 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1885895
氮化鎵(GaN)電動車充電器市場機會、成長促進因素、產業趨勢分析及預測(2025-2034年)Gallium Nitride (GaN) EV Charger Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
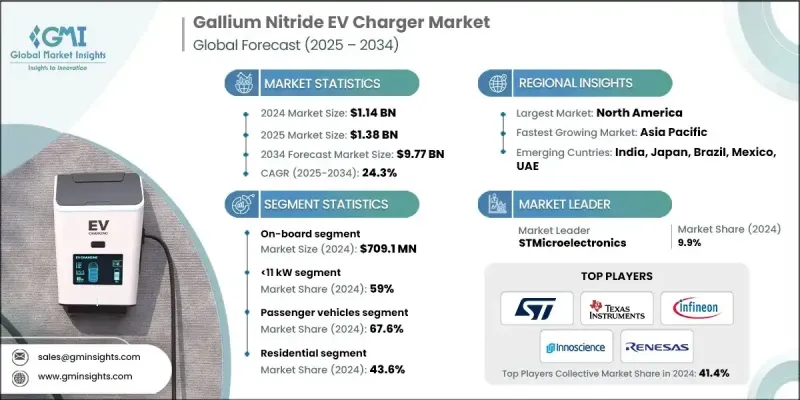
2024 年全球氮化鎵 (GaN) 電動車充電器市值為 11.4 億美元,預計到 2034 年將以 24.3% 的複合年成長率成長至 97.7 億美元。
市場正從獨立的離散裝置向整合式半橋級和模組轉型,這些整合式半橋級和模組將氮化鎵(GaN)開關與驅動器和保護功能相結合。這種整合降低了佈局敏感性和電磁干擾(EMI),同時提高了散熱性能。公私合作計畫加速了寬禁帶(WBG)技術的商業化,推動了車載充電器(OBC)和電動車電源系統採用整合式GaN解決方案。汽車製造商正日益整合多功能電源域,從而支援更高水準的裝置整合。 OBC轉換器的展示表明,與矽基系統相比,GaN可以將功率密度提高170%,重量減輕79%,並在6.6 kW雙有源橋原型中實現了99%的峰值效率。 GaN元件可以以比矽更高的頻率和更低的導通損耗進行開關,從而可以縮小磁性元件和冷卻系統的尺寸,同時在先進的電動車轉換器中將損耗降低60-80%。設計團隊也正在最佳化開關頻率,以平衡轉換器性能和馬達寄生損耗。研究表明,採用高HfO2閘極介質的1.2 kV GaN MOSFET可實現極低的閘極漏電流和更高的電流密度。一旦襯底和製程技術成熟,垂直GaN元件有望在1.2 kV應用領域與SiC元件展開競爭。然而,由於成本和可靠性方面的考慮,800 V以上和150 kW牽引應用的汽車級認證仍在開發中,預計要到本世紀末才能實現。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 11.4億美元 |
| 預測值 | 97.7億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 24.3% |
橫向氮化鎵元件市場佔有率達到70%,預計從2025年到2034年將以16.1%的複合年成長率成長。橫向氮化鎵裝置在電動車電力電子領域佔據主導地位,應用於車用電池、直流-直流轉換器和高達650V的輔助系統。與矽相比,其在矽基板上的AlGaN/GaN HEMT結構具有高電子遷移率和臨界場強,在高阻斷電壓下可實現低導通電阻。
中壓(100-650V)市場在2024年佔據了67%的市場佔有率,預計到2034年將以16%的複合年成長率成長。中壓GaN元件已廣泛應用,因為大多數車載電池(目前為400V,未來將上升至800V)和許多DC-DC轉換器都屬於此電壓範圍。 GaN的高頻性能可直接提升6.6-19.2kW車載電池系統中功率因數校正和LLC或諧振轉換器級的效率和功率密度。
預計到2024年,中國氮化鎵(GaN)電動車充電器市場規模將達到7,340萬美元。中國電動車銷量佔全球近三分之二,其龐大的市場規模使其成為GaN裝置最大的潛在市場,因為每輛電動車都需要車載充電器、DC-DC轉換器和相容的充電基礎設施。這一產能規模使中國遙遙領先日本、韓國和印度等其他區域市場。
全球氮化鎵 (GaN) 電動車充電器市場的主要參與者包括 Transphorm、Navitas、德州儀器 (Texas Instruments)、GaN Systems、EPC、意法半導體 (STMicroelectronics)、羅姆半導體 (ROHM Semiconductor)、英飛凌科技 (Infineon Technologies Technologies)、Ingrscience 和 Infinations。各公司正透過加大研發投入來提升 GaN 裝置的效能、效率和可靠性,進而鞏固自身市場地位。與汽車製造商和充電器製造商的策略合作加速了 GaN 技術的普及應用。拓展產品組合,推出中高壓解決方案,取得汽車產業認證,以及開發整合模組,均有助於提高市場滲透率。此外,各公司也致力於透過襯底創新、擴大產能和最佳化供應鏈來降低成本。
目錄
第1章:方法論
- 市場範圍和定義
- 研究設計
- 研究方法
- 資料收集方法
- 資料探勘來源
- 全球的
- 地區/國家
- 基準估算和計算
- 基準年計算
- 市場估算的關鍵趨勢
- 初步研究和驗證
- 原始資料
- 預報
- 研究假設和局限性
第2章:執行概要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系分析
- 供應商格局
- 利潤率分析
- 成本結構
- 每個階段的價值增加
- 影響價值鏈的因素
- 中斷
- 產業影響因素
- 成長促進因素
- 電動車普及率不斷上升
- 能源效率和永續性
- 車隊電氣化
- 政府政策和激勵措施
- 氮化鎵技術的進步
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 初始成本高
- 整合挑戰
- 市場機遇
- 與再生能源的融合
- 高功率工業車隊充電
- 公共充電網路的擴展
- 智慧充電與電網管理
- 成長促進因素
- 成長潛力分析
- 監管環境
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
- 技術與創新格局
- 目前技術
- 新興技術
- 氮化鎵元件架構及技術變體
- 橫向氮化鎵半金屬薄膜電晶體架構(300-650V 商用)
- 垂直氮化鎵發展路線圖(目標電壓>1.2 kV)
- 雙向氮化鎵開關(BDS)技術
- 寬禁帶半導體技術概況
- 矽(Si)基準性能及局限性
- GAN技術概述及優勢
- 碳化矽(SIC)技術概述
- GAN 與矽的性能比較
- 專利分析
- 價格趨勢分析
- 按組件
- 按地區
- 成本分解分析
- 生產統計
- 生產中心
- 消費中心
- 進出口
- 永續性和環境方面
- 永續實踐
- 減少廢棄物策略
- 生產中的能源效率
- 環保舉措
- 碳足跡考量
- 製造流程及成本結構
- GaN元件製造流程
- 外延生長(MOCVD、MBE)
- 晶圓加工與光刻
- 切丁和包裝
- 測試與品質控制
- 製造成本細分(美元/千瓦)
- 熱管理注意事項
- 高開關頻率的散熱挑戰
- 散熱器設計與最佳化
- 液冷與風冷
- 熱界面材料
- 結溫管理
- 電磁干擾/電磁相容性合規性及緩解措施
- 高 DV/DT 和 DI/DT 挑戰
- 傳導排放
- 輻射發射
- 用於氮化鎵充電器的EMI濾波器設計
- PCB佈局最佳實踐
- 屏蔽和接地策略
- 可靠性和資格標準
- AEC-Q101(汽車分立半導體)
- AEC-Q100(汽車積體電路)
- 汽車業資格要求
- 長期可靠性測試
- 柵極氧化層可靠性
- 動態導通電阻退化
- 貿易分析及進出口動態
- 全球氮化鎵裝置貿易流
- 主要出口國(中國、台灣、德國、美國)
- 主要進口國
- 關稅與貿易壁壘
- 貿易政策影響(美中關係)
- 回流和近岸外包趨勢
- 案例研究與實際應用
- ORNL 6.6 kW GaN OBC 演示
- 台達電子氮化鎵充電器部署
- 英飛凌 300 毫米 GaN 中試生產
- Navitas GaNFast IC 汽車設計獲獎
- Chargepoint GaN 直流電快速充電器
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 公司市佔率分析
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 主要市場參與者的競爭分析
- 競爭定位矩陣
- 戰略展望矩陣
- 重要新聞和舉措
- 併購
- 合作夥伴關係與合作
- 新產品發布
- 擴張計劃和資金
第5章:市場估算與預測:依產品分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- 車用充電器
- 外接充電器
- 住宅
- 商業的
- 公共/高功率
第6章:市場估算與預測:依充電容量分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- 小於11千瓦
- 11-22千瓦
- 大於22千瓦
第7章:市場估價與預測:依車輛類型分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- 搭乘用車
- 掀背車
- 轎車
- SUV
- 商用車輛
- 低容量性狀
- MCV
- C型肝炎
第8章:市場估算與預測:依應用領域分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- 住宅
- 商業的
- 民眾
- 工業的
第9章:市場估算與預測:依配銷通路分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- OEM
- 售後市場
第10章:市場估計與預測:依地區分類,2021-2034年
- 主要趨勢
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 北歐
- 荷蘭
- 俄羅斯
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳新銀行
- 新加坡
- 泰國
- 越南
- 韓國
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
第11章:公司簡介
- 全球參與者
- ABB E-Mobility
- Infineon Technologies
- ON Semiconductor
- Power Integrations
- Renesas Electronics (Transphorm)
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens eMobility
- STMicroelectronics
- Texas Instruments
- 區域玩家
- BTC Power
- ChargePoint
- EVBox (Engie)
- GaN Systems
- Nexperia
- Panasonic
- Tritium
- Wallbox
- VisIC Technologies
- Chanan
- 新興參與者和顛覆者
- Cambridge GaN Devices (CGD)
- EPC
- Innoscience Technology
- Navitas Semiconductor
11.3.5 奧德賽半導體技術公司
The Global Gallium Nitride (GaN) EV Charger Market was valued at USD 1.14 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 24.3% to reach USD 9.77 billion by 2034.

The market is transitioning from standalone discrete devices to integrated half-bridge stages and modules that combine GaN switches with drivers and protection features. This integration reduces layout sensitivity and EMI while improving thermal performance. Public-private initiatives have accelerated the commercialization of wide-bandgap (WBG) technologies, driving the adoption of integrated GaN solutions for onboard chargers (OBCs) and electric vehicle power systems. Automakers are increasingly integrating multifunctional power domains, which support higher levels of device integration. Demonstrations of OBC converters indicate that GaN can increase power density by 170% and reduce weight by 79% compared to silicon-based systems, achieving peak efficiencies of 99% in a 6.6 kW dual active bridge prototype. GaN devices can switch at higher frequencies with lower conduction losses than silicon, allowing smaller magnetics and cooling systems while reducing losses by 60-80% in advanced EV converters. Design teams are also optimizing switching frequencies to balance converter performance with motor parasitic losses. Research has shown that 1.2 kV GaN MOSFETs using high-HfO2 gate dielectrics achieve very low gate leakage and higher current density. This positions vertical GaN devices to compete with SiC for 1.2 kV applications once substrate and process technologies mature. However, automotive qualification for 800 V+ and 150 kW traction applications remains under development, with readiness expected toward the end of the decade due to cost and reliability considerations.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $1.14 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $9.77 Billion |
| CAGR | 24.3% |
The lateral GaN devices segment held 70% share and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 16.1% from 2025 to 2034. Lateral GaN devices dominate EV power electronics for OBCs, DC-DC converters, and auxiliary systems up to 650 V. Their AlGaN/GaN HEMT structure on silicon provides high electron mobility and critical field strength, delivering low on-resistance at high blocking voltages compared to silicon.
The medium voltage segment (100-650 V) accounted for a 67% share in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16% through 2034. Mid-voltage GaN devices are widely deployed because most OBCs (400 V today, rising to 800 V) and many DC-DC converters fall within this range. GaN's high-frequency performance directly boosts efficiency and power density in power factor correction and LLC or resonant converter stages in 6.6-19.2 kW OBC systems.
China Gallium Nitride (GaN) EV Charger Market generated USD 73.4 million in 2024. Accounting for nearly two-thirds of global EV sales, China's scale generates the largest addressable market for GaN devices, as every EV requires onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, and compatible charging infrastructure. This production volume positions China far ahead of other regional markets like Japan, South Korea, and India.
Key players in the Global Gallium Nitride (GaN) EV Charger Market include Transphorm, Navitas, Texas Instruments, GaN Systems, EPC, STMicroelectronics, ROHM Semiconductor, Infineon Technologies, Innoscience, and Power Integrations. Companies are strengthening their position by investing in R&D to improve GaN device performance, efficiency, and reliability. Strategic collaborations with automakers and charger manufacturers accelerate adoption. Expanding product portfolios with medium- and high-voltage solutions, securing automotive qualification certifications, and developing integrated modules enhances market penetration. Firms also focus on reducing costs through substrate innovations, scaling production capacity, and optimizing supply chains.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis, 2021 - 2034
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Product
- 2.2.2 Charging capacity
- 2.2.3 Vehicle
- 2.2.4 Application
- 2.2.5 Distribution channel
- 2.2.6 Regional
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2026-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin analysis
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Rising EV adoption
- 3.2.1.2 Energy efficiency and sustainability
- 3.2.1.3 Electrification of fleets
- 3.2.1.4 Government policies and incentives
- 3.2.1.5 Technological advancements in GaN
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High initial cost
- 3.2.2.2 Integration challenges
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Integration with renewable energy
- 3.2.3.2 High-power industrial fleet charging
- 3.2.3.3 Expansion of public charging networks
- 3.2.3.4 Smart charging and grid management
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle east and Africa
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technology
- 3.7.2 Emerging technology
- 3.7.3 GaN device architectures & technology variants
- 3.7.3.1 Lateral GaN hemt architecture (300-650v commercial)
- 3.7.3.2 Vertical GaN development roadmap (>1.2 kv target)
- 3.7.3.3 Bidirectional GaN switch (bds) technology
- 3.7.4 Wide-bandgap semiconductor technology landscape
- 3.7.4.1 Silicon (si) baseline performance & limitations
- 3.7.4.2 Gan technology overview & advantages
- 3.7.4.3 Silicon carbide (sic) technology overview
- 3.7.4.4 Gan vs silicon performance comparison
- 3.8 Patent analysis
- 3.9 Price Trends Analysis
- 3.9.1 By component
- 3.9.2 By region
- 3.10 Cost Breakdown Analysis
- 3.11 Production statistics
- 3.11.1 Production hubs
- 3.11.2 Consumption hubs
- 3.11.3 Export and import
- 3.12 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.12.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.12.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.12.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.12.4 Eco-friendly initiatives
- 3.12.5 Carbon footprint considerations
- 3.13 Manufacturing Process & Cost Structure
- 3.13.1 GaN device fabrication process flow
- 3.13.2 Epitaxial growth (MOCVD, MBE)
- 3.13.3 Wafer processing & lithography
- 3.13.4 Dicing & packaging
- 3.13.5 Testing & quality control
- 3.13.6 Manufacturing cost breakdown ($/kW)
- 3.14 Thermal management considerations
- 3.14.1 Heat dissipation challenges at high switching frequency
- 3.14.2 Heatsink design & optimization
- 3.14.3 Liquid cooling vs air cooling
- 3.14.4 Thermal interface materials
- 3.14.5 Junction temperature management
- 3.15 Emi/emc compliance & mitigation
- 3.15.1 High DV/DT & DI/DT challenges
- 3.15.2 Conducted emissions
- 3.15.3 Radiated emissions
- 3.15.4 Emi filter design for GaN chargers
- 3.15.5 Pcb layout best practices
- 3.15.6 Shielding & grounding strategies
- 3.16 Reliability & qualification standards
- 3.16.1 Aec-q101 (automotive discrete semiconductors)
- 3.16.2 Aec-q100 (automotive integrated circuits)
- 3.16.3 Automotive qualification requirements
- 3.16.4 Long-term reliability testing
- 3.16.5 Gate oxide reliability
- 3.16.6 Dynamic on-resistance degradation
- 3.17 Trade analysis & import/export dynamics
- 3.17.1 Global GaN device trade flows
- 3.17.2 Major exporting countries (China, Taiwan, Germany, U.S.)
- 3.17.3 Major importing countries
- 3.17.4 Tariffs & trade barriers
- 3.17.5 Trade policy impact (U.S.-China relations)
- 3.17.6 Reshoring & nearshoring trends
- 3.18 Case Studies & Real-World Implementations
- 3.18.1 ORNL 6.6 kW GaN OBC demonstration
- 3.18.2 Delta electronics GaN charger deployment
- 3.18.3. Infineon 300 mm GaN pilot production
- 3.18.4 Navitas GaNFast IC automotive design wins
- 3.18.5 Chargepoint GaN-enabled dc fast chargers
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key news and initiatives
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New Product Launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion Plans and funding
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Product, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 On-Board Chargers
- 5.3 Off-Board Chargers
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial
- 5.3.3 Public / High-Power
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Charging Capacity, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 <11 kW
- 6.3 11-22 kW
- 6.4 >22 kW
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Vehicle, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Passenger vehicles
- 7.2.1 Hatchback
- 7.2.2 Sedan
- 7.2.3 SUV
- 7.3 Commercial vehicles
- 7.3.1 LCV
- 7.3.2 MCV
- 7.3.3 HCV
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Residential
- 8.3 Commercial
- 8.4 Public
- 8.5 Industrial
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Distribution channel, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 OEM
- 9.3 Aftermarket
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 US
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.3.6 Nordics
- 10.3.7 Netherlands
- 10.3.8 Russia
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 ANZ
- 10.4.5 Singapore
- 10.4.6 Thailand
- 10.4.7 Vietnam
- 10.4.8 South Korea
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.6 MEA
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Global Players
- 11.1.1 ABB E-Mobility
- 11.1.2 Infineon Technologies
- 11.1.3 ON Semiconductor
- 11.1.4 Power Integrations
- 11.1.5 Renesas Electronics (Transphorm)
- 11.1.6 ROHM Semiconductor
- 11.1.7 Schneider Electric
- 11.1.8 Siemens eMobility
- 11.1.9 STMicroelectronics
- 11.1.10 Texas Instruments
- 11.2 Regional Players
- 11.2.1 BTC Power
- 11.2.2 ChargePoint
- 11.2.3 EVBox (Engie)
- 11.2.4 GaN Systems
- 11.2.5 Nexperia
- 11.2.6 Panasonic
- 11.2.7 Tritium
- 11.2.8 Wallbox
- 11.2.9 VisIC Technologies
- 11.2.10 Chanan
- 11.3 Emerging players and disruptors
- 11.3.1 Cambridge GaN Devices (CGD)
- 11.3.2 EPC
- 11.3.3 Innoscience Technology
- 11.3.4 Navitas Semiconductor
11.3.5 Odyssey Semiconductor Technologies











