 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1802915
AI 副駕駛與物聯網程式碼產生:智慧助理協助嵌入式開發變革AI Copilots & Code Generation for the IoT: Transforming Embedded Development with Intelligent Assistants |
||||||
本報告內容
人工智慧徹底改變了軟體開發。開發工具提供者正在利用生成式人工智慧和自然語言處理的快速發展,幫助工程師自動化大量編碼任務並加速原型設計。儘管人工智慧助理能夠顯著提升生產力,但嵌入式工程組織必須謹慎對待,因為自動化本身就存在安全性和品質風險。能夠透過客製化防護機制、工具整合、最佳實踐指導和模型優化,有效平衡安全性、品質和流程加速的商業解決方案,將在這個年輕且快速成長的 AI 副駕駛和程式碼生成解決方案市場中佔先機,搶佔先機。
本報告對物聯網和嵌入式軟體開發中的 AI 副駕駛和程式碼產生生態系統進行了全面分析。本報告探討了目前基於代理的 AI 和 AI 編碼工具的功能和局限性、它們與領先的 IDE、DevOps 流水線和嵌入式工具鏈的整合,以及這些工具在多大程度上滿足物聯網和邊緣計算部署的性能和監管要求。
本報告也分析了相關的併購交易、LLM 生態系統、授權策略、對基於代理程式的 IDE 和 AI 產生程式碼的擔憂,以及主要供應商的概況。該報告還提供了 2024 年至 2029 年的市場規模和預測,並按產品類型(通用解決方案 vs. 專用解決方案)、地區、垂直行業和主要供應商對市場進行了細分和解釋。
探討了哪些問題?
- 哪些因素推動了對 AI 增強型副駕駛和程式碼產生解決方案的需求?
- 開發工具提供者如何增強其產品組合,以滿足對 AI 驅動的開發解決方案的需求?
- 哪些垂直市場將推動這個快速成長領域的市場成長?
- 安全及安保關鍵產業何時會大規模採用 AI 程式碼產生?
- 為什麼工程師喜歡基於代理的解決方案而不是輕量級助手?
- 哪些公司正在推動產品創新並影響市場?
本報告的技術供應商
|
|
|
報告摘錄
利用人工智慧提高專案進度達標率
目錄
該報告的內容
摘要整理
- 主要調查結果
調查範圍和調查手法論
- 了解人工智慧
- AI Copilot 和程式碼產生工具
全球市場概覽
- 代理程式改變人工智慧程式碼生成,課題 Copilot
- 策略考慮因素
- 法學碩士 (LLM) 的選擇和支持直接影響市場可及性
- 人工智慧工具授權策略和趨勢
- JetBrains 與 Cursor,人工智慧的崛起IDE
- 安全性和程式碼品質問題阻礙 AI 的普及
- 最近的趨勢
- M&A
地區趨勢與預測
- 南北美洲
- 歐洲,中東·非洲
- 亞太地區
垂直市場趨勢與預測
- 航太及防衛
- 汽車
- 通訊與網路
- 工業自動化
競爭情形
- 現有的嵌入式軟體解決方案供應商必須適應 AI 驅動的顛覆性變革
最終用戶洞察
- 嵌入式工程組織對採用 AI 持謹慎態度AI 助手,變革迫在眉睫
- 使用 AI 可提高專案進度執行率
- 使用 AI 產生程式碼的嵌入式工程師對軟體堆疊表現出強烈的偏好
- 不同組織類型的工程師使用 AI 執行類似任務
關於作者
Inside this Report
AI has fundamentally reshaped software development. Development tool providers have successfully leveraged the rapid evolution of generative AI and natural language processing to help engineers automate large portions of the coding process and accelerate prototyping. Despite massive productivity benefits, automation comes with inherent security and quality risks that force embedded engineering organizations to approach AI-powered assistants with caution. Commercial solutions that can effectively blend security, quality, and process acceleration through custom guardrails, tool integrations, best practices guidance, and model refinement will reap early share in this young but rapidly emerging space for AI copilots and code generation solutions.
This report delivers a comprehensive analysis of the AI copilots and code generation ecosystem as it applies to IoT and embedded software development. It examines the capabilities and limitations of current agentic AI and AI coding tools, their integration with popular IDEs, DevOps pipelines, and embedded toolchains, and the extent to which these tools can meet the performance and regulatory requirements of IoT and edge computing deployments. The report also includes an analysis of relevant mergers and acquisitions, LLM ecosystems, licensing strategies, agentic IDEs, concerns with AI generated code, and profiles of leading vendors. The study includes market sizing and forecasts from 2024 to 2029 with commentary and segmentations by product type (general purpose versus application-specialized solutions), region vertical market, and leading vendors.
What Questions are Addressed?
- What factors are driving demand for AI-enhanced copilots and code generation solutions?
- How can development tool providers strengthen their portfolios to capitalize on demand for AI- powered development solutions?
- Which vertical markets will lead market growth in this burgeoning sector?
- When will safety- and security-critical industries adopt AI code generation at scale?
- Why do engineers favor agentic solutions over lightweight assistants?
- Which companies are driving product innovation and influencing the market?
Who Should Read this Report?
This report was written for those making critical decisions regarding product, market, channel, and competitive strategy and tactics. This report is intended for senior decision-makers who are developing, or are a part of the ecosystem of, AI assistants and code generation tools, including:
|
|
Technology Providers in this Report:
|
|
|
Demand-side Research Overview
VDC launches numerous surveys of the IoT and embedded engineering ecosystem every year using an online survey platform. To support this research, VDC leverages its in-house panel of more than 30,000 individuals from various roles and industries across the world. Our global Voice of the Engineer survey recently captured insights from a total of 600 qualified respondents. This survey was used to inform our insight into key trends, preferences, and predictions within the engineering community.
Executive Summary
AI code generation is emerging as one of the most disruptive forces in IoT software development since the advent of open source. Enterprise/IT organizations eagerly adopted AI-powered coding tools with little hesitation, but demand for code generation capabilities from embedded engineering organizations has lagged behind, resulting in a blossoming opportunity for AI copilot and code generation vendors beginning primarily in 2025. AI copilots accelerate software development, helping engineering organizations cope with the increasing complexity of software codebases and their core role in product-level differentiation. For engineering and product development organizations across industries, AI promises to bridge skill gaps, reduce time to market, and improve developer productivity.
This acceleration in automated coding, however, also increases the need for rigorous quality assurance, compliance checks, and additional security. Currently, there is a large gap in the market for a complete solution that offers safety-critical software testing and analysis alongside standards-compliant code generation. AI-generated code can introduce vulnerabilities, licensing risks, or inefficiencies that are difficult to detect without robust testing and software composition analysis (SCA) in the background. Many of the leading AI development tool vendors do not have partnerships or experience in embedded software development, creating an opportunity for organizations with a long tenure in embedded engineering to partner with AI leaders to safely and securely bring AI-generated code to the IoT for all use cases.
Copilots and code generation will take hold in embedded engineering over the next five years. In the near term, adoption will be strongest in non-safety-critical IoT segments such as communications & networking, consumer electronics, and smart home, where AI-assisted coding can quickly prove ROI without extensive regulatory overhead. As certification bodies and standards organizations formalize guidelines for AI-generated code, safety-critical engineering organizations will adopt copilots more eagerly. To capture a portion of the growing safety-critical market share, vendors must add compliance support, code provenance tracking, and integrate with popular software verification and validation tools.
Key Findings:
- Demand for application- and domain-specialized code generation will accelerate rapidly as embedded engineering organizations embrace AI to add greater amounts of software-driven value to their products.
- As secure, purpose-built AI copilots go to market, the automotive vertical will grow the fastest as OEMs transition toward software-defined vehicle architectures and value-added software features that generate recurring revenue.
- Agentic AI will not only transform code generation but also the complete software development lifecycle as it automates design planning, QA, and project management.
- The Americas is a home market for many of the world's leading AI copilot and code generation solution vendors, contributing to its early market leadership.
- VDC's Voice of the Engineer survey data shows that AI tooling is effectively accelerating project timelines, helping engineers meet and exceed deadlines.
Report Excerpt
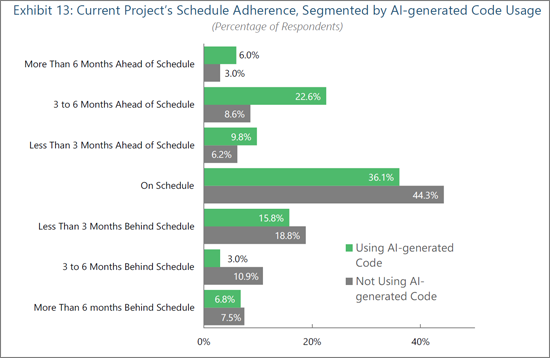
AI Usage Improves Project Schedule Adherence

Organizations leveraging AI for code generation are measurably outperforming their peers in project execution timelines. Engineering organizations employing AI-generated code are significantly more likely to beat expectations, with 38% reportedly ahead of their project schedules (2.1x more likely than organizations not using AI code generation). This discrepancy reflects AI's ability to automate foundational coding tasks, accelerate iteration cycles, and reduce delays caused by manual development bottlenecks.
The sharp difference in three to six month delays (3.0% of AI users versus 10.9% of non-AI users) and overall reduction in delays among AI code users suggest that engineering organizations benefit from AI's ability to preempt errors and improve code reliability earlier in the lifecycle. AI code generation tools that generate boilerplate or repetitive code components allow engineers to focus on architecture, integration, and optimization, which are key elements for fueling product innovation and differentiation in traditional workflows. In edge AI contexts, where deployment environments are heterogeneous and performance tuning is critical, complex task automation (e.g., model integration or hardware abstraction) enables teams to compress development cycles and better align with shifting project requirements. AI-integrated software development strategies free up developers to work proactively on value-creating features. As a result, solution providers should position AI code generation not just as a developer aid, but as a catalyst for predictable, repeatable acceleration, which is especially compelling in embedded markets defined by deployment complexity and constrained engineering resources.
Table of Contents
Inside this Report
Executive Summary
- Key Findings
Report Scope & Methodology
- Understanding AI
- AI Copilots & Code Generation Tools
Global Market Overview
- Agents Will Transform AI Code Generation and Challenge Copilots
- Strategic Considerations
- LLM Selection and Support Directly Impacts Market Addressability
- AI Tool Licensing Strategies and Trends
- JetBrains Versus Cursor and the Rise of AI IDEs
- Security and Code Quality Concerns Deter AI Adoption
- Recent Developments
- Mergers and Acquisitions
Regional Trends & Forecast
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- Asia-Pacific
Vertical Market Trends & Forecast
- Aerospace & Defense
- Automotive
- Communications & Networking
- Industrial Automation
Competitive Landscape
- Incumbent Embedded Software Solution Providers Must Adapt to AI Disruption
End-User Insights
- Embedded Engineering Organizations are Slow to Adopt AI Assistants, but Change is Imminent
- AI Usage Improves Project Schedule Adherence
- Embedded Engineers Using AI-generated Code Demonstrate Strong Software Stack Preferences
- Engineers Use AI for Similar Tasks Across Organization Types
About the Authors
List of Exhibits:
- Exhibit 1: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Tool Type
- Exhibit 2: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Tool Type
- Exhibit 3: Current Concerns About AI-generated Software Code
- Exhibit 4: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Geographic Region
- Exhibit 5: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Geographic Region
- Exhibit 6: Amount of Trust in AI-generated Software Code Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 7: Global Revenue of Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 8: Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Vertical Market
- Exhibit 9: 2024 Percentage of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Leading Vendors
- Exhibit 10: 2025 Estimated Market Share of Global Revenue from Copilots & Code Generation Tools & Related Services Segmented by Leading Vendors:
- Exhibit 11: Consideration/Use of AI-generated Software/Code (e.g., Use of Copilot and/or Prompt-based Code Creation)
- Exhibit 12: Expected Changes in Use of AI-generated Software in the Next Three Years
- Exhibit 13: Current Project's Schedule Adherence Segmented by AI-generated Code Usage
- Exhibit 14: Embedded Software Stack Components Required on Current/Most Recent Project Segmented by AI-generated Code Usage
IoT & Embedded Engineering Survey (Partial list):
- Exhibit 1: Primary Role Within Company/Organization
- Exhibit 2: Respondent's Organization's Primary Industry
- Exhibit 3: Total Number of Employees at Respondent's Organization
- Exhibit 4: Primary Region of Residence
- Exhibit 5: Primary Country of Residence
- Exhibit 6: Type of Most Current or Recent Project
- Exhibit 7: Involvement with Engineering of an Embedded/Edge, Enterprise/IT, HPC, AI/ML, or Mobile/System Device or Solution
- Exhibit 8: Type of Purchase by Respondent's Organization
- Exhibit 9: Primary Industry Classification of Project
- Exhibit 10: Type of Aerospace & Defense Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 11: Type of Automotive In-Vehicle Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 12: Type of Communications & Networking Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 13: Type of Consumer Electronics Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 14: Type of Digital Security Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 15: Type of Digital Signage Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 16: Type of Energy and Utilities Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 17: Type of Gaming Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 18: Type of Industrial Automation Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 19: Type of Media & Broadcasting Application for Most Recent Project
- Exhibit 20: Type of Medical Device Application for Most Current Project
- Exhibit 21: Type of Mobile Phone
- Exhibit 22: Type of Office/Business Automation Application for Most Recent Project







