 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1690769
馬來西亞 CEP(快遞包裹):市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢和統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
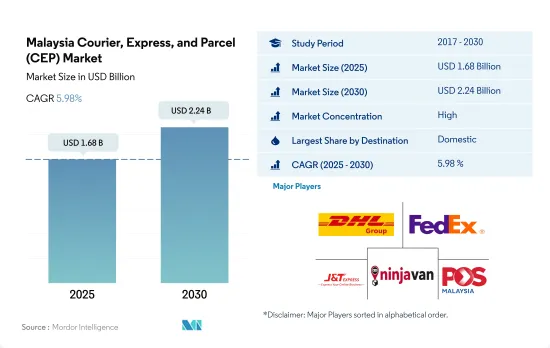
馬來西亞 CEP(快遞包裹)市場規模預計在 2025 年為 16.8 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 22.4 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 5.98%。
蓬勃發展的電子商務產業中電子子區隔的成長正在推動 CEP 細分市場的擴張
- 2024 年 2 月,聯邦快遞實現了一個里程碑,完成了首次從馬來西亞到新加坡使用電動車 (EV) 的跨國快遞。這項壯舉被馬來西亞紀錄大全認定為「首個零排放跨境交付」。這段長達 406 公里的旅程始於剪切機的聯邦快遞站,終於新加坡樟宜機場的聯邦快遞設施。在柔佛州僅充電一次後,與傳統柴油貨車相比,這款電動車的廢氣二氧化碳排放就減少了 100 公斤。
- 為了滿足快速成長的需求,CEP市場正經歷大幅擴張。例如,百世集團已擴展其在馬來西亞的物流網路,目前包括全國 100 多個最後一哩服務站、270 個銷售辦事處和 7 個分類中心。新的跨境物流服務將允許馬來西亞消費者從淘寶和京東等中國電子商務網站購物,小包裹只需六個工作天即可送達。此外,預計於 2026 年完工的東海岸鐵路 (ECRL) 將縮短馬來西亞東海岸和西海岸之間的運輸時間。
馬來西亞 CEP(快遞包裹)市場趨勢
儘管外國直接投資虧損達 725 萬美元,馬來西亞運輸和倉儲業仍將在 2022 年實現年增與前一年同期比較%
- 「一帶一路」計劃正在推動馬來西亞基礎設施發展。東海岸鐵路(ECRL)旨在改善東海岸的吉蘭丹、登嘉樓和彭亨與西海岸的森美蘭、雪蘭莪和布城之間的連通性。這些地區目前缺乏完整的鐵路連通。預計東部鐵路將推動馬來西亞經濟成長高達 2.7%。而且,預計建成20年後,馬來西亞的經濟成長率將達到4.6%。 ECRL計劃預計於2026年12月完工,並於2027年1月開始營運。
- 捷運3號線是吉隆坡城市軌道運輸網的最後一條主要線路,全長50.8公里,貫穿吉隆坡郊區。預計建設將於 2023 年初開始,並於 2030 年全面竣工,第一階段的營運將於 2028 年開始。透過酵母鐵路連接 (ECRL),雙軌鐵路連通基礎設施計劃於 2017 年啟動,其中包括 20 個車站:14 個客運站、5 個客貨合一站和 1 個貨運站。
正在討論取消柴油補貼,使零售燃油價格與市場價格保持一致
- 馬來西亞計劃自 2024 年 6 月起取消柴油補貼,並將零售價格與市場價格保持一致,為每公升 3.35 馬來西亞林吉特(0.75 美元),比 2.15 馬來西亞林吉特(0.48 美元)上漲 55%。儘管可能產生政治影響,但預計這項變化對通膨的影響較小。 2023 年的柴油補貼預計將達到 145 億馬來西亞林吉特(32.8 億美元),政府預計補貼合理化每年可節省約 40 億馬來西亞林吉特(9 億美元)。該國的柴油補貼高達每月 10 億馬來西亞林吉特(2.2 億美元),而每天因洩漏造成的損失高達 450 萬馬來西亞林吉特(102 萬美元)。
- 作為馬來西亞總理安瓦爾·易卜拉欣 (Anwar Ibrahim) 長期努力改革國家燃油補貼制度的一部分,2024 年 6 月馬來西亞的柴油價格上漲了 50% 以上。改革旨在透過取消普遍能源補貼、將援助重點放在最需要的人身上來減輕公共財政壓力。此舉也旨在解決補貼柴油被走私到鄰國並以高價交易的問題。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章執行摘要和主要發現
第2章 報告要約
第 3 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
- 調查方法
第4章 產業主要趨勢
- 人口統計
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 經濟活動帶來的 GDP 成長
- 通貨膨脹率
- 經濟表現及概況
- 電子商務產業趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 交通運輸倉儲業生產毛額
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 物流績效
- 基礎設施
- 法律規範
- 馬來西亞
- 價值鏈與通路分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 送貨速度
- 表達
- 非快遞
- 模型
- 企業對企業 (B2B)
- 企業對消費者 (B2C)
- 消費者對消費者(C2C)
- 運輸重量
- 重型貨物
- 輕型貨物
- 中等重量貨物
- 運輸方式
- 航空郵件
- 路
- 其他
- 最終用戶
- 電子商務
- 金融服務(BFSI)
- 衛生保健
- 製造業
- 一級產業
- 批發零售(線下)
- 其他
第6章 競爭格局
- 主要策略趨勢
- 市場佔有率分析
- 業務狀況
- 公司簡介
- City-Link Express
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GDEX Group
- J&T Express
- Ninja Van
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
第7章:執行長的關鍵策略問題
第 8 章 附錄
- 世界概況
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球價值鏈分析
- 市場動態(DRO)
- 技術進步
- 資訊來源和進一步閱讀
- 圖表清單
- 關鍵見解
- 資料包
- 詞彙表
簡介目錄
Product Code: 71524
The Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 1.68 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 2.24 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.98% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Growth in the electronics subsegment of the booming e-commerce industry is driving the expansion of the CEP segment
- In February 2024, FedEx Express achieved a milestone by executing the inaugural cross-border delivery from Malaysia to Singapore with an electric vehicle (EV). This feat was acknowledged by the Malaysia Book of Records as the 'first zero-emission cross-border delivery.' Spanning 406 km, the journey commenced at a FedEx station in Shah Alam and wrapped up at a FedEx facility in Changi Airport, Singapore. The EV recharged only once in Johor, managed to cut down tailpipe CO2 emissions by 100 kg when juxtaposed with conventional diesel vans.
- To meet the surging demand, the CEP market is witnessing significant expansions. For example, Best has broadened its logistics network in Malaysia, now encompassing over 100 last-mile service stations, alongside 270 operational stations and seven sorting centers nationwide. A new cross-border logistics service will allow Malaysian consumers to shop from Chinese e-commerce sites like Taobao and JD.com, with parcels arriving in just six working days. Additionally, the East Coast Railway Line (ECRL), set for completion in 2026, will reduce shipping times between Malaysia's east and west coasts.
Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
Malaysia's transportation and storage sector experienced 33.42% YoY growth in 2022, despite USD 7.25 million FDI deficit
- The Belt and Road Initiative is driving Malaysia's infrastructure growth. The East Coast Rail Link (ECRL) seeks to improve connectivity between Kelantan, Terengganu, and Pahang in the East Coast with Negeri Sembilan, Selangor, and Putrajaya in the West Coast. These areas currently lack complete railway connections. The ECRL is forecasted to boost Malaysia's economic growth by up to 2.7%. Furthermore, two decades after its construction, Malaysia's economic growth is expected to reach 4.6%. The ECRL project is set to finish by December 2026 and is expected to start operating in January 2027.
- The MRT3 is the last critical route to complete the Kuala Lumpur urban rail network; the line is 50.8 km long and runs around Kuala Lumpur's outskirts. Its construction began in early 2023 and is slated for full completion by 2030, while operations for the first phase are anticipated to commence in 2028. Through East Coast Rail Link (ECRL), a double-track railway linking infrastructure project, which includes 20 stations, began in 2017, with 14 passenger stations, five combined passenger and freight stations, and one freight station.
Elimination of Diesel subsidies under discussions, in order to align retail fuel prices to align with market rates
- Starting in June 2024, Malaysia plans to eliminate diesel subsidies, allowing retail prices to align with the market rate of MYR 3.35 (USD 0.75) per litre, marking a 55% increase from MYR 2.15 (USD 0.48). Despite potential political consequences, this change is projected to have minimal impact on the country's inflation rate. In 2023, diesel subsidies amounted to MYR 14.5 billion (USD 3.28 billion), and the government anticipates saving approximately MYR 4 billion (USD 0.90 billion) annually through this Subsidy Rationalization. Diesel subsidies in the country amount to MYR 1 billion (USD 0.22 billion) monthly, with daily losses from leaks totaling MYR 4.5 million (USD 1.02 million).
- Diesel prices in Malaysia surged by over 50% in June 2024 as part of Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim's efforts to reform the country's long-standing fuel subsidy system. The restructuring aimed to alleviate pressure on national finances by eliminating universal energy subsidies and focusing assistance on those most in need. This move also aims to address issues like the smuggling of subsidized diesel to neighboring countries, where it fetches higher prices.
Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The Malaysia Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fairly consolidated, with the major five players in this market being DHL Group, FedEx, J&T Express, Ninja Van and POS Malaysia Bhd (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 Malaysia
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 City-Link Express
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 FedEx
- 6.4.4 GDEX Group
- 6.4.5 J&T Express
- 6.4.6 Ninja Van
- 6.4.7 POS Malaysia Bhd
- 6.4.8 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.9 SkyNet Worldwide Express
- 6.4.10 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219








