 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850380
施工機械租賃:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Construction Equipment Rental - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
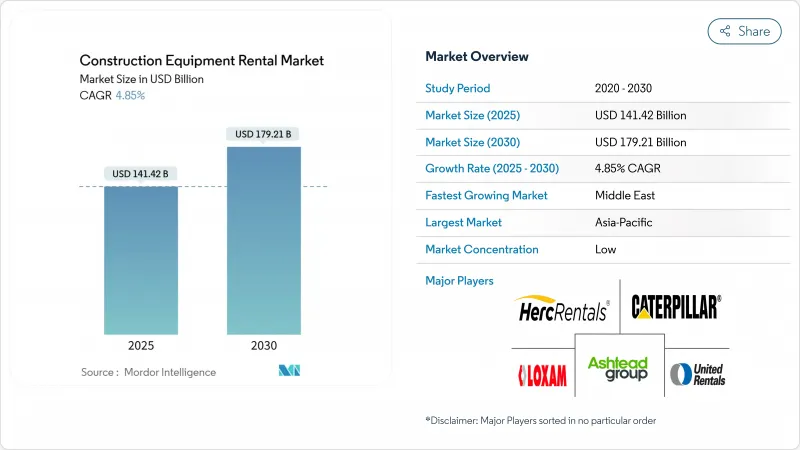
預計到 2025 年,施工機械租賃市場規模將達到 1,414.2 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 1,792.1 億美元,年複合成長率為 4.85%。
這一發展勢頭源於創紀錄的公共部門基礎設施建設項目、傾向於輕資產模式的承包商擴張以及租賃交易的快速數位化。電子機械和氫燃料電池機械的日益普及,以及基於績效的服務契約,正在重塑車隊戰略並開闢高階定價市場。亞太地區憑藉著持續的公路、鐵路和城市重建項目,保持著規模主導,而中東地區則在「2030願景」大型企劃的推動下,成為成長最快的地區。隨著主要參與者加速收購以獲得地域覆蓋率和技術能力,競爭日益激烈。遠端資訊處理驅動的車隊最佳化正在成為提高運轉率和客戶維繫的關鍵手段,在一定程度上抵消了技術純熟勞工短缺和維護多個品牌的不利影響。
全球施工機械租賃市場趨勢與洞察
基礎設施獎勵策略方案:大量計劃儲備
美國1.2兆美元的《基礎設施投資與就業法案》和印度1.4兆美元的國家基礎建設規劃正在推動多年設備需求週期。據聯合租賃公司(United Rental)稱,大型企劃在租賃訂單中所佔佔有率不斷成長,從而確保了計劃整個生命週期內設備的可預測利用率。承包商越來越傾向於為各個階段租賃專用機械,以避免資金閒置,而這些專案中的可再生能源部分正在推動氫動力和純電動土方機械的早期應用。亞太和北美地區受益最大,這得益於其密集的物流網路和成熟的租賃分店,能夠提供多樣化的設備組合。公共規模也鼓勵小型供應商透過數位化交易平台進行設備企業聯合組織,將服務範圍擴展到一線城市以外的地區。
承包商從資本支出轉向營運支出
高利率和不穩定的訂單迫使車隊管理者租賃高達 80% 的現場設備,從而顯著降低資產負債率。 37% 的美國承包商表示推遲了採購,這印證了營運支出模式日益成長的吸引力。設備即服務 (EaaS) 合約將維護和殘值風險轉移給租賃專家,使承包商能夠將資金重新投入核心計劃交付。中小企業可以透過獲得以前預算以外的高階機械設備來獲得競爭優勢。同時,租賃公司受益於更高的設備周轉率和更快的車隊更新能力,確保符合日益嚴格的排放法規。
熟練操作人員短缺會增加停機風險
到2026年,將需要新增8萬多名重型設備操作員,而現有操作員中有41%將退休。人手不足導致工地租賃設備利用率不足,延長計劃工期並降低租賃收益。經驗不足的操作員引發的安全事故也會推高保險和維修成本。大型租賃公司目前提供基於模擬器的培訓,據稱已將新員工培訓時間從六個月縮短至七週,並將責任索賠減少了兩位數。然而,人才缺口限制了先進電動和氫燃料電池設備的快速部署,因為這些設備需要更高的技術水平。
細分市場分析
預計到2024年,土木機械將佔全球施工機械租賃市場收入的40.98%。挖土機和後鏟式裝載機是道路、地基和溝槽施工的主力設備,高峰期運轉率超過70%。在這一類別中,受都市區噪音和廢氣排放法規的推動,電動小型挖土機的複合年成長率將達到8.81%。
由於亞洲和海灣國家高層建築的激增,起重機和加長型堆高機等物料輸送設備的重要性下降。而土木機械車隊的遠端資訊處理整合,則增強了預測性維護能力,從而延長了資產壽命,並提高了客戶滿意度。
售後服務領域也出現了類似的轉變,租賃公司將操作員培訓和全天候現場支援合約捆綁在一起,以此證明提高每日租金的合理性。大型平土機和推土機的數位雙胞胎正在進行試驗,以模擬磨損模式並確定最佳更換週期。結合推土機自主控制系統的維修,這些技術進步可望進一步提高生產效率,但不同地區的監管接受度不一。因此,車隊所有者正在優先考慮並分散投資於運轉率更高的都會區計劃,同時密切關注農村地區的需求彈性。
到2024年,內燃機仍將維持85.74%的市場佔有率,這得益於完善的加氫基礎設施和操作人員的熟悉程度。然而,隨著各國政府強制要求在人口密集的都市區地區實現零排放,施工機械租賃市場正在改變。氫燃料電池原型機預計到2030年將以16.99%的複合年成長率成長,成為成長最快的領域,這得益於其快速加氫和比電池系統更長的運作週期。電池電動馬達型在小型挖土機和剪式升降機成長最為迅速,這些機型可以有效緩解里程焦慮,並允許在現場進行夜間充電。
混合動力系統可以作為一種過渡技術。聯合租賃公司(United Rental)報告稱,將發電機與電池儲能組結合使用,可節省高達 80% 的燃料,並降低 34% 的成本。然而,要推廣應用,必須對殘值有清楚的了解。高容量鋰電池售後市場價格的不確定性阻礙了車隊的積極部署。為了降低風險,大型租賃業者正在採用基於訂閱的升級模式,以便在技術或法規變更時快速切換。
這份施工機械租賃報告按設備類型(土木機械(例如後鏟式裝載機)、其他)、驅動類型(內燃機、其他)、應用領域(住宅建築、其他)、租賃管道(線下、線上)、服務類型(短期租賃、其他)和地區(北美、其他)進行細分。市場預測以價值(美元)和數量(台)為單位。
區域分析
2024年,亞太地區佔全球租賃收入的39.01%,這主要得益於中國「一帶一路」計劃的推進、印度創紀錄的資本支出以及日本持續穩定的公共工程項目。 2024年,中國整車製造商(OEM)佔全球電動施工機械出貨量的75%,並積極向東南亞出口。印度的建築業預計在2030年為GDP貢獻1兆美元,這將推動大型租賃公司在全國擴張。日本在經歷了兩個季度的機械訂單萎縮後,隨著半導體分店投資的增加,於2025年初恢復成長。
中東是成長最快的地區,預計到2030年年均複合成長率將達到7.56%。在沙烏地阿拉伯,包括利雅德地鐵和NEOM新城計劃在內的「2030願景」規劃正在推動租賃需求以每年超過12%的速度成長。阿拉伯聯合大公國(阿拉伯聯合大公國)也同樣受益於大型走廊和綜合用途開發項目,例如耗資80億澳元的馬薩爾社區。起重機和加長型堆高機製造商正將其車隊遷往海灣地區,以利用當地的高運轉率和可觀的收益。
北美地區維持6.58%的健康複合年成長率。大規模的基礎建設和強勁的私人企業建設支撐著穩定的運轉率。歐洲的成長放緩至5.30%,但嚴格的第五階段柴油排放標準和市政零碳排放指令使其在低排放氣體市場佔據領先地位。南美洲的複合年成長率達到7.34%,這得益於交通走廊的現代化和商品產業的復甦。非洲的平均成長率為6.90%,但各市場的資金籌措管道和監管透明度仍不均衡。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 大型基礎設施獎勵策略計劃儲備
- 承包商資本支出向營運支出轉變
- 嚴格的ESG目標推動電力租賃
- 按付費使用制和基於績效的合約模式
- 新興市場數位租賃平台的爆炸性成長
- 數據驅動的車輛最佳化可提高客戶投資報酬率
- 市場限制
- 維護多個品牌的複雜性
- 熟練操作人員短缺會增加停機風險
- OEM廠商蠶食直接面對消費者的租賃業務
- 鋰電池資產殘值波動
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管格局
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
5. 市場規模及成長預測(價值,十億美元)
- 按設備
- 土木機械
- 後鏟式裝載機
- 裝載機
- 挖土機
- 推土機
- 滑移裝載機
- 其他土木工程
- 物料輸送設備
- 起重機
- 堆高機
- 自動卸貨卡車
- 加長型堆高機
- 其他物料輸送
- 混凝土及道路施工機械
- 電力和能源設備
- 其他設備
- 土木機械
- 按驅動類型
- 內燃機
- 混合
- 電
- 氫燃料電池
- 透過使用
- 住宅建設
- 商業建築
- 工業/製造業
- 基礎建設(道路、橋樑、港口)
- 採礦和採石
- 石油和天然氣
- 租賃頻道
- 離線(基於分店)
- 線上平台
- 按服務類型
- 短期租賃(少於1個月)
- 中期租賃(1至12個月)
- 長期出租(1年或以上)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 其他亞太地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- United Rentals Inc.
- Ashtead Group plc(Sunbelt Rentals)
- Herc Rentals Inc.
- H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- Loxam
- Caterpillar Inc.(Cat Rental Store)
- Sumitomo Corp.
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co. Ltd.
- Liebherr-International AG
- Kanamoto Co. Ltd.
- CNH Industrial NV
- HSS Hire Group plc
- Boels Rental
- Cramo Oyj
- Ahern Rentals
- Maxim Crane Works
- Ramirent
- Coates Hire
- Sarens nv/sa
- MyCrane
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The construction equipment rental market reached USD 141.42 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to expand at a 4.85% CAGR, lifting revenue to USD 179.21 billion by 2030.

Momentum stems from record public-sector infrastructure pipelines, widening contractor preference for asset-light models, and rapid digitalization of rental transactions. Rising adoption of electric and hydrogen fuel cell machinery, combined with outcome-based service contracts, is reshaping fleet strategies and opening premium pricing niches. Asia-Pacific maintains scale leadership on the back of sustained highway, rail, and urban-renewal programs, while the Middle East delivers the fastest regional growth supported by Vision 2030 mega-projects. Competitive intensity is increasing as larger players accelerate acquisitions to gain geographic density and technology capabilities. Telematics-enabled fleet optimization is emerging as a critical lever for utilization gains and customer retention, partly offsetting headwinds from skilled-labor shortages and multi-brand maintenance complexity.
Global Construction Equipment Rental Market Trends and Insights
Infrastructure-Stimulus Megaproject Pipeline
The USD 1.2 trillion U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and India's USD 1.4 trillion National Infrastructure Pipeline are fuelling multi-year equipment demand cycles. United Rentals reports that megaprojects already account for a rising share of rental orders, underpinning predictable utilisation across full project lifecycles. Contractors increasingly prefer renting specialised machines for discrete phases to avoid idle capital, while renewable-energy components of these programmes are driving early uptake of hydrogen and battery-electric earthmovers. Asia-Pacific and North America benefit most, given their dense logistics networks and established rental branches able to supply a diverse fleet mix. The scale of public works is also encouraging smaller providers to syndicate equipment via digital exchanges, widening access beyond tier-one cities.
Shift from CAPEX to OPEX Among Contractors
High interest rates and volatile backlogs are prompting fleet managers to rent up to 80% of site equipment, significantly reducing balance-sheet leverage. Deferred purchases, reported by 37% of U.S. contractors, underline the growing appeal of operational expenditure models. Equipment-as-a-Service agreements transfer maintenance and residual-value risks to rental specialists, enabling contractors to redeploy capital toward core project execution. Smaller firms gain competitive parity by accessing premium machines previously beyond their budget. Rental firms, in turn, profit from higher equipment rotation rates and the ability to refresh fleets faster, ensuring compliance with tightening emission norms.
Skilled-Operator Scarcity Elevates Downtime Risk
More than 80,000 additional heavy-equipment operators will be needed by 2026, while 41% of current operators approach retirement. Under-staffed sites struggle to utilise rented machinery fully, inflating project timelines and eroding rental yield. Safety incidents linked to inexperienced operators also raise insurance and repair costs. Leading renters now offer simulator-based training that compresses onboarding from six months to seven weeks, a move credited with reducing damage claims by double digits. Nevertheless, the talent gap limits rapid deployment of advanced electric and hydrogen models that require additional technical proficiency.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Stringent ESG Targets Accelerating Electric Rentals
- Digital Rental-Platform Explosion in Emerging Markets
- High Multi-Brand Maintenance Complexity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Earthmoving machinery accounted for 40.98% of the global construction equipment rental market revenue in 2024. Excavators and backhoe loaders remain staple choices for roadbeds, foundations, and trenching, with utilisation rates often surpassing 70% during peak seasons. Within this class, electric mini-excavators are recording an 8.81% CAGR, propelled by urban noise and emission restrictions.
Material-handling units such as cranes and telehandlers are given secondary importance due to high-rise expansions in Asia and the Gulf states. Telematics integration across earthmoving fleets is bolstering predictive maintenance, thereby extending asset life and raising customer satisfaction indexes.
A parallel shift is visible in aftermarket services, where renters bundle operator training and 24/7 field support agreements to justify premium day rates. Digital twins of large graders and dozers are being trialled to simulate wear patterns, informing optimal replacement cycles. Coupled with autonomous control retrofits on bulldozers, these advancements promise step-change productivity, though regulatory acceptance varies by jurisdiction. Fleet owners are therefore staggering investments, prioritising high-utilisation metro projects while monitoring rural demand elasticity.
Internal-combustion units retained an 85.74% share in 2024, underscoring entrenched refuelling infrastructure and operator familiarity. Yet the construction equipment rental market is witnessing an inflection as governments roll out zero-emission mandates for dense urban zones. Hydrogen fuel cell prototypes log the highest forecast CAGR at 16.99% through 2030, buoyed by quick refuelling and extended duty cycles relative to battery systems. Battery-electric models are scaling fastest in compact excavators and scissor lifts, segments where range anxiety is limited and charging can occur overnight on-site.
Hybrid power systems act as a bridge technology. United Rentals reports up to 80% fuel savings and 34% cost reductions when pairing generators with battery energy-storage packs. Adoption, however, hinges on clear residual-value outlooks: uncertain aftermarket pricing for high-capacity lithium batteries dampens aggressive fleet rollouts. To mitigate risk, leading renters use subscription-based upgrades, allowing rapid turnover should technology or regulation shift.
The Construction Equipment Rental Report is Segmented by Equipment Type (Earthmoving Equipment (Backhoe Loaders and More), and More), Drive Type (IC Engine and More), Application (Residential Construction and More), Rental Channel (Offline and Online), Service Type (Short-Term Rental, and More), and Geography (North America and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 39.01% of global rental revenue in 2024, underpinned by China's Belt and Road extensions, India's record capital-expenditure outlays, and Japan's steady public-works pipeline. Chinese OEMs captured 75% of global electric construction-equipment shipments in 2024, exporting aggressively to Southeast Asia. India's construction sector is on course to add USD 1 trillion to GDP by 2030, energising nationwide branch expansion by leading renters. Japan, recovering from two quarters of machinery order contraction, returned to growth in early 2025 as semiconductor-plant investments escalated.
The Middle East represents the fastest-growing territory at 7.56% CAGR through 2030. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 pipeline, including Riyadh Metro and NEOM city projects, is pushing rental demand beyond 12% annualised growth. The UAE likewise benefits from large corridors and mixed-use developments such as the AED 8 billion Masaar community. Companies with crane and telehandler specialities are relocating fleets to the Gulf to capitalise on strong utilisation rates and attractive yields.
North America shows a healthy 6.58% CAGR. Large infrastructure packages and robust private-sector industrial builds underpin stable fleet utilisation. Europe posts slower 5.30% growth, yet leads in low-emission rentals thanks to stringent Stage V diesel norms and municipal zero-carbon mandates. South America advances at 7.34% CAGR, fuelled by transport-corridor modernisation and commodity-sector revitalisation. Africa averages 6.90% growth, although access to financing and regulatory clarity remains uneven across markets.
- United Rentals Inc.
- Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt Rentals)
- Herc Rentals Inc.
- H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- Loxam
- Caterpillar Inc. (Cat Rental Store)
- Sumitomo Corp.
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co. Ltd.
- Liebherr-International AG
- Kanamoto Co. Ltd.
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- HSS Hire Group plc
- Boels Rental
- Cramo Oyj
- Ahern Rentals
- Maxim Crane Works
- Ramirent
- Coates Hire
- Sarens n.v./s.a.
- MyCrane
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Infrastructure-stimulus megaproject pipeline
- 4.2.2 Shift from CAPEX-to-OPEX among contractors
- 4.2.3 Stringent ESG targets accelerating electric rentals
- 4.2.4 Pay-per-use & outcome-based contracting models
- 4.2.5 Digital rental-platform explosion in emerging markets
- 4.2.6 Data-driven fleet optimisation boosts customer ROI
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High multi-brand maintenance complexity
- 4.3.2 Skilled-operator scarcity elevates downtime risk
- 4.3.3 OEMs' direct-to-customer rental cannibalisation
- 4.3.4 Residual-value volatility for lithium-battery assets
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Equipment Type
- 5.1.1 Earthmoving Equipment
- 5.1.1.1 Backhoe Loaders
- 5.1.1.2 Loaders
- 5.1.1.3 Excavators
- 5.1.1.4 Bulldozers
- 5.1.1.5 Skid-Steer Loaders
- 5.1.1.6 Other Earthmoving
- 5.1.2 Material Handling Equipment
- 5.1.2.1 Cranes
- 5.1.2.2 Forklifts
- 5.1.2.3 Dump Trucks
- 5.1.2.4 Telehandlers
- 5.1.2.5 Other Material Handling
- 5.1.3 Concrete & Road Construction Equipment
- 5.1.4 Power & Energy Equipment
- 5.1.5 Other Equipment
- 5.1.1 Earthmoving Equipment
- 5.2 By Drive Type
- 5.2.1 IC Engine
- 5.2.2 Hybrid
- 5.2.3 Electric
- 5.2.4 Hydrogen Fuel Cell
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Residential Construction
- 5.3.2 Commercial Construction
- 5.3.3 Industrial / Manufacturing
- 5.3.4 Infrastructure (Roads, Bridges, Ports)
- 5.3.5 Mining & Quarrying
- 5.3.6 Oil & Gas
- 5.4 By Rental Channel
- 5.4.1 Offline (Branch-based)
- 5.4.2 Online Platforms
- 5.5 By Service Type
- 5.5.1 Short-Term Rental (less than 1 Month)
- 5.5.2 Medium-Term Rental (1 - 12 Months)
- 5.5.3 Long-Term Rental (Over 1 Year)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of APAC
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Chile
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East & Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global-level Overview, Market-level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 United Rentals Inc.
- 6.4.2 Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt Rentals)
- 6.4.3 Herc Rentals Inc.
- 6.4.4 H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- 6.4.5 Loxam
- 6.4.6 Caterpillar Inc. (Cat Rental Store)
- 6.4.7 Sumitomo Corp.
- 6.4.8 Hitachi Construction Machinery Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Liebherr-International AG
- 6.4.10 Kanamoto Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.11 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.12 HSS Hire Group plc
- 6.4.13 Boels Rental
- 6.4.14 Cramo Oyj
- 6.4.15 Ahern Rentals
- 6.4.16 Maxim Crane Works
- 6.4.17 Ramirent
- 6.4.18 Coates Hire
- 6.4.19 Sarens n.v./s.a.
- 6.4.20 MyCrane










