 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1690189
美國數位貨運:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢和成長預測(2025-2030 年)United States Digital Freight Forwarding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
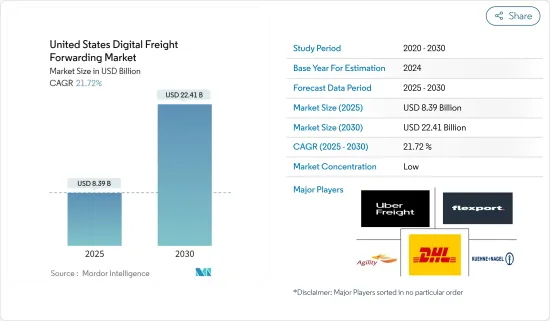
預計 2025 年美國數位貨運代理市場規模為 83.9 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 224.1 億美元,預測期間(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 21.72%。
主要亮點
- 各行業業務成長的主要驅動力之一是手動流程的自動化。此外,由於電子商務的普及和自由貿易協定的增加,數位貨運代理市場正在成長和擴大。
- 大多數產業正在進行數位轉型,貨運也不例外。數位貨運代理商使用科技來規劃和管理他們的貨運。
- 數位貨運代理使行業相關人員能夠利用當前的技術進步來簡化參與航運計劃的相關人員之間的溝通。為了向客戶提供最優惠的價格,Digital Freight Forwarding 還使用完全透明的雲端基礎的系統,可以輕鬆比較多種貨運價格。
- 數位化仍然是美國經濟成長的主要驅動力之一。 Convoy、Uber Freight 和 uShip 等公司正在開發新平台來填補物流行業的空白。數位貨運減少了手動流程。數位貨運代理的一些主要優勢包括即時報價、透明定價、費率和承運人比較、追蹤和簡單的文件記錄。物流業正在發展成為無紙化、數位化的產業,支持了市場的成長。
- 現在許多企業都開始採用數位貨運服務。截至 2021 年 4 月的六個月內,Uber Freight 業主營運商的啟動量幾乎加倍,截至 2021 年 5 月,新授權承運人的數量與前一年同期比較成長了 300% 以上。 2021 年第一季,該公司密切關注了這一驅動供應轉變以及影響該行業的其他宏觀趨勢,包括美國勞動力趨勢和供應鏈瓶頸。
美國數位貨運市場的趨勢
電子商務正在推動市場
2021年上半年,美國零售電商銷售額達約4,380億美元。 2021年4月至6月的銷售額超過2,220億美元,高於第一季的2,150億美元。整體而言,零售電商銷售額超過了2020年創下的季度銷售記錄。根據美國商務部的資料,十多年來電商銷售額一直在逐步成長,過去兩年成長顯著。美國電子商務總銷售額從 2020 年的 8,116 億美元成長 18.3% 至 2021 年的 9,599 億美元。
根據Digital Commerce 360對美國商務部資料的分析,繼疫情第一年成長45%-50%之後,2022年第二季度是美國電子商務支出連續第四個季度實現個位數成長。不過,2021年初以來,線上銷售與前一年同期比較首次超過了實體店。
美國商務部數據顯示,第二季數位銷售額達到 2,521.4 億美元,較去年同期的 2,348.9 億美元成長 7.3%。這還不到2021年第二季美國電子商務成長率15.4%的一半,也遠低於2020年第二季封鎖和商店關閉期間53.4%的增幅。
線上客戶期望訂單準確、當天或當天送達以及免費退貨。電子商務公司正在尋找減少訂單交付時間和營運成本的方法。電子商務產業正在推動對透明度、可負擔性、便利性、交貨速度和無摩擦退貨的需求。為了滿足這些需求,必須透過數位化物流業務和自動化物料輸送系統、倉庫管理系統和交付管理系統來創建新的經營模式和解決方案。這使得履約服務更快、更靈活,特別是在最後一哩交付和簡化退貨程序方面。
海運業呈現強勁成長
海運業需要創新。這個市場開始被物流科技公司填補。由於世界要求商品能夠像 Uber 或亞馬遜完成訂單那樣快速地送達,我們將看到電子商務公司轉向第三方物流,而第三方物流又轉向電子商務公司。
一旦產品進口到美國,零售商和品牌就會停止追蹤。亞馬遜效應及其創造的由總週期時間驅動的倉庫直通意味著更多的賣家在貨物到達原產港後立即接受庫存訂單。這將海運貨櫃轉變為未來倉庫的現代化版本,提高消費者和供應鏈專業人士對海運的認知。
大多數產業正在進行數位轉型,貨運也不例外。數位貨運代理使用科技來規劃和管理貨運。根據波羅的海貨運指數 (Freightos Baltic Index) 的數據,目前從中國運送一個 40 英尺貨櫃到美國西海岸的價格約為每箱 5,400 美元,較 2022 年 1 月下降了 60%。
目前,從亞洲到歐洲運輸一個貨櫃的成本為 9,000 美元,比 2022 年初下降了約 42%。這兩條航線的運費在 2021 年 9 月的高峰都超過了 2 萬美元,超過了疫情前的水準。
沃爾瑪和其他大型零售商由於預計會出現運輸延誤和最終未能實現的需求,爭先恐後地比平時更早進口商品,導致 2022 年庫存過剩。
美國數位貨運產業概況
美國數位貨運代理市場競爭激烈且分散,參與者眾多。主要參與者包括 Flexport、Uber Freight、DHL Group、Agility Logistics Pvt。 Ltd 和 Kuehne+Nagel International。
數位貨運代理 (DFF) 使用數位平台提供比市場和連接提供者更廣泛的物流服務。 DFF 的核心價值提案是圍繞無縫用戶體驗,即將貨物從一個地點運送到另一個地點,透過單一用戶介面在一個平台上匯總資訊。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 調查前提條件
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 當前市場狀況
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 投資前景
- 政府法規和舉措
- 線上貨運和數位平台的技術發展
- 美國電子商務物流及貨運概況
- 電子平台價值提案與競爭力
- COVID-19 市場影響
第5章 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 限制因素
- 機會
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第6章 市場細分
- 按運輸方式
- 海洋
- 航空
- 土地
- 按公司類型
- 中小型企業
- 大企業和政府
第7章 競爭格局
- 市場集中度概覽
- 公司簡介
- Flexport
- Twill
- Forto
- Expeditors International
- InstaFreight
- Transporteca
- Kontainers
- Kuehne+Nagel International(KN Freight Net)
- Turvo
- iContainers
- DHL Group
- NYSHEX
- Agility Logistics Pvt. Ltd
- Convoy
- Uber Freight
- uShip*
第8章 市場機會與未來趨勢
第9章 免責聲明
The United States Digital Freight Forwarding Market size is estimated at USD 8.39 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 22.41 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.72% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- One of the main factors propelling the expansion of businesses across all industries is the automation of manual processes. Additionally, the market for digital freight forwarding is growing and expanding due to the spread of e-commerce and the rise in free trade agreements.
- The majority of sectors are undergoing digital transformations, and freight forwarding is no exception. Technology is used by digital freight forwarders to plan and manage cargo transit.
- Through the use of digital freight forwarding, industry participants can take advantage of current technological advancements to streamline contact between all parties involved in a shipping project. In order to give customers the best deal, digital freight forwarding also involves the use of a totally transparent cloud-based system that makes it simple to compare multiple shipping prices.
- Digitization continues to be one of the key drivers supporting the growth of the US economy. Companies like Convoy, Uber Freight, and uShip are developing new platforms to fill in the gaps in the logistics industry. With digital freight forwarding, the manual process will be reduced. The major benefits of digital freight forwarding include instant quotes, transparent pricing, comparison of rates and carriers, tracking, easy documentation, and others. The logistics industry is developing into a paperless digitized industry, supporting the market's growth.
- Many companies are now embracing digital freight services. In the six months before April 2021, Uber Freight's owner-operator activation nearly doubled, and by May 2021, the number of new authority carriers had increased by more than 300% year over year. In the first quarter of 2021, the company closely monitored this driver supply shift as well as other macro developments affecting the industry, such as the US labor trends and supply-chain bottlenecks.
US Digital Freight Forwarding Market Trends
E- Commerce is driving the market
In the first half of 2021, US retail e-commerce sales amounted to almost USD 438 billion. Sales revenue from April to June of 2021 exceeded USD 222 billion, up from USD 215 billion in the first quarter. Overall, retail e-commerce sales outdid the quarterly sales records registered in 2020. According to data from the US Department of Commerce, e-commerce sales have increased gradually for more than ten years, with a notable rise in the last two years. Total US e-commerce sales increased by 18.3% from USD 811.6 billion in 2020 to USD 959.9 billion in 2021.
According to a Digital Commerce 360 analysis of the US Department of Commerce data, following the 45%-50% increases during the first year of the pandemic, US e-commerce spending in Q2 2022 recorded its fourth consecutive quarter of single-digit growth. But for the first time since early 2021, the year-over-year increase in online sales also topped that of physical locations.
According to figures from the Commerce Department, digital revenue reached USD 252.14 billion in the second quarter, an increase of 7.3% from USD 234.89 billion for the same period in the previous year. This was less than half of the 15.4% US e-commerce growth in Q2 2021 and far less than the 53.4% increase that occurred amid lockdowns and store closings in Q2 2020.
Online customers expect order accuracy, same-day or same-hour delivery, and free returns. E-commerce companies are exploring ways to reduce order delivery times and operational costs. The e-commerce industry drives the demand for transparency, affordability, convenience, speed in delivery, and compelling frictionless returns. To cater to this need, it is essential to create new business models and solutions by digitalizing logistics operations and automating material handling systems, warehouse management systems, and distribution management systems. This has made fulfilment services speedier and more diverse, especially in terms of last-mile delivery alternatives and simple return procedures.
The Ocean freight segment showing significant growth
Innovation in the area of ocean freight is required. The market is starting to be filled by logistics technology companies. It is anticipated that e-commerce firms will transition to being 3PLs, and 3PLs will transition to become e-commerce companies, as the world wants things to be delivered as rapidly as Uber and Amazon can fulfill orders.
Once a product is imported into the United States, retailers and brands stop tracking it. More sellers accept inventory orders as soon as it ships at the port of origin, thanks to the Amazon effect and the warehouse pull-through it generates, which emphasizes total cycle times. This transforms ocean containers into the modern and future-day equivalent of warehouses, increasing consumer and supply chain experts' awareness of maritime freight.'
The majority of sectors are undergoing digital transformations, and freight forwarding is no exception. Technology is used by digital freight forwarders to plan and manage cargo transit. According to Freightos Baltic Index, the price to transport a 40-foot container from China to the US West Coast is currently around $5,400 per box, down 60% from January 2022.
Currently, the cost of shipping a container to Europe from Asia is $9,000, which is roughly 42% less than what was seen in early 2022. The rate for both routes peaked in September 2021 at more than $20,000, above pre-pandemic values.
Walmart and other large retailers in 2022 ended up with excess inventory as a result of almost rushing to import their products earlier than normal in anticipation of shipping delays and demand that ultimately did not materialize.
US Digital Freight Forwarding Industry Overview
The US digital freight forwarding market is competitive and fragmented, with many players. Some major players are Flexport, Uber Freight, DHL Group, and Agility Logistics Pvt. Ltd, Kuehne + Nagel International, and many more.
Digital freight forwarders (DFFs) use a digital platform to offer a broader range of logistics services than marketplaces and connectivity providers. DFFs build their core value proposition around a seamless user experience of shipping goods from one point to another while aggregating information on one platform with a single user interface.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Investment Scenarios
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.5 Technology Development in Online Freight Forwarding and Digital Platforms
- 4.6 Overview on E-commerce Logistics and Freight Forwarding in the United States
- 4.7 Value Propositions of E-platforms Vs Competitors
- 4.8 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.3 Opportunities
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size By Value)
- 6.1 By Mode of Transportation
- 6.1.1 Ocean
- 6.1.2 Air
- 6.1.3 Land
- 6.2 By Firm Type
- 6.2.1 SMEs
- 6.2.2 Large Enterprises and Governments
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Flexport
- 7.2.2 Twill
- 7.2.3 Forto
- 7.2.4 Expeditors International
- 7.2.5 InstaFreight
- 7.2.6 Transporteca
- 7.2.7 Kontainers
- 7.2.8 Kuehne + Nagel International (KN Freight Net)
- 7.2.9 Turvo
- 7.2.10 iContainers
- 7.2.11 DHL Group
- 7.2.12 NYSHEX
- 7.2.13 Agility Logistics Pvt. Ltd
- 7.2.14 Convoy
- 7.2.15 Uber Freight
- 7.2.16 uShip*









