 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1836623
細菌生物防治劑:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Bacterial Biopesticides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
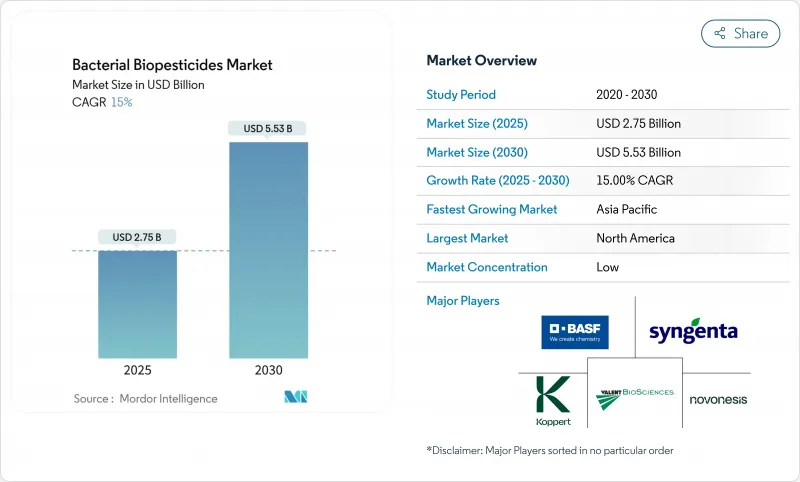
細菌生物農藥市場規模預計在 2025 年達到 27.5 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 55.3 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 15%。
市場成長的動力來自監管部門的快速核准、消費者對無農藥殘留農產品日益成長的需求、有機農業的擴張以及提高製劑穩定性和田間藥效的技術進步。根據 FiBL 預測,2023 年全球有機農業面積將達到 9,890 萬公頃,成長 2.6%。蘇力菌(Bt) 佔據市場主導地位,銷售額佔比達 74%,而枯草芽孢桿菌則因其兼具病蟲害防治和植物生長促進特性而呈現快速成長。精準種子處理應用、用於受控環境農業的液體製劑以及主要農化公司的產品組合整合正在支持市場擴張。細菌生物農藥的採用率受到低溫運輸儲存要求和與化學替代品相比藥效較慢的影響,各公司正在努力在競爭日益激烈的市場中應對這些挑戰。
全球細菌生物農藥市場趨勢與洞察
監管和政策支持
歐洲生物農藥的核准流程已從九年縮短至約三年,涵蓋了100多種待核准物質。歐盟委員會計劃於2025年實施新的歐盟法規,以在第四季前最佳化生物農藥的核准流程。 2026年《生物技術法案》將著重於填補當前的監管空白。巴西也取得了類似的進展,核准了一種惰性伯克氏菌細胞的生物農藥產品。美國環保署(EPA)正在減少《聯邦殺蟲劑、殺菌劑和滅鼠劑法案》(FIFRA)下的申請積壓。這些監管變化將擴大登記機會,降低合規成本,並使小型企業能夠進入細菌生物農藥市場。
人們越來越意識到傳統農藥的危害
研究表明,合成農藥會導致生物多樣性喪失和土壤劣化,這正在影響高階零售通路的購買決策。麻省理工學院的一項2025年研究顯示,全球31%的農業土壤面臨農藥污染的高風險。北美和歐洲的零售商正在實施嚴格的殘留限量,並青睞零殘留生物製品。隨著種植者適應這些要求,細菌已從一種僅限有機的解決方案發展成為綜合蟲害管理方案的重要組成部分。這種轉變正在推動細菌生物農藥市場的成長,尤其是對於收穫前間隔較短的作物。
低溫運輸物流限制生物製藥的保存期限
活孢子製劑通常在25°C以上就會失去活力,需要冷藏運輸和儲存,增加了最終成本。這項挑戰在赤道地區市場尤其明顯,因為這些地區的經銷網路規模較小,缺乏溫控儲存設施。雖然新的封裝技術可以提高細胞在室溫下的活力,減少分銷限制,但生產規模擴大和法規核准過程需要多個培養期。這些物流限制限制了市場滲透,並使細菌生物農藥的競爭力低於保存期限更長、儲存要求更低的化學農藥。
報告中分析的其他促進因素和限制因素
- 無農藥農產品需求推動Bt解決方案
- 受控環境農業的擴展推動液體製劑的發展
- 對擊倒速度慢的認知降低了農場的採用率
細分分析
Bt 將在細菌生物農藥市場保持主導地位,到 2024 年將佔總收益的 74%。這一市場領先地位歸功於其針對鱗翅目幼蟲的靶向毒性、廣泛的有機認證以及全球監管核准。由於新型封裝技術能夠提高 Bt 產品在強紫外線條件下的田間持效性,預計 Bt 產品的市場規模將進一步擴大。 2024 年的一項研究證實了 Bt 毒素對鱗翅目、鞘翅目、半翅目、雙翅目和線蟲類害蟲的有效性。
枯草桿菌展現出強勁的成長潛力,尤其是在高價值園藝領域,由於其具有抑制疾病和促進植物生長的雙重功效,預計複合年成長率為17%。螢光假單胞菌已在控制土壤傳播病原體方面確立了其作用,而沙雷氏菌和鏈黴菌則因其幾丁質酶活性和產生抗生素代謝的能力,在特殊應用領域越來越受歡迎。
區域分析
北美將保持主導地位,到2024年將佔全球銷售額的38%。美國正透過在大規模玉米和大豆種植中廣泛整合細菌解決方案來推動市場規模成長。加拿大的溫室叢集正在透過使用與水耕施肥系統相容的液體接種劑來刺激區域需求。 2023年,加拿大920個商業溫室蔬菜生產基地將生產802,163噸蔬菜,比2022年增加7%。
預計亞太地區將呈現最強勁的成長軌跡,到2030年複合年成長率將達到18%。中國的五年期綠色病蟲害防治計畫和印度的生物投入補貼計畫將鼓勵國內生產和應用。日本和新加坡的垂直農業正在為受控環境農業開發的液體製劑市場開闢新天地。
儘管歐洲對生物防治劑的監管一直很嚴格,但最近的變化加速了這些措施的實施。歐盟委員會的2025年快速通道法規縮短了檔案審查時間,使其與北美標準保持一致,促進了更多產品註冊,並鼓勵製造商擴大歐盟產品標籤的使用範圍。斯堪的納維亞半島學校膳食的公共採購政策以及德國「從農場到餐桌」的農藥減量目標,推動了對生物防治劑的需求成長,Bt和枯草葉面噴布產品尤其受益。東歐的穀物種植者已開始測試基於芽孢桿菌的種子處理劑,以應對出口市場嚴格的殘留要求,並將應用範圍擴展到傳統的高價值園藝應用之外。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場動態
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 法規和政策支持
- 人們越來越意識到傳統農藥造成的危害
- 無農藥農產品需求推動Bt解決方案
- 受控環境農業的擴張將推動對液體細菌製劑的需求
- 越來越多採用綜合蟲害管理(IPM)策略
- 配方和輸送系統的技術進步
- 市場限制
- 低溫運輸物流限制生物農藥的保存期限
- 生產和配方挑戰
- 對擊倒速度慢的認知降低了農場的採用率
- 成本高於傳統農藥
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章市場區隔
- 依產品類型
- 蘇力菌
- 枯草桿菌
- 螢光假單胞菌
- 其他類型
- 採用噴塗法
- 葉面噴布
- 種子處理
- 土壤處理
- 後處理
- 按作物類型
- 水果和蔬菜
- 穀物和穀類
- 油籽和豆類
- 草坪和觀賞作物
- 種植作物
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 其他南美
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 英國
- 西班牙
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲國家
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 其他亞太地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭態勢
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Certis Biologicals
- Valent BioSciences
- Bayer CropScience AG
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- BASF SE
- UPL Limited
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Limited
- Koppert Biological Systems
- Novonesis
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
The Bacterial Biopesticides Market size is estimated at USD 2.75 billion in 2025, and is anticipated to reach USD 5.53 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The market growth is driven by expedited regulatory approvals, increasing consumer demand for residue-free produce, expansion of organic farming, and technological advancements that enhance formulation stability and field efficacy. According to FiBL, the global organic farming area reached 98.9 million hectares in 2023, representing a 2.6% increase. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) dominates the market with a 74% revenue share, while Bacillus subtilis shows rapid growth due to its combined pest control and plant growth promotion capabilities. Precision seed treatment applications, liquid formulations for controlled-environment agriculture, and the consolidation of portfolios among major agrochemical companies support the market expansion. Adoption rate of the bacterial biopesticides is affected by cold-chain storage requirements and slower efficacy compared to chemical alternatives, as companies work to address these challenges in an increasingly competitive market.
Global Bacterial Biopesticides Market Trends and Insights
Regulatory and Policy Support
The European approval process for biopesticides has reduced from nine years to approximately three years, addressing a backlog of over 100 pending substances. The European Commission intends to implement new EU regulations in 2025 to optimize biopesticide approval processes by Q4. The 2026 Biotech Act will focus on filling current regulatory gaps. Brazil has demonstrated similar progress by approving bio-insecticidal products derived from inactivated Burkholderia cells. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is reducing application backlogs under FIFRA (Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act). These regulatory changes expand registration opportunities, reduce compliance costs, and enable smaller companies to enter the bacterial biopesticides market.
Rising Awareness of the Harms of Conventional Pesticides
Research demonstrating biodiversity loss and soil degradation from synthetic pesticides influences purchasing decisions in premium retail channels. A 2025 Massachusetts Institute of Technology study revealed that 31% of global agricultural soils faced high risks from pesticide contamination. North American and European retailers implement strict residue limits, favoring zero-residue biological products. As growers adapt to these requirements, bacterial agents have evolved from organic-only solutions to essential components of integrated pest management programs. This transition drives growth in the bacterial biopesticides market, especially for crops with short pre-harvest intervals.
Cold-Chain Logistics Limiting Shelf-Life of Biologicals
Live spore formulations typically lose viability at temperatures above 25°C, necessitating refrigerated transport and storage, which increases the final cost. This challenge is particularly significant in equatorial markets where small-scale distribution networks lack temperature-controlled storage facilities. While new encapsulation technologies are improving cell viability at room temperature and reducing distribution constraints, the processes for scale-up and regulatory approval require multiple growing seasons. These logistical limitations restrict market penetration, reducing the competitiveness of bacterial biopesticides against chemical pesticides that offer extended shelf life and minimal storage requirements.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Demand for Residue-Free Produce Driving Bt Solutions
- Expansion of Controlled-Environment Agriculture Boosting Liquid Formulations
- Perceived Slower Knock-Down Reducing Adoption in Farms
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Bt accounted for 74% of 2024 revenue, maintaining its dominant position in the bacterial biopesticides market. This market leadership stems from its targeted toxicity against lepidopteran larvae, extensive organic certifications, and regulatory acceptance worldwide. The market size for Bt products is projected to expand due to new encapsulation technologies that improve field persistence in high-UV conditions. A 2024 study confirmed Bt toxins' effectiveness against lepidopteran, coleopteran, hemipteran, dipteran, and nematode pests.
Bacillus subtilis shows strong growth potential with a projected 17% CAGR, driven by its dual benefits of disease suppression and plant growth promotion, particularly in high-value horticulture. Pseudomonas fluorescens has established its role in controlling soil-borne pathogens, while Serratia and Streptomyces species are gaining traction in specialized applications through their chitinase activity and antibiotic metabolite production capabilities.
The Bacterial Biopesticides Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Bacillus Thuringiensis, Bacillus Subtilis, Pseudomonas Fluorescens, and Other Types), Mode of Application (Seed Treatment, Foliar Spray, and More ), Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Oilseeds and Pulses, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America maintained its dominant position with a 38% share of the 2024 global revenue. The United States drives market volumes through widespread integration of bacterial solutions in large-scale corn and soybean operations. Canadian greenhouse clusters strengthen regional demand by utilizing liquid inoculants compatible with hydroponic fertigation systems. In 2023, Canada's 920 commercial greenhouse vegetable operations produced 802,163 metric tons of vegetables, a 7% increase from 2022.
Asia-Pacific demonstrates the strongest growth trajectory with an anticipated 18% CAGR through 2030. China's five-year green pest-control plan and India's bio-input subsidy programs encourage domestic production and adoption. Japan and Singapore's vertical farming operations provide established markets for liquid formulations specifically developed for controlled environment agriculture.
Europe maintains strict regulations for biopesticides, though recent changes have accelerated their adoption. The European Commission's 2025 fast-track regulation reduced dossier review times to align with North American standards, enabling more product registrations and encouraging manufacturers to expand their EU product labels. The demand for biopesticides has increased through Scandinavian public procurement policies for school meals and Germany's Farm-to-Fork pesticide reduction targets, particularly benefiting Bt and B. subtilis foliar products. Eastern European grain producers have initiated Bacillus-based seed treatment trials in response to export markets' stricter residue requirements, expanding beyond traditional high-value horticultural applications.
- Certis Biologicals
- Valent BioSciences
- Bayer CropScience AG
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- BASF SE
- UPL Limited
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Limited
- Koppert Biological Systems
- Novonesis
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Regulatory and Policy Support
- 4.2.2 Rising Awareness of the Harms of Conventional Pesticides
- 4.2.3 Demand for residue-free produce driving Bt solutions
- 4.2.4 Expansion of controlled-environment agriculture boosting demand for liquid bacterial formulations
- 4.2.5 Increasing adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies
- 4.2.6 Technological advancements in formulation and delivery systems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cold-chain logistics limiting shelf-life of Biological biopesticides
- 4.3.2 Production and Formulation Challenges
- 4.3.3 Perceived slower knock-down reducing adoption in farms
- 4.3.4 Higher costs compared to conventional pesticides
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Bacillus thuringiensis
- 5.1.2 Bacillus subtilis
- 5.1.3 Pseudomonas fluorescens
- 5.1.4 Other Types
- 5.2 By Mode of Application
- 5.2.1 Foliar Spray
- 5.2.2 Seed Treatment
- 5.2.3 Soil Treatment
- 5.2.4 Post-Harvest Treatment
- 5.3 By Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.2 Cereals and Grains
- 5.3.3 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.3.4 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.3.5 Plantation Crops
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Chile
- 5.4.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 France
- 5.4.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.4 Spain
- 5.4.3.5 Italy
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Africa
- 5.4.4.1 South Africa
- 5.4.4.2 Egypt
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.5 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5.1 China
- 5.4.5.2 India
- 5.4.5.3 Japan
- 5.4.5.4 South Korea
- 5.4.5.5 Australia
- 5.4.5.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Certis Biologicals
- 6.3.2 Valent BioSciences
- 6.3.3 Bayer CropScience AG
- 6.3.4 Syngenta AG
- 6.3.5 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.3.6 BASF SE
- 6.3.7 UPL Limited
- 6.3.8 FMC Corporation
- 6.3.9 Nufarm Limited
- 6.3.10 Koppert Biological Systems
- 6.3.11 Novonesis










