|
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1803889
自規則系統成像雷達的專利形勢的分析(2025年)Imaging Radar for Autonomous Systems Patent Landscape Analysis 2025 |
|||||||
成像雷達:高解析度自動駕駛的核心驅動力
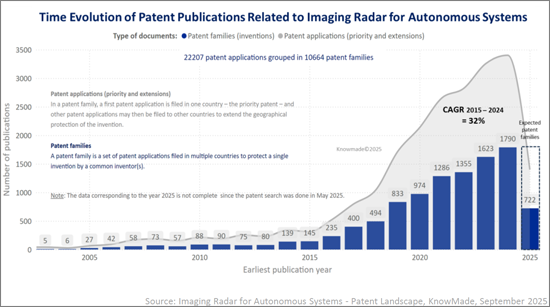
成像雷達是新一代雷達感測技術,旨在突破傳統雷達僅限於基本距離和速度測量的限制。透過同時獲取距離、速度、方位角和仰角,成像雷達可實現高解析度3D/4D感知。這些密集的雷達點雲可實現高階感知功能,例如物件分類、自由空間探測、地圖繪製和場景重建。由於其在惡劣天氣、低光源和複雜操作環境下的穩健性,成像雷達正成為安全可靠的自動駕駛系統的基礎。其應用範圍廣泛,從ADAS、L2-L4自動駕駛和機器人計程車平台等地面移動應用,到空中無人機、船舶、機器人、太空和國防應用。專利活動的快速成長反映了這一勢頭。全球已確認超過 22,200 件專利申請,涵蓋超過 10,600 個專利家族(發明),其中包括超過 2,800 個與成像雷達領域高度相關的核心專利家族。這一強勁的智慧財產權 (IP) 動態表明,成像雷達正在從一種補充感測器轉變為主要的感知模式,塑造著自動駕駛的未來,並推動著先進感測領域競爭最激烈的智慧財產權戰場之一。
全球智慧財產權趨勢及策略參與者
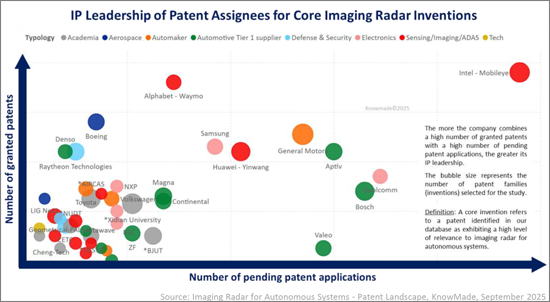
成像雷達專利格局正經歷前所未有的加速發展。 2015 年至 2024 年間,成像雷達專利家族的出版數量增加了 1,100% 以上,從 145 件增加到 1,790 件,複合年增長率為 32%,開啟了爆炸性創新時代。這一激增反映了技術向 4D 成像雷達、基於人工智慧的感知和多感測器融合的轉變。美國和中國在該領域佔主導地位,合計佔全球申請的大部分佔有率,而歐洲則透過博世、採埃孚和法雷奧等一級供應商保持強勢地位。英特爾-Mobileye、博世、通用汽車、Alphabet-Waymo、華為-印網和麥格納等現有企業擁有涵蓋雷達硬體、感知軟體和感測器融合的多元化專利組合。同時,Arbe Robotics、Uhnder、Aptiv 和 Metawave 等專業創新者正在建立專注於 4D 雷達晶片組、點雲處理和即時環境感知的組合。包括西安電子科技大學、電子科技大學、北航和中科院航空工業研究院在內的學術機構,持續在波形、天線設計和波束賦形領域推動基礎創新。產業領袖、新創公司和研究機構之間錯綜複雜的互動,定義了先進感測領域競爭最激烈的智慧財產權領域之一。
跨應用與科技層面的智慧財產權創新
成像雷達專利分為六大應用領域:陸地、空中、海上、航太、機器人和國防。此外,專利格局分為五個技術層面,涵蓋11項關鍵賦能技術,涵蓋波形設計和系統平台、校準、感知和感測器融合等各個。我們的分析表明,陸地移動出行是最具活力、技術最先進的領域,這得益於ADAS、L2-L4自動駕駛和自動駕駛計程車的部署。其他領域,如無人機導航、海事感測和國防應用,也不斷擴展。在整個技術堆疊中,創新涵蓋了從FMCW和MIMO訊號處理到AI增強感知和多感測器融合的各個領域,凸顯了成像雷達在下一代自動駕駛中的核心作用。
本報告提供全球自規則系統成像雷達產業調查分析,超過1萬600件的專利的Excel資料庫之外又加上,全球專利趨勢的說明,及主要企業的IP簡介等。
本報告拿起的企業(摘錄)
|
|
等等。
目錄
簡介
摘要整理
專利形勢概要
- 知識產權動態
- 專利公佈趨勢:依國家/地區
- 主要專利持有人(按專利族、專利申請和核心發明;按類型、法律狀態和國內/全球智慧財產權策略分類)
- 知識產權公司時間線
- 專利持有人智慧財產權領導力
- 主要公司專利的地理覆蓋範圍
- 已授權專利組合中具有影響力的專利持有人
- 知識產權生態系統
- 輔助品牌和內部部門
- 合資企業 - IP共同所有模式
- 收購相關企業
- 主要的共同所有IP
專利的市場區隔
- 市場區隔定義
- 專利的市場區隔 - 用途
- 市場區隔概要(專利系列數,積極的發明專利權者數,主要的發明專利權者,IP新加入廠商者,其他)
- 關於各市場區隔(陸上,航空,機器人工學,宇宙,海上,防衛)
- 專利組合概要(IP動態,地理範圍等)
- 發明專利權者的IP龍頭
- 值得注意的專利
- 陸上用途主要的發明專利權者的排行榜
- 專利的市場區隔 - 技術
- 市場區隔概要(專利系列數,積極的發明專利權者數,主要的發明專利權者,IP新加入廠商者等)
- 關於各市場區隔(11技術所構成的5個技術層)
- 成像雷達的各技術的引進
- 專利組合概要(IP動態,地理範圍等)
- 值得注意的專利
- 4D成像雷達的發明專利權者的IP龍頭
發明專利權者的IP簡介
- General Motors,Intel - Mobileye,Bosch,Huawei -Yinwang,Magna,Alphabet - Waymo
- 各企業相關
- 專利組合概要(IP動態,市場區隔,法律上的現狀,地理範圍,引用,專利系列擴張比率,其他)
- 值得注意的專利
- 值得注意的申請中的專利
- 各企業相關
專利訴訟
附錄
KnowMade的簡報
The global IP battlefield is heating up: who are the key players, and which technologies will shape the future of imaging radar for autonomous mobility?
Key features:
- PDF >150 slides
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report (>10,600 patent families), including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database.
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers in the different segments.
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio.
- IP ecosystems including sub-brands, JV with shared IP ownership, main co-owned IP, etc.
- Patents categorized by 6 application domains (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, defense) and 5 technology layers comprising 11 techniques (FMCW, MIMO, Beamforming, 4D imaging radar, SAR, ISAR, calibration, point cloud, SLAM, tracking, AI and sensor fusion), with a focus on terrestrial applications and 4D imaging radar.
- IP profile of key players (patent portfolio overview, technical coverage, geographical coverage, notable granted and pending patents, etc.)
Imaging Radar A Core Driver of High-Resolution Autonomy
Imaging radar represents the next generation of radar sensing technologies, designed to overcome the limitations of conventional radars that provide only basic range and velocity measurements. By simultaneously capturing range, velocity, azimuth and elevation, imaging radar produces high-resolution 3D/4D perception. These dense radar point clouds enable advanced perception functions including object classification, free space detection, mapping and scene reconstruction. Thanks to its robustness in adverse weather, low light and complex operating environments, imaging radar is becoming a cornerstone for safe and reliable autonomous systems. Its deployment spans terrestrial mobility such as ADAS, L2-L4 autonomous driving and robotaxi platforms, as well as aerial drones, marine vessels, robotics, space, and defense applications. The rapid acceleration of patenting activity reflects this momentum. More than 22,200 patent applications grouped into over 10,600 patent families (inventions) have been identified worldwide, including more than 2,800 core patent families that demonstrate a high degree of relevance to the imaging radar domain. This strong intellectual property (IP) dynamic demonstrates that imaging radar is transitioning from a complementary sensor to a primary perception modality, shaping the future of autonomy and driving one of the most competitive IP battlefields in advanced sensing.

Global IP Trends and Strategic Players
The patent landscape for imaging radar has experienced an unprecedented acceleration. From 2015 to 2024, imaging radar patent family publications grew from 145 to 1,790, an increase of over 1100% and a CAGR of 32% marking a period of explosive innovation. This surge reflects the technological transition toward 4D imaging radar, AI-driven perception and multi-sensor fusion. The United States and China dominate the field, together accounting for more than half of global filings, while Europe maintains a strong position through Tier-1 suppliers such as Bosch, ZF and Valeo. Established players including Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, General Motors, Alphabet - Waymo, Huawei-Yinwang and Magna hold diversified patent portfolios that span radar hardware, perception software and sensor fusion. At the same time, specialized innovators such as Arbe Robotics, Uhnder, Aptiv and Metawave are building targeted portfolios in 4D radar chipsets, point cloud processing and real-time environmental perception. Academic institutions, notably Xidian University, UESTC, BUAA and AIRCAS, continue to shape foundational innovation in waveforms, antenna design and beamforming. This complex interplay of industrial leaders, startups and research institutes defines one of the most competitive IP domains in advanced sensing.
IP Innovation Across Applications and Technical Layers
Imaging radar patents are classified into six main application domains: terrestrial, aerial, marine, space, robotics and defense. The patent landscape has been further structured into five technology layers encompassing 11 key enabling techniques, ranging from waveform design and system platforms to calibration, perception and sensor fusion. Our analysis indicates that terrestrial mobility is the most active and technically advanced area, driven by ADAS, Level 2 to Level 4 autonomy and robotaxi deployment. Other domains such as UAV navigation, maritime sensing and defense applications are also expanding. Across the technology stack, innovation spans from FMCW and MIMO signal processing to AI-enhanced perception and multi-sensor fusion, highlighting the central role of imaging radar in next generation autonomy.

A Competitive and Rapidly Evolving IP Landscape
The imaging radar IP landscape is highly dynamic. Established OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers maintain strong positions, but new entrants are rapidly reshaping the field, with radar startups and ADAS suppliers particularly active. IP leadership now depends not only on the size of a portfolio but also on enforceability, geographic reach and technological impact. Companies such as GM, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch and Huawei-Yinwang combine extensive portfolios with a high volume of patent applications, while patent assignees like Arbe Robotics and Uhnder have demonstrated high IP strength and influence per patent.
In addition to individual patent portfolios, the IP ecosystem is shaped by sub-brands, joint ventures with shared IP ownership and co-owned patent families, all of which highlight the strategic role of IP in driving both competition and collaboration.
From Key Players to the Entire IP Landscape
This report provides in-depth insights into the IP strategies of the main actors shaping the imaging radar domain. It includes detailed profiles of General Motors, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, Huawei-Yinwang, Magna and Alphabet-Waymo, covering portfolio dynamics, notable granted and pending patents, legal status and global coverage. Beyond these key players, the report delivers a comprehensive classification of all identified patent assignees including automakers, Tier-1 suppliers, sensing and ADAS companies, electronics manufacturers, technology firms, academia, and defense and aerospace players. Within each segment, we identify both the established IP leaders and the IP newcomers, providing a clear view of how innovation and competition are distributed across the ecosystem.
For executives, IP professionals and R&D teams, the report delivers a comprehensive overview of a fast-evolving and competitive technology space. By aligning patent intelligence with strategic planning, companies can strengthen their innovation roadmap, secure competitive advantage and position themselves at the forefront of autonomous mobility and advanced sensing.
Useful Excel patent database
This report includes an extensive Excel database with the 10,600+ patent families (inventions) analyzed in this study, including patent information (publication numbers, assignees, dates, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and structured classification by application segments (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, and defense), five technology layers with 11 key technique segments (FMCW, MIMO, beamforming, 4D imaging radar, SAR, ISAR, calibration, point cloud, SLAM, tracking, AI and sensor fusion), as well as the identified core inventions. This database supports advanced multi-criteria searches and provides direct access to updated records, enabling users to benchmark portfolios, monitor competitors, identify potential partners or acquisition targets and evaluate freedom-to-operate constraints.
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive):
|
|
and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Context of the report
- Scope and objectives of the report
- Reading guide
- Excel database
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- IP dynamics
- Time evolution of patent publications by countries
- Main patent assignees (according to number of patent families, number of patent applications, number of core inventions; classified by typology, by legal status, by domestic vs. global IP strategies, etc.)
- Timeline of IP players
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Geographical coverage of main players' patents
- High-impact patent assignees for granted patent portfolios
- IP ecosystems
- Sub-brands and Internal Divisions
- Joint Ventures - Shared IP Ownership Models
- Acquisition-related Companies
- Main co-owned IP
PATENT SEGMENTATION
- Segments definition
- Patent segmentation - applications
- Segmentation overview (number of patent families, number of active patent assignees, main patent assignees, IP newcomers, etc)
- For each segment (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, and defense):
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, geographic coverage, etc.)
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Notable patents
- Main patent assignees ranking for terrestrial applications
- Patent segmentation - technologies
- Segmentation overview(number of patent families, number of active patent assignees, main patent assignees, IP newcomers, etc)
- For each segment (five technology layers comprising 11 techniques) :
- Introduction of each technology for imaging radar
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, geographic coverage, etc.)
- Notable patents
- IP leadership of patent assignees for 4D imaging radar
IP PROFILE OF A SELECTION OF PATENT ASSIGNEES
- General Motors, Intel - Mobileye, Bosch, Huawei -Yinwang, Magna and Alphabet - Waymo
- For each player:
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, segments, legal status, geographic coverage, citations, patent family extension ratio, etc.)
- Notable granted patents
- Notable pending patents
- For each player:
PATENT LITIGATION
ANNEX
- Methodology for patent search, selection and analysis
- Methodology to identify key patents
- Terminology












