 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1740954
運輸燃料電池市場機會、成長動力、產業趨勢分析及 2025 - 2034 年預測Transport Fuel Cell Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
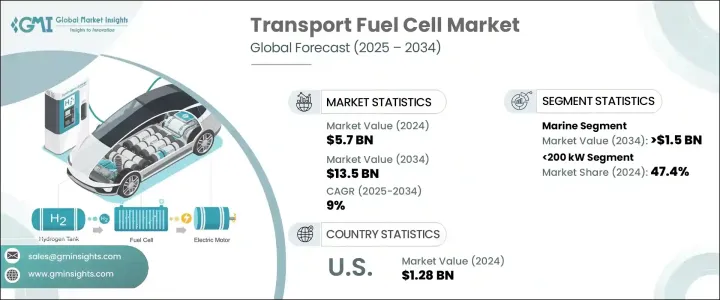
2024 年全球運輸燃料電池市場價值為 57 億美元,預計到 2034 年將以 9% 的複合年成長率成長,達到 135 億美元,這得益於政府對清潔能源應用的支持力度加大以及持續努力發展加氫基礎設施。隨著各國加快實現運輸脫碳目標並擴大接受公路、鐵路、海運和空運等各種運輸方式的氫動力出行,市場正獲得強勁發展勢頭。 PEM 燃料電池技術的進步,加上對建構彈性氫生態系統的更大關注,正在重塑零排放運輸的未來。隨著綠色氫氣生產規模的擴大和燃料電池電動車 (FCEV) 競爭力的增強,該產業有望經歷變革性成長。航空和航運等領域對可靠、可擴展的氫能的需求激增,這為製造商創造了新的機遇,並推動了對高需求環境的尖端燃料電池設計的投資。
然而,運輸燃料電池市場並非一帆風順。不斷變化的國際貿易格局帶來了巨大的阻力。美國政府對來自中國和墨西哥等主要製造業中心的進口產品徵收新關稅,擾亂了全球供應鏈。這些措施推高了燃料電池電動車(FCEV)所用關鍵零件(例如燃料電池電堆、電力電子設備和先進系統)的成本結構。隨著生產和採購成本的上升,製造商面臨艱難的抉擇,這可能導致汽車價格上漲,使FCEV在價格敏感的市場中難以普及。這可能會推遲FCEV在尚未實現與內燃機(ICE)汽車成本平價的地區的普及。
| 市場範圍 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 預測年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 57億美元 |
| 預測值 | 135億美元 |
| 複合年成長率 | 9% |
預計到2034年,運輸燃料電池市場中的船舶部分將創造15億美元的產值。這一成長主要源自於整個航運業持續進行的改裝工作,例如渡輪、拖船和貨船等船舶正在配備低排放推進系統。產業領導者正在設計專門的燃料電池解決方案,以滿足海上嚴格的性能和耐用性標準。同時,世界各地的港口當局正在大力投資加氫基礎設施,這體現了將氫能納入清潔航運走廊和零排放港口策略的更廣泛承諾。
預計到2034年,200千瓦至1兆瓦的燃料電池系統將以8%的複合年成長率成長。這些中高容量模組憑藉其模組化特性、系統冗餘和車隊營運的可擴展性,正迅速成為重型運輸應用的首選。隨著綠氫能的日益普及,中國和韓國等國正推出數千輛搭載200-300千瓦燃料電池堆的公車和物流卡車。
2024年,美國運輸燃料電池市場產值達12.8億美元,這得益於其強大的政策環境,包括為氫氣生產、FCEV採購和基礎設施建設提供激勵措施和稅收抵免。旨在減少排放和加速向清潔交通轉型的聯邦和州級項目正在顯著推動市場成長。這種政策驅動的勢頭,加上公私合作對加氫樞紐和加氫站的投資,使美國成為全球向零排放出行轉型的重要參與者。
運輸燃料電池產業的主要參與者包括豐田汽車、Stellantis、PowerCell Sweden、Quantron、尼古拉公司、ElringKlinger、本田汽車、沃爾沃集團、通用汽車和 Hyzon Motors。各公司正在大力投資垂直整合、合資企業和區域擴張策略。許多公司正在提升研發能力,以開發耐用、經濟高效的燃料電池堆,同時擴大產能,使其更貼近目標市場。與物流公司和公共交通機構的合作有助於獲得長期合約並擴大氫能基礎設施的規模。一些公司專注於為特定車輛類別(船舶、鐵路或商用車隊)提供客製化解決方案,根據特定的最終用途需求客製化燃油效率和系統性能。
目錄
第1章:方法論與範圍
第2章:執行摘要
第3章:行業洞察
- 產業生態系統
- 川普政府關稅分析
- 對貿易的影響
- 貿易量中斷
- 報復措施
- 對產業的影響
- 供應方影響(原料)
- 關鍵材料價格波動
- 供應鏈重組
- 生產成本影響
- 需求面影響(售價)
- 價格傳導至終端市場
- 市佔率動態
- 消費者反應模式
- 供應方影響(原料)
- 受影響的主要公司
- 策略產業反應
- 供應鏈重組
- 定價和產品策略
- 政策參與
- 展望與未來考慮
- 對貿易的影響
- 監管格局
- 產業衝擊力
- 成長動力
- 產業陷阱與挑戰
- 成長潛力分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
第4章:競爭格局
- 介紹
- 戰略儀表板
- 創新與技術格局
第5章:市場規模及預測:依產能,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- < 200 千瓦
- 200千瓦-1兆瓦
- ≥1兆瓦
第6章:市場規模及預測:依產品,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 質子交換膜燃料電池
- 直接甲醇燃料電池
- 固態氧化物燃料電池
- 平安金融中心及亞洲金融中心
- MCFC
第7章:市場規模及預測:依最終用途,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 海洋
- 鐵路
- 燃料電池電動車
- 其他
第8章:市場規模及預測:按地區,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趨勢
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 奧地利
- 亞太地區
- 日本
- 韓國
- 中國
- 印度
- 菲律賓
- 越南
- 中東和非洲
- 南非
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 秘魯
- 墨西哥
第9章:公司簡介
- Toyota Motors
- Honda Motors
- Nikola Corporation
- PowerCell Sweden
- ElringKlinger
- Volvo Group
- General Motors
- Stellantis
- Hyzon
- Quantron
The Global Transport Fuel Cell Market was valued at USD 5.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 9% to reach USD 13.5 billion by 2034, driven by rising government support for clean energy adoption and ongoing efforts to develop hydrogen refueling infrastructure. The market is gaining strong momentum as nations accelerate their transport decarbonization goals and increasingly accept hydrogen-powered mobility across a wide range of transportation modes, including road, rail, marine, and air. Advances in PEM fuel cell technologies, combined with a greater focus on building resilient hydrogen ecosystems, are reshaping the future of zero-emission transportation. As green hydrogen production scales up and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) become more competitive, the industry is positioned to experience transformative growth. Sectors like aviation and shipping are witnessing a surge in demand for reliable, scalable hydrogen power, creating new opportunities for manufacturers and fueling investment into cutting-edge fuel cell designs tailored for high-demand environments.

However, the transport fuel cell market is not without challenges. Evolving international trade dynamics are presenting major headwinds. The introduction of new tariffs by the U.S. government on imports from key manufacturing hubs such as China and Mexico is disrupting global supply chains. These measures are driving up the cost structure of critical components like fuel cell stacks, power electronics, and advanced systems used in FCEVs. With rising production and sourcing costs, manufacturers are facing tough decisions that could result in higher vehicle pricing, making FCEVs less accessible in price-sensitive markets. This could delay adoption in regions where cost parity with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles has yet to be achieved.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $5.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $13.5 Billion |
| CAGR | 9% |
The marine segment within the transport fuel cell market is projected to generate USD 1.5 billion by 2034. Much of this growth comes from ongoing retrofitting efforts across the maritime sector, where vessels such as ferries, tugboats, and cargo ships are being outfitted with low-emission propulsion systems. Industry leaders are designing specialized fuel cell solutions that meet the rigorous performance and durability standards required at sea. At the same time, port authorities worldwide are heavily investing in hydrogen refueling infrastructure, reflecting a broader commitment to integrating hydrogen into clean shipping corridors and zero-emission port strategies.
Fuel cell systems ranging from 200 kW to 1 MW are expected to grow at a CAGR of 8% through 2034. These medium- to high-capacity modules are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for heavy-duty transport applications, thanks to their modular nature, system redundancy, and scalability for fleet operations. With green hydrogen becoming increasingly available, countries like China and South Korea are rolling out thousands of buses and logistics trucks powered by fuel cell stacks in the 200-300 kW range.
The United States transport fuel cell market generated USD 1.28 billion in 2024, supported by a robust policy environment that offers incentives and tax credits for hydrogen production, FCEV procurement, and infrastructure development. Federal and state programs aimed at cutting emissions and accelerating the transition to clean transportation are significantly driving market growth. This policy-driven momentum, combined with public-private investments in hydrogen hubs and refueling stations, positions the U.S. as a major player in the global shift toward zero-emission mobility.
Key players in the transport fuel cell industry include Toyota Motors, Stellantis, PowerCell Sweden, Quantron, Nikola Corporation, ElringKlinger, Honda Motors, Volvo Group, General Motors, and Hyzon Motors. Companies are investing heavily in vertical integration, joint ventures, and regional expansion strategies. Many are enhancing their R&D capabilities to develop durable, cost-efficient fuel cell stacks while expanding manufacturing capacity closer to target markets. Partnerships with logistics firms and public transit agencies are helping secure long-term contracts and scale hydrogen infrastructure. Several players are focusing on customized solutions for specific vehicle classes-marine, rail, or commercial fleets-tailoring fuel efficiency and system performance to specific end-use demands.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Research design
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast model
- 1.4 Primary research & validation
- 1.4.1 Primary sources
- 1.4.2 Data mining sources
- 1.5 Market definitions
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021 – 2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem
- 3.2 Trump administration tariff analysis
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key material
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (selling price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Supply chain reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and product strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4 Industry impact forces
- 3.4.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.5 Growth potential analysis
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.6.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.6.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 3.6.3 Threat of new entrants
- 3.6.4 Threat of substitutes
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Strategic dashboard
- 4.3 Innovation & technology landscape
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Capacity, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 < 200 kW
- 5.3 200 kW - 1 MW
- 5.4 ≥ 1 MW
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Product, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 PEMFC
- 6.3 DMFC
- 6.4 SOFC
- 6.5 PAFC & AFC
- 6.6 MCFC
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Marine
- 7.3 Railways
- 7.4 FCEVs
- 7.5 Others
Chapter 8 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 North America
- 8.2.1 U.S.
- 8.2.2 Canada
- 8.3 Europe
- 8.3.1 Germany
- 8.3.2 UK
- 8.3.3 France
- 8.3.4 Italy
- 8.3.5 Spain
- 8.3.6 Austria
- 8.4 Asia Pacific
- 8.4.1 Japan
- 8.4.2 South Korea
- 8.4.3 China
- 8.4.4 India
- 8.4.5 Philippines
- 8.4.6 Vietnam
- 8.5 Middle East & Africa
- 8.5.1 South Africa
- 8.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 8.5.3 UAE
- 8.6 Latin America
- 8.6.1 Brazil
- 8.6.2 Peru
- 8.6.3 Mexico
Chapter 9 Company Profiles
- 9.1 Toyota Motors
- 9.2 Honda Motors
- 9.3 Nikola Corporation
- 9.4 PowerCell Sweden
- 9.5 ElringKlinger
- 9.6 Volvo Group
- 9.7 General Motors
- 9.8 Stellantis
- 9.9 Hyzon
- 9.10 Quantron







