 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910630
智慧馬達:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Smart Motors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
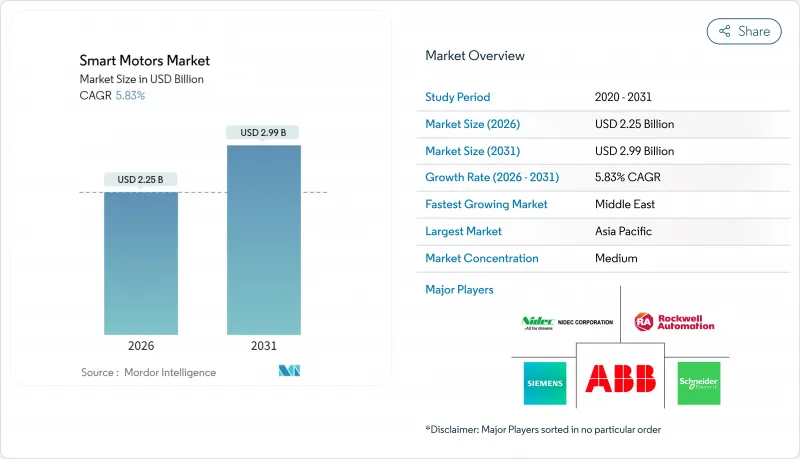
2025年智慧馬達市值為21.3億美元,預計到2031年將達到29.9億美元,高於2026年的22.5億美元。
預計在預測期(2026-2031 年)內,複合年成長率將達到 5.83%。
隨著製造商、商業建築業主和基礎設施營運商尋求降低能源成本並提高運轉率,邊緣人工智慧、先進電力電子和工業自動化平台的日益整合正在加速其應用。此外,對馬達效率的監管要求、對預測性維護日益成長的關注以及確保馬達網路安全的需求也進一步推動了市場需求,而這些需求在企業資料技術領域佔據著舉足輕重的地位。儘管技術仍存在一定程度的分散性,但競爭格局已然清晰。能夠將控制邏輯、邊緣分析和安全連接整合到緊湊型機殼中的供應商正在迅速搶佔市場佔有率。在資料中心冷卻、離岸風電系統和自主移動機器人等領域,緊湊型高性能驅動器能夠顯著提高生產力,因此市場機會正在不斷擴大。
全球智慧馬達市場趨勢與洞察
透過與邊緣人工智慧整合,實現智慧馬達控制的設備內最佳化
邊緣人工智慧正在將馬達智慧從集中式PLC轉移到能夠在本地執行推理的嵌入式微控制器。意法半導體(STMicroelectronics)的STM32系列整合了人工智慧加速器,可將響應延遲從毫秒級降低到微秒級。德克薩斯(TI)的C2000即時裝置運行機器學習模型,可在故障發生前30天偵測到軸承和繞組故障,使維修人員能夠在不中斷生產的情況下安排維修。瑞薩電子在機器人組裝單元的馬達驅動器中實施了自適應扭矩演算法,並觀察到效率提高了15-20%。這種效果在諸如取放機器人等應用中尤其重要,因為瞬時運動曲線決定了吞吐量。邊緣處理透過將運行資料保留在本地,也滿足了資料主權法規的要求。
歐洲和中國的強制性工業能效標準
歐盟法規 2019/1781 提高了大多數工業應用領域 IE3 電機的最低標準,並建議在高能耗環境下使用 IE4-IE5 電機,從而有效地推動了智慧駕駛融入合規戰略。中國的「十四五」規劃目標是到 2025 年將工業能源強度降低 13.5%,並將智慧馬達定位為核心推動因素。 IEC 60034-30-1 和 IEC 60034-2-1 提供了製造商必須滿足的分類標準和調查方法。因此,在冶金、水泥和化學等行業(電機消耗的電力消耗的 70%),工業工廠正擴大將資本預算重新分配給高效能、配備豐富感測器的驅動系統。由於智慧馬達可以即時記錄和報告能源性能,從而便於合規檢驗,因此監管最低標準的實施正在加速智慧馬達的普及應用。
網路化馬達系統中的網路安全漏洞
將數千台驅動器連接到乙太網路會擴大攻擊者可攻擊的面。美國標準與技術研究院 (NIST) 警告稱,電機網路分段不當可能導致攻擊者從單一驅動器橫向移動到工廠的整體控制層。 ICS-CERT 在 2024 年發布的警報中記錄了惡意軟體事件,其中受損的逆變器導致速度異常,損壞了泵浦和生產批次。即時性限制使修補程式的修復變得複雜,因為驅動器無法容忍標準IT安全工具相關的通訊延遲。因此,化學、水務和電力企業通常會推遲智慧馬達的部署,直到供應商展示其驅動器專用的安全協定堆疊並通過 IEC 62443 認證。
細分市場分析
2025年,變頻驅動器在智慧馬達市場佔據主導地位,市佔率高達47.82%,長期以來一直是馬達連接自動化網路的主要方式。然而,整合式馬達驅動組件預計將以6.85%的複合年成長率成為成長最快的產品,因為買家看重的是能夠安裝整合了電力電子、控制設備和感測器的單一密封單元。這種方法減少了對外部機櫃的需求,縮短了佈線距離,從而縮小了工廠面積。這對於食品、飲料和製藥加工企業來說極具吸引力,尤其是那些需要接受健康和安全審核、對裸露電纜配線架有較高要求的企業。此外,整合式驅動器還能輕鬆通過電磁相容性測試,節省數週的設計迭代時間。
碳化矽 (SiC) 和氮化鎵 (GaN) 電晶體技術的進步,使得裝置能夠以更高的開關頻率運作並降低損耗,從而實現了幾年前還會導致過熱的更高密度封裝。 ABB 的整合解決方案每公升功率比分立式解決方案高出 30-40%,同時還整合了振動、溫度和電流感測器,並將分析資料傳輸到邊緣 PC。這些診斷功能使維修團隊能夠從每月巡檢轉變為基於狀態的維護計劃,從而降低人事費用並防止意外故障。雖然獨立逆變器在維修專案中仍然很受歡迎,但由於其生命週期成本優勢,整合解決方案在新計畫中也越來越受歡迎。工廠自動化供應商擴大在整合電機中預裝多重通訊協定韌體,使用戶可以通過軟體更新而非硬體更換來重新配置通訊,從而進一步加速了整合解決方案的普及。
截至2025年,1-10kW功率範圍的智慧馬達佔了智慧馬達市場60.74%的佔有率。這主要歸功於中型機械設備(例如輸送機、攪拌機和壓縮機)在離散製造和流程製造業的持續普及。此輸出範圍的馬達由於在長運作週期內可累積節能,因此能夠快速收回投資。然而,1kW以下功率範圍的馬達應用最為廣泛,其銷量以7.02%的複合年成長率成長。實驗室自動化、醫療診斷和取放式送料器等應用需要超緊湊型驅動裝置,這些驅動器需具備精細的速度控制、低雜訊和高定位精度。在這些應用中,小功率智慧電機取代了簡單的陰極電機和步進電機,顯著提高了出貨量。
整合化趨勢與高功率領域類似,但更重視功率密度。德克薩斯展示了一款參考設計,採用緊湊型 C2000 微控制器、閘極驅動器和磁場定向控制韌體,所有這些都可以在一個手掌大小的機殼內控制三相電流。低於 1kW 的驅動裝置也為建築自動化開闢了更廣泛的應用場景,例如風機盤管、智慧百葉窗和暖通空調水循環系統中的微型水泵。分散式建築設備的數量可能高達數千台,因此即使是小型馬達也能影響整個市場。同時,10kW 以上的系統仍然較保守。石油鑽井平台和礦山優先考慮系統的穩健性和可靠的性能,而不是尖端的控制技術,這導致升級週期更長。
區域分析
到2025年,亞太地區將佔全球收入的37.42%,這主要得益於中國降低工業能源強度的努力以及印度與生產連結獎勵計畫(PIs),該措施旨在為先進自動化提供補貼。日本機器人單元製造商需要抖動小於毫秒級的伺服,推動了對高性能智慧驅動器的需求。同時,韓國造船廠正在整合使用壽命長達25年或以上的耐鹽馬達。台灣和中國當地半導體代工廠的快速成長進一步推動了對低振動、高純度無塵室馬達的需求。在地採購縮短了供應鏈,使亞洲原始設備製造商(OEM)能夠在不犧牲功能的前提下,以低於國際競爭對手的價格銷售產品。
到2031年,中東地區將以6.35%的複合年成長率引領產業發展。沙烏地阿拉伯的「2030願景」計劃將向石化、採礦和綠色氫能計劃注入數十億美元,每個計畫都指定採用具備先進診斷功能的馬達系統,以最大限度地減少前往偏遠沙漠地區的維護次數。阿拉伯聯合大公國的高層建築正在採用智慧空調驅動裝置,以滿足永續性評估標準。沿岸地區的近海海水淡化廠正在採用耐腐蝕智慧電機,透過在發生嚴重故障之前檢測軸承磨損來保護水生產。
在北美,製造業回流趨勢正推動新型自動化工廠投入運作,同時老舊設備也不斷更新換代。美國聯邦政府對高效電機的稅收優惠政策與加州和紐約州的建築規範相輔相成。這些規範強制要求在功率超過一定馬力的暖通空調系統中使用變速驅動器。基於美國國家標準與技術研究院 (NIST) 框架的網路安全要求正在推動市場對符合 IEC 62443-4-2 認證標準的驅動器的需求。在歐洲,2019/1781 號法規已全面實施,該法規要求即使是小規模工坊也必須更換不符合 IE3 標準的馬達。德國汽車集團率先採用支援 PROFINET 的智慧驅動器來控制和協調噴漆車間的輸送機和焊接機器人。東歐憑藉著低廉的勞動成本,正崛起為契約製造中心,並成為智慧電機供應商極具潛力的投資目的地。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 透過與邊緣人工智慧整合,實現智慧馬達控制的設備內最佳化
- 歐洲和中國的強制性工業能效標準
- 商業建築空調系統的快速電氣化
- 自主移動機器人與AGV領域應用日益廣泛
- 離岸風力發電機俯仰偏航系統的日益普及
- SiC/GaN功率元件降低整合式馬達和驅動器封裝的成本
- 市場限制
- 網路化馬達系統中的網路安全漏洞
- 碎片化的通訊協定環境限制了互通性
- 電力電子元件供應鏈長期受阻
- 基於狀態的維護分析中的技能差距
- 產業價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
- 宏觀經濟因素的影響
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按組件
- 變速驅動
- 引擎
- 整合馬達驅動
- 按額定輸出
- 小於1千瓦
- 1~10kW
- 10千瓦或以上
- 透過通訊協定
- Ethernet/IP
- PROFINET
- Modbus TCP
- 其他通訊協定
- 透過使用
- 產業
- 石油和天然氣
- 金屬和採礦
- 水和污水處理
- 食品/飲料
- 化學品
- 其他行業
- 商業的
- 暖通空調和建築自動化
- 資料中心
- 其他商業領域
- 車
- 航太/國防
- 產業
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地區
- 中東
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- ABB Ltd
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Nidec Corporation
- Safran Electrical and Power
- Nanotec Electronic GmbH and Co. KG
- Turntide Technologies Inc.
- Fuji Electric Co. Ltd
- Moog Inc.
- Dunkermotoren GmbH(Ametek Inc.)
- Shanghai Moons'Electric Co. Ltd
- WEG SA
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Parker Hannifin Corporation
- SEW-Eurodrive GmbH and Co KG
- Brook Crompton Holdings Ltd
- Bonfiglioli Riduttori SpA
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Applied Motion Products Inc.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The smart motors market was valued at USD 2.13 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 2.25 billion in 2026 to reach USD 2.99 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.83% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

The heightened convergence of edge artificial intelligence, advanced power electronics, and industrial automation platforms is accelerating adoption as manufacturers, commercial building owners, and infrastructure operators seek to reduce energy bills and enhance uptime. Demand is further driven by regulatory mandates on motor efficiency, growing interest in predictive maintenance, and the need to secure motor networks that now reside firmly within enterprise information-technology perimeters. While the technology remains moderately fragmented, the direction of competition is clear: vendors that can integrate control logic, edge analytics, and secure connectivity within compact housings are rapidly capturing market share. Opportunities are expanding in data center cooling, offshore wind systems, and autonomous mobile robotics, where compact, high-performance drives provide measurable productivity gains.
Global Smart Motors Market Trends and Insights
Convergence of Smart Motor Controls with Edge AI for On-Device Optimization
Edge AI is moving motor intelligence from centralized PLCs toward embedded microcontrollers that can execute inference locally. STMicroelectronics' STM32 family now integrates AI accelerators that cut response latency from milliseconds to microseconds. Texas Instruments' C2000 real-time devices run machine-learning models that flag bearing or winding failures up to 30 days before breakdown, allowing maintenance staff to schedule repairs without disrupting production. Renesas Electronics measured 15-20% efficiency improvements after loading adaptive torque algorithms onto motor drives serving robotic assembly cells. These gains are significant in applications such as pick-and-place robotics, where split-second motion profiles determine throughput. Edge processing also addresses data sovereignty rules by keeping operational data on-premises.
Mandates on Industrial Energy Efficiency Standards in Europe and China
The European Union's Regulation 2019/1781 raises the minimum standard for IE3 motors for most industrial applications and promotes IE4-IE5 in high-consumption settings, effectively drawing intelligent drives into compliance strategies. China's 14th Five-Year Plan targets a 13.5% cut in industrial energy intensity by 2025, naming smart motors as core enablers. IEC 60034-30-1 and IEC 60034-2-1 supply the classification and test methodology that manufacturers must satisfy. Industrial plants in metallurgy, cement, and chemicals-where motors absorb as much as 70% of electricity-are therefore reshuffling capital budgets toward high-efficiency, sensor-rich drives. Regulatory floors accelerate adoption because smart motors can log and report energy performance in real time, validating compliance audits.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in Networked Motor Systems
Linking thousands of drives onto Ethernet networks expands the attack surface that adversaries can exploit. NIST warns that poorly segmented motor networks can allow lateral movement from a single drive to plant-wide control layers. ICS-CERT alerts from 2024 documented malware incidents in which compromised inverters caused speed excursions, damaging pumps and production batches. Real-time constraints complicate patching because drives cannot tolerate the communication latency associated with standard IT security tools. As a result, chemical, water, and power utilities often defer smart motor rollouts until vendors demonstrate drive-native security stacks certified under IEC 62443.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Electrification of HVAC Systems in Commercial Buildings
- Increasing Adoption in Autonomous Mobile Robots and AGVs
- Fragmented Communication Protocol Ecosystem Limiting Interoperability
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Variable speed drives dominated the smart motors market with a 47.82% share in 2025, as they have long served as the principal link between motors and automation networks. Integrated motor-drive packages, however, are experiencing the fastest 6.85% CAGR because buyers value the ability to install a single, sealed unit that combines power electronics, controls, and sensors. The approach eliminates external cabinets and reduces wiring runs, resulting in a cleaner plant floor footprint that appeals to food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processors, particularly those subject to hygiene or safety audits that penalize exposed cable trays. Integrated drives also pass electromagnetic-compatibility tests more readily, saving weeks in design iterations.
Advances in silicon carbide and gallium nitride transistors, operating at higher switching frequencies and lower losses, now permit dense packaging that would have overheated just a few years ago. ABB's integrated solutions deliver 30-40% more power per liter than discrete counterparts while embedding vibration, temperature, and current sensors that stream analytics data to edge PCs. These diagnostics help maintenance teams transition from monthly route-based inspections to condition-based plans, trimming labor and preventing surprise failures. In retrofit environments, stand-alone inverters continue to sell steadily, while new greenfield projects increasingly default to integrated form factors because lifecycle economics favor them. As more factory automation vendors preload multi-protocol firmware onto integrated motors, users gain the flexibility to reconfigure communications through software updates rather than hardware swaps, further stimulating adoption.
The 1-10 kW tranche retained a 60.74% share of the smart motors market size in 2025, as mid-range machines-such as conveyors, mixers, and compressors-remain prevalent across both discrete and process industries. Motors in this band see rapid payback when energy savings compound across long duty cycles. Nonetheless, adoption momentum is strongest below 1 kW, where unit sales are expanding at a 7.02% CAGR. Laboratory automation, medical diagnostics, and pick-and-place feeders require ultra-compact drives that mix fine speed control with low acoustic noise and high positional accuracy. Here, fractional-horsepower smart motors replace simple shaded-pole or stepper designs, resulting in a dramatic increase in shipment volumes.
Integration trends mirror those in higher ratings but with heightened emphasis on power density. Texas Instruments demonstrates reference designs featuring a tiny C2000 microcontroller, gate drivers, and field-oriented control firmware, all housed within a palm-sized enclosure that can still manage three-phase currents. Below 1 kW drives also unlock broader building automation use cases, including fan-coil units, smart blinds, and micro-pumps in HVAC hydronic loops. Because distributed building devices number in the thousands, even small motors collectively move the market needle. Above-10 kW systems, in contrast, stay conservative; oil rigs and mines value ruggedness and proven performance over bleeding-edge controls, so upgrades follow longer refresh cycles.
The Smart Motors Market Report is Segmented by Component (Variable Speed Drive, Integrated Motor-Drive, and More), Power Rating (Below 1 KW, 1-10 KW, and More), Communication Protocol (Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, and More), Application (Industrial, Commercial, Automotive, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
The Asia Pacific region held 37.42% of global revenue in 2025, underscored by China's push to reduce industrial-energy intensity and India's Production Linked Incentive schemes, which channel subsidies toward advanced automation. Japanese robotic cell makers require servos with sub-millisecond jitter, fueling demand for high-performance smart drives, while South Korean shipyards integrate ruggedized motors to endure salt-laden atmospheres over 25-year lifecycles. Taiwan and mainland China, home to booming semiconductor foundries, add further pull for low-vibration, high-purity clean-room motors. Local supply chains shorten lead times, letting Asian OEMs undercut foreign rivals on pricing without sacrificing features.
The Middle East is the pacesetter with a 6.35% CAGR through 2031. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 plans channel billions into petrochemical, mining, and green-hydrogen projects, each specifying motor systems with advanced diagnostics to minimize maintenance trips to remote desert sites. United Arab Emirates mega-buildings adopt intelligent HVAC drives to comply with sustainability ratings. Offshore desalination plants along the Gulf rely on corrosion-resistant smart motors that flag bearing wear before catastrophic failures, protecting water output.
North America continues to upgrade legacy assets as reshoring trends bring new automated factories online. U.S. federal tax incentives for efficient motors complement California and New York building codes, which mandate the use of variable-speed drives in HVAC systems over certain horsepower thresholds. Cybersecurity stipulations under the NIST framework elevate demand for drives certified to IEC 62443-4-2. In Europe, Regulation 2019/1781 is in full effect, obliging even small workshops to swap out sub-IE3 motors. German automotive groups are early adopters of PROFINET-enabled smart drives to control and coordinate paint-shop conveyors and welding robots. Eastern Europe, with its lower labor costs, is emerging as a contract-manufacturing hub and a successive investment wave for smart motor suppliers.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- ABB Ltd
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Nidec Corporation
- Safran Electrical and Power
- Nanotec Electronic GmbH and Co. KG
- Turntide Technologies Inc.
- Fuji Electric Co. Ltd
- Moog Inc.
- Dunkermotoren GmbH (Ametek Inc.)
- Shanghai Moons' Electric Co. Ltd
- WEG S.A.
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Parker Hannifin Corporation
- SEW-Eurodrive GmbH and Co KG
- Brook Crompton Holdings Ltd
- Bonfiglioli Riduttori S.p.A.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Applied Motion Products Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Convergence of Smart Motor Controls with Edge AI for On-Device Optimization
- 4.2.2 Mandates on Industrial Energy Efficiency Standards in Europe and China
- 4.2.3 Rapid Electrification of HVAC Systems in Commercial Buildings
- 4.2.4 Increasing Adoption in Autonomous Mobile Robots and AGVs
- 4.2.5 Rising Deployment in Offshore Wind Turbine Pitch and Yaw Systems
- 4.2.6 Declining Cost of Integrated Motor-Drive Packages Due to SiC/GaN Power Devices
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in Networked Motor Systems
- 4.3.2 Fragmented Communication Protocol Ecosystem Limiting Interoperability
- 4.3.3 Prolonged Supply Chain Constraints for Power Electronics Components
- 4.3.4 Skills Gap in Condition-Based Maintenance Analytics
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Variable Speed Drive
- 5.1.2 Motor
- 5.1.3 Integrated Motor-Drive
- 5.2 By Power Rating
- 5.2.1 Below 1 kW
- 5.2.2 1-10 kW
- 5.2.3 Above 10 kW
- 5.3 By Communication Protocol
- 5.3.1 Ethernet/IP
- 5.3.2 PROFINET
- 5.3.3 Modbus TCP
- 5.3.4 Other Communication Protocol
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Industrial
- 5.4.1.1 Oil and Gas
- 5.4.1.2 Metal and Mining
- 5.4.1.3 Water and Wastewater
- 5.4.1.4 Food and Beverage
- 5.4.1.5 Chemicals
- 5.4.1.6 Other Industrial
- 5.4.2 Commercial
- 5.4.2.1 HVAC and Building Automation
- 5.4.2.2 Data Centers
- 5.4.2.3 Other Commercial
- 5.4.3 Automotive
- 5.4.4 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.1 Industrial
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 Middle East
- 5.5.4.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.4.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.4.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.4.2 Africa
- 5.5.4.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.4.2.2 Egypt
- 5.5.4.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.4.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Siemens AG
- 6.3.2 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.3.3 ABB Ltd
- 6.3.4 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.3.5 Nidec Corporation
- 6.3.6 Safran Electrical and Power
- 6.3.7 Nanotec Electronic GmbH and Co. KG
- 6.3.8 Turntide Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.9 Fuji Electric Co. Ltd
- 6.3.10 Moog Inc.
- 6.3.11 Dunkermotoren GmbH (Ametek Inc.)
- 6.3.12 Shanghai Moons' Electric Co. Ltd
- 6.3.13 WEG S.A.
- 6.3.14 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- 6.3.15 Parker Hannifin Corporation
- 6.3.16 SEW-Eurodrive GmbH and Co KG
- 6.3.17 Brook Crompton Holdings Ltd
- 6.3.18 Bonfiglioli Riduttori S.p.A.
- 6.3.19 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.3.20 Applied Motion Products Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment










