 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1852140
精密陶瓷:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Advanced Ceramics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
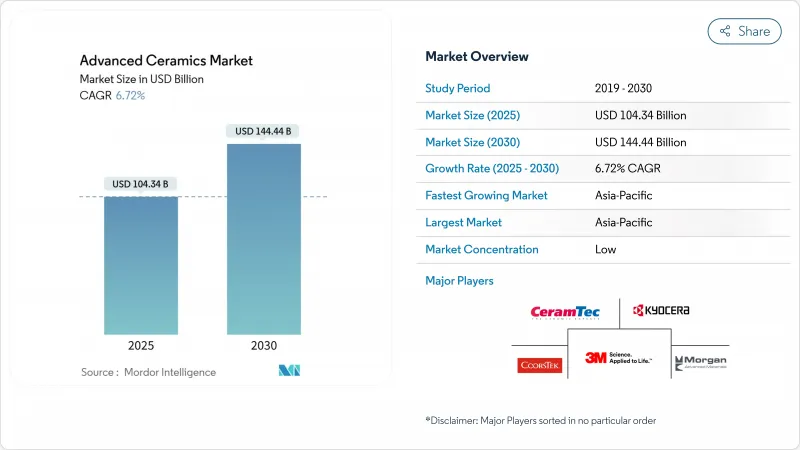
預計到 2025 年,精密陶瓷市場規模將達到 1,043.4 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 1,444.4 億美元,年複合成長率為 6.72%。
對輕質、高強度和耐熱材料日益成長的需求正推動航太、電子、能源和醫療保健行業的製造商逐步淘汰金屬和高性能聚合物。材料創新,特別是鈦酸鹽基電陶瓷和陶瓷基質複合材料,正在為供應商拓展更多機會。亞太地區以強勁的半導體資本投資維持主導地位,而隨著生物陶瓷取代金屬植入物,醫療應用領域正經歷兩位數成長。儘管不斷上漲的生產成本和複雜的燒結製程仍然是阻礙因素,但自動化、積層植入和閉合迴路回收等方面的努力正在穩步改善成本曲線和環境足跡。
全球精密陶瓷市場趨勢與洞察
擴大用作金屬和塑膠的替代品
精密陶瓷具有金屬所不具備的硬度、耐磨性和溫度穩定性。與鎳基高溫合金相比,噴射引擎熱端零件複合材料的陶瓷基質可減輕零件重量30%,並將燃料燃燒效率提高15%。由氮化矽製成的汽車渦輪增壓轉子能夠承受超過1000°C的高溫廢氣,同時保持尺寸精度。由氧化鋁或氧化鋯製成的工業泵殼在磨蝕性漿料中的使用壽命是不銹鋼的三到五倍。
醫療產業需求不斷成長
氧化鋁和氧化鋯等生物陶瓷具有良好的生物相容性和極低的離子釋放量,可延長植入的使用壽命並減少再次手術。外科醫生擴大使用根據患者解剖結構客製化的3D列印氮化矽脊柱融合器。整形外科器械製造商也在嘗試使用生物活性玻璃塗層來促進骨整合,以及藥物釋放型多孔陶瓷進行局部治療。
複雜的製造過程
在1600 度C下,對大批量工件保持±5 度C的溫度均勻性是一項挑戰。即使是微小的溫度梯度也會產生殘餘應力,降低機械強度,迫使供應商進行額外的檢驗和分類。對於複雜幾何形狀,全燒結零件的精密研磨產量比率通常低於85%。積層製造技術,例如黏著劑噴塗,在製造近淨成形零件方面展現出潛力,這些零件只需極少的後續加工,但其生產效率和表面光潔度仍落後於傳統製程。
細分市場分析
到2024年,氧化鋁將佔據精密陶瓷市場41%的佔有率,這得益於其均衡的性價比和成熟的供應鏈。這種材料廣泛應用於基板、切削刀具、生物醫學頭部和耐磨部件。持續的製程改進使得亞微米級晶粒尺寸得以實現,從而將斷裂韌性提高到6 MPa·m<sup>1/2</sup>,使得在不犧牲性能的前提下製造出更薄的部件成為可能。在需求方面,交通運輸和電網的電氣化正在推動對富含氧化鋁的絕緣硬體的需求。
鈦酸鹽陶瓷是成長最快的材料類別,預計到2030年將以7.8%的複合年成長率成長。鈦酸鋇多層電容器仍是智慧型手機和電動車電源管理電路的核心元件。同時,無鉛鈮酸鉀鈉作為鋯鈦酸鉛的永續替代品,在聲納換能器領域正日益受到關注。近期研究顯示,ZnTiO3-ZnO奈米複合塗層可直接殺死97%的金黃色葡萄球菌,進一步拓展了鈦酸鹽在抗菌表面應用的潛力。
到2024年,整體式陶瓷將佔據精密陶瓷市場78%的佔有率,因為單相氧化鋁、氧化鋯和氮化矽等材料技術成熟,且規模化生產成本效益高。 ISO 602和ASTM C1327測試方法的標準化簡化了航太和醫療產業的准入認證流程,從而維持了銷售量動能。生產商透過控制粉末形貌不斷提高可靠性,使結構級陶瓷的威布爾模量超過20,並降低了零件間的差異。
陶瓷基複合材料雖然目前以金額為準較小,但其複合年成長率高達8.12%,徹底改變了重量/強度之間的平衡。排氣系統和新一代噴嘴導流葉片現在採用碳化矽纖維增強碳化矽基複合材料,無需主動冷卻即可承受1400°C的高溫氣流。空中巴士和通用電氣正在進行氧化物陶瓷基複合材料的飛行測試,以增強機身結構,從而降低維護成本。電化學能源公司正在將碳纖維增強氧化鋁應用於固體氧化物燃料電池的互連材料,以延長電池堆的使用壽命。從實驗室概念到商業化的快速轉化證實,複合材料是精密陶瓷產業中一股顛覆性的力量。
區域分析
到2024年,亞太地區將佔據全球精密陶瓷市場54%的佔有率,這主要得益於密集的電子產業叢集、成熟的粉末供應鏈以及政府對高價值材料的扶持政策。中國的「十四五」規劃將精密陶瓷列為戰略產業,並為試點生產線提供扣除額和津貼。
在北美,航太、國防和醫療產業的消費量正在成長。美國研究實驗室正積極資助輕質CMC燃燒室襯裡的研究,以延長噴射引擎的維護週期。印第安納州和田納西州的整形外科器械中心大量採購氧化鋯增強氧化鋁用於髖關節零件,使得該地區的需求更加集中。
歐洲憑藉德國先進的機械設備和義大利的衛浴設備技術,在國際市場上保持著舉足輕重的地位。歐盟委員會的「先進材料引領產業」計劃高度重視永續性和可回收性,並為低碳燒結和循環經濟試點計畫提供研究資金。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 擴大其作為金屬和塑膠替代品的應用
- 醫療產業需求不斷成長
- 環保性和可靠性
- 來自電子和半導體行業的需求增加
- 在航太和國防領域不斷擴展的應用
- 市場限制
- 高昂的生產成本
- 複雜的製造過程
- 消費品末端回收的挑戰限制了ESG(環境、社會和治理)的採用
- 價值鏈分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 專利分析
- 定價分析
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依材料類型
- 氧化鋁
- 氧化鋯
- 鈦酸鹽
- 碳化矽
- 氮化矽
- 氮化鋁
- 矽酸鎂
- 熱解
- 其他
- 按班級
- 單片陶瓷
- 陶瓷基質複合材料
- 陶瓷塗層
- 透過使用
- 結構陶瓷
- 生物陶瓷
- 電陶瓷
- 磨損和腐蝕部件
- 隔熱/UHTC零件
- 觸媒撐體和過濾器
- 其他(環境和能源系統)
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- 電氣和電子
- 運輸
- 醫療的
- 產業
- 國防與安全
- 化學
- 其他終端用戶產業(能源和環境)
- 按地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東和非洲
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 亞太地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- 3M
- AGC Inc.
- Blasch Precision Ceramics, Inc.
- CeramTec GmbH
- CoorsTek Inc.
- Corning Incorporated
- Elan Technology
- International Syalons(Newcastle)Limited
- KYOCERA Corporation
- MARUWA Co., Ltd.
- Materion Corporation
- McDanel Advanced Material Technologies LLC
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- Rauschert Heinersdorf-Pressig GmbH
- Saint-Gobain
- SPT-Group
- Vesuvius
- Wonik QnC Corporation
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The advanced ceramics market is valued at USD 104.34 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 144.44 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.72% CAGR.

Rising demand for materials that combine lightweight, high hardness, and thermal resilience is pushing aerospace, electronics, energy, and healthcare manufacturers to shift away from metals and high-performance polymers. Material innovation, particularly around titanate-based electroceramics and ceramic matrix composites, enlarges the addressable opportunity set for suppliers. Asia-Pacific retains its leadership position due to strong semiconductor capital expenditure, while medical applications record double-digit growth as bioceramics replace metal implants. Although elevated production costs and complex sintering pathways remain headwinds, automation, additive manufacturing, and closed-loop recycling initiatives steadily improve cost curves and environmental footprints.
Global Advanced Ceramics Market Trends and Insights
Rise in Use as Alternative to Metals and Plastics
Advanced ceramics deliver hardness, wear resistance, and temperature stability that metals cannot match. Ceramic matrix composites in jet-engine hot sections cut component weight by 30% and improve fuel burn by 15% compared with nickel super-alloys. Automotive turbocharger rotors fabricated from silicon nitride withstand exhaust streams above 1,000 °C while maintaining dimensional accuracy. Industrial pump housings made from alumina and zirconia now last three to five times longer than stainless variants in abrasive slurries.
Growing Demand in the Medical Industry
Bioceramics such as alumina and zirconia exhibit proven biocompatibility and minimal ion release, which lengthens implant lifespans and decreases revision surgeries. Surgeons increasingly rely on 3D-printed silicon-nitride spinal cages tailored to patient anatomy, an advance made possible by low-temperature stereolithography. Orthopedic device makers also experiment with bioactive glass coatings that stimulate osteointegration and with drug-eluting porous ceramics for localized therapeutics.
Complex Manufacturing Process
Maintaining +-5 °C uniformity at 1,600 °C across large load sizes is challenging. Even minor temperature gradients create residual stresses that downgrade mechanical strength, forcing suppliers to perform additional inspection and culling. Precision grinding of fully sintered parts often records yields below 85% on complicated geometries. Additive manufacturing technologies such as binder jetting show promise by building near-net-shape parts that need minimal finishing, but throughput and surface finish still trail conventional routes
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Eco-friendliness and Reliability of Use
- Increasing Demand from Electronics and Semiconductors Industry
- End-of-Life Recycling Challenges Limiting ESG Adoption
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Alumina dominated the advanced ceramics market with a 41% share in 2024, supported by its balanced cost-performance profile and established supply chains. The material is entrenched in substrates, cutting tools, biomedical heads, and wear parts. Continuous process refinements now deliver sub-micron grain sizes that lift fracture toughness to 6 MPa*m1/2, enabling thinner components without performance trade-offs. On the demand side, electrification of transport and grid storage drives purchases of alumina-rich insulating hardware.
Titanate ceramics are the fastest-expanding material group at a 7.8% CAGR through 2030. Barium titanate multilayer capacitors remain the backbone of power-management circuits in smartphones and electric vehicles. Concurrently, lead-free potassium sodium niobate titanates gain traction in sonar transducers as a sustainable replacement for lead zirconate titanate. Recent research demonstrated ZnTiO3-ZnO nanocomposite coatings that kill 97% of Staphylococcus aureus on contact, widening titanate potential in antimicrobial surfaces.
Monolithic ceramics held 78% of the advanced ceramics market size in 2024 because single-phase alumina, zirconia, and silicon nitride are well understood and cost-efficient at scale. Standardization around ISO 602 and ASTM C1327 test methods simplifies qualification for aerospace or medical entry, sustaining volume momentum. Producers continue to improve reliability through powder morphology control, resulting in Weibull moduli above 20 for structural grades, which reduces part-to-part variability.
Although smaller in dollar terms, Ceramic matrix composites exhibit an 8.12% CAGR owing to their transformational weight-to-strength trade-off. Exhaust systems and next-generation nozzle guide vanes now use silicon-carbide fiber-reinforced silicon-carbide matrices that tolerate 1,400 °C gas streams without active cooling. Airbus and GE are flight-testing oxide-oxide CMCs in fuselage stiffeners to curb maintenance costs. Electrochemical energy companies apply carbon-fiber-reinforced alumina in solid-oxide fuel-cell interconnects to extend stack life. The rapid conversion of laboratory concepts into commercial runs underscores the composite class as a major disruptive force within the advanced ceramics industry.
The Advanced Ceramics Market Report Segments the Industry by Material Type (Alumina, Zirconia, Titanate, Silicon Carbide, and More), Class Type (Monolithic Ceramics, Ceramic Matrix Composites, and Ceramic Coatings), Application (Structural Ceramics, Bioceramics, Electroceramics, and More), End-User Industry (Electrical and Electronics, Transportation, Medical, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, and More).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific possessed 54% of the advanced ceramics market in 2024, underpinned by dense electronics clusters, established powder supply chains, and government incentives for high-value materials. China's 14th Five-Year Plan classifies advanced ceramics as a strategic segment, unlocking tax credits and grant funding for pilot lines.
North America is witnessing a rise in consumption owing to robust aerospace, defense, and medical verticals. The United States Air Force Research Laboratory actively funds lightweight CMC combustor liners to extend jet-engine service intervals. Orthopedic device hubs in Indiana and Tennessee procure large volumes of zirconia-toughened alumina for hip components, driving concentrated regional demand.
Europe maintains a prominent footprint through Germany's advanced machinery and Italy's sanitary ware expertise. The European Commission's Advanced Materials for Industrial Leadership initiative emphasizes sustainability and recyclability, ensuring research budgets flow into low-carbon sintering and circular-economy pilots.
- 3M
- AGC Inc.
- Blasch Precision Ceramics, Inc.
- CeramTec GmbH
- CoorsTek Inc.
- Corning Incorporated
- Elan Technology
- International Syalons (Newcastle) Limited
- KYOCERA Corporation
- MARUWA Co., Ltd.
- Materion Corporation
- McDanel Advanced Material Technologies LLC
- Morgan Advanced Materials
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- Rauschert Heinersdorf-Pressig GmbH
- Saint-Gobain
- SPT- Group
- Vesuvius
- Wonik QnC Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise in Use as Alternative to Metals and Plastics
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand in the Medical Industry
- 4.2.3 Eco-friendliness and Reliability of Use
- 4.2.4 Increasing Demand from Electronics and Semiconductors Industry
- 4.2.5 Rising Usage in Aerospace and Defense Sector
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Production Costs
- 4.3.2 Complex Manufacturing Process
- 4.3.3 End-of-Life Recycling Challenges Limiting ESG Adoption
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Patent Analysis
- 4.7 Price Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Alumina
- 5.1.2 Zirconia
- 5.1.3 Titanate
- 5.1.4 Silicon Carbide
- 5.1.5 Silicon Nitride
- 5.1.6 Aluminum Nitride
- 5.1.7 Magnesium Silicate
- 5.1.8 Pyrolytic Boron Nitride
- 5.1.9 Others
- 5.2 By Class Type
- 5.2.1 Monolithic Ceramics
- 5.2.2 Ceramic Matrix Composites
- 5.2.3 Ceramic Coatings
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Structural Ceramics
- 5.3.2 Bioceramics
- 5.3.3 Electroceramics
- 5.3.4 Wear and Corrosion Components
- 5.3.5 Thermal Barrier and UHTC Components
- 5.3.6 Catalyst Supports and Filters
- 5.3.7 Others (Environmental and Energy Systems)
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.4.2 Transportation
- 5.4.3 Medical
- 5.4.4 Industrial
- 5.4.5 Defense and Security
- 5.4.6 Chemical
- 5.4.7 Other End-user Industries (Energy and Environmental)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global overview, Market overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 3M
- 6.4.2 AGC Inc.
- 6.4.3 Blasch Precision Ceramics, Inc.
- 6.4.4 CeramTec GmbH
- 6.4.5 CoorsTek Inc.
- 6.4.6 Corning Incorporated
- 6.4.7 Elan Technology
- 6.4.8 International Syalons (Newcastle) Limited
- 6.4.9 KYOCERA Corporation
- 6.4.10 MARUWA Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Materion Corporation
- 6.4.12 McDanel Advanced Material Technologies LLC
- 6.4.13 Morgan Advanced Materials
- 6.4.14 Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Rauschert Heinersdorf-Pressig GmbH
- 6.4.16 Saint-Gobain
- 6.4.17 SPT- Group
- 6.4.18 Vesuvius
- 6.4.19 Wonik QnC Corporation
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment
- 7.2 Increasing Applications of Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN)











