 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1906275
工業機械:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2026-2031)Industrial Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
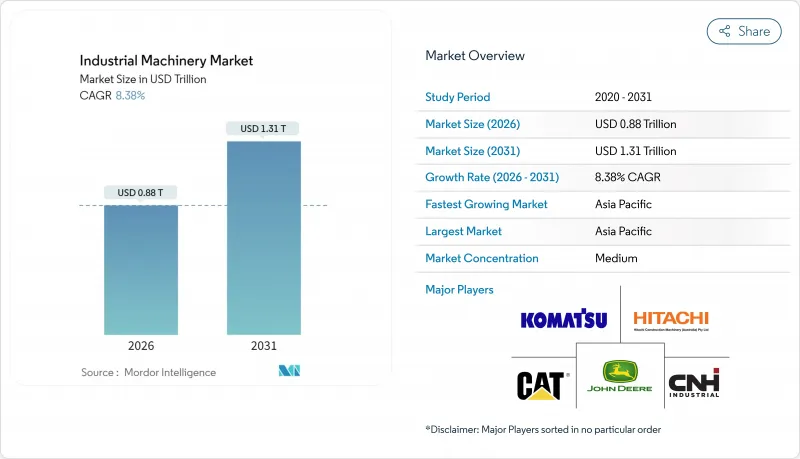
預計工業機械市場將從 2025 年的 8,100 億美元成長到 2026 年的 8,800 億美元,到 2031 年將達到 1.31 兆美元,2026 年至 2031 年的複合年成長率為 8.38%。
這一成長反映了持續的基礎設施投資、工廠自動化進程的加速以及零排放設備的日益普及。終端用戶增加了對基於人工智慧的預測性維護平台的投入,以減少計劃外停機時間,而製造商則致力於採用模組化機器設計以加快交付速度。亞太地區在2024年繼續保持其主導地位,這主要得益於中國和印度產能的快速擴張。北美和歐洲的買家則專注於便於回流生產的多進程機器,這些機器能夠在產品線之間快速切換,以增強其國內供應鏈的韌性。數控工具機和機器人領域的熟練勞動力短缺使得自動化需求居高不下,並推動了設備即服務(EaaS)模式的普及,這種模式可以降低初始資本投入。
全球工業機械市場趨勢與洞察
採用工業4.0和智慧製造
全球製造商紛紛採用感測器、雲端分析和數位雙胞胎來減少停機時間並提高生產效率。西門子的Senseye平台每分鐘可處理超過一百萬個機器資料點,將預測準確率提高85%,並將維護成本降低高達40%。設備製造商已整合邊緣分析模組,以開拓新的訂閱收入來源並實現設備即服務(EaaS)合約。數位雙胞胎使操作人員能夠在不停止生產的情況下測試週期時間的變化,從而有助於證明資本投資的合理性。這些功能可加快投資報酬率,並促進自動化技術的採用,即使是預算緊張的中型工廠也不例外。為了應對日益增強的網路安全意識,供應商正在透過設備端加密和網路分段來增強設備控制器的功能。
來自建築和基礎設施計劃的需求不斷成長
亞太和中東地區多年公共工程預算持續推動土木機械、起重機和混凝土設備的訂單。為滿足不斷變化的低排放氣體和低噪音法規,電池驅動的緊湊型裝載機在都市區越來越受歡迎。凱斯工程機械的12EV電動緊湊型輪式裝載機配備23kWh電池,載重能力達1.15噸,且實現零排放。承包商也開始為大型挖土機採用混合動力系統,以降低怠速時的油耗。來自原廠配套租賃公司的彈性融資方案和殘值擔保幫助承包商抵消了高昂的前期成本,進一步提振了市場需求。
高昂的資本投資和維修成本
高精度銑床和自動化焊接單元的初始購置成本對許多小規模加工廠來說都是一道障礙。Caterpillar公司報告稱,2025年第一季銷售額為142億美元,年減10%,原因是經濟情勢的不確定性導致一些客戶推遲了設備升級。計劃外停機時間仍平均佔生產成本的24%,凸顯了老舊資產帶來的財務風險。原始設備製造商(OEM)推出了按機器工時運作模式,將維護、軟體和耗材捆綁在一起。 SKF的「一切皆服務」(Everything-as-a-Service)方案使加工廠能夠按軸承性能付費,而不是按所有權付費,從而減輕了其資產負債表的負擔。
細分市場分析
2025年,受全球公路、住宅和能源計劃發展的推動,土木工程和施工機械佔工業機械市場佔有率的30.85%。高功率推土機和挖土機是進行大規模土方作業的必備設備,但隨著成熟市場車隊更新換代完成,需求趨於平穩。工業機器人和自動化單元是成長最快的產品類別,到2031年複合年成長率將達到12.57%。隨著製造商採用協作機器人與工人安全協作,其裝置量達到165億美元。機器人即服務(RoA)合約的廣泛應用降低了前期成本,並使視覺引導機械手臂即使在小規模車間也能進行取放操作。壓縮機和泵浦受益於變速驅動裝置的升級,降低了能源成本,從而促進了銷售成長。
設備製造商將人工智慧整合到動作控制器中,以縮短循環時間並提高揀選精度。受特斯拉超級工廠自動化模式的啟發,汽車製造商將固定式和自主式移動機器人結合,按需運輸零件並減少在製品庫存。物流中心的物料輸送設備需求持續成長,滿足了電履約中心對高吞吐量輸送機和分類機的需求。隨著精準噴灑系統和自動曳引機的普及,農業機械也隨之發展,以緩解農村地區的勞動力短缺問題。產品多樣化持續推進,推出了諸如用於室內物流的電動加長型堆高機和用於城市高層建築的混合動力履帶起重機等專用機械。
預計到2025年,建築業仍將佔據工業機械市場29.12%的最大佔有率,這反映了交通網路的持續更新和公共產業的擴張。建築商在城市計劃中優先考慮低噪音、零排放的機械設備,這催生了超越簡單馬力的新規格標準。農業應用成長最快,複合年成長率達10.71%。自動駕駛曳引機、無人機引導噴藥機和智慧收割機在提高產量的同時,減少了化學投入。迪爾公司計畫投資200億美元用於美國工廠,部署自動化技術以緩解農業勞動力短缺問題。食品加工廠實現了托盤裝載和品質檢測的自動化,人工智慧視覺技術則減少了廢棄物。
汽車製造商擴大了電動車產能,並為電池機殼採用了高精度雷射切割系統。化學和製藥廠採用了具有遠端監控功能的原位就地清洗(CIP) 撬裝包裝,以滿足更嚴格的安全和可追溯性法規。紡織製造商部署了小型機器人來實現縫紉線的自動化,並扭轉了境外外包趨勢。發電工程,特別是風力發電機安裝和電網級電池組裝,需要客製化設計的物料輸送鑽機。印刷公司實施了支援工業 4.0 的工作流程軟體,以最佳化印刷機的運轉率並擴大模組化後加工設備的市場。每項應用都需要專門的自動化,從而促進了各種設備的銷售。
區域分析
預計到2025年,亞太地區將維持42.35%的市場佔有率,複合年成長率達8.42%,進一步鞏固其在工業機械市場的主導地位。中國自動化設備供應商推出了具有競爭力的伺服驅動器和PLC產品,並以本地化的價格與進口品牌競爭。印度的生產關聯激勵政策支持了機械進口,並促進了本土製造合資企業的建立。日本和韓國專注於超精密機器人和半導體設備,維持了較高的單價。台灣電子代工製造商需要持續投資表面黏著技術裝機和檢測設備,從而支撐了對專用送料器和相機的需求。
在北美,聯邦基礎設施建設資金和私營部門回流舉措起到了推動作用。製造商們實施了模組化加工單元,透過加快零件更換速度來支援準時生產,並擴大了現有工廠。加拿大礦場引進自動駕駛運輸卡車,顯示該地區對高科技重型機械的需求旺盛。貨幣穩定和低成本能源的供應吸引了更多投資進入石化和電池生產線,從而帶動了壓縮機、泵浦和捲材處理系統的訂單成長。教育合作推動了機器人技術員培訓計畫的發展,以解決技術純熟勞工短缺的問題。
歐洲市場需求穩定,企業持續投資多功能機械設備以因應不斷上漲的能源成本,保持競爭力。德國製造商向東歐的汽車和家電工廠供應高精度成型壓力機。斯堪地那維亞的木材加工廠安裝了智慧鋸切生產線,以最佳化每根原木的出材率。英國啟動了津貼零排放施工機械補貼計劃,旨在促進小型電動挖土機在城市改造中的廣泛應用。由於預測分析的需求不斷成長,以延長機械設備的使用壽命,歐洲的維修、保養和大修產業也隨之發展壯大。
南美洲、中東和非洲成為新的成長區域。巴西的基礎設施建設需要大規模土木機械和混凝土泵,但外匯波動限制了進口。日立建機和丸紅在巴西成立了一家礦業設備服務合資企業,以實現在地化支援並減少停機時間。波灣合作理事會(GCC)成員國投資海水淡化和可再生能源計劃,需要耐腐蝕泵浦和大容量起重機。非洲各國政府優先發展農業機械化,透過補貼曳引機購買和支持銷售低馬力設備來實現這一目標。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 採用工業4.0和智慧製造
- 建築和基礎設施計劃需求增加
- 新興經濟體的快速工業化
- 對小型零排放機械的需求(都市區維修)
- 預測性維護訂閱模式推動了更換需求。
- 生產回流推動了對彈性多工序機械的需求
- 市場限制
- 高昂的資本投資和維護成本
- 原物料價格波動
- 先進數控和機器人技術領域技術純熟勞工短缺
- 連網裝置的網路安全風險
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 宏觀經濟因素的影響
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依產品類型
- 土木工程施工機械
- 物料輸送設備
- 農業機械
- 工業機器人和自動化單元
- 其他(壓縮機、泵浦等)
- 按應用產業
- 印刷
- 食物
- 纖維
- 建造
- 製藥
- 化學
- 車
- 農業
- 發電
- 按最終使用者所有權
- OEM
- 契約製造
- 租賃公司
- 政府和地方政府
- 按自動化級別
- 傳統手動操作型
- 半自動/CNC
- 全自動/無人值守單元
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 英國
- 北歐國家
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 台灣
- 韓國
- 日本
- 印度
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲地區
- 中東
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Komatsu Ltd.
- Deere & Company
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- CNH Industrial NV
- Sandvik AB
- Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.
- Volvo Construction Equipment AB
- Liebherr-International AG
- JC Bamford Excavators Ltd.(JCB)
- Terex Corporation
- Manitowoc Company, Inc.
- Astec Industries, Inc.
- Illinois Tool Works Inc.
- Lincoln Electric Holdings, Inc.
- AGCO Corporation
- Alamo Group Inc.
- Wacker Neuson SE
- SANY Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
- XCMG Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
- Kubota Corporation
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Atlas Copco AB
- ABB Ltd.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The industrial machinery market is expected to grow from USD 0.81 trillion in 2025 to USD 0.88 trillion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 1.31 trillion by 2031 at 8.38% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Expansion reflected sustained infrastructure investment, accelerated factory automation, and the growing availability of zero-emission equipment. End-users increased spending on artificial-intelligence-enabled predictive maintenance platforms to curb unplanned downtime, while manufacturers pursued modular machine designs to shorten delivery cycles. Asia-Pacific held a commanding lead in 2024, helped by rapid capacity additions in China and India. North American and European buyers focused on reshoring-ready, multi-process machines that can switch quickly between product lines, supporting domestic supply-chain resilience. Tight skilled-labor pools for CNC and robotics roles kept automation demand elevated and encouraged Equipment-as-a-Service models that lower initial capital needs.
Global Industrial Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Adoption of Industry 4.0 & Smart Manufacturing
Manufacturers worldwide adopted sensors, cloud analytics, and digital twins to curb downtime and enhance throughput. Siemens' Senseye platform processed more than 1 million machine data points per minute and lifted forecast accuracy by 85%, cutting maintenance costs by as much as 40%. Equipment builders embedded edge analytics modules that unlock new subscription revenue and enable Equipment-as-a-Service contracts. Digital twins let operators test cycle-time changes without stopping production, helping to justify capital upgrades. These capabilities drove faster paybacks and encouraged mid-sized plants to adopt automation despite tight budgets. Rising cybersecurity awareness prompted vendors to harden machine controllers with on-device encryption and network segmentation.
Growing Demand from Construction & Infrastructure Projects
Multi-year public-works budgets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East continued to boost orders for earth-moving machines, cranes, and concrete equipment. Battery-powered compact loaders gained traction on urban job sites because they meet evolving low-emission and noise regulations. CASE Construction Equipment's 12EV electric compact wheel loader delivered a 1.15-ton payload using a 23 kWh battery while eliminating exhaust emissions . Contractors also adopted hybrid drivetrains in large excavators to cut fuel consumption during idling. Flexible finance packages and residual-value guarantees from OEM-linked leasing units helped contractors offset high upfront prices, further strengthening demand.
High Capex and Maintenance Costs
Initial purchase prices for high-precision multitasking lathes and automated welding cells deterred many small plants. Caterpillar recorded a 10% year-over-year sales decline to USD 14.2 billion in Q1 2025 as some customers delayed fleet renewals amid economic uncertainty. Unplanned downtime still averaged 24% of production costs, underscoring the financial risk of older assets. OEMs introduced subscription models where buyers pay per machine-hour, bundling maintenance, software, and consumables. SKF's Everything-as-a-Service offering let factories pay for bearing performance instead of ownership, easing balance-sheet pressure.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Industrialisation in Emerging Economies
- Demand for Compact Zero-Emission Machinery (Urban Retrofit)
- Raw-Material Price Volatility
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Earth-moving equipment captured 30.85% of industrial machinery market share in 2025 as global highway, housing, and energy projects progressed. High-horsepower dozers and excavators remained essential for bulk earthworks, but demand plateaued in mature markets where fleets had been refreshed. Industrial robots and automation cells were the fastest-growing product, advancing at a 12.57% CAGR toward 2031. The installed base reached USD 16.5 billion as manufacturers adopted collaborative robots that work safely next to operators. Wider use of Robot-as-a-Service contracts reduced upfront costs, permitting small job-shops to deploy vision-guided arms for pick-and-place tasks. Compressors and pumps benefited from upgrades to variable-speed drives that lower energy bills, supporting incremental sales.
Equipment builders integrated artificial intelligence into motion controllers to cut cycle times and improve pick accuracy. Tesla's gigafactory automation model inspired automakers to blend fixed robots with autonomous mobile robots that deliver parts on demand, trimming work-in-progress inventory. Material-handling equipment held steady demand from e-commerce fulfillment centers that required high-throughput conveyors and sorters. Agricultural machinery also advanced, helped by precision spraying systems and autonomous tractors that address rural labor shortages. The products segment continued to diversify as vendors introduced specialty machines, including electric-drive telehandlers for indoor logistics and hybrid-powered crawler cranes for urban high-rise construction.
Construction retained the largest application share at 29.12% of the industrial machinery market size in 2025, reflecting ongoing transport-network upgrades and utility expansions. Contractors prioritized low-noise, zero-emission machines for city projects, creating new specification points beyond raw horsepower. Agricultural applications recorded the fastest growth at a 10.71% CAGR. Autosteering tractors, drone-guided sprayers, and smart harvesters supported yield gains while reducing chemical inputs. Deere and Company earmarked USD 20 billion for United States factory investments that will roll out autonomous technologies to mitigate farm labor gaps. Food-processing facilities automated palletizing and quality inspection, leveraging artificial-vision to cut waste.
Automotive manufacturers expanded electric-vehicle capacity and installed high-tolerance laser-cutting systems for battery enclosures. Chemical and pharmaceutical plants adopted clean-in-place skid packages with remote monitoring, meeting stricter safety and traceability rules. Textile producers deployed compact robots to automate sewing lines, reversing offshoring trends. Power-generation projects, especially wind-turbine installation and grid-scale battery assembly, required purpose-built material-handling rigs. Printing firms embraced Industry 4.0 workflow software to optimize press utilization, extending the market for modular finishing machines. Each application segment demanded tailored automation, underpinning broad-based equipment sales.
The Global Industrial Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Earth-Moving Equipment, Material-Handling and More), Application Industry (Printing, Food, Textile, Construction, and More), End-User Ownership (OEMs, Contract Manufacturers, and More), Automation Level (Conventional Manually Operated, Semi-Automated/CNC, and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific maintained a 42.35% revenue share in 2025 and recorded an 8.42% CAGR, strengthening its dominance in the industrial machinery market. Chinese automation suppliers introduced competitive servo drives and PLCs, enabling localized price points that challenged imported brands. India's Production-Linked Incentive schemes supported machinery imports and encouraged joint ventures for domestic manufacture. Japan and South Korea focused on ultraprecise robotics and semiconductor equipment, sustaining high unit values. Taiwan's contract electronics manufacturing required continuous investment in surface-mount and inspection machines, preserving demand for specialty feeders and cameras.
North America benefited from federal infrastructure funding and private-sector reshoring initiatives. Manufacturers expanded brownfield sites with modular machining cells that switch quickly between parts, supporting just-in-time delivery. Autonomous haul trucks deployed in Canadian mining underscored the region's appetite for high-technology heavy equipment. Currency stability and access to low-cost energy attracted further investment in petrochemical and battery production lines, bolstering orders for compressors, pumps, and web-handling systems. Education partnerships addressed skilled-labor shortages by promoting robotics technician programs.
Europe saw steady demand as firms invested in multi-process machinery to defend competitiveness against rising energy costs. German builders supplied high-tolerance forming presses to Eastern European automotive and appliance plants. Scandinavian wood-processing mills installed intelligent saw lines that optimise yield from every log. The United Kingdom launched grants for zero-emission construction machinery, promoting adoption of compact electric excavators in urban redevelopment. The European repair-maintenance-overhaul sector grew as operators extended machine lifespans with predictive analytics.
South America and the Middle East and Africa represented emerging growth pockets. Brazilian infrastructure upgrades needed large earth-moving fleets and concrete pumps, but exchange-rate volatility constrained imports. Hitachi Construction Machinery and Marubeni set up a mining-equipment service venture in Brazil to localise support and shorten downtime. Gulf Cooperation Council nations invested in desalination and renewable-energy projects, requiring corrosion-resistant pumps and high-capacity cranes. African governments prioritised agricultural mechanisation by subsidising tractor purchases, aiding sales of low-horsepower machines.
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Komatsu Ltd.
- Deere & Company
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Sandvik AB
- Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.
- Volvo Construction Equipment AB
- Liebherr-International AG
- J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd. (JCB)
- Terex Corporation
- Manitowoc Company, Inc.
- Astec Industries, Inc.
- Illinois Tool Works Inc.
- Lincoln Electric Holdings, Inc.
- AGCO Corporation
- Alamo Group Inc.
- Wacker Neuson SE
- SANY Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
- XCMG Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
- Kubota Corporation
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Atlas Copco AB
- ABB Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Adoption of Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand from Construction and Infrastructure Projects
- 4.2.3 Rapid Industrialisation in Emerging Economies
- 4.2.4 Demand for Compact Zero-Emission Machinery (Urban Retrofit)
- 4.2.5 Predictive-Maintenance Subscription Models Spur Replacements
- 4.2.6 Reshoring Fuels Flexible Multi-Process Machinery Demand
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Capex and Maintenance Costs
- 4.3.2 Raw-Material Price Volatility
- 4.3.3 Skilled-Labour Shortage for Advanced CNC and Robotics
- 4.3.4 Cyber-Security Risks in Connected Equipment
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Earth-Moving Equipment
- 5.1.2 Material-Handling Equipment
- 5.1.3 Agricultural Machinery
- 5.1.4 Industrial Robots and Automation Cells
- 5.1.5 Others (Compressors, Pumps, etc.)
- 5.2 By Application Industry
- 5.2.1 Printing
- 5.2.2 Food
- 5.2.3 Textile
- 5.2.4 Construction
- 5.2.5 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.2.6 Chemical
- 5.2.7 Automotive
- 5.2.8 Agriculture
- 5.2.9 Power Generation
- 5.3 By End-User Ownership
- 5.3.1 OEMs
- 5.3.2 Contract Manufacturers
- 5.3.3 Rental / Leasing Companies
- 5.3.4 Government and Municipalities
- 5.4 By Automation Level
- 5.4.1 Conventional Manually-Operated
- 5.4.2 Semi-Automated / CNC
- 5.4.3 Fully-Automated / Lights-Out Cells
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.4 Nordics
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Taiwan
- 5.5.3.3 South Korea
- 5.5.3.4 Japan
- 5.5.3.5 India
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Mexico
- 5.5.4.3 Argentina
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Caterpillar Inc.
- 6.4.2 Komatsu Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Deere & Company
- 6.4.4 Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.6 Sandvik AB
- 6.4.7 Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Volvo Construction Equipment AB
- 6.4.9 Liebherr-International AG
- 6.4.10 J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd. (JCB)
- 6.4.11 Terex Corporation
- 6.4.12 Manitowoc Company, Inc.
- 6.4.13 Astec Industries, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Illinois Tool Works Inc.
- 6.4.15 Lincoln Electric Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.16 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.17 Alamo Group Inc.
- 6.4.18 Wacker Neuson SE
- 6.4.19 SANY Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.20 XCMG Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.22 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.23 Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.24 Atlas Copco AB
- 6.4.25 ABB Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment










