 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850355
固定線路通訊:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Fixed-Line Communications - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
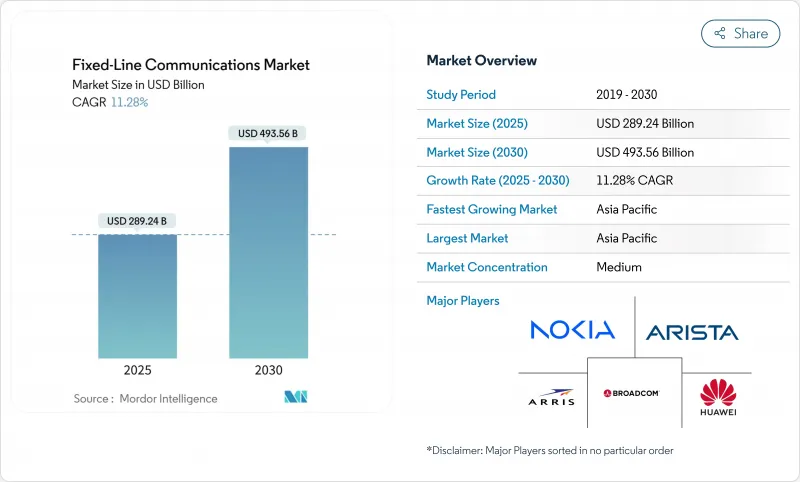
預計到 2025 年,固定線路通訊市場規模將達到 2,892.4 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 4,935.6 億美元,在此期間的複合年成長率為 11.28%。
持續成長反映了固定通訊市場如何支援雲端運算、人工智慧工作負載和5G回程傳輸需求,鞏固了其作為基礎數位基礎設施的地位。歐盟、美國和亞太地區多個國家政府採納的對稱Gigabit目標持續加速光纖部署,而資料主權規則則鼓勵企業將對延遲敏感的流量保留在國家網路內。超大規模資料中心的快速建設給傳統骨幹網路帶來了壓力,促使營運商進行800G和Terabit光纖升級,並增加了設備需求。同時,開放標準計劃和軟體定義網路正在將競爭優勢從硬體能力轉移到可編程平台,為能夠滿足低延遲服務等級承諾的新供應商創造了機會。監管機構不斷施壓以簡化道路使用許可流程,這表明,固定通訊市場能否迅速滿足潛在需求,將取決於其普及速度,而非最終用戶的意願。
全球固定通訊市場趨勢與洞察
城市叢集對Gigabit寬頻的需求日益成長
主要亮點
- 遠距辦公、多流 4K 視訊和雲端遊戲使得千兆Gigabit服務成為大城市的基本需求。營運商再也不能依賴曾經抑制容量成本的超額訂閱規則。相反,他們正在多用戶住宅深處部署對稱光纖,以確保高吞吐量路徑。混合用途建築中的企業租戶也要求保證上行鏈路速度,用於雲端備份和視訊協作,這使得通訊業者能夠捆綁高級服務等級協定 (SLA),並提高每用戶平均收益。人口密集的地區縮短了光纖建設的投資回收期,促使營運商採取積極的促銷定價策略,以在 5G 固定無線替代方案普及之前搶佔市場佔有率。市政數位股權政策透過為低收入家庭提供網路連線補貼,進一步促進了光纖的普及,並在光纖部署後間接提高了高級連線套餐的普及率。
現有營運商和OrtoNet正在大規模部署光纖到戶服務。
隨著AT&T承諾在2026年前為3,000萬戶家庭提供光纖到府(FTTH)服務,現有通訊業者正從逐步升級銅纜轉向全面光纖替換。一項極具挑戰性的替代網路計畫(altonet)在基礎設施資金的支持下,正積極拓展服務不足的郊區,迫使急於維護自身網路覆蓋的傳統營運商加快行動。美國的BEAD計畫等補貼計畫正將數十億美元投入農村地區建設,進一步降低了成本,使深層光纖部署更具優勢。更快的部署技術(例如微溝槽挖掘、連接式光纖接入)結合管道再利用,即使在中等密度地區也能降低每戶的資本支出,並保持可觀的內部收益率。從長遠來看,建立無所不在的光纖平台將使營運商能夠提升銷售邊緣運算託管和私有5G服務。
最後一公里光纖建設:高資本投入和較長的投資回報週期
在農村地區,光纖入戶的成本可能超過1,000美元,在岩石或山區,成本還會更高。規模較小的通訊業者缺乏規模經濟,資金籌措成本顯著更高,而且其債務契約通常限制了網路部署進度。當施工人員需要在電線電線杆安裝光纖時,關於前期準備和安裝費用的法律糾紛會導致數月延誤。認證光纖連接器的薪資上漲也使問題更加複雜,有些市場甚至提供以前只有行動網路工程師才能獲得的簽約獎金。雖然政府補貼有助於降低部分建設成本,但供應商和技術的限制會進一步推高計劃總成本,超出投資者通常的投資回收期。
細分市場分析
光纖電纜鞏固了其作為固定線路通訊市場骨幹網路的地位,預計到2024年將佔總收入的28.3%。對800G連貫傳輸日益成長的需求正推動營運商加快外部線路升級,相關的光線路終端和被動分路器也推動接入設備支出以13.9%的複合年成長率成長。隨著營運商用可插拔光纜取代傳統的100G光纜,傳輸設備供應商從中受益,因為可插拔光纜可將每位元功耗降低一半,從而提高整體網路效率。隨著軟體定義控制平面對中心局高效能葉脊式網路架構的需求,交換設備收益也將同步成長。
隨著家庭用戶普遍採用 Wi-Fi 7 路由器和網狀網路節點,用戶端設備 (CPE) 也持續邁向Gigabit網路時代。供應商現在將託管式 Wi-Fi 分析功能與 CPE 捆綁銷售,使營運商能夠遠端排查家庭網路效能問題,從而減少上門服務次數。同時,固定無線 CPE 的出貨量將在 2024 年超過 DOCSIS 數據機,這表明即使光纖網路繼續主導通訊網路市場,無線方案也能在某些部署場景中佔據優勢。
到2024年,固定寬頻資訊服務將佔總收入的68.9%,這證實了按分鐘收費向頻寬收益的不可逆轉的轉變。 IPTV和其他增值平台將緊隨其後,複合年成長率將達到12.4%,反映出營運商正在將其光纖投資轉化為內容和雲端遊戲的經常性收益。隨著企業轉向雲端PBX服務,家庭用戶完全依賴行動設備,傳統固定語音正穩步下滑。
將網路連線、網路安全和編配結合的託管服務套件正日益受到歡迎,尤其是在沒有內部 IT 團隊的中型企業中。由網路內 AI 引擎驅動的影片分析能夠實現精準廣告投放,在無需額外資本支出的情況下提高淨利率。
固定線路通訊市場報告按產品類型(傳輸設備、交換設備、其他)、服務類型(固定語音、固定寬頻數據、其他)、技術(數位用戶線路、同軸電纜(Docsis)、其他)、最終用戶(住宅用戶、中小企業、大型企業、其他)和地區進行細分。
區域分析
預計亞太地區將鞏固其作為全球最大通訊市場的地位,到2024年將佔全球收入的38.7%,年複合成長率達11.42%。中國10G城市網路的強制性建設將推動全國範圍內的光纖部署,而印度的「數位印度」(Digital Bharat)計畫將促使公私合營企業每年新增超過50萬公里的線路。日本和韓國的營運商將升級到25G和50G PON,以支援沉浸式媒體和工業自動化。
在北美,BEAD計劃正在幫助縮小農村地區的網路差距。一級營運商正在加快都市區的網路建設,並與衛星寬頻營運商競爭,以獲取長期用戶。 Verizon固定無線用戶的成長凸顯了替代風險,但隨著電線杆安裝改革縮短了許可等待時間,光纖部署量創下以季度為基礎新高。加拿大的開放接取規則迫使現有業者批發光纖環路,從而促進了零售競爭,在不損害網路所有者經濟利益的前提下刺激了收購率。
歐洲的《Gigabit基礎設施法案》將透過簡化溝槽核准和實施「一次挖掘」調整措施,使土木工程成本降低兩位數。法國和西班牙的光纖到戶(FTTH)普及率已超過75%,顯示一旦Gigabit服務普及,市場需求將保持強勁。德國起步緩慢,但在私人企業Altonet的支持下,發展速度加快;英國的「Gigabit計劃」競標正在將網路覆蓋範圍擴展到偏遠鄉村。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 都市區叢集對Gigabit寬頻的需求日益成長
- 現有營運商和OrtoNet公司大規模部署FTTH(光纖到府)網路
- 雲端/超大規模資料中心回程傳輸需求
- 政府普遍服務和補貼計劃(BEAD、RDOF、歐盟CEF-2)
- 重複利用傳統銅管可降低土木工程成本(未經充分通報)
- 邊緣運算密集化需要超低延遲的固定連結(未充分通報)
- 市場限制
- 最後一公里光纖鋪設需要高資本投入和較長的投資回收期。
- 5G FWA 與衛星寬頻之間的替代風險
- 光纖熔接和測試領域技術純熟勞工短缺
- 市政道路通行權和電線杆安裝延誤(漏報)
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管格局
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 投資分析
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依產品類型
- 傳動設備
- 開關設備
- 接取設備(DSLAM、OLT 等)
- 用戶端設備(路由器、機上盒、光網路終端)
- 光纖電纜
- 其他
- 按服務類型
- 固定語音
- 固定寬頻數據
- IPTV/附加價值服務
- 依技術
- 數位用戶線路
- 同軸(Docsis)
- 光纖(FTTx/FTTH)
- 混合光纖同軸
- 最終用戶
- 住宅
- 小型企業
- 主要企業
- 政府和公共部門
- 資料中心
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- ASEAN
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲國家
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Nokia Corp.
- ZTE Corp.
- Broadcom Inc.
- Arris(CommScope)
- Arista Networks Inc.
- Avaya Inc.
- Allied Telesis Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Prysmian Group
- Adtran Inc.
- Calix Inc.
- DZS Inc.
- Ribbon Communications
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- FiberHome Telecommunication
- CommScope Holding Co.
- NEC Corp.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The fixed-line communications market size reaches USD 289.24 billion in 2025 and is forecast to touch USD 493.56 billion by 2030, advancing at an 11.28% CAGR over the period.

Sustained growth reflects how the fixed-line communications market underpins cloud computing, artificial intelligence workloads, and 5G back-haul requirements, cementing its role as foundational digital infrastructure. Symmetric gigabit targets adopted by the European Union, the United States, and multiple Asia-Pacific governments continue to accelerate fiber roll-outs, while data-sovereignty rules spur enterprises to keep latency-sensitive traffic on national networks. Rapid hyperscale data-center construction strains legacy backbones, pushing operators toward 800 G and terabit optical upgrades that lift equipment demand. In parallel, open-standards initiatives and software-defined networking shift competitive advantage from hardware features toward programmable platforms, creating opportunities for new vendors that can match low-latency service-level commitments. Mounting regulatory pressure to streamline right-of-way permits suggests that deployment speed, not end-user appetite, will determine how fast the fixed-line communications market captures its addressable demand.
Global Fixed-Line Communications Market Trends and Insights
Rising demand for gigabit-speed broadband in urban clusters
Key Highlights
- Remote work, multi-stream 4K video, and cloud gaming have made multi-gigabit service a baseline expectation in major cities. Operators can no longer rely on oversubscription rules that once kept capacity costs in check; instead, they push symmetric fiber deeper into apartment blocks to guarantee high-throughput paths. Enterprise tenants in mixed-use buildings additionally request guaranteed uplink speeds for cloud backup and video collaboration, allowing carriers to bundle premium SLAs at higher average revenue per user. Dense geography shortens fiber build paybacks, encouraging aggressive promotional pricing that locks in market share before 5G fixed-wireless alternatives gain traction. Municipal digital-equity policies further amplify adoption by underwriting low-income household connections, indirectly boosting take rates for premium tiers once the fiber is in place.
Massive fiber-to-the-home roll-outs by incumbents and altnets
Incumbent telcos have shifted from incremental copper upgrades to full-scale fiber replacement, as seen in AT&T's pledge to pass 30 million premises with FTTH by 2026. Challenger altnets, backed by infrastructure funds, pick off pockets of under-served suburbs, forcing faster reactions from legacy operators eager to defend their base. Subsidy frameworks such as BEAD in the United States redirect billions toward rural builds, further tilting the cost equation in favor of deep fiber. The combination of faster deployment techniques (micro-trenching, connectorized drops) and duct re-use lowers capex per home, keeping internal rates of return attractive even in mid-density territories. Longer term, establishing a ubiquitous fiber platform positions carriers to upsell edge-compute hosting and private 5G services.
High capex and long ROI cycles for last-mile fiber
Passing a single rural premise can cost more than USD 1,000, a figure that climbs sharply in rocky or mountainous terrain. Smaller carriers without scale economics shoulder significantly higher financing costs, and their debt covenants often dictate slower roll-out schedules. Where crews must attach fiber to utility poles, make-ready work and legal disputes over attachment fees add months of delay. Wage inflation for certified fiber splicers compounds the problem, with some markets offering signing bonuses that previously only mobile-network engineers received. Although government grants defray part of the build expense, restrictions on permissible vendors or technology can push total project cost back up, stretching payback periods beyond typical investor horizons.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cloud/hyperscale data-center back-haul requirements
- Government universal-service and subsidy programs (BEAD, RDOF, EU CEF-2)
- Substitution risk from 5G fixed-wireless and satellite broadband
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fiber-optic cables generated 28.3% of revenue in 2024, cementing their position as the volume backbone of the fixed-line communications market. Intensifying demand for 800 G coherent transmission pushes operators to accelerate outside-plant upgrades, while associated optical line terminals and passive splitters lift access-equipment spend at a 13.9% CAGR. Transmission-equipment vendors benefit as carriers swap legacy 100 G optics for pluggables that halve power per bit, enhancing total network efficiency. Switching gear revenue expands in tandem because software-defined control planes require high-performance leaf-spine fabrics inside central offices.
Customer-premises equipment continues to ride the multi-gigabit wave as households adopt Wi-Fi 7 routers and mesh nodes. Vendors now bundle managed Wi-Fi analytics that let carriers troubleshoot in-home performance remotely, reducing truck rolls. Meanwhile, fixed-wireless CPE shipments overtook DOCSIS modems in 2024, showing that wireless substitution can capture specific deployment scenarios even as the fixed-line communications market size for fiber remains dominant.
Fixed broadband data services accounted for 68.9% of total 2024 revenue, confirming the irreversible pivot from minutes-based billing to bandwidth monetization. IPTV and other value-added platforms follow with a 12.4% CAGR, reflecting how carriers translate sunk fiber investments into recurring content and cloud-gaming revenue. Traditional fixed voice continues its secular slide as enterprises migrate to cloud PBX offerings and households rely exclusively on mobile.
Managed service bundles that merge connectivity with cybersecurity and edge-compute orchestration gain favor, especially among mid-sized enterprises lacking in-house IT teams. Enhanced video analytics powered by on-network AI engines enable ultra-targeted advertising, adding incremental margins without additional capex.
The Fixed-Line Communication Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Transmission Equipment, Switching Equipment, and More), Service Type (Fixed Voice, Fixed Broadband Data, and More), Technology (Digital Subscriber Line, Coaxial (Docsis), and More), End User (Residential, Small and Medium Enterprises, Large Enterprises, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific retained 38.7% of 2024 revenue and is projected to expand at an 11.42% CAGR, cementing its position as the largest fixed-line communications market. China's mandate for 10 G city networks drives nationwide fiber deployment, while India's Digital Bharat program triggers public-private joint ventures that add more than 0.5 million route-kilometers annually. Japanese and Korean operators upgrade to 25 G and 50 G PON to support immersive media and industrial automation.
North America leverages the BEAD program to close rural gaps. Tier-1 carriers accelerate urban builds, racing satellite broadband players to lock in long-term subscribers. Verizon's fixed-wireless subscriber gains highlight substitution risk, yet fiber build counts hit new quarterly highs as pole-attachment reforms shorten permitting queues. Canadian open-access rules compel incumbents to wholesale fiber loops, fostering retail competition that stimulates take-rates without eroding network-owner economics.
Europe's Gigabit Infrastructure Act streamlines trenching approvals and enforces "dig-once" coordination, cutting civil-works costs by double digits. France and Spain now post FTTH take-up rates above 75%, proving demand elasticity once ubiquitous gigabit service is available. Germany's late start accelerates on the back of private-equity-funded altnets, while the United Kingdom's Project Gigabit auctions extend coverage to hard-to-reach hamlets.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Nokia Corp.
- ZTE Corp.
- Broadcom Inc.
- Arris (CommScope)
- Arista Networks Inc.
- Avaya Inc.
- Allied Telesis Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Prysmian Group
- Adtran Inc.
- Calix Inc.
- DZS Inc.
- Ribbon Communications
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- FiberHome Telecommunication
- CommScope Holding Co.
- NEC Corp.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for gigabit-speed broadband in urban clusters
- 4.2.2 Massive fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) roll-outs by incumbents and altnets
- 4.2.3 Cloud/hyperscale data-center back-haul requirements
- 4.2.4 Government universal-service and subsidy programs (BEAD, RDOF, EU CEF-2)
- 4.2.5 Repurposing of legacy copper ducts lowers civil-works cost (under-reported)
- 4.2.6 Edge-compute densification needs ultra-low-latency fixed links (under-reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capex and long ROI cycles for last-mile fiber
- 4.3.2 Substitution risk from 5G FWA and satellite broadband
- 4.3.3 Skilled-labor shortages for fiber splicing and testing
- 4.3.4 Municipal right-of-way and pole-attachment delays (under-reported)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Transmission Equipment
- 5.1.2 Switching Equipment
- 5.1.3 Access Equipment (DSLAM, OLT, etc.)
- 5.1.4 Customer-Premises Equipment (Routers, STB, ONT)
- 5.1.5 Fiber-optic Cables
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Fixed Voice
- 5.2.2 Fixed Broadband Data
- 5.2.3 IPTV / Value-added Services
- 5.3 By Technology
- 5.3.1 Digital Subscriber Line
- 5.3.2 Coaxial (Docsis)
- 5.3.3 Fiber (FTTx/FTTH)
- 5.3.4 Hybrid Fiber-Coax
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Residential
- 5.4.2 Small and Medium Enterprises
- 5.4.3 Large Enterprises
- 5.4.4 Government and Public Sector
- 5.4.5 Data Centers
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- 6.4.2 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.3 Nokia Corp.
- 6.4.4 ZTE Corp.
- 6.4.5 Broadcom Inc.
- 6.4.6 Arris (CommScope)
- 6.4.7 Arista Networks Inc.
- 6.4.8 Avaya Inc.
- 6.4.9 Allied Telesis Inc.
- 6.4.10 Corning Inc.
- 6.4.11 Prysmian Group
- 6.4.12 Adtran Inc.
- 6.4.13 Calix Inc.
- 6.4.14 DZS Inc.
- 6.4.15 Ribbon Communications
- 6.4.16 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.17 Juniper Networks Inc.
- 6.4.18 FiberHome Telecommunication
- 6.4.19 CommScope Holding Co.
- 6.4.20 NEC Corp.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment








