarcity across Australia and Northern China accelerates variable-rate irrigation uptake, driving cross-border knowledge transfer and hardware imports.
Europe embeds variable rate technology adoption within sweeping climate policy. The Common Agricultural Policy for 2023-27 allocates EUR 269.5 billion (USD 312.4 billion), nearly half aimed at climate objectives that include reduced fertilizer leaching and pesticide drift. Each member state must earmark at least 25% of direct payments for eco-schemes, many of which list precision application as a qualifying practice. Countries such as the Netherlands fund digitization grants that reimburse up to 40% of sensor installations, hastening implementation. Data sovereignty rules raise compliance costs as platforms adapt to General Data Protection Regulation obligations. Nonetheless, consortium projects like Germany's 5G Testbed Agriculture expedite confidence in secure connectivity, and Pan-European carbon initiatives depend on traceable input data generated by rate controllers.
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Valmont Industries, Inc.
- Lindsay Corporation
- EarthOptics
- Hexagon AB
- CropX Technologies
- TeeJet Technologies (Spraying Systems)
- DJI
- DroneDeploy
- The Climate Corporation (Bayer AG)
- EOS Data Analytics,Inc
- SoilOptix
- Frontier Agriculture Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid digitalization of farms
- 4.2.2 Government subsidies and incentive schemes
- 4.2.3 Rising agriculture labour shortage
- 4.2.4 Satellite NB-IoT-enabled sub-acre prescriptions
- 4.2.5 Carbon credit monetization demanding input traceability
- 4.2.6 On-equipment AI chips for offline VRT analytics
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capital expenditure of VRT-ready machinery
- 4.3.2 Patchy rural connectivity infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Data ownership and sharing ambiguities
- 4.3.4 Shortage of VRT skilled agronomic service providers
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Crop Type
- 5.1.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.1.2 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.1.3 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.1.4 Commercial Crops
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Fertilizers
- 5.2.2 Crop-protection Chemicals
- 5.2.3 Soil Sensing
- 5.2.4 Yield Monitoring
- 5.2.5 Irrigation
- 5.2.6 Others (variable-rate seeding/planting, variable-rate lime and soil-amendment application)
- 5.3 By Offering
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.2 Software
- 5.3.3 Services
- 5.4 By Implementation Method
- 5.4.1 Map-based VRT
- 5.4.2 Sensor-based VRT
- 5.5 By Farm Size
- 5.5.1 Large Farms (greater than 1,000 ha)
- 5.5.2 Medium Farms (200-1,000 ha)
- 5.5.3 Small Farms (less than 200 ha)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 France
- 5.6.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East
- 5.6.4.1 Turkey
- 5.6.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.4.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5 Africa
- 5.6.5.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2 Egypt
- 5.6.5.3 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Deere & Company
- 6.4.2 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.3 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.4 Valmont Industries, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Lindsay Corporation
- 6.4.6 EarthOptics
- 6.4.7 Hexagon AB
- 6.4.8 CropX Technologies
- 6.4.9 TeeJet Technologies (Spraying Systems)
- 6.4.10 DJI
- 6.4.11 DroneDeploy
- 6.4.12 The Climate Corporation (Bayer AG)
- 6.4.13 EOS Data Analytics,Inc
- 6.4.14 SoilOptix
- 6.4.15 Frontier Agriculture Ltd





