 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1911737
鋰離子電池石墨陽極:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Graphite Anode For LIB - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
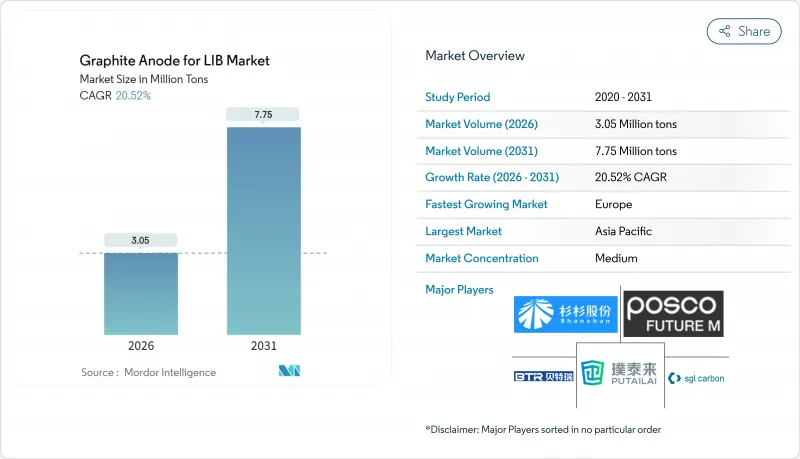
2025年鋰離子電池(LIB)石墨陽極市場規模為253萬噸,預計2031年將達到775萬噸,高於2026年的305萬噸。
預計在預測期(2026-2031 年)內,複合年成長率將達到 20.52%。
電動車電池容量的提升、固定式儲能計劃的擴張以及鼓勵國內採購的在地採購政策,都在加速石墨的普及。合成石墨憑藉其能夠滿足快速充電需求的工程化微觀結構,仍是市場主導。然而,成本敏感的天然石墨正透過精煉技術縮小與合成石墨的性能差距,這些技術能夠以更低的成本達到車用級純度。從美國的《通貨膨脹控制法案》到印度的《生產連結獎勵計畫計畫》,區域性激勵措施正在推動供應鏈向超級工廠附近的區域叢集多元化發展。這種轉變降低了物流成本,同時提高了對原產地規則的遵守程度。市場競爭依然激烈:中國現有企業正將業務垂直整合到前體焦炭領域;日本和韓國的專業企業則憑藉專有的塗層化學技術實現差異化;而西方新參與企業則利用政府融資建設低碳設施。同時,出口管制風險、排放法規以及富矽陽極的即將出現,促使電池製造商採用合成和天然原料的雙重來源,進一步重塑了鋰離子電池市場石墨陽極的籌資策略。
全球鋰離子電池石墨陽極市場趨勢及分析
由於電動車需求不斷成長,鋰離子電池產能迅速提升
2024年1月至2025年10月期間,已公佈的超級工廠專案增加了標準石墨負載下的陽極材料需求。寧德時代(CATL)位於德布勒森的工廠和比亞迪位於羅勇的工廠預計將於2027年提供新增產能。同時,特斯拉位於德克薩斯的工廠通過為期10年的承購協議,獲得了Sira Resources公司路易斯安那州產量的相當一部分。為了滿足美國《通膨控制法案》和歐盟電池法規規定的含量標準,電池製造商現在必須將陽極生產線設定在距離最終組裝廠200公里以內。這項策略不僅確保了合規性,也保障了來自本地供應商的上游供應。這種廣泛的擴張,加上產能擴張速度超過需求成長,預計將在2027年之前造成鋰離子電池(LIB)石墨陽極市場的結構性供不應求。
中國擴大生產規模降低了合成石墨的成本。
2024年,中國產合成石墨的單價顯著下降。這項改變主要歸功於內蒙古和四川省新爐的運作。一體化生產商利用與中國石油化工集團公司(中石化)的契約,以折扣價採購石油針狀焦。高產運轉率運行艾奇遜爐,降低了成本,並將這些成本優勢傳遞給了電池製造商。價格下降使中國在入門級電動車和摩托車市場相對於日本和韓國的競爭對手獲得了優勢。然而,歐盟的臨時反傾銷稅目前削弱了中國在歐洲市場的優勢。因此,這種成本主導的替代現像不僅推動了銷售成長,也加劇了鋰離子電池石墨陽極市場的地緣政治緊張局勢。
天然石墨的供應集中與出口管制
2024年,中國在全球天然石墨礦開採和球化加工能力方面佔據主導地位。 2023年12月,隨著出口許可證的擴大,北京當局目前控制所有電池石墨片的出口,導致中國以外地區的交貨延誤。 2024年初,由於許可證核准延誤,LG能源解決方案公司位於弗羅茨瓦夫的工廠被迫關閉,而三星SDI則選擇了成本更高的合成原料。儘管三星SDI擴大了位於莫三比克巴拉馬礦和馬達加斯加莫羅礦的營運規模,但預計到2026年,來自中國以外地區的石墨總供應量仍將持續短缺,這將加劇鋰離子電池(LIB)石墨陽極市場的波動。
細分市場分析
由於合成石墨在NMC和NCA電池體系中擁有無與倫比的循環壽命,並且相容於超快充電通訊協定,預計到2025年,合成石墨將佔電池供應量的56.78%。同時,天然石墨在入門級磷酸鐵鋰電池(LFP電池)領域找到了市場定位。儘管這些電池的首圈效率較低,但其成本優勢卻顯著。這種成本效益正推動市場強勁成長,預計到2031年將達到24.10%的複合年成長率。因此,用於鋰離子電池(LIB)石墨陽極的天然石墨產品市場預計將顯著擴張。同時,合成石墨的產量預計將成長較為緩慢。先進的提純技術,實現了金屬雜質含量低於10 ppm和碳純度高達99.95%的卓越性能,彌合了兩者之間的性能差距。比亞迪Blade電池在其售價低於2.5萬美元的電動車產品線中大量使用天然材料,便印證了這種新獲得的可靠性。
塗層技術不斷發展,目前兩種材料都利用瀝青衍生碳層或奈米碳管來提高初始庫侖效率。儘管存在這種融合趨勢,合成石墨在保持使用壽命方面仍然具有優勢,這對於提供15萬英里保固的汽車製造商至關重要。歐盟的碳排放法規正推動標準續航里程車型轉向使用天然石墨,而美國的國內含量抵免計畫則促使高階車型重新採用合成石墨。這一趨勢導致鋰離子電池市場石墨陽極材料的替代呈現區域性而非全球性模式。由此產生的行業兩極化,在高銷量、價格敏感的天然石墨市場和專注於工程應用的高階合成石墨小眾市場之間形成了明顯的鴻溝。
本鋰離子電池石墨陽極市場報告陽極材料類型(合成石墨與天然石墨)、最終用途(電動車、能源儲存系統、家用電子電器及其他)和地區(亞太地區、北美地區、歐洲地區及世界其他地區)進行分析。市場預測以銷售量(噸)和價值(美元)為單位。
區域分析
亞太地區將佔2025年全球出貨量的73.85%,這主要得益於中國龐大的製造能力。中國在一個省級產業叢集內實現了精煉焦炭煅燒、石墨化、球化和電池組裝等製程的無縫整合。中國擁有許多優勢,包括低成本電力、省級土地優惠和快速核准程序,鞏固了其成本領先地位。同時,日本和韓國正將重點轉向採用專有塗層技術增強的高利潤合成石墨。特別是三菱化學的MAGE-M系列產品,憑藉其亞3奈米塗層技術實現了長循環壽命,在鋰離子電池(LIB)石墨陽極市場佔據了一席之地。
預計到2031年,歐洲將實現最快成長,複合年成長率將達到28.05%。這主要得益於汽車製造商為遵守歐盟電池法規所做的努力,該法規將於2027年強制執行國產化率基準值。瑞典的Northvolt公司已率先採用水性冶金製程進行大規模石墨回收,並計劃擴大產能。同時,BASF位於施瓦茨海德的工廠正在利用可再生能源每年生產合成石墨,從而降低生產過程(從搖籃到大門)的碳排放強度。此外,法國的Vercors公司和義大利的Italvolt公司已成立合資企業,以擴大年產量,進一步鞏固了歐洲市場的地位。然而,歐洲的現金成本仍遠高於亞太地區,因此碳排放邊境調整對於維持鋰離子電池陽極市場的競爭力至關重要。
北美在2024年的石墨產量佔有率較低,但預計到2030年,在45X條款稅收優惠政策的支持下,其佔有率將翻倍以上。席勒公司位於維達利亞的工廠在2025年實現了顯著的產能提升,並利用國內生產溢價直接向特斯拉位於德克薩斯德克薩斯的超級工廠供貨。在田納西州,諾沃尼克斯公司在能源部貸款擔保下,計劃在2026年前推出合成石墨產能,並開始向附近的福特和通用汽車公司供貨。同時,加拿大魁北克省的礦場正在提高天然石墨片的供應量,但聯邦核准流程緩慢,這意味著其顯著影響要到2027年或更晚才能顯現。墨西哥在電極塗層和電池組組裝方面具有成本競爭力,但缺乏關鍵的石墨化設備預計將在短期內限制北美的石墨供應。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 由於電動車需求不斷成長,鋰離子電池產能迅速提升
- 中國擴大生產規模降低了合成石墨的成本。
- 政府對國內電池供應鏈的激勵措施
- 高能耗電子設備的需求快速成長
- 快速充電架構中對高倍率陽極的需求
- 市場限制
- 天然石墨供應集中度及出口限制
- 石墨爐排放氣體法規
- 向富矽和鋰金屬陽極過渡
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模和成長預測(價值和數量)
- 依陽極材料類型
- 合成石墨
- 天然石墨
- 最終用途
- 電動車
- 能源儲存系統
- 家用電子電器
- 其他(電動工具和電動車)
- 地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 韓國
- 印度
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 英國
- 義大利
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 世界其他地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- Beterui New Materials Group Co. Ltd
- Guangdong Kaijin New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- Hunan Zhongke Electric Co. Ltd(Hunan Zhongke Xingcheng Graphite Co. Ltd)
- JFE Chemical Corporation
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Nippon Carbon Co. Ltd
- POSCO CHEMICAL
- SGL Carbon
- Shanghai Putailai New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- Shangtai Technology
- Shanshan Co. Ltd
- Shenzhen Sinuo Industrial Development Co. Ltd
- Shenzhen Xiangfenghua Technology Co. Ltd
- Showa Denko KK
- Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Graphite Anode for LIB Market was valued at 2.53 million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 3.05 million tons in 2026 to reach 7.75 million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 20.52% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Rising electric-vehicle (EV) cell capacity, expanding stationary storage projects, and localization mandates that reward domestic content are collectively accelerating adoption. Synthetic graphite retains its volume leadership because its engineered microstructure tolerates fast-charge demands; however, cost-sensitive natural graphite is closing the performance gap as purification routes reach automotive-grade purity at a lower cost. Regional incentive packages-from the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act to India's Production-Linked Incentive scheme-are fragmenting supply chains into local clusters located near gigafactories, a shift that compresses logistics costs while improving compliance with origin rules. Competitive intensity remains high as Chinese incumbents extend vertical integration into precursor coke, Japanese and Korean specialists differentiate through proprietary coating chemistries, and Western newcomers attract government loans to build low-carbon facilities. Simultaneously, export-control risks, emissions regulations, and the impending arrival of silicon-rich anodes are prompting cell makers to dual-source synthetic and natural feedstocks, further reshaping procurement strategies for the graphite anode in the LIB market.
Global Graphite Anode For LIB Market Trends and Insights
Surging EV-Driven Li-ion Cell Capacity Expansions
Between January 2024 and October 2025, announced gigafactory projects led to an incremental anode requirement at standard graphite loadings. By 2027, CATL's Debrecen and BYD's Rayong projects are expected to contribute additional capacity. Meanwhile, Tesla's Texas facility has secured a significant portion of Syrah Resources' Louisiana output through a decade-long offtake agreement. To meet the content thresholds set by the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and EU Battery Regulation, cell manufacturers are now required to position anode lines within 200 km of their final assembly points. This strategy not only ensures compliance but also secures upstream volumes from local suppliers. As commissioning struggles to keep pace with demand, this widespread expansion is set to create a structural deficit in the graphite anode market for lithium-ion batteries (LIB) until 2027.
Cost Decline of Synthetic Graphite from Chinese Scale-Ups
In 2024, unit prices for Chinese synthetic graphite experienced a significant decline, a shift attributed to the activation of new furnaces in Inner Mongolia and Sichuan. Integrated producers, leveraging Sinopec contracts, procure petroleum needle-coke at discounted rates. They operate Acheson furnaces at a high utilization rate, subsequently passing these savings on to their cell customers. While this price drop gives an edge over Japanese and Korean competitors in the entry-level EV and two-wheeler markets, provisional EU anti-dumping duties now moderate this advantage within the European market. As a result, this cost-driven substitution not only propels volume growth but also heightens geopolitical tensions in the graphite anode market for lithium-ion batteries.
Natural Graphite Supply Concentration and Export Controls
In 2024, China dominated the world's mined natural graphite production and global spheroidization capacity. Following an expansion of export licenses in December 2023, Beijing now oversees all battery-grade flake exports, causing delays for shipments outside China. In early 2024, LG Energy Solution faced a shutdown at its Wroclaw plant due to permit delays, while Samsung SDI opted for a pricier synthetic feedstock. Despite scaling operations at Mozambique's Balama and Madagascar's Molo mines, the total supply from non-Chinese sources is projected to fall short until 2026, leading to heightened volatility in the graphite anode market for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Incentives for Domestic Battery Supply Chains
- High-Energy Consumer-Electronics Demand Spike
- Emissions Scrutiny on Graphitization Furnaces
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Synthetic graphite captured 56.78% of 2025 volume, thanks to its unmatched cycle life in NMC and NCA chemistries, as well as its compatibility with ultra-fast charging protocols. Meanwhile, natural graphite found its niche in entry-level LFP batteries. These batteries, although they accept a lower first-cycle efficiency, offer a cost advantage. This cost efficiency is driving robust growth, forecasted to propel a 24.10% CAGR forecast to 2031. As a result, the market for natural graphite products used in graphite anodes for LIBs is set to surge significantly. In contrast, synthetic volumes are anticipated to grow at a more modest rate. Advanced purification techniques, which achieve metallic impurities below 10 ppm and carbon purity of 99.95%, have bridged the performance gap. This newfound confidence is evident as BYD's Blade Battery opts for a high percentage of natural feedstock in its sub-USD 25,000 EV line.
Coating technologies are evolving, with both materials now utilizing pitch-derived carbon or carbon-nanotube layers to boost initial coulombic efficiency. Despite this convergence, synthetic graphite maintains an edge in calendar-life retention. This advantage is pivotal for automakers providing 150,000-mile warranties. While EU carbon regulations may steer standard-range models towards natural graphite, U.S. domestic-content credits are incentivizing premium vehicles to lean back towards synthetic graphite. This dynamic is creating a regional, rather than a global, pattern of material substitution in the graphite anode for the LIB market. Consequently, the industry is splitting into two distinct segments: a high-volume, price-sensitive natural-graphite sector and a premium, engineered synthetic niche.
The Graphite Anode for LIB Market Report is Segmented by Anode Material Type (Synthetic Graphite and Natural Graphite), End-Use Application (Electric Vehicles, Energy Storage Systems, Consumer Electronics, and Others), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and Rest of the World). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Tons) and Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific supplied 73.85% of 2025 shipments, largely driven by China's significant manufacturing capacity. This capacity seamlessly integrates processes like refinery coke calcination, graphitization, spheroidization, and cell assembly within single provincial clusters. China's edge comes from low-cost electricity, provincial land discounts, and expedited permitting, solidifying its cost leadership. Meanwhile, Japan and South Korea are pivoting towards high-margin synthetics, enhanced with proprietary coatings. Notably, Mitsubishi Chemical's MAGE-M series commands a premium for its sub-3 nm coatings, boasting high full-depth cycles, highlighting a performance-centric niche in the graphite anode market for lithium-ion batteries (LIB).
Europe is expected to exhibit the steepest regional growth, at a 28.05% CAGR, to 2031, driven by automakers' efforts to align with the EU Battery Regulation, which mandates a regional content threshold by 2027. Northvolt's site in Sweden is already ahead of the curve, recycling graphite through a hydrometallurgical loop with significant output and plans for expansion. Concurrently, BASF's Schwarzheide facility produces synthetic graphite annually, harnessing renewable energy to reduce its cradle-to-gate carbon intensity. Further bolstering the region, France's Verkor and Italy's Italvolt have initiated joint ventures aimed at increasing annual production. However, challenges loom as European cash costs are still significantly higher than those in the Asia-Pacific region, making carbon-border adjustments crucial for competitiveness in the graphite anode market for LIBs.
North America, which accounted for a smaller share of the 2024 volume, is poised to more than double its share by 2030, driven by Section 45X credits that offer subsidies. Syrah's Vidalia plant achieved a notable run-rate in 2025, directly supplying Tesla's Texas gigafactory, capitalizing on a premium for domestic origin. In Tennessee, Novonix, with backing from a Department of Energy loan guarantee, is set to launch synthetic capacity by 2026, catering to Ford and GM within a close radius. While Canada's Quebec mines are ramping up natural-flake supply, they're grappling with extended federal permitting, pushing their significant impact to post-2027. Mexico stands out for its cost-effective electrode coating and pack assembly, yet the absence of major graphitization assets keeps the North American supply constrained in the short term.
- Beterui New Materials Group Co. Ltd
- Guangdong Kaijin New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- Hunan Zhongke Electric Co. Ltd (Hunan Zhongke Xingcheng Graphite Co. Ltd)
- JFE Chemical Corporation
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Nippon Carbon Co. Ltd
- POSCO CHEMICAL
- SGL Carbon
- Shanghai Putailai New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- Shangtai Technology
- Shanshan Co. Ltd
- Shenzhen Sinuo Industrial Development Co. Ltd
- Shenzhen Xiangfenghua Technology Co. Ltd
- Showa Denko KK
- Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging EV-driven Li-ion cell capacity expansions
- 4.2.2 Cost decline of synthetic graphite from Chinese scale-ups
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for domestic battery supply chains
- 4.2.4 High-energy consumer electronics demand spike
- 4.2.5 Fast-charge architectures needing high-rate anodes
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Natural graphite supply concentration and export controls
- 4.3.2 Emissions scrutiny on graphitisation furnaces
- 4.3.3 Shift toward Si-rich and Li-metal anodes
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Anode Material Type
- 5.1.1 Synthetic Graphite
- 5.1.2 Natural Graphite
- 5.2 By End-use Application
- 5.2.1 Electric Vehicles
- 5.2.2 Energy Storage Systems
- 5.2.3 Consumer Electronics
- 5.2.4 Others (Power Tools and e-Mobility)
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 Japan
- 5.3.1.3 South Korea
- 5.3.1.4 India
- 5.3.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 France
- 5.3.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 Rest of the World
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Beterui New Materials Group Co. Ltd
- 6.4.2 Guangdong Kaijin New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.4.3 Hunan Zhongke Electric Co. Ltd (Hunan Zhongke Xingcheng Graphite Co. Ltd)
- 6.4.4 JFE Chemical Corporation
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- 6.4.6 Nippon Carbon Co. Ltd
- 6.4.7 POSCO CHEMICAL
- 6.4.8 SGL Carbon
- 6.4.9 Shanghai Putailai New Energy Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.4.10 Shangtai Technology
- 6.4.11 Shanshan Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Shenzhen Sinuo Industrial Development Co. Ltd
- 6.4.13 Shenzhen Xiangfenghua Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.4.14 Showa Denko KK
- 6.4.15 Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment









