 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851781
基礎設施即服務 (IaaS):市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測 (2025-2030)Infrastructure As A Service - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
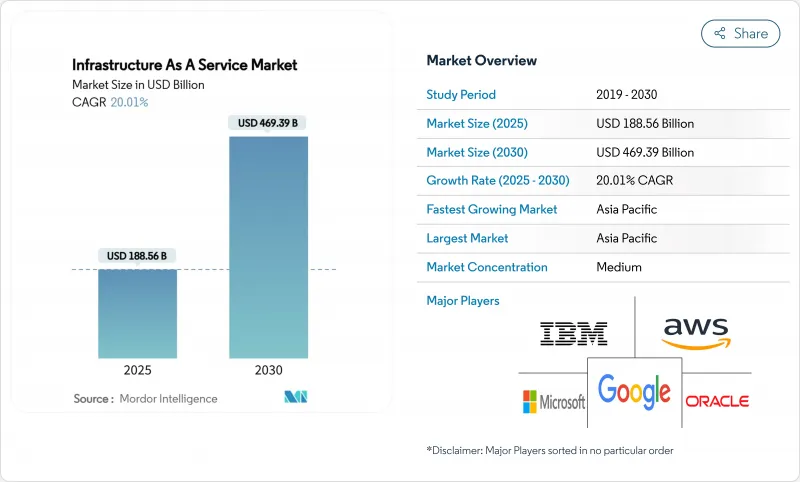
預計到 2025 年,基礎設施即服務 (IaaS) 市場規模將達到 1,885.6 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 4,693.9 億美元,在預測期(2025-2030 年)內,複合年成長率將達到 20.01%。
生成式人工智慧訓練的需求、企業混合雲遷移的加速以及每年超過2500億美元的超大規模資本支出將支撐這一發展趨勢。液冷資料中心設計、支援5G延遲的邊緣部署以及自主人工智慧計畫共同推動了高投資水準的持續成長。隨著超大規模資料中心業者競相拓展區域容量,而國家級服務供應商則利用資料居住要求,競爭日益激烈。由於營運商需要緩解電網壓力並滿足嚴格的永續性目標,再生能源購電協議的期限和規模都在不斷擴大。雲端基礎設施市場正邁入下一個階段,即地理分散式、人工智慧賦能的成長階段。
全球基礎設施即服務 (IaaS) 市場趨勢與洞察
對生成式人工智慧基礎設施的需求正在加速成長
據估計,生成式人工智慧訓練集群每個晶片需要700W的GPU機架,這將推動液冷技術在資料中心的普及率從2024年的10%成長到2025年的20%。 DataCenterFrontier指出,超大規模資料中心營運商目前正在圍繞1MW液冷機架重新設計其園區,並採用400V直流配電標準以降低轉換損耗。近40%的資料中心營運商計劃在2026年使用液冷技術來託管人工智慧工作負載。這項技術變革正在重塑資料中心的設計藍圖,使人工智慧賦能的設計成為整個雲端基礎設施市場的預設要求。
企業混合雲和多重雲端遷移激增
為了平衡成本和合規性,企業現在正將工作負載分佈在多個雲端平台。 IBM 於 2024 年以 64 億美元收購 HashiCorp,這將進一步深化多重雲端編配自動化。 Oracle 和 Google 的多重雲端合作關係消除了 Google 區域內Oracle資料庫的出口費用,從而掃清了工作負載可攜性的長期障礙。銀行業採用率尤其強勁,70% 的金融機構已完成試點部署,這主要得益於資料駐留規則和營運彈性測試的推動。隨著混合雲模式的擴展,專業服務供應商在管治和安全諮詢領域獲得了新的收入,從而強化了雲端基礎設施市場的良性循環。
日益成長的電網約束
2023年,資料中心已消耗了美國4.4%的電力。到2028年,這一比例可能達到12%,對傳統電網帶來巨大壓力。曾經的資料中心樞紐——北維吉尼亞和德克薩斯州,如今都已限制兆瓦級配額,迫使營運商轉向印第安納州和密西西比州尋求新的電力容量。在愛爾蘭,預計到2030年,該國高達70%的電力將用於數位負載,促使一些郡縣暫停了相關建設。營運商正在採用浸沒式冷卻技術來應對,該技術可將設施的能耗降低95%,但這些維修需要新的資金投入和更長的建設週期。因此,電力短缺正在減緩雲端基礎設施市場近期的擴張。
細分市場分析
到2024年,公共雲端將佔總營收的71.0%,這反映了過去十年來企業逐漸擺脫本地部署架構的趨勢。然而,到2030年,混合雲將以24.0%的複合年成長率(CAGR)實現最快成長,因為受監管產業需要將本地控制與外部部署規模結合。金融服務業的領導者認為,混合雲架構有助於他們在滿足客戶體驗目標的同時,順利通過監管審核。預計到2030年,混合雲部署的雲端基礎設施市場規模將達到1,420億美元,凸顯了混合雲在平衡對延遲敏感和對合規性要求高的工作負載方面發揮的關鍵作用。
AWS Outposts 和 Azure Stack 等私有連線選項的激增正在推動這股混合雲浪潮。芝加哥商品交易所集團 (CME Group) 在奧羅拉的 Google Cloud 私人區域展示如何在利用公共雲端工具的同時,將關鍵交易業務保留在本地。 IBM 與 HashiCorp 合作開發的多功能編配軟體降低了複雜性門檻。隨著雲端基礎設施技術的日趨成熟,產業越來越傾向於將部署決策視為整體方案,而非非此即彼的選擇。
IaaS(基礎設施即服務)市場按部署類型(公共雲端、私有雲端、混合雲端)、服務類型(計算即服務 (CaaS)、儲存即服務 (STaaS)、資料庫/分析即服務 (DBaaS) 等)、最終用戶行業(銀行、金融服務和保險 (BFSI)、IT 和電信、醫療保健和生命科學)以及地區進行細分。
區域分析
到2024年,亞太地區將佔全球收入的43.2%,並維持21.4%的最快複合年成長率,這主要得益於中國、日本和印度政府的人工智慧計畫對國內雲端運算的補貼。光是中國的「東數據西」舉措每年就將向八個叢集投入4,000億元人民幣,將運算資源重新分配到內陸地區,緩解沿海地區的擁擠。到2030年,日本資料中心的價值將接近2兆日圓(約134億美元),這主要得益於AWS承諾的150億美元投資和Oracle承諾的80億美元投資。印度將受益於NTT的15億美元擴張計劃以及當地有利於數位基礎設施建設的稅收優惠政策。
北美仍然是第二大雲端服務中心,但由於傳統資料中心的飽和,其相對成長速度正在放緩。能源限制促使計劃流向一些先前被忽視的州:AWS 將在印第安納州投資 110 億美元,Compass 將在密西西比州破土動工建設價值 100 億美元的園區,STACK 將在維吉尼亞北部投資超過 1 吉瓦。加拿大的「數位雄心」計畫正在加速聯邦政府採用雲端運算。
歐洲正在努力平衡需求與碳中和目標。諸如DORA之類的法規迫使金融公司實現供應商多元化,而都柏林和阿姆斯特丹等傳統資料中心則因國家能源上限的限制而容量受限。由於可再生能源電網和有利的授權製度,柏林、華沙、奧斯陸、蘇黎世、米蘭、維也納和馬賽等新興城市正在崛起。歐盟在2030年實現資料中心零碳排放的目標正在推動對熱能再利用方案和離岸風力發電併網的投資,從而塑造雲端基礎設施市場的下一階段。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 對新一代人工智慧基礎設施的需求加速成長,並逐漸成為主流。
- 企業混合雲和多重雲端遷移激增
- 超大規模資料中心營運商的資本支出競爭將佔據主導地位(到2025年將超過2,500億美元)。
- 5G時代主流的邊緣到邊緣延遲要求
- 低調的長期綠色能源購電協議為新的資料中心選址開闢了道路。
- 政府自主人工智慧沙盒正在建設中,本地IaaS節點授權
- 市場限制
- 主流能源電網約束日益增加
- 主流資料主權與域外管轄權之間的衝突
- 液冷供應鏈中隱藏的瓶頸
- 超過100兆瓦的超大規模園區保險費飆升
- 價值/供應鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望(人工智慧加速器、液冷、零信任架構)
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過部署模式
- 公共雲端
- 私有雲端
- 混合雲
- 按服務類型
- Compute as a Service(CaaS)
- Storage as a Service(STaaS)
- 網路與 CDN
- Database / Analytics as a Service(DBaaS)
- Disaster-Recovery as a Service(DRaaS)
- 託管主機/專用雲
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- BFSI
- 資訊科技與電信
- 醫療保健與生命科學
- 媒體與娛樂
- 零售與電子商務
- 政府和公共機構
- 製造業/汽車
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Amazon Web Services(AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform(GCP)
- Alibaba Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure(OCI)
- Tencent Cloud
- Huawei Cloud
- OVHcloud
- DigitalOcean
- Rackspace Technology
- Hetzner
- Equinix Metal
- Cloudflare Workers/R2
- Linode/Akamai
- Oracle Cloud(Japan)
- Liquid Sky(Africa)
- Wasabi Technologies
- Scaleway
- SAP Business Technology Platform(BTP-IaaS portion)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Infrastructure As A Service Market size is estimated at USD 188.56 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 469.39 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 20.01% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Demand from generative-AI training, accelerating enterprise hybrid migrations, and hyperscaler capital expenditure above USD 250 billion per year underpin this trajectory. Liquid-cooled data-center designs, edge deployments supporting 5G latency, and sovereign AI initiatives together keep investment levels high. Competition intensifies as hyperscalers chase regional capacity while domestic providers leverage data-residency mandates. Power-purchase agreements for renewables are growing in length and scale because operators need to mitigate grid constraints and meet tightening sustainability targets. Collectively, these forces propel the cloud infrastructure market into its next phase of geographically distributed, AI-ready growth.
Global Infrastructure As A Service Market Trends and Insights
Accelerating Gen-AI Infrastructure Demand
Generative-AI training clusters require GPU racks drawing 700 W per chip, pushing liquid cooling adoption from 10% of data halls in 2024 to an estimated 20% in 2025. Hyperscalers now redesign campuses around 1 MW liquid-cooled racks, standardizing 400 V DC power distribution to curtail conversion losses, DataCenterFrontier. Enterprises echo the trend: nearly 40% of data-center operators plan to use liquid cooling by 2026 to host AI workloads. These technical shifts reshape facility blueprints, making AI-ready designs a default requirement across the cloud infrastructure market.
Enterprise Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Migration Spike
Organizations now spread workloads across multiple clouds to balance cost and compliance. IBM's USD 6.4 billion HashiCorp acquisition in 2024 deepens automation for multi-cloud orchestration. Oracle's and Google's multicloud tie-up eliminates egress fees for Oracle Database inside Google regions, removing a long-standing barrier to workload portability. Banking adoption is especially strong: 70% of institutions have moved beyond pilots, spurred by data-residency rules and operational-resilience tests. As hybrid patterns scale, specialized service providers find new revenue in governance and security advisory, reinforcing a virtuous cycle for the cloud infrastructure market.
Escalating Energy-Grid Constraints
Data centers already drew 4.4% of US electricity in 2023; the share may hit 12% by 2028, stressing legacy grids. Northern Virginia and Texas, once prime hubs, now ration megawatt allocations, sending operators to Indiana or Mississippi for fresh capacity. Ireland anticipates up to 70% of national power heading to digital loads by 2030, prompting moratoriums in some counties. Operators respond with immersion cooling that cuts facility power use by 95%, yet those retrofits demand fresh capital and extended build timelines. Limited electricity, therefore, slows the near-term expansion of the cloud infrastructure market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Hyperscaler CAPEX Race Exceeding USD 250 Billion
- Edge-to-Core Latency Requirements in the 5G Era
- Data-Sovereignty and Extraterritoriality Conflicts
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Public cloud held 71.0% of revenue in 2024, a reflection of a decade-long migration away from on-premises stacks. The hybrid tier, however, records the fastest 24.0% CAGR through 2030 as regulated industries mesh on-prem control with off-prem scale. Financial-services leaders credit hybrid setups for meeting customer-experience targets while passing regulatory audits. The cloud infrastructure market size for hybrid deployments is projected to reach USD 142 billion by 2030, underscoring its role in balancing latency-sensitive and compliance-critical workloads.
A sharp increase in private connectivity options such as AWS Outposts and Azure Stack supports this hybrid wave. CME Group's private Google Cloud region in Aurora illustrates how mission-critical trading stays local yet leverages public-cloud tooling. Multifaceted orchestration software-boosted by IBM's HashiCorp deal-lowers complexity barriers. As maturity rises, the cloud infrastructure industry increasingly views deployment decisions as a portfolio exercise rather than a binary choice.
The Infrastructure As A Service Market is Segmented by Deployment Mode (Public Cloud, Private Cloud and Hybrid Cloud), Service Type(Compute As A Service (CaaS), Storage As A Service (STaaS), Database / Analytics As A Service (DBaaS) and More), End-User Industry(BFSI, IT and Telecom, Healthcare and Life Sciences) and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific owns 43.2% of global revenue in 2024 and sustains the fastest 21.4% CAGR as sovereign AI programs in China, Japan, and India funnel subsidies into domestic clouds. China's East Data-West initiative alone channels CNY 400 billion annually toward eight megaclusters, redistributing computing inland and lowering coastal congestion. Japan approaches JPY 2 trillion (USD 13.4 billion) in data-center value by 2030, buoyed by AWS's USD 15 billion and Oracle's USD 8 billion pledges. India gains from NTT's USD 1.5 billion expansion and local tax incentives favoring digital infrastructure.
North America remains the second-largest base but sees relative growth slow as legacy hubs saturate. Energy limitations redirect projects to overlooked states: AWS earmarks USD 11 billion for Indiana, Compass breaks ground on a USD 10 billion Mississippi campus, and STACK commits over 1 GW in Northern Virginia. Canada's Digital Ambition program accelerates federal cloud adoption, propelled by Shared Services Canada's brokerage role.
Europe balances demand with carbon-neutral targets. Regulations such as DORA compel financial firms to diversify providers while national energy caps limit capacity in traditional locations like Dublin and Amsterdam. Alternative metros-Berlin, Warsaw, Oslo, Zurich, Milan, Vienna, and Marseille-rise thanks to renewable grids and supportive permitting regimes. The EU's aim for zero-carbon data centers by 2030 spurs investment in heat-reuse schemes and offshore wind tie-ins, shaping the next phase of the cloud infrastructure market.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Alibaba Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- Tencent Cloud
- Huawei Cloud
- OVHcloud
- DigitalOcean
- Rackspace Technology
- Hetzner
- Equinix Metal
- Cloudflare Workers / R2
- Linode / Akamai
- Oracle Cloud (Japan)
- Liquid Sky (Africa)
- Wasabi Technologies
- Scaleway
- SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP-IaaS portion)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Mainstream Accelerating Gen-AI infrastructure demand
- 4.2.2 Mainstream Enterprise hybrid & multi-cloud migration spike
- 4.2.3 Mainstream Hyperscaler CAPEX race (>$250 bn in 2025)
- 4.2.4 Mainstream Edge-to-core latency requirements in 5G era
- 4.2.5 Under-the-radar Long-duration green-energy PPAs unlocking new DC sites
- 4.2.6 Under-the-radar Government sovereign-AI sandboxes mandating local IaaS nodes
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Mainstream Escalating energy-grid constraints
- 4.3.2 Mainstream Data-sovereignty & extraterritoriality conflicts
- 4.3.3 Under-the-radar Liquid-cooling supply-chain bottlenecks
- 4.3.4 Under-the-radar Surging insurance premiums for >100 MW hyperscale campuses
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (AI accelerators, liquid cooling, Zero-Trust fabrics)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment Mode
- 5.1.1 Public Cloud
- 5.1.2 Private Cloud
- 5.1.3 Hybrid Cloud
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Compute as a Service (CaaS)
- 5.2.2 Storage as a Service (STaaS)
- 5.2.3 Networking & CDN
- 5.2.4 Database / Analytics as a Service (DBaaS)
- 5.2.5 Disaster-Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
- 5.2.6 Managed Hosting / Dedicated Cloud
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 BFSI
- 5.3.2 IT & Telecom
- 5.3.3 Healthcare & Life Sciences
- 5.3.4 Media & Entertainment
- 5.3.5 Retail & e-Commerce
- 5.3.6 Government & Public Sector
- 5.3.7 Manufacturing & Automotive
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.2 Germany
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Russia
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 Australia
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 UAE
- 5.4.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- 6.4.2 Microsoft Azure
- 6.4.3 Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- 6.4.4 Alibaba Cloud
- 6.4.5 IBM Cloud
- 6.4.6 Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- 6.4.7 Tencent Cloud
- 6.4.8 Huawei Cloud
- 6.4.9 OVHcloud
- 6.4.10 DigitalOcean
- 6.4.11 Rackspace Technology
- 6.4.12 Hetzner
- 6.4.13 Equinix Metal
- 6.4.14 Cloudflare Workers / R2
- 6.4.15 Linode / Akamai
- 6.4.16 Oracle Cloud (Japan)
- 6.4.17 Liquid Sky (Africa)
- 6.4.18 Wasabi Technologies
- 6.4.19 Scaleway
- 6.4.20 SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP-IaaS portion)
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment









