 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910523
物流自動化:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Logistics Automation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
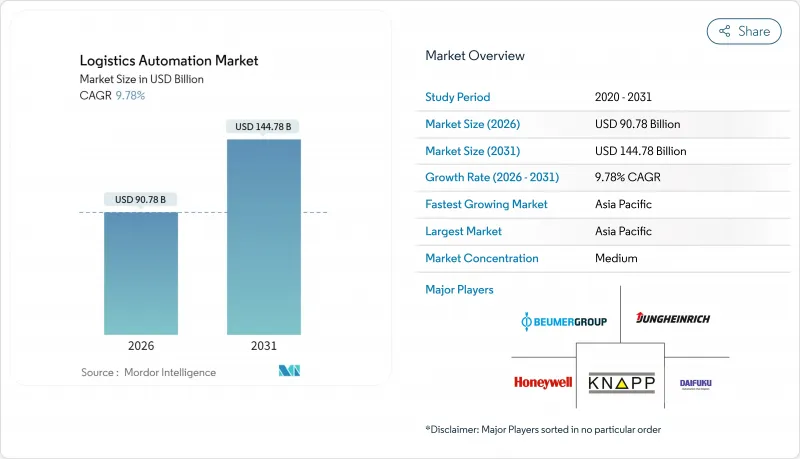
預計到 2026 年,物流自動化市場規模將達到 907.8 億美元,高於 2025 年的 826.9 億美元。
預計到 2031 年,市場規模將達到 1,447.8 億美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 9.78%。
在電子商務小包裹量激增、勞動力嚴重短缺以及企業不斷擴大的淨零排放目標的推動下,自動化已從一種戰術性選擇演變為現代供應鏈設計的關鍵支柱。零售商如今將自動化訂單履行能力視為抵禦薪資上漲的利器。倉庫中5G和專用LTE網路的整合也實現了機器人與堆場車輛之間前所未有的即時協作。環境目標也影響資本支出優先事項,綠色債券資金籌措擴大與用於揀貨、儲存和運輸的節能系統投資掛鉤。雖然半自動化部署目前已成為主流,但隨著人工智慧視覺技術和功能安全晶片認證門檻的降低以及執行風險認知的下降,全自動化計劃正在迅速擴展。亞太地區展現出新的發展態勢,政府補貼、新設施的增加以及專用5G試點計畫的激增使其成為規模最大、成長最快的市場。
全球物流自動化市場趨勢與洞察
快速成長的電子商務小包裹量推動基礎設施現代化
如今,履約公司面臨全年訂單高峰的挑戰,迫使它們從批次揀貨轉向持續的「貨到人」流,從而在不增加人手的情況下縮短週期。像克羅格這樣的零售商加強了與Ocado的自動化合作,以確保當日送達的生鮮配送服務水平,而這種水平如果採用人工方式是無法實現的。同時,最佳化包裝規模技術的進步使UPS能夠在維持穩定吞吐量目標的同時,減少30%的包裝廢棄物。高密度城市微型倉配中心正在迅速發展,預計到2027年,光是在印度,其面積就將超過3,500萬平方英尺。這進一步推動了對高效自動化的需求,使成本受限的城市倉庫能夠充分利用每一立方英尺的空間。機器人技術正在整合到電子商務工作流程的各個環節,對自動化紙箱封口、貼標和最後一公里配送的速度要求也越來越高。這些因素共同推動了物流自動化市場的近期成長。
勞動力短缺加劇,自動化投資週期加速。
人口結構變化帶來的不利影響使得勞動力供應成為策略性瓶頸,尤其是在北美和歐洲。儘管印度的採購經理人指數(PMI)在2024年3月創下16年來的新高,但像NIDO集團這樣的整合商正在向面臨技術純熟勞工短缺的區域城市部署無人貨運平台。協作式自主移動機器人(AMR)正在緩解這種壓力。根據Fleet Feet報道,移動機器人透過接管重複性的運輸任務,使生產力提高了兩到三倍,從而使員工能夠專注於異常情況的處理。隨著企業尋求季節性產能而無需承擔長期人事費用成本,機器人服務合約正在不斷增加。在亞太地區,製造業擴張速度超過勞動力成長速度,這種模式正在重新定義部署的經濟效益。勞動力供應限制和靈活的資金籌措選擇共同推動了物流自動化市場的發展。
高昂的初始投資阻礙了中小企業採用該系統。
綜合性倉庫計劃,包括結構維修和新設備購置,成本可能超過500萬美元,令許多中小企業望而卻步。 AutoStore的「按揀貨收費」訂閱方案可將網格安裝成本降低高達40%,但並未免除建造和系統整合成本。新興市場同樣面臨貨幣波動,資金籌措難度加大,風險意識也日益增強。因此,採用租賃和服務模式的供應商正在崛起,而大型整合商則收購專注於特定領域的機器人公司,並建立更容易獲得貸款機構批准的承包工程方案。儘管取得了一些進展,但資本支出(CAPEX)仍然是物流自動化市場近期發展面臨的最大阻力。
細分市場分析
到2025年,倉儲營運將佔物流自動化市場收入的59.55%,構成比物料驅動揀貨站、自動化倉庫和機器人分類系統能夠為企業帶來快速的投資回報。這些成熟的技術在可控環境下效果最佳,使零售商能夠在不增加員工的情況下縮短訂單到出貨週期。儘管目前運輸自動化規模較小,但隨著自動駕駛卡車和場內牽引車從試點階段過渡到商業化應用,尤其是在可靠的貨運走廊沿線,預計到2031年,運輸自動化將以11.05%的複合年成長率成長。
倉儲領域的領先地位將透過持續創新得以維持。 AutoStore 的 CarouselAI 計劃於 2025 年部署,它將實現可改造相容的機器人揀選功能,從而無需建造混凝土夾層即可擴展現有設施。然而,功能邊界正在變得模糊。例如,CJ 物流等物流設施的私人 5G 部署正在整合室內機器人和自動駕駛車輛,從而建立統一的資料基礎,減少裝卸貨平台的擁塞。儘管在預測期內,整合編配平台可能會促使支出轉向跨功能解決方案,但倉儲仍將是物流自動化市場的主要驅動力。
區域分析
預計到2025年,亞太地區將佔全球營收的31.30%,並在2031年之前以11.56%的複合年成長率成長,使其成為規模最大、成長最快的物流自動化市場中心。中國已連續11年成為全球最大的工業機器人採購國,2023年產量達43萬台,並為國內市場提供約17.5%的資本成本補貼,以促進工業機器人的普及應用。印度市場也展現出強勁的成長動能。在國家物流政策將物流成本降低至GDP的10%的目標以及都市區微型倉配需求快速成長的推動下,預計到2027年,印度A級倉庫的庫存面積將從2.9億平方英尺擴大到4億平方英尺。
北美仍然是關鍵市場,複雜的傳統IT系統和嚴格的網路安全法規延長了計劃週期,而高昂的人事費用則提高了自動化投資的回報率。美國自由貿易區的擴張支持了分散式庫存策略,使自動化中心在最終銷售前免受關稅影響,並增強了跨境電子商務的競爭力。歐洲也呈現類似的趨勢,但同時也增加了碳減排的監管激勵措施,推動了資金流入節能型自動化倉儲/零售系統(AS/RS)和人工智慧路徑規劃工具。
拉丁美洲和中東及非洲地區尚處於物流自動化應用的早期階段。儘管資金短缺和整合商生態系統有限表面上減緩了成長速度,但人口結構變化和電子商務的快速發展表明,這些地區存在巨大的潛在需求。隨著資金籌措機制的完善和本地供應商業務的拓展,這些地區有望成為全球物流自動化市場的下一批重要貢獻者。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 分析師支持(3個月)
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 電子商務小包裹數量快速成長
- 勞動力短缺加劇和薪資壓力上升
- 企業為實現淨零物流所做的努力
- 免稅微型倉配區法規
- 5G與專用LTE在倉庫中的融合
- 開放原始碼機器人作業系統(ROS-2)的成熟
- 市場限制
- 高昂的初始投資成本
- 與現有IT系統整合的複雜性
- 功能安全認證人工智慧晶片短缺
- OT網路的網路保險保費正在上漲
- 供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 宏觀經濟因素如何影響市場
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按功能
- 倉庫自動化
- 按組件
- 硬體
- 移動機器人(AGV、AMR)
- 自動化倉庫系統(AS/RS)
- 自動分類系統
- 卸垛/碼垛系統
- 輸送機系統
- 自動識別和數據採集(AIDC)
- 揀貨
- 軟體
- 服務
- 硬體
- 按組件
- 運輸自動化
- 按組件
- 硬體
- 軟體
- 服務
- 按組件
- 倉庫自動化
- 按自動化級別
- 全自動系統
- 半自動系統
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 電子商務和小包裹遞送
- 食品/飲料
- 食品零售
- 服裝與時尚
- 製造業
- 其他終端用戶產業
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 東南亞
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地區
- 中東
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Dematic Corp.(KION Group AG)
- Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Jungheinrich AG
- Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- KNAPP AG
- TGW Logistics Group GmbH
- Kardex Holding AG
- Mecalux, SA
- BEUMER Group GmbH & Co. KG
- SSI SCHAFER AG
- Vanderlande Industries BV
- WITRON Logistik+Informatik GmbH
- Interroll Holding AG
- GreyOrange Pte Ltd.
- Locus Robotics Corp.
- Geek+Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ocado Group plc(Ocado Intelligent Automation)
- AutoStore Holdings Ltd.
- Exotec SAS
- Fetch Robotics Inc.(Zebra Technologies)
- Korber Supply Chain GmbH
- Cimcorp Oy
- Manhattan Associates Inc.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
Logistics automation market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 90.78 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 82.69 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 144.78 billion, growing at 9.78% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Rising e-commerce parcel volumes, acute labor shortages, and expanding corporate net-zero commitments are transforming automation from a tactical option into an essential pillar of modern supply chain design. Retailers now treat automated order-fulfillment capacity as a hedge against wage inflation, while the convergence of 5G and private LTE networks inside warehouses enables real-time orchestration between robots and yard vehicles that was previously impossible. Environmental targets are also influencing capital-spending priorities, with green-bond financing increasingly tied to energy-efficient systems for picking, storage, and transport. Against this backdrop, semi-automated deployments currently dominate, but fully automated projects are scaling quickly as AI vision and functional-safety chips clear certification hurdles, thereby lowering perceived execution risk. Geographically, Asia-Pacific is rewriting the playbook: government subsidies, greenfield facility growth, and a surge in private 5G pilots are combining to make the region both the largest and fastest-growing market node.
Global Logistics Automation Market Trends and Insights
Rapid E-Commerce Parcel Volumes Drive Infrastructure Modernization
Fulfillment operators now face holiday-level order velocity all year, forcing a shift from batch-picking to continuous, goods-to-person flows that shrink cycle times without expanding headcount. Retailers such as Kroger deepened automation partnerships with Ocado to guarantee same-day grocery delivery service levels that manual processes cannot sustain.Parallel advances in right-sizing technology enable UPS to cut packaging waste by 30% while maintaining steady throughput targets. Dense urban micro-fulfillment hubs are proliferating, and India alone is projected to reach more than 35 million ft2 of such space by 2027, intensifying demand for high-cube automation capable of monetizing every cubic foot in cost-constrained city warehouses. The velocity mandate now extends to automated carton closing, labeling, and last-mile hand-off, embedding robotics across the full e-commerce workflow. Together, these forces anchor the near-term growth engine for the logistics automation market.
Rising Labor Shortages Accelerate Automation Investment Cycles
Demographic headwinds have turned labor availability into a strategic bottleneck, especially in North America and Europe. The Indian PMI reached a 16-year high in March 2024, yet integrators such as NIDO Group are rolling out unmanned goods-movement platforms for Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, where skilled labor is scarce. Collaborative AMRs are easing the pinch: Fleet Feet reported productivity gains of 2-3X when mobile robots assumed repetitive transport chores, freeing human associates for exception handling tasks. Robotics-as-a-service contracts are rising because businesses want seasonal capacity without long-term payroll commitments. In the Asia-Pacific region, where manufacturing expansion outpaces workforce growth, these models are redefining adoption economics. The combination of constrained labor supply and flexible financing options is propelling the logistics automation market forward.
High Upfront Capital Requirements Constrain SME Adoption
Comprehensive warehouse projects can exceed USD 5 million when structural retrofits are combined with new equipment, keeping many small enterprises on the sidelines. Pay-per-pick subscription programs, championed by AutoStore, lower grid installation costs by up to 40% but do not eliminate construction and systems integration expenses. Access to affordable financing is toughest in emerging markets that also face currency volatility, elevating perceived risk. As a result, vendors with rental or service-based models are gaining share, and larger integrators are acquiring niche robotics firms to assemble turnkey packages that are easier for lenders to underwrite. Despite progress, CAPEX remains the most stubborn near-term brake on the logistics automation market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate Net-Zero Commitments Reshape Facility Design Priorities
- Customs-Free Micro-Fulfillment Zones Enable Distributed Inventory Models
- Integration Complexity with Legacy IT Systems Delays Implementation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Warehouse operations captured 59.55% of the 2025 revenue within the logistics automation market share, underscoring the immediate ROI companies achieve from goods-to-person pick stations, automated storage, and robotic sortation. These proven technologies thrive in controlled environments, letting retailers compress order-to-ship cycles without adding workers. Transportation automation is currently smaller but is slated for an 11.05% CAGR to 2031 as autonomous trucks and yard tractors transition from pilots to revenue service, especially along reliable freight corridors.
Continued innovation sustains warehouse leadership: AutoStore's 2025 launch of CarouselAI delivers retrofit-friendly robotic piece-picking, enabling existing sites to scale without concrete mezzanine work. Yet the functional boundary is blurring. Private 5G deployments at sites like CJ Logistics integrate indoor robots and autonomous yard vehicles, creating a unified data fabric that reduces dock-door congestion. Over the forecast horizon, integrated orchestration platforms could shift spending toward cross-functional solutions, but warehouses will remain the volume anchor of the logistics automation market.
The Logistic Automation Market Report is Segmented by Function (Warehouse Automation and Transportation Automation), Automation Level (Fully Automated Systems and Semi-Automated Systems), End-User Industry (E-Commerce and Parcel, Grocery Retail, Manufacturing, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region accounted for 31.30% of 2025 revenue and is projected to grow at a 11.56% CAGR to 2031, earning the region a dual distinction as both the largest and fastest-growing node of the logistics automation market. China has been the world's top industrial-robot buyer for 11 consecutive years, producing 430,000 units in 2023 while subsidizing roughly 17.5% of equipment costs to accelerate domestic uptake. India brings complementary momentum; Grade A warehouse inventory is on track to increase from 290 million to 400 million ft2 by 2027, driven by the National Logistics Policy's push to reduce logistics costs to 10% of GDP and by surging urban micro-fulfillment demand.
North America remains a cornerstone market, thanks to high labor costs that strengthen the payback math for automation, even as complex legacy IT systems and strict cybersecurity rules lengthen project cycles. The expansion of U.S. Foreign Trade Zones supports distributed inventory strategies, freeing automated hubs from duty liabilities until final sale and sharpening cross-border e-commerce competitiveness. Europe mirrors many of these patterns, with an added regulatory premium on carbon reduction, which is funneling capital toward energy-efficient AS/RS and AI route-planning tools.
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are in earlier stages of adoption. Capital scarcity and limited integrator ecosystems slow headline growth, yet demographic trends and rapid e-commerce penetration outline substantial latent demand. As financing mechanisms evolve and local vendor footprints expand, these regions are positioned to become the next wave of contributors to the global logistics automation market.
- Dematic Corp. (KION Group AG)
- Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Jungheinrich AG
- Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- KNAPP AG
- TGW Logistics Group GmbH
- Kardex Holding AG
- Mecalux, S.A.
- BEUMER Group GmbH & Co. KG
- SSI SCHAFER AG
- Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- WITRON Logistik + Informatik GmbH
- Interroll Holding AG
- GreyOrange Pte Ltd.
- Locus Robotics Corp.
- Geek+ Technology Co., Ltd.
- Ocado Group plc (Ocado Intelligent Automation)
- AutoStore Holdings Ltd.
- Exotec SAS
- Fetch Robotics Inc. (Zebra Technologies)
- Korber Supply Chain GmbH
- Cimcorp Oy
- Manhattan Associates Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid e-commerce parcel volumes
- 4.2.2 Rising labor shortages and wage inflation
- 4.2.3 Corporate net-zero logistics commitments
- 4.2.4 Customs-free micro-fulfilment zoning laws
- 4.2.5 Convergence of 5G and private-LTE inside warehouses
- 4.2.6 Open-source robotics operating systems (ROS-2) maturation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront CAPEX
- 4.3.2 Integration complexity with brown-field IT
- 4.3.3 Scarcity of functional-safety certified AI chips
- 4.3.4 Rising cyber-insurance premiums for OT networks
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Warehouse Automation
- 5.1.1.1 By Component
- 5.1.1.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1.1.1 Mobile Robots (AGV, AMR)
- 5.1.1.1.1.2 Automated Storage And Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
- 5.1.1.1.1.3 Automated Sorting Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.4 De-Palletizing/Palletizing Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.5 Conveyor Systems
- 5.1.1.1.1.6 Automatic Identification and Data Collection (AIDC)
- 5.1.1.1.1.7 Order Picking
- 5.1.1.1.2 Software
- 5.1.1.1.3 Services
- 5.1.1.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 By Component
- 5.1.2 Transportation Automation
- 5.1.2.1 By Component
- 5.1.2.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.2.1.2 Software
- 5.1.2.1.3 Services
- 5.1.2.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Warehouse Automation
- 5.2 By Automation Level
- 5.2.1 Fully-automated Systems
- 5.2.2 Semi-automated Systems
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 E-commerce and Parcel
- 5.3.2 Food and Beverage
- 5.3.3 Grocery Retail
- 5.3.4 Apparel and Fashion
- 5.3.5 Manufacturing
- 5.3.6 Other End-user Industries
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.4.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Dematic Corp. (KION Group AG)
- 6.4.2 Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.4 Jungheinrich AG
- 6.4.5 Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- 6.4.6 KNAPP AG
- 6.4.7 TGW Logistics Group GmbH
- 6.4.8 Kardex Holding AG
- 6.4.9 Mecalux, S.A.
- 6.4.10 BEUMER Group GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.11 SSI SCHAFER AG
- 6.4.12 Vanderlande Industries B.V.
- 6.4.13 WITRON Logistik + Informatik GmbH
- 6.4.14 Interroll Holding AG
- 6.4.15 GreyOrange Pte Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Locus Robotics Corp.
- 6.4.17 Geek+ Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Ocado Group plc (Ocado Intelligent Automation)
- 6.4.19 AutoStore Holdings Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Exotec SAS
- 6.4.21 Fetch Robotics Inc. (Zebra Technologies)
- 6.4.22 Korber Supply Chain GmbH
- 6.4.23 Cimcorp Oy
- 6.4.24 Manhattan Associates Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment









