 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1910483
塑合板:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Particle Board - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
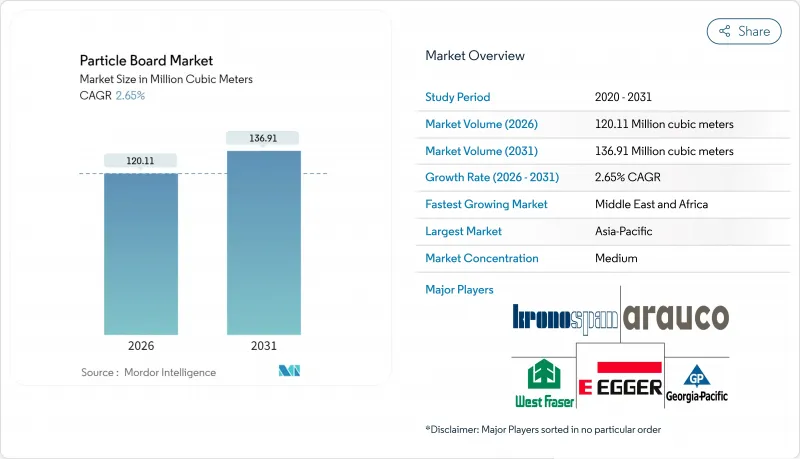
2025 年塑合板市場價值為 1.1702 億立方米,預計到 2031 年將達到 1.3691 億立方米,高於 2026 年的 1.2011 億立方米,在預測期(2026-2031 年)內以 2.65% 的複合年成長率成長。
這種擴張速度固然印證了產業的成熟度,但也凸顯了一個策略轉折點。這些轉折點包括原料多元化,轉向農業殘餘物;全球排放法規日益嚴格;以及技術主導生產商與產能驅動型競爭對手之間日益擴大的績效差距。為了因應北美和歐盟更嚴格的甲醛法規,產業領導企業正在投資低排放樹脂系統、穩定的原料供應和製程自動化,以保障利潤率。組裝家具需求的成長、都市區中產階級消費的增加以及新興市場持續的基礎設施投資,共同支撐著銷售在競爭日益激烈的價格環境下持續成長。同時,製糖產業的脫碳進程正在釋放甘蔗渣作為供應來源的潛力,使製造商能夠對沖木纖維風險並提升其永續性形象。這些因素正日益影響建築材料採購商和家具原始設備製造商的採購決策。
全球塑合板市場趨勢與洞察
全球組裝和RTA家具產量快速成長
組裝家具需要可預測的基材厚度和密度,而塑合板在大規模生產中始終能滿足這些規格要求。跨國零售商對板材要求進行標準化,以簡化全球採購流程,從而使生產規模受區域住宅週期的影響較小,並更符合家具更換需求——家具的周轉率率高於傳統實木家具。均勻的密度有助於精確計算重量,提高貨櫃裝載率,並將物流成本降低高達 20%。 RTA(即裝即用)組裝工廠的自動化鑽孔和緊固設備進一步鞏固了塑合板作為主要基材的地位,因為其結構能夠承受反覆加工而不會造成明顯的工具磨損。全球採購團隊擴大透過談判達成長期供應協議,以確保獲得符合 CARB 2 或 EPA TSCA Title VI 認證的合格板材。這為受監管的製造商提供了更清晰的需求預測,使他們能夠更有信心地投資產能擴張。
亞洲二、三線城市的快速都市化推動了價格適中的住宅用品需求。
印度、越南、印尼和菲律賓的二線城市叢集正吸引來自農村的移民,從而催生了對經濟實惠的室內家具的需求。政府補貼的公寓項目指定採用模組化櫥櫃和衣櫃系統,並因其成本、易加工性和與層壓板的兼容性而青睞塑合板。隨著每戶平均居住面積的減少,設計師傾向於採用嵌入式儲物空間,以最大限度地利用每一平方公尺的空間。塑合板易於加工,可以製作緊湊、多功能的家具,既能解決空間限制,又不會超出預算。位置家俱生產集群300公里範圍內的本地板材廠縮短了前置作業時間,並降低了利潤微薄的原始設備製造商(OEM)的庫存持有成本。儘管都市區的住宅量出現週期性放緩,但這些趨勢仍支撐著全部區域的穩定大規模生產成長。
超薄中密度纖維板在組裝家具領域競爭。
精煉和壓制技術的進步使中密度纖維板 (MDF) 生產商能夠生產厚度為 4-6 毫米的板材。與同等厚度的塑合板相比,MDF 具有更優異的邊緣強度和螺絲固定力。家具設計師利用這些特性來減少包裝尺寸和運輸重量,從而在全球物流鏈中節省成本。隨著 MDF 工廠擴大薄板生產,傳統的價格差異正在縮小,RTA(即裝即用)品牌開始將 MDF 用於可見零件,而將塑合板僅用於隱藏區域。塑合板供應商正在透過投資更細的表層和後壓表面拋光生產線來提高層壓板的黏合力,但預計在薄板尺寸穩定性達到可比水平之前,競爭壓力將持續存在。
細分市場分析
到2025年,木材殘渣將佔全球產量的76.20%,從而支撐起一條連接同一工業園區內鋸木廠和壓板廠的成熟供應鏈。這條原料供應路線降低了運輸成本,並確保了纖維的均質性,使連續壓機操作員運作高速生產線。依賴木材殘渣的塑合板市場規模預計將以2.25%的複合年成長率溫和成長,這反映了成熟經濟體住宅維修活動的整體趨勢。甘蔗渣目前佔市場佔有率的12.15%,預計將以3.38%的複合年成長率實現最高成長,這主要得益於糖業的政策獎勵以及對低碳材料日益成長的需求。這些因素綜合起來,預計到2031年,甘蔗渣的市佔率將達到13.10%,吸收約335萬立方公尺的新增產能。原料多元化有助於生產商降低原木價格波動,並符合歐盟的實質審查法規,該法規對與森林砍伐相關的纖維材料進行嚴格審查。雖然以小麥秸稈、油棕櫚葉和椰子殼等替代農業廢棄物為原料製成的塑合板市場佔有率小規模,但加拿大和馬來西亞的先導工廠已證明其技術可行性,這表明一旦供應集中度瓶頸得到解決,該領域仍有長期成長空間。
轉向非木質原料也影響資本投資模式。甘蔗渣最佳化型工廠正在安裝去屑滾筒、額外的乾燥區域和高通量分類機,以彌補水分含量和髓心含量的差異。製程改善所需的額外資本投資為每立方公尺年產能80-100美元,考慮到該原料良好的生命週期碳排放特性,此可控範圍有助於擴大綠色債券資金籌措。領先採用這些技術的工廠正在為那些尋求LEED和BREEAM認證積分的建築商提供出口溢價,凸顯了農業廢棄物板材在小眾市場之外的戰略重要性。
塑合板市場報告按原料(木屑、甘蔗渣及其他原料)、應用領域(家具、建築、基礎設施及其他應用)和地區(亞太、北美、歐洲、南美、中東和非洲)進行細分。市場預測以體積(立方米)為單位。
區域分析
至2025年,亞太地區將佔全球塑合板產量的45.30%,約約5,300萬立方公尺。這得歸功於密集的製造群,這些集群將木材特許經營權、樹脂廠和家具出口商與高效的物流走廊連接起來。中國地方政府持續鼓勵將產能從沿海省份轉移到內陸地區,以使產業成長與區域發展政策相契合。同時,由於模組化廚房在中等收入家庭的普及,印度國內塑合板需求正以每年4.1%的速度成長。越南將作為加工中心,在2024年1月至11月期間進口508萬立方公尺的塑合板和木片,並將其加工成家具後再出口。
北美和歐洲合計佔全球產量的38.20%,但成長較為溫和,預計2031年年複合成長率(CAGR)僅1.5%。與室內空氣品質標準相關的監管要求促使鋸木廠優先考慮樹脂排放技術的資本支出,而非新的資本投資,這限制了供應,並在住宅開工量低迷的情況下支撐了價格穩定。在美國,對加拿大軟木材徵收的關稅促使一些建築商轉向工程板材,這有利於符合加州空氣資源委員會(CARB)2標準的美國本土製造商。歐洲的需求呈現兩極化:一是注重價格的東歐買家,二是注重永續性的西方市場,這推動了再生木材含量達到30%或以上的板材的普及。中東和非洲地區的成長速度最快,複合年成長率為3.55%,但基礎產量仍較低,僅555萬立方公尺。由於沙烏地阿拉伯的NEOM計劃等大型經濟多元化項目以及國際盛事前飯店建築的擴張,室內裝飾板材的需求保持穩定。儘管沙烏地阿拉伯森林資源有限,依賴進口不可避免,但埃及和海灣國家的合資企業已開始運作連續壓機生產線,將人工林木材與進口木片混合使用,這表明向本地化生產的過渡尚處於初期階段。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 全球平板包裝和組裝式家具產量激增
- 亞洲二、三線城市的快速都市化推動了價格適中的住宅用品需求。
- 在非承重應用中,與中密度纖維板和膠合板相比,具有成本優勢
- 排放標準的脲醛樹脂推動了歐盟和北美地區的進口需求。
- 製糖業脫碳將釋放甘蔗渣的原料。
- 市場限制
- 組裝家具中超薄中密度纖維板帶來的競爭威脅
- 樹脂和甲醇價格波動對利潤率造成壓力。
- 水分膨脹限制了戶外應用
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按原料
- 木材殘渣
- 渣
- 其他成分
- 透過使用
- 家具
- 建造
- 基礎設施
- 其他用途
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 東南亞國協
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 俄羅斯
- 北歐國家
- 其他歐洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- ARAUCO
- Associate Decor
- Boise Cascade Company
- Century Prowud
- Century Plyboards(India)Ltd
- EGGER
- Georgia-Pacific
- Kastamonu Entegre
- Krifour Industries Pvt. Ltd.
- Kronoplus Limited
- Roseburg Forest Products
- Siam Riso Wood Products Co., Ltd.
- Sonae Arauco
- SWISS KRONO Group
- Timber Products Company
- West Fraser Timber Co.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Particle Board Market was valued at 117.02 Million cubic meters in 2025 and estimated to grow from 120.11 Million cubic meters in 2026 to reach 136.91 Million cubic meters by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.65% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

The expansion pace confirms a maturing industry yet highlights strategic inflection points: raw-material diversification toward agricultural residues, stricter global emission rules, and a widening performance gap between technology-enabled producers and capacity-driven competitors. Segment leaders channel capital into low-emission resin systems, feedstock security, and process automation to defend margins as formaldehyde regulations tighten in North America and the EU. Elevated demand from flat-pack furniture, rising urban middle-class consumption, and ongoing infrastructure investments in emerging economies combine to sustain volume growth even as price competition intensifies. Meanwhile, sugar-sector decarbonization frees up bagasse, allowing manufacturers to hedge wood-fiber risk and bolster sustainability credentials, factors that increasingly influence procurement decisions among construction buyers and furniture OEMs.
Global Particle Board Market Trends and Insights
Surging Global Flat-Pack and RTA Furniture Production
Flat-pack furniture relies on predictable substrate thickness and density, specifications that particle board delivers consistently across large-scale production runs. Multinational retailers standardize panel requirements to streamline global sourcing; as a result, volumes remain less sensitive to regional housing cycles and more aligned with replacement furniture demand that turns faster than traditional solid-wood pieces. Uniform density permits precise weight calculations, raising container utilization rates and lowering logistics expenses by up to 20%. Automated boring and fastening equipment in RTA assembly plants further entrenches particle board as the primary substrate because its structure tolerates repeat machining without significant tool wear. Global procurement teams increasingly negotiate long-term supply contracts to secure qualified boards certified under CARB 2 or EPA TSCA Title VI, reinforcing demand visibility for compliant producers and allowing them to invest confidently in capacity upgrades.
Rapid Urbanisation in Tier-2/3 Asian Cities Boosting Affordable Housing Interiors
Secondary urban clusters in India, Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines absorb rural migration and generate demand for cost-effective interior fixtures. Government-subsidized apartment schemes specify modular cabinetry and wardrobe systems that favor particle board for its balance of cost, machinability, and laminate compatibility. As average living space per household declines, designers favor built-in storage that maximizes every square meter; particle board's ease of profiling enables compact, multifunctional furniture that meets space constraints without inflating budgets. Local panel mills, often located within 300 km of furniture clusters, shorten lead times and reduce inventory carrying costs for OEMs that operate on slim margins. These dynamics underpin stable, volume-driven growth across the region despite periodic slowdowns in tier-1 metropolitan housing starts.
Competitive Threat from Ultra-Thin MDF in Ready-To-Assemble Furniture
Advances in refining and pressing allow MDF producers to manufacture 4-6 mm boards that maintain edge integrity and screw-holding capacity superior to particle board at equivalent thickness. Furniture designers exploit these attributes to shrink package dimensions and shipping weight, driving incremental cost savings across global logistics chains. As MDF mills scale thin-panel output, the historical price gap narrows, prompting RTA brands to shift visible components to MDF while relegating particle board to concealed parts. Particle board suppliers respond by investing in finer-particle surface layers and post-press surface sanding lines to improve laminate adhesion, yet competitive pressure persists until they achieve comparable thin-panel dimensional stability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost Advantage vs. MDF and Plywood for Non-Load-Bearing Uses
- Emission-Compliant Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Unlocking Import Demand in EU and NA
- Volatile Resin and Methanol Prices Squeezing Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Wood residue controlled 76.20% of global volume in 2025, underscoring the entrenched supply chains that connect sawmills to board presses situated in the same industrial parks. This raw-material pathway lowers inbound freight outlays and secures fiber homogeneity, enabling continuous-press operators to run high-speed lines with minimal downtime. The particle board market size tied to wood residue is expected to edge up at 2.25% CAGR, mirroring overall housing refurbishment activity in mature economies. Bagasse, though currently at 12.15% share, posts the highest growth at 3.38% CAGR, propelled by sugar-sector policy incentives and rising buyer preference for low-carbon materials; together these factors could lift bagasse to 13.10% share by 2031, absorbing roughly 3.35 million m3 of incremental capacity. Greater feedstock plurality helps producers cushion log-price volatility and meet EU due-diligence regulations that scrutinize deforestation-linked fiber sources. The particle board market share for alternative agricultural residues such as wheat straw, oil-palm frond, and coconut husk remains modest, yet pilot plants in Canada and Malaysia demonstrate technical feasibility, suggesting long-term upside once supply aggregation bottlenecks resolve.
The transition toward non-wood inputs also influences capital-investment patterns. Mills optimized for bagasse integrate de-pithing drums, additional dryer zones, and higher-throughput classifiers to compensate for moisture and pith variability. Process modifications carry incremental capex of USD 80-100 per m3 of annual capacity, a manageable uplift that is increasingly financed through green-bond instruments given the feedstock's favorable life-cycle carbon profile. Early-adopter mills secure export premiums in markets where builders pursue LEED or BREEAM points, validating the strategic relevance of agricultural-waste panels beyond niche positioning.
The Particle Board Market Report is Segmented by Raw Material (Wood Residue, Bagasse, and Other Raw Materials), Application (Furniture, Construction, Infrastructure, and Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Cubic Meters).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific contributed 45.30% of global volume in 2025, translating to roughly 53.0 million m3, underpinned by dense manufacturing clusters that link timber concessions, resin plants, and furniture exporters along efficient logistics corridors. Provincial governments in China continue to incentivize capacity relocation from coastal provinces to inland sites, aiming to align industrial growth with regional development policies. India, meanwhile, logs a 4.1% annual uptick in domestic particle board demand as modular kitchen penetration rises among middle-income households. Vietnam functions as a processing hub, importing 5.08 million m3 of raw panels and chips during January-November 2024 for re-export as fabricated furniture.
North America and Europe together account for 38.20% of global output but deliver subtler growth, averaging 1.5% CAGR through 2031. Regulatory strings attached to indoor-air-quality standards motivate mills to channel capex toward resin-emission abatement rather than new capacity, thereby constraining supply and supporting price stability even amid subdued housing starts. In the U.S., tariffs on Canadian softwood lumber shift some builders toward engineered panels, benefiting domestic mills that maintain CARB 2 compliance. European demand bifurcates between price-sensitive Eastern European buyers and Western European markets that prioritize sustainability credentials, stimulating uptake of panels with >=30% recycled wood content. The Middle East and Africa register the fastest regional expansion at 3.55% CAGR, albeit from a lower base of 5.55 million m3. Mega-projects tied to economic diversification-such as Saudi Arabia's NEOM-and widespread hotel pipeline growth ahead of global events channel steady demand for interior panels. Limited indigenous forest resources compel reliance on imports; however, joint ventures in Egypt and the Gulf are commissioning continuous-press lines using a blend of plantation wood and imported chips, signaling an embryonic shift toward local production.
- ARAUCO
- Associate Decor
- Boise Cascade Company
- Century Prowud
- Century Plyboards (India) Ltd
- EGGER
- Georgia-Pacific
- Kastamonu Entegre
- Krifour Industries Pvt. Ltd.
- Kronoplus Limited
- Roseburg Forest Products
- Siam Riso Wood Products Co., Ltd.
- Sonae Arauco
- SWISS KRONO Group
- Timber Products Company
- West Fraser Timber Co.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Global Flat-Pack and RTA Furniture Production
- 4.2.2 Rapid Urbanisation in Tier-2/3 Asian Cities Boosting Affordable Housing Interiors
- 4.2.3 Cost Advantage Vs. MDF and Plywood for Non-Load-Bearing Uses
- 4.2.4 Emission-Compliant Urea-Formaldehyde Resins Unlocking Import Demand in EU And NA
- 4.2.5 Sugar-Industry Decarbonisation Policy Freeing Up Bagasse Feedstock
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Competitive Threat from Ultra-Thin MDF in Ready-To-Assemble Furniture
- 4.3.2 Volatile Resin and Methanol Prices Squeezing Margins
- 4.3.3 Moisture-Related Swelling Limiting Exterior Applications
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Raw Material
- 5.1.1 Wood Residue
- 5.1.2 Bagasse
- 5.1.3 Other Raw Materials
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Furniture
- 5.2.2 Construction
- 5.2.3 Infrastructure
- 5.2.4 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 NORDIC Countries
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ARAUCO
- 6.4.2 Associate Decor
- 6.4.3 Boise Cascade Company
- 6.4.4 Century Prowud
- 6.4.5 Century Plyboards (India) Ltd
- 6.4.6 EGGER
- 6.4.7 Georgia-Pacific
- 6.4.8 Kastamonu Entegre
- 6.4.9 Krifour Industries Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Kronoplus Limited
- 6.4.11 Roseburg Forest Products
- 6.4.12 Siam Riso Wood Products Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Sonae Arauco
- 6.4.14 SWISS KRONO Group
- 6.4.15 Timber Products Company
- 6.4.16 West Fraser Timber Co.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment










