 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1552536
全球網路中心戰市場(2024-2034)Global Network Centric Warfare Market 2024-2034 |
||||||
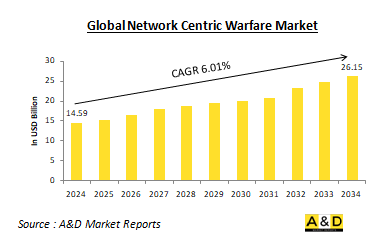
2024年全球網路中心戰市場規模預計為145.9億美元,預測期內(2024-2034年)年複合成長率為6.01%,到2034年將達到261.5億美元。
全球以網路為中心的戰鬥市場概述
全球網路中心戰(NCW)代表了軍事行動的典範轉移,強調先進資訊科技的整合以提高戰鬥力。網路中心戰概念於20 世紀 90年代末提出,其根源在於卓越的資訊和通訊能力可以在戰爭中提供決定性優勢。 NCW 將感測器、決策者和武器系統聯網,以創建統一的作戰圖景,提高態勢感知、加快決策速度並提高軍事行動的整體節奏。 NCW的發展與資訊時代密切相關,快速收集、處理和傳播資訊的能力非常重要。這種方法透過利用促進即時通訊和協調的互連系統,使部隊能夠在陸地、空中、海上和網路空間更有效地作戰。隨著世界各地的軍隊採用NCW原則,他們改變傳統的指揮和控制結構,並轉向更分散和敏捷的作戰模式。科技對全球網路中心戰市場的影響
科技對網路中心戰(NCW)的影響是革命性的,一些重要的進步顯著影響其實施。網路中心戰的核心是追求資訊優勢,其中包括比對手更有效地收集、分析和傳播資訊的能力。先進感測器、衛星通訊和資料分析等技術對於實現這一優勢非常重要。互通性是NCW的另一個重要方面,強調了各種軍事平台和系統之間無縫整合的需求。這是透過標準化的通訊協定和資料格式來實現的,允許不同的系統有效地協同工作並增強聯合作戰。即時資料共享是網路作戰的基石,在雲端運算和安全通訊網路等技術的推動下,可以實現部隊之間的快速資訊交換,提高態勢感知能力並加快決策速度。包括無人機和機器人平台在內的自主系統的整合代表了NCW的重大技術飛躍。這些無人系統可以自主執行情報收集、監視甚至目標交戰等任務,為指揮官提供關鍵情報和作戰彈性。人工智慧(AI)日益在 NCW 中用於處理大量資料、識別模式和支援決策。人工智慧支援預測分析,使軍事領導人能夠預測敵人的行為並主動應對。最後,網路安全是網路中心戰不可或缺的一部分,因為對互連系統的依賴會使軍事行動面臨網路威脅。發展強大的網路能力對於確保通訊網路的完整性和安全性以及保護敏感資訊非常重要。
全球以網路為中心的作戰市場的關鍵驅動因素
有幾個因素推動網路中心戰(NCW)世界的採用和發展。地緣政治動態發揮關鍵作用。以不對稱戰爭和混合威脅為特徵的全球衝突性質不斷變化,需要更靈活和反應靈敏的軍事戰略。 NCW 提供了一個框架,透過提高態勢感知和操作靈活性來應對這些挑戰。高速互聯網、行動通訊和先進感測器等資訊和通訊技術的快速發展使得網路中心戰概念變得越來越可行。這些技術實現了即時資料共享和協作,改變了戰場。此外,許多國家進行目的是實現武裝部隊現代化的軍事轉型工作,而網路作戰人員往往是這些努力的核心要素。 NCW 原則與提高營運有效性和效率的目標是一致的。盟國之間聯合和聯合作戰的增加進一步增加了對互通性和有效通信的需求,NCW 透過加強不同部隊之間的協調和提高集體能力來解決這一問題。預算限制也會影響 NCW 的採用。隨著國防預算面臨審查,軍事組織尋求具有成本效益的解決方案來增強其能力。 NCW 提供了一種透過改進協調和資訊共享來最大限度地提高現有資源效率的方法。最後,公眾和政治對軍事行動問責制和透明度的壓力增加了資訊共享與合作的重要性。 NCW 透過幫助軍事領導人向決策者和公眾提供及時、準確的資訊來滿足這些期望。
全球以網路為中心的戰鬥市場的區域趨勢
網路中心戰(NCW)的採用因地區而異,並受到地區軍事能力、地緣政治背景和技術準備的影響。在北美,美國領導 NCW,並自20 世紀 90年代末以來已將其原則納入軍事理論。美國國防部對以網路為中心的能力進行了大量投資,並致力於聯合作戰和軍種間互通性,在情報、監視和偵察(ISR)能力方面取得了重大進展。在歐洲,隨著歐洲國家尋求提高其軍事效能,網路武器的採用日益增加。北約聯盟認識到互通性和共享態勢感知的重要性,因此採取了整合成員國軍隊的措施。英國和法國等國家投資先進的通訊系統以支援這些聯合行動。在亞太地區,隨著軍事能力的提高和地區緊張局勢的背景,人們對網路中心戰的興趣日益濃厚。中國和印度等國家正大力投資先進技術,以提高軍事效能,其中中國特別注重符合網路戰原則的資訊戰和網路能力。在中東,網路中心戰的概念迅速獲得接受,特別是在參與不對稱戰爭的國家。以色列等國家利用先進技術和以網路為中心的方法,在複雜的安全環境中保持戰略優勢。相比之下,拉丁美洲和非洲的NCW 則發展遲緩。然而,隨著這些地區國家的軍事武庫現代化,其成長潛力仍然存在。加強與國際合作夥伴的合作和技術投資可能會促進這些地區採用網路中心。
網路中心戰的主要計畫
英國開發了自己的網路中心戰(NCW)版本,稱為 NEC(網路支援能力)。這種方法的重點是利用先進技術來增強指揮、控制和通訊。 Morpheus NEC 計畫耗資 32億英鎊,目的是更新戰術通訊和資訊系統,並表明英國致力於將 NCW 原則納入軍事行動。
印度陸軍準備對其以網路為中心的戰場和軍事後勤系統進行重大檢修。幾個重要的技術驅動計畫進行中,以增強戰場態勢感知和網路中心戰能力。現代化工作包括用高精度防禦地圖升級砲兵作戰指揮和控制系統(ACCCS),並為陸軍引進新的態勢感知模組(SAMA)。這種轉變的一個關鍵面向是先進戰場監視系統的發展。作為現代化建設的一部分,陸軍將2023年定為 "轉型年" ,這些計畫目的是重組和重新構想作戰流程,以實現能力的重大飛躍。
目錄
以網路為中心的競爭市場:報告定義
以網路為中心的競爭市場區隔
- 依地區
- 依類型
- 依平台
以網路為中心的競爭市場分析(未來10年)
以網路為中心的戰鬥市場的市場技術
全球網路中心戰市場預測
網路中心戰市場:區域趨勢與預測
- 北美
- 促進/抑制因素和挑戰
- PEST分析
- 市場預測與情境分析
- 主要公司
- 供應商層級狀況
- 企業基準比較
- 歐洲
- 中東
- 亞太地區
- 南美洲
以網路為中心的競爭市場:國家分析
- 美國
- 防禦規劃
- 最新趨勢
- 專利
- 該市場目前的技術成熟度等級
- 市場預測與情境分析
- 加拿大
- 義大利
- 法國
- 德國
- 荷蘭
- 比利時
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 希臘
- 澳洲
- 南非
- 印度
- 中國
- 俄羅斯
- 韓國
- 日本
- 馬來西亞
- 新加坡
- 巴西
以網路為中心的競爭市場:市場機會矩陣
以網路為中心的競爭市場:專家對研究的看法
結論
關於航空和國防市場報告
The Global Network Centric Warfare Market is estimated at USD 14.59 billion in 2024, projected to grow to USD 26.15 billion by 2034 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.01% over the forecast period 2024-2034

Introduction to Global Network Centric Warfare Market:
Global Network Centric Warfare (NCW) represents a paradigm shift in military operations, emphasizing the integration of advanced information technology to enhance combat effectiveness. Coined in the late 1990s, the concept of NCW is rooted in the idea that superior information and communication capabilities can provide a decisive advantage in warfare. It involves the networking of sensors, decision-makers, and weapon systems to create a cohesive operational picture that enhances situational awareness, accelerates decision-making, and improves the overall tempo of military operations. The evolution of NCW is closely tied to the Information Age, where the ability to collect, process, and disseminate information rapidly is paramount. This approach enables forces to operate more effectively across various domains-land, air, sea, and cyberspace-by leveraging interconnected systems that facilitate real-time communication and coordination. As military organizations worldwide adopt NCW principles, they are transforming traditional command-and-control structures, moving towards more decentralized and agile operational models.
Technology Impact on Global Network Centric Warfare Market:
The impact of technology on Network-Centric Warfare (NCW) is transformative, with several key advancements significantly shaping its implementation. Central to NCW is the pursuit of information superiority, which involves the ability to collect, analyze, and disseminate information more effectively than adversaries. Technologies such as advanced sensors, satellite communications, and data analytics are pivotal in achieving this edge. Interoperability is another crucial aspect of NCW, emphasizing the need for seamless integration among various military platforms and systems. This is achieved through standardized communication protocols and data formats, allowing different systems to work together efficiently and enhancing joint operations. Real-time data sharing is a cornerstone of NCW, facilitated by technologies like cloud computing and secure communication networks, which enable rapid information exchange between units, thereby improving situational awareness and accelerating decision-making. The integration of autonomous systems, including drones and robotic platforms, represents a significant technological leap within NCW. These unmanned systems can perform tasks such as intelligence gathering, surveillance, and even target engagement autonomously, providing commanders with critical information and operational flexibility. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly utilized in NCW to process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and support decision-making. AI enhances predictive analytics, allowing military leaders to anticipate enemy actions and respond proactively. Finally, cybersecurity is a vital component of NCW, as the dependence on interconnected systems exposes military operations to cyber threats. Developing robust cyber capabilities is essential for ensuring the integrity and security of communication networks, thereby protecting sensitive information.
Key Drivers in Global Network Centric Warfare Market:
Several factors are driving the global adoption and evolution of Network-Centric Warfare (NCW). Geopolitical dynamics play a crucial role, as the changing nature of global conflicts, characterized by asymmetric warfare and hybrid threats, demands more agile and responsive military strategies. NCW offers a framework for addressing these challenges by enhancing situational awareness and operational flexibility. Technological advancements are another significant driver; the rapid development of information and communication technologies, including high-speed internet, mobile communications, and advanced sensors, has made NCW concepts increasingly feasible. These technologies enable real-time data sharing and collaboration, transforming the battlefield. Additionally, many nations are undergoing military transformation initiatives aimed at modernizing their forces, with NCW often being a central component of these efforts. The principles of NCW align with the goal of achieving greater operational effectiveness and efficiency. The rise in joint and coalition operations among allied nations further drives the need for interoperability and effective communication, which NCW facilitates by enhancing collaboration between diverse forces and boosting collective capabilities. Budgetary constraints also influence the adoption of NCW; as defense budgets face scrutiny, military organizations seek cost-effective solutions to enhance their capabilities. NCW provides a means to maximize the effectiveness of existing resources through improved coordination and information sharing. Lastly, public and political pressure for accountability and transparency in military operations has increased the emphasis on information sharing and collaboration. NCW meets these expectations by enabling military leaders to provide timely and accurate information to decision-makers and the public.
Regional Trends in Global Network Centric Warfare Market:
The implementation of Network-Centric Warfare (NCW) varies significantly across regions, shaped by local military capabilities, geopolitical contexts, and technological readiness. In North America, the United States leads in NCW, having integrated its principles into military doctrine since the late 1990s. The U.S. Department of Defense has made substantial investments in network-centric capabilities, emphasizing joint operations and interoperability among its armed services, which has resulted in notable advancements in intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. In Europe, the adoption of NCW is growing as European nations seek to enhance their military effectiveness. The NATO alliance, recognizing the importance of interoperability and shared situational awareness, has driven initiatives to integrate member states' forces. Countries like the United Kingdom and France are investing in advanced communication systems to support these joint operations. In the Asia-Pacific region, there is increasing interest in NCW driven by rising military capabilities and regional tensions. Nations such as China and India are investing heavily in advanced technologies to boost their military effectiveness, with China particularly focusing on information warfare and cyber capabilities in line with NCW principles. The Middle East has rapidly embraced NCW concepts, especially among nations engaged in asymmetric warfare. Countries like Israel utilize advanced technology and network-centric approaches to maintain a strategic advantage in a complex security environment. In contrast, Latin America and Africa have seen slower development of NCW. However, there is potential for growth as nations in these regions seek to modernize their military forces. Increased collaboration with international partners and investments in technology may facilitate the adoption of network-centric principles in these areas.
Key Global Network Centric Warfare Program:
The UK has developed its own version of Network-Centric Warfare (NCW), known as Network Enabled Capability (NEC). This approach focuses on enhancing command, control, and communication through advanced technologies. The Morpheus NEC Programme, a £3.2 billion initiative, aims to upgrade tactical communication and information systems, demonstrating the UK's commitment to integrating NCW principles into its military operations.
The Indian Army is preparing for a significant overhaul of its network-centric battlefield and military logistics systems. Several key technology-driven projects are underway to enhance battlefield situational awareness and network-centric warfare capabilities. The modernization efforts include upgrading the Artillery Combat Command and Control System (ACCCS) with highly accurate defense maps and introducing a new Situational Awareness Module for the Army (SAMA). A crucial aspect of this transformation is the development of an advanced battlefield surveillance system. As part of its modernization drive, the Army has designated 2023 as the 'Year of Transformation,' with these projects aimed at reshaping and re-engineering operational processes to achieve a major leap in capabilities.
Table of Contents
Network centric warfare Report Definition
Network Centric Warfare Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Platform
Network centric warfare Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year network centric warfare analysis would give a detailed overview of network centric warfare growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Network centric warfare
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Network centric warfare Forecast
The 10-year network centric warfare forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Network centric warfare Trends & Forecast
The regional network centric warfare trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Network centric warfare
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Network centric warfare
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Network centric warfare Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2022-2032
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2022-2032
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Platform, 2022-2032
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2022-2032
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2022-2032
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Platform, 2022-2032
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2022-2032
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Defense Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 2: Global Defense Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Region, 2022-2032
- Figure 3: Global Defense Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Platform, 2022-2032
- Figure 4: Global Defense Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Type, 2022-2032
- Figure 5: North America, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 6: Europe, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 7: Middle East, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 8: APAC, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 9: South America, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 10: United States, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 11: United States, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 12: Canada, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 13: Canada, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 14: Italy, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 15: Italy, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 16: France, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 17: France, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 18: Germany, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 19: Germany, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 22: Belgium, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 23: Belgium, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 24: Spain, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 25: Spain, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 26: Sweden, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 27: Sweden, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 28: Brazil, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 29: Brazil, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 30: Australia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 31: Australia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 32: India, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 33: India, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 34: China, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 35: China, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 38: South Korea, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 39: South Korea, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 40: Japan, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 41: Japan, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 44: Singapore, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 45: Singapore, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2022-2032
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2022-2032
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2022-2032
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (CAGR), 2022-2032
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (Cumulative Market), 2022-2032
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (CAGR), 2022-2032
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2022-2032
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (CAGR), 2022-2032
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Cumulative Market, 2022-2032
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Global Market, 2022-2032
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2022-2032
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2022-2032
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2022-2032
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2022-2032
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2022-2032
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2022-2032
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2022-2032
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2022-2032
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Defense Network Centric Warfare Market, 2022-2032






