 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906866
顏料:市佔率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Pigments - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
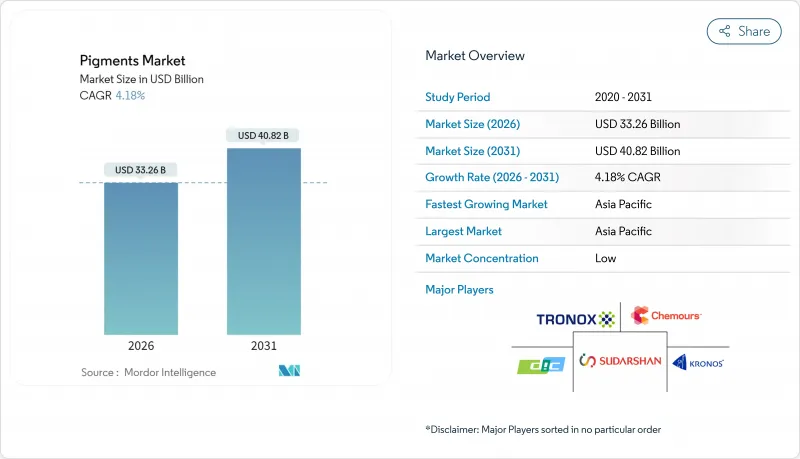
2025年顏料市值為319.3億美元,預計從2026年的332.6億美元成長到2031年的408.2億美元,在預測期(2026-2031年)內複合年成長率為4.18%。
儘管生產商正在應對供應鏈重組和安全法規日益嚴格的挑戰,但建築、包裝和運輸領域的強勁需求仍然支撐著這一擴張。無機顏料在建築塗料領域保持著成本優勢,而有機和特殊化學品則在高性能汽車和電子應用領域佔據越來越大的佔有率。二氧化鈦 (TiO2) 來源的地域多角化,以及逐步淘汰 PFAS(全氟不對稱合成化合物)和其他受限物質的努力,正在加速顏料市場的產品配方改良。產業整合進一步塑造了競爭格局,例如 Cronos Worldwide 於 2024 年 7 月收購 Louisiana Pigment Company,這使得規模更大的企業能夠簡化原料採購流程並加強下游分銷網路的擴張。
全球顏料市場趨勢與洞察
新興經濟體對油漆和塗料的需求快速成長
印尼、奈及利亞和越南的基礎設施發展計畫正推動建築塗料需求的穩定成長,印尼塗料產量在2024年10月突破100萬噸便印證了這一點。在撒哈拉以南非洲,受中國援助的9個計劃(已於2023年完工)和5個項目(計劃於2024年開工)的推動,水泥產能的擴張持續提振著建築顏料的需求。政府大力推廣水性塗料和低VOC配方,迫使供應商提供既能滿足更嚴格排放標準又具有成本競爭力的分散體。這為中型顏料生產商創造了更大的市場基礎,使他們能夠在主要建築叢集附近開展配方和物流業務。中期來看,住宅和交通基礎設施的持續投入預計將促成多年期供應合約的簽訂,即使私部門的翻新週期放緩,也能穩定產量。
監管部門推動環保/生物基顏料的發展
世界各地的監管機構正在逐步縮小可接受的顏料化學品範圍。加州的AB418法案將於2025年1月起禁止在食品中使用二氧化鈦,紐西蘭將於2026年12月起禁止在化妝品中使用全氟烷基和多氟烷基物質(PFAS)。歐萊雅等大型配方商已承諾在2030年使用95%的生物基成分,整個產業正向可再生著色劑轉型。學術界和工業界正在利用酵素輔助萃取方法和動態空化技術,將海藻衍生的藻膽蛋白和岩藻黃素商業化,從而獲得與傳統偶氮顏料相當的顯色強度。隨著現有化學品合規成本的上升,小規模生物基供應商或許能夠利用先前大眾市場無法企及的價格優勢。然而,生物基產品的廣泛應用將取決於能否克服新建生物煉製基礎設施的資本成本,以及能否滿足外牆塗料等高要求終端應用的耐久性要求。
嚴格的環境和毒理學法規
OEKO-TEX於2024年10月在其限制性物質檢測通訊協定中新增了PFAS的鹼性水解篩檢。加拿大全國範圍內的煤焦油禁令將於2025年3月生效,歐盟REACH法規第79條也於同月引入了PFHxA的限制。美國多個州將於2025年1月起禁止在紡織品使用PFAS。每項新法規都要求顏料供應商檢驗替代化學品,並建立雙重庫存系統以適應不同司法管轄區的不同閾值。合規需要基於ISO 22716標準的複雜品管體系,而增加的固定成本對於中小型生產者而言難以負擔。其直接影響是成熟市場的產能精簡,降低了戰術性的價格競爭,同時提高了新進入者的策略准入門檻。
細分市場分析
到2025年,無機顏料市場叢集將保持在75.42%,這主要得益於二氧化鈦(TiO2)的應用,它在建築和包裝應用中對遮蓋力和白度至關重要。在這一類別中,鐵基顏料因其成本和耐久性優勢,繼續在建築塗料和建材領域佔據主導地位。有機顏料雖然目前銷量小規模,但預計到2031年將以5.18%的複合年成長率成長,這得益於監管政策為那些需要高飽和度色彩和低重金屬含量的應用提供了發展空間。高性能的Quinacridones和Perylenes顏料廣泛應用於汽車底塗層,DIKETO-PYRROLO-PYRROLES紅色顏料則擴大應用於機殼。感溫變色顏料和磁性顏料等特殊顏料已在安全印刷和電子元件標記領域獲得了高價值合約。
二氧化鈦原料成本的上漲導致一些軟包裝應用中出現了高遮蓋力有機顏料的替代,但功能等效性的限制阻礙了完全替代。防曬油化妝品中氧化鋅紫外線阻隔劑的引入推動了礦物顏料的增量成長,抵消了傳統造紙應用領域需求的下降。炭黑在導電聚合物複合複合材料和墨粉系統中保持穩定的地位。整體而言,隨著無機顏料領域的成熟,競爭重點正轉向製程效率,而有機顏料供應商則透過分子層面的創新和與終端用戶的合作來展開競爭。
本顏料報告按產品類型(無機顏料、有機顏料、特殊顏料及其他產品類型)、應用領域(油漆塗料、紡織品、印刷油墨、塑膠、皮革及其他應用領域)和地區(亞太地區、北美地區、歐洲地區、南美地區以及中東和非洲地區)進行細分。市場預測以美元以金額為準。
區域分析
預計到2025年,亞太地區將佔全球營收的45.60%,並在2031年之前維持5.32%的年複合成長率,成為成長最快的地區,鞏固其在規模和發展動能方面的主導地位。中國約佔該地區顏料產量的一半,並透過二氧化鈦(TiO2)產能的波動和能源強度課稅持續影響著全球價格。印度已推出與特種化學品生產掛鉤的激勵措施,促進與日本和歐洲主要顏料生產商的合資企業,並擴大了該地區的產品線。預計到2024年底,印尼的建築塗料產量將超過100萬噸,隨著國內市場對品質要求的不斷提高,市場也日益成熟。
北美和歐洲正轉向高價值的細分市場,這些市場整體產量較低,更注重技術差異化和價值鏈穩定性。在美國,根據《國防授權法》,聯邦政府對特種化學品的撥款已流入國內顏料中間體產業,這在一定程度上保護了買家免受地緣政治動盪的影響。
中東和非洲正崛起為充滿成長機會的地區。波灣合作理事會(GCC)成員國正投資氯化鈦(TiO2)產業,以實現下游業務多元化;同時,北非的紡織產業叢集正吸引尋求從鄰國採購原料的歐洲品牌。南美洲的成長軌跡取決於宏觀經濟的穩定和大宗商品出口週期,而這些因素又會影響基礎建設支出和汽車組裝量。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 新興經濟體對油漆和塗料的需求快速成長
- 監管部門推動環保/生物基顏料的發展
- 高性能和特效顏料的廣泛應用
- 奈米技術賦能的數位與3D列印應用
- 促進美國和歐盟供應鏈本地化的措施
- 市場限制
- 嚴格的環境和毒理學法規
- 原料價格波動(二氧化鈦、氧化鐵等原料)
- 食品級奈米顆粒禁用(E171,化妝品限制)
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭程度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依產品類型
- 無機顏料
- 二氧化鈦
- 氧化鋅
- 其他產品種類(碳顏料、乾土、群青顏料、鎘、鉻酸鉛等)
- 有機顏料
- 特殊顏料和其他產品類型(功能性顏料、磁性顏料等)
- 無機顏料
- 透過使用
- 油漆和塗料
- 纖維
- 印刷油墨
- 塑膠
- 皮革
- 其他用途
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- ASEAN
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 義大利
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率(%)/排名分析
- 公司簡介
- ALTANA
- Cathay Industries
- DIC Corporation
- Heubach GmbH
- Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- Lanxess
- LB Group
- Shepherd Color
- Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited(Heubach GmbH)
- The Chemours Company
- Tronox Holdings Plc
- Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- Venator Materials PLC
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Pigments Market was valued at USD 31.93 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 33.26 billion in 2026 to reach USD 40.82 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.18% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Resilient demand for construction, packaging, and mobility applications underpins this expansion even as producers navigate supply chain realignments and tightening safety rules. Inorganic grades retain cost-based advantages in bulk architectural coatings, while organic and specialty chemistries capture share in high-performance automotive and electronics uses. Regional diversification of titanium dioxide (TiO2) sourcing, coupled with initiatives to phase out PFAS and other restricted substances, is accelerating product reformulation activity across the pigments market. Competitive dynamics are further shaped by consolidation, exemplified by Kronos Worldwide's July 2024 acquisition of Louisiana Pigment Company, which is allowing scale players to streamline raw-material procurement and reinforce downstream distribution reach.
Global Pigments Market Trends and Insights
Surging Paints and Coatings Demand in Emerging Economies
Infrastructure programs in Indonesia, Nigeria, and Vietnam are driving a steady uptick in architectural coatings volumes, evidenced by Indonesia's paint output surpassing 1.00 million tons in October 2024. Growing cement capacity across sub-Saharan Africa-bolstered by nine Chinese-backed projects completed in 2023 and five more slated for 2024-continues to lift demand for construction-grade pigments. Governments' drive toward water-based, low-VOC formulations is forcing suppliers to deliver cost-competitive dispersions compatible with stricter emission limits. The result is a larger addressable base for mid-tier pigment producers able to localize blending and logistics operations near major construction clusters. Over the medium term, recurring housing and transport infrastructure outlays are expected to translate into multi-year offtake contracts that stabilize volumes even when private sector repaint cycles slow.
Regulatory Push Toward Eco-Friendly/Bio-Based Pigments
Global regulators are methodically narrowing the palette of allowable pigment chemistries. California's AB 418 will prohibit TiO2 in foods from January 2025, while New Zealand's cosmetics ban on PFAS enters force in December 2026. Large formulators such as L'Oreal have pledged to source 95% bio-based ingredients by 2030, signaling an industry-wide pivot toward renewable colorants. Academic and industrial programs are commercializing seaweed-derived phycobiliproteins and fucoxanthin using enzyme-assisted extraction and hydrodynamic cavitation, achieving color strength comparable with conventional azo pigments. As compliance costs rise for incumbent chemistries, early-scale bio-based suppliers can exploit a pricing corridor that was previously unavailable in volume markets. Adoption, however, hinges on overcoming the capital cost of new biorefinery infrastructure and meeting the durability expectations of demanding end uses such as outdoor coatings.
Stringent Environmental and Toxicology Regulations
OEKO-TEX updated its restricted-substance testing protocol in October 2024 to include alkaline hydrolysis screening for PFAS, and Canada enacted a nationwide coal-tar ban in March 2025. EU REACH Entry 79 introduced PFHxA controls in the same month, while several U.S. states imposed PFAS prohibitions on textiles from January 2025. Each new rule forces pigment suppliers to validate alternative chemistries and establish dual inventories to serve jurisdictions with divergent thresholds. Compliance requires sophisticated quality-management systems under ISO 22716, raising fixed costs that smaller producers struggle to absorb. The immediate impact is a wave of capacity rationalization in mature markets, reducing tactical price competition but heightening strategic barriers for new entrants.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Adoption of High-Performance and Effect Pigments
- Nano-Enabled Digital and 3-D Printing Applications
- Raw-Material Price Volatility (TiO2, Iron-Oxide Feedstocks)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The inorganic cluster maintained 75.42% share of the pigments market in 2025, a position anchored by TiO2's indispensability for opacity and whiteness in architectural and packaging formulations. Within this cohort, iron oxides continue to dominate masonry coatings and construction materials thanks to cost and durability advantages. Organic pigments, although smaller in volume, are set to advance at a 5.18% CAGR to 2031, leveraging superior chroma and regulatory headroom in applications that demand low heavy-metal content. High-performance quinacridones and perylenes now populate automotive basecoats, while diketopyrrolo-pyrrole reds are penetrating consumer electronics housings. Specialty sub-segments, such as thermochromic and magnetic pigments, are winning premium contracts in security printing and electronic component marking.
Cost inflation for titania feedstock is tilting certain flexible-packaging jobs toward high-opacity organic alternatives, though functional equivalence still limits broader substitution. The introduction of zinc-oxide UV blockers in sun-care cosmetics is driving incremental growth for mineral pigments, offsetting softer demand in legacy paper applications. Carbon blacks retain a stable foothold in conductive polymer compounds and toner systems. Overall, the inorganic segment's maturity has shifted competitive emphasis toward process efficiency, whereas organic suppliers compete on molecular innovation and end-user collaboration.
The Pigments Report is Segmented by Product Type (Inorganic Pigments, Organic Pigments, and Specialty Pigments and Other Product Types), Application (Paints and Coatings, Textiles, Printing Inks, Plastics, Leather, and Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held a 45.60% share of global revenue in 2025 and is expected to post the fastest 5.32% CAGR through 2031, cementing its lead in both scale and momentum. China accounts for roughly half of regional pigment output and continues to influence global price discovery through its TiO2 capacity swings and energy-intensity levies. India's production-linked incentives for specialty chemistry are encouraging joint ventures with Japanese and European pigment majors, thereby broadening the region's product breadth. Indonesia's output of architectural coatings exceeded 1.00 million tons in late 2024, signaling a maturing domestic market with rising quality expectations.
North America and Europe, though collectively smaller in volume, are pivoting toward value-add niches that reward technical differentiation and supply-chain security. U.S. federal funding for specialty chemicals under defense authorization acts is channeling capital into domestic pigment intermediates, partially insulating buyers from geopolitical disruptions.
The Middle East and Africa are emerging as opportunistic growth zones. Gulf Cooperation Council countries are investing in chloride-route TiO2 as part of downstream diversification, while North African textile clusters are courting European brands seeking near-shore sourcing. South America's trajectory is tied to macroeconomic stabilization and commodity export cycles that affect infrastructure spending and automotive assembly volumes.
- ALTANA
- Cathay Industries
- DIC Corporation
- Heubach GmbH
- Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- Lanxess
- LB Group
- Shepherd Color
- Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited (Heubach GmbH)
- The Chemours Company
- Tronox Holdings Plc
- Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- Venator Materials PLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging paints and coatings demand in emerging economies
- 4.2.2 Regulatory push toward eco-friendly/bio-based pigments
- 4.2.3 Rising adoption of high-performance and effect pigments
- 4.2.4 Nano-enabled digital and 3-D printing applications
- 4.2.5 Supply-chain localization incentives in US-EU
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent environmental and toxicology regulations
- 4.3.2 Raw-material price volatility (TiO2, iron-oxide feedstocks)
- 4.3.3 Nano-particle food-grade bans (E171, cosmetics limits)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Inorganic Pigments
- 5.1.1.1 Titanium Dioxide
- 5.1.1.2 Zinc Oxide
- 5.1.1.3 Other Product Types (Carbon Pigments, Dry Earth, Ultramarine Pigments, Cadmium, Lead Chromate, and Others)
- 5.1.2 Organic Pigments
- 5.1.3 Specialty Pigments and Other Product Types (Functional Pigments, Magnetic Pigments, and Others)
- 5.1.1 Inorganic Pigments
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Paints and Coatings
- 5.2.2 Textiles
- 5.2.3 Printing Inks
- 5.2.4 Plastics
- 5.2.5 Leather
- 5.2.6 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 ASEAN
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 Italy
- 5.3.3.4 France
- 5.3.3.5 Spain
- 5.3.3.6 Russia
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ALTANA
- 6.4.2 Cathay Industries
- 6.4.3 DIC Corporation
- 6.4.4 Heubach GmbH
- 6.4.5 Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- 6.4.6 Lanxess
- 6.4.7 LB Group
- 6.4.8 Shepherd Color
- 6.4.9 Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited (Heubach GmbH)
- 6.4.10 The Chemours Company
- 6.4.11 Tronox Holdings Plc
- 6.4.12 Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Venator Materials PLC
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment








