 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851590
銀行業物聯網:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Internet Of Things In Banking - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
預計到 2025 年,銀行業物聯網市場規模將達到 391.6 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 1,806.1 億美元,年複合成長率為 32.8%。
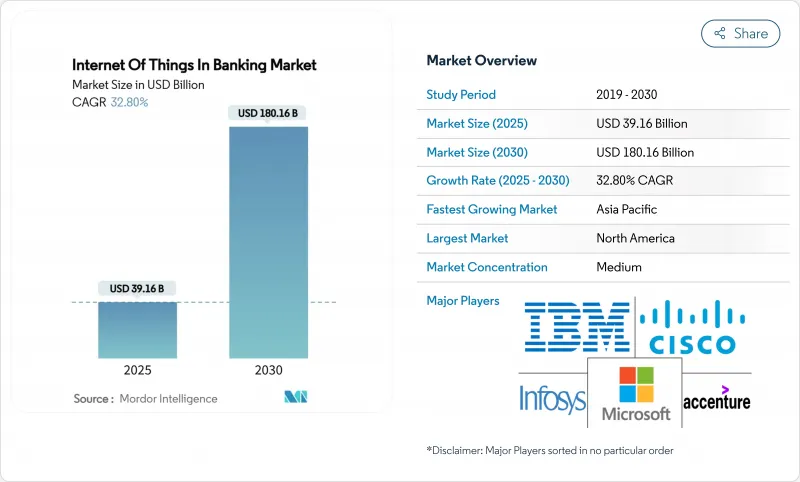
這種成長速度反映了銀行業正向感測器密集型營運模式、即時數據流和嵌入式支付轉型,將金融服務與日常設備使用連接起來。銀行正在為ATM機、分店和行動裝置配備連網感測器,以簡化現金操作、觸發情境化優惠,並實現汽車和智慧家電支付的自動化。以美國消費者金融保護局(CFPB)的開放銀行法規為首的監理趨勢(該法規將於2026年4月生效)正在加速API的開發,使第三方開發者能夠將物聯網訊號與銀行資料整合。在歐洲,支付服務指令3(PSD3)和擬議的支付服務條例是並行的強制性要求,旨在擴大強身份驗證要求,並為物聯網交易建立安全通道。儘管半導體供應鏈的限制和5G網路部署的不均衡仍然限制設備的部署,但感測器成本的下降和邊緣運算技術的進步表明,未來十年物聯網在銀行業的應用將持續擴展。
全球銀行業物聯網市場趨勢與洞察
打造全通路客戶體驗
銀行正在為自動櫃員機、行動應用和穿戴式裝置配備感測器,以實現實體環境和數位環境之間的無縫銜接。國民威斯敏斯特銀行(NatWest)升級了5,500台自動櫃員機,配備了19吋觸控螢幕和即時遙測功能,可在系統故障發生前發出預警。該銀行還發布了一款適用於Apple Vision Pro的零售銀行應用,讓客戶透過視線或手勢進行轉帳。這些整合使金融機構能夠將地理位置、設備健康狀況和購買模式等資訊融合起來,從而預測客戶需求,在成熟的推廣應用中,交叉銷售的準確率提高了三分之一。感測器分析功能支援到店前分店人員配備、排隊提醒和動態個人化優惠,使顧客滿意度提升兩位數。因此,物聯網在銀行業正帶來用戶留存率提高和營運成本降低的雙重效益。
即時詐欺偵測和安全
分散式感測器將資料輸入異常引擎,該引擎可在毫秒內標記可疑模式。結合設備遙測和交易流的聯邦學習模型實現了 96.3% 的欺詐檢測準確率,同時將資料本地化以保護隱私。智慧攝影機和環境感測器監控 ATM 和自動提款機,偵測可能表示存在盜刷設備或篡改的異常溫度升高。邊緣應用的區塊鏈哈希技術創建了不可篡改的日誌,用於爭議解決,而設備端 AI 則減少了曾經困擾客戶的誤報。早期採用者報告稱,在部署的第一年,詐騙降低了 20% 以上。儘管存在與網路犯罪相關的顧慮,但安全方面的緊迫性推動了持續投資,從而加強了銀行業物聯網的發展。
資料隱私和網路安全問題
歐盟網路安全法規要求製造商在出貨時提供自動安全更新,這使得無法提供空中修補程式的供應商面臨風險。銀行必須遵守各種法規,從加州的《消費者隱私法案》到印度的《數位個人資料保護法案》,這增加了合規成本。如果網路隔離措施薄弱,單一感測器的漏洞就可能危及銀行的核心系統。儘管聯邦學習試點計畫已證明,在不匯出原始資料的情況下,模型準確率可達99.94%,但大多數金融機構在保護其設備群方面仍面臨技能缺口。不斷上漲的網路保險費推高了計劃成本,並可能減緩物聯網在銀行業的應用。
細分市場分析
到2024年,服務收入將佔總收入的58%,這凸顯了專業知識、監管洞察力和全天候支援在決定複雜部署專案成功與否方面的重要性。預計銀行業物聯網市場規模將以33.37%的複合年成長率成長,這反映了整合商將感測器嵌入傳統核心系統和雲端架構的需求。為了降低風險,銀行通常會將威脅建模、合規性映射和設備生命週期管治。解決方案涵蓋硬體套件、軟體平台和連接捆綁包,並受益於雲端原生轉型,這使得金融機構能夠淘汰本地資料中心。諸如IBM-Wipro的AI賦能平台、捆綁分析和網路安全加固等聯合產品,加劇了解決方案供應商之間的競爭。
第二代部署方案傾向於按需計量收費的託管服務,規模較小的銀行更傾向於採用承包方案,而非資本密集的內部建置。供應商將邊緣運算節點與預先認證的開放銀行API連接器打包在一起,從而加快價值實現速度。由於硬體利潤仍然微薄,供應商正在轉向以設備監控和預測性維護為中心的年金模式。隨著雲端供應商發布金融級邊緣堆棧,銀行業物聯網市場正進一步向以服務為中心的經濟模式傾斜。
至2024年,安全應用將佔總營收的36.2%,複合年成長率(CAGR)為34.73%。預計2025年,銀行業物聯網安全市場規模將達到141.7億美元,2030年將超過710億美元。智慧型ATM可以偵測溫度異常、衝擊事件和竄改模式,並自動鎖定提款機。高階終端現在預設包含裝置級加密和信任根晶片,從而縮短了合規性審核所需的時間。
監控、資料管理和客戶體驗模組共用基礎設施,但在分析能力方面有所不同。該銀行利用遠端檢測最佳化分店的能源使用,因此較去年同期降低高達 12% 的電力成本。客戶體驗引擎將客流量感測器與客戶關係管理 (CRM) 歷史記錄連接起來,以便在分店內提供個人化問候。一個在同一感測器網路上託管多個應用程式的統一平台降低了總體擁有成本 (TCO),並有助於擴大物聯網在銀行業市場的整體吸引力。
全球銀行業物聯網市場報告按組件(解決方案和服務)、應用(安全、監控、其他)、組織規模(大型企業和中小企業)、最終用戶(零售銀行、公司銀行、投資銀行、其他)和地區進行細分。
區域分析
北美地區將在2024年繼續保持領先地位,佔據38.5%的收入佔有率,這主要得益於強力的網路安全立法以及金融科技公司與銀行的早期合作。配備感測器的分店將使生產力提高30-40%,而量子試驗演算法的運行速度比傳統最佳化器快1000倍。加拿大正透過連網社群ATM推動現金普及化,而墨西哥則利用基於物聯網的匯款自助終端來降低交易費用。在銀行業物聯網市場,聯邦政府正在支援5G網路向服務欠缺地區擴展,以縮小各大洲之間的延遲差距。
亞太地區是成長引擎,年複合成長率高達33.86%。中國的人工智慧銀行擁有超過1億客戶,其微服務核心融合了物聯網數據,實現個人化貸款。印度正在部署邊緣微型資料中心,以將行動銀行擴展到光纖稀缺的農村地區。東南亞的超級應用整合了叫車、外送和即時信貸功能,同時物聯網感測器追蹤駕駛員表現,實現動態保險定價。區域監管機構正在加快沙盒核准核准,確保銀行業物聯網能夠充分利用智慧型手機日益普及的優勢。
歐洲預計將在隱私和ESG(環境、社會和治理)方面取得進展。 PSD3和PSR強制要求進行身份驗證和API協調,從而促進安全設備存取。各機構將整合能源監測感測器來測量碳足跡,並履行其對淨零排放藍圖圖的承諾。設備製造商將採用節能晶片來支援物聯網電力消耗量監測。在拉丁美洲、中東和非洲等新興地區,支付現代化專案和行動支付方案為突破性發展提供了沃土。例如,巴西的PIX和奈及利亞的eNaira Rail使物聯網終端能夠發起即時支付,從而為銀行業物聯網市場拓展了收入來源。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 打造全通路客戶體驗
- 即時詐欺偵測和安全
- 監理開放銀行義務
- 感測器最佳化分店/ATM成本
- 利用物聯網(汽車和家用電器)的嵌入式支付
- 主導分析驅動的超個人化小額貸款
- 市場限制
- 資料隱私和網路安全問題
- 設備/平台互通性差距
- 農村地區 5G 延遲瓶頸
- ESG對物聯網能源消耗的審查
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 主要用例和案例研究
- 貸款承銷原料庫存追蹤
- 靈活貸款條款下的企業產出分析
- 基於物聯網的網路攻擊防禦系統
- 零售銀行業現狀
- 摩根大通預先宣布推出支援Beacon技術的ATM機
- 為殘障客戶提供的分店服務(巴克萊銀行)
- Beacon 讓閒置的銀行分行重煥生機(美國銀行和花旗銀行)
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按組件
- 解決方案
- 服務
- 透過使用
- 安全
- 監測
- 資料管理
- 客戶體驗管理
- 其他用途
- 按組織規模
- 主要企業
- 小型企業
- 最終用戶
- 零售銀行
- 企業銀行
- 投資銀行
- 非銀行金融公司
- 保險
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- ASEAN
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- Accenture plc
- Temenos AG
- Infosys Limited
- Software AG
- Vodafone Group plc
- Tibbo Systems
- SAP SE
- Capgemini SE
- Intel Corporation
- Amazon Web Services
- FIS Global
- NCR Atleos
- Thales Group
- Diebold Nixdorf
- HPE(Aruba)
- Huawei Technologies
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Internet of Things in Banking market stands at USD 39.16 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 180.61 billion by 2030, advancing at a 32.8% CAGR.

The growth pace mirrors banks' shift toward sensor-rich operating models, real-time data flows, and embedded payments that link financial services to daily device usage. Institutions are layering connected sensors on ATMs, branches, and mobile endpoints to streamline cash operations, trigger context-aware offers, and automate payments initiated from vehicles and smart appliances. Regulatory push, notably the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau's open-banking rule effective April 2026, is accelerating API readiness that lets third-party developers fuse IoT signals with banking data. Parallel mandates in Europe under PSD3 and the proposed Payment Services Regulation expand strong-authentication requirements and create secure rails for IoT-enabled transactions. Banks that orchestrate these capabilities report 30-40% efficiency gains and 20-30% uplifts in product-recommendation hit rates when omnichannel IoT programs mature.Supply-chain constraints around semiconductors and uneven 5G rollout still temper device deployments, yet falling sensor costs and edge-compute advances point to sustained expansion of the Internet of Things in the Banking market through the decade.
Global Internet Of Things In Banking Market Trends and Insights
Omnichannel Customer-Experience Push
Banks wire sensors into ATMs, mobile apps, and wearables to create journeys that pivot seamlessly across physical and digital environments. NatWest upgraded 5,500 ATMs with 19-inch touchscreens and live telemetry that flags downtime before it occurs. The bank also released a retail-banking app for Apple Vision Pro so clients can move funds using gaze and gesture. Such integrations let institutions blend geolocation, device health, and purchase patterns to anticipate needs, lifting cross-sell accuracy by one-third on mature rollouts. Sensor analytics enable pre-visit branch staffing, queue alerts, and dynamic personalized offers that raise customer satisfaction scores by double digits. The Internet of Things in Banking market, therefore, benefits from higher user stickiness and reduced operating costs.
Real-Time Fraud Detection and Security
Distributed sensors feed anomaly engines that flag suspicious patterns in milliseconds. A federated-learning model combining device telemetry with transaction streams now achieves 96.3% fraud-detection accuracy while keeping data local for privacy. Smart cameras and environmental sensors guard ATMs and cash machines, detecting skimming devices or abnormal temperature spikes that hint at tampering. Blockchain hashes applied at the edge create immutable logs for dispute resolution, and on-device AI reduces false positives that once annoyed customers. Early adopters report fraud-loss reductions of more than 20% in the first implementation year. Security urgency propels continual investment, fortifying the Internet of Things in the Banking market against cybercrime-related hesitancy.
Data-Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns
The EU Cyber Resilience Act obliges manufacturers to ship devices with automatic security updates, exposing vendors that cannot maintain over-the-air patching. Banks must track diverging rules from California's Consumer Privacy Act to India's Digital Personal Data Protection law, adding compliance overhead. Breaches at a single sensor can undermine banking cores if segmentation is weak. Federated-learning pilots show 99.94% model accuracy without exporting raw data, but most lenders still face skills gaps in securing device fleets. Rising insurance premiums for cyber coverage inflate project costs and can slow adoption within the Internet of Things in Banking market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Regulatory Open-Banking Mandates
- IoT-Enabled Embedded Payments (Cars and Appliances)
- Device / Platform Interoperability Gaps
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Services hold 58% of 2024 revenue, underscoring that domain expertise, regulatory insight, and 24-hour support tilt outcomes in complex rollouts. The Internet of Things in Banking market size for services is projected to expand at 33.37% CAGR, reflecting demand for integrators who stitch sensors into legacy cores and cloud fabrics. Banks often outsource threat modeling, compliance mapping, and device-life-cycle governance to reduce risk. Solutions cover hardware kits, software platforms, and connectivity bundles, and they benefit from cloud-native shifts that let lenders retire on-premises data centers. Joint offers, such as IBM-Wipro's AI-enabled platform, bundle analytics and cyber hardening, amplifying competition among solution providers.
Second-generation deployments favor pay-as-you-grow managed services, pushing smaller banks to embrace turnkey bundles rather than capex-heavy in-house builds. Vendors are packaging edge-compute nodes with pre-certified connectors for open-banking APIs, trimming time to value. Hardware margins remain thin, so suppliers pivot to annuity models around device monitoring and predictive maintenance. As cloud vendors release financial-grade edge stacks, the Internet of Things in Banking market further tilts toward service-centric economics.
Security applications captured 36.2% of 2024 revenue and expand at 34.73% CAGR, riding regulatory imperatives and growing attack vectors. The Internet of Things in Banking market size for security reached USD 14.17 billion in 2025 and is forecast to exceed USD 71 billion by 2030. Smart ATMs detect temperature anomalies, shock events, or tampering patterns and can lock dispensers automatically. Device-level encryption and root-of-trust chips now ship by default in premium terminals, reducing compliance audit time.
Monitoring, data management, and customer experience modules share infrastructure but vary in analytics heft. Banks leverage telemetry to optimize branch energy use, cutting power costs by up to 12% year over year. Customer-experience engines marry foot-traffic sensors with CRM histories to trigger in-branch personalized greetings. Integrated platforms that host multiple applications on the same sensor grid help reduce overall TCO, broadening appeal across the Internet of Things in the Banking market.
The Global Internet of Things in Banking Market Report is Segmented by Component (Solutions and Services), Application (Security, Monitoring, and More), Organization Size (Large Enterprises and Small and Medium Enterprises), End User (Retail Banking, Corporate Banking, Investment Banking, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
North America retains leadership with 38.5% of 2024 revenue, buoyed by solid cyber legislation and early fintech-bank partnerships. Sensor-enabled branches post 30-40% productivity uplifts, and quantum-trial algorithms run 1,000 times faster than legacy optimizers. Canada advances cash-circle inclusion through connected community ATMs, while Mexico leverages IoT-based remittance kiosks that cut transaction fees. The Internet of Things in Banking market sees federal support for 5G expansion into underserved zones, flattening latency disparities across the continent.
Asia-Pacific is the growth engine, charging ahead at 33.86% CAGR. China's AIBank serves more than 100 million customers on microservices cores that ingest IoT data to personalize lending. India deploys edge mini-data centers to extend mobile banking into rural districts where fiber remains sparse. Southeast Asian super-apps fuse ride-hailing, food delivery, and instant credit, with IoT sensors tracking driver performance for dynamic insurance pricing. Regional regulators fast-track sandbox approvals, ensuring the Internet of Things in Banking market captures rising smartphone penetration.
Europe predicates progress on privacy and ESG. PSD3 and the pending PSR impose mandatory authentication and harmonized APIs, fostering secure device onboarding. Institutions integrate energy-monitoring sensors to gauge carbon footprints, aligning with commitments to net-zero roadmaps. Device makers embed power-thrifty chips, addressing scrutiny over IoT electricity draw. In emerging regions of Latin America and the Middle East and Africa, payments modernization programs and mobile-money regimes create fertile ground for leapfrogging deployments. For instance, Brazil's PIX and Nigeria's eNaira rails allow IoT endpoints to initiate real-time payments, diversifying revenue sources within the Internet of Things in Banking market.
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- Accenture plc
- Temenos AG
- Infosys Limited
- Software AG
- Vodafone Group plc
- Tibbo Systems
- SAP SE
- Capgemini SE
- Intel Corporation
- Amazon Web Services
- FIS Global
- NCR Atleos
- Thales Group
- Diebold Nixdorf
- HPE (Aruba)
- Huawei Technologies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Omnichannel customer-experience push
- 4.2.2 Real-time fraud detection and security
- 4.2.3 Regulatory open-banking mandates
- 4.2.4 Branch/ATM cost-optimization via sensors
- 4.2.5 IoT-enabled embedded payments (cars and appliances)
- 4.2.6 Edge-analytics-driven hyper-personalized microlending
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Data-privacy and cybersecurity concerns
- 4.3.2 Device / platform interoperability gaps
- 4.3.3 Rural 5G latency bottlenecks
- 4.3.4 ESG scrutiny on IoT energy consumption
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Key Use-cases and Case Studies
- 4.8.1 Tracking raw-material inventory for loan underwriting
- 4.8.2 Farm-output analytics for flexible lending terms
- 4.8.3 IoT-driven cyber-attack prevention systems
- 4.9 Retail Banking Landscape
- 4.9.1 Beacon-enabled ATM pre-announce (JPM Chase)
- 4.9.2 In-branch navigation for disabled customers (Barclays)
- 4.9.3 Beacon revival of under-used branches (US Bank and Citi)
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Solutions
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Security
- 5.2.2 Monitoring
- 5.2.3 Data Management
- 5.2.4 Customer Experience Management
- 5.2.5 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Organization Size
- 5.3.1 Large Enterprises
- 5.3.2 Small and Medium Enterprises
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Retail Banking
- 5.4.2 Corporate Banking
- 5.4.3 Investment Banking
- 5.4.4 Non-Banking Financial Companies
- 5.4.5 Insurance
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.2 Microsoft Corporation
- 6.4.3 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.4 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.5 Accenture plc
- 6.4.6 Temenos AG
- 6.4.7 Infosys Limited
- 6.4.8 Software AG
- 6.4.9 Vodafone Group plc
- 6.4.10 Tibbo Systems
- 6.4.11 SAP SE
- 6.4.12 Capgemini SE
- 6.4.13 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.14 Amazon Web Services
- 6.4.15 FIS Global
- 6.4.16 NCR Atleos
- 6.4.17 Thales Group
- 6.4.18 Diebold Nixdorf
- 6.4.19 HPE (Aruba)
- 6.4.20 Huawei Technologies
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment








