 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851561
液化天然氣(LNG):市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
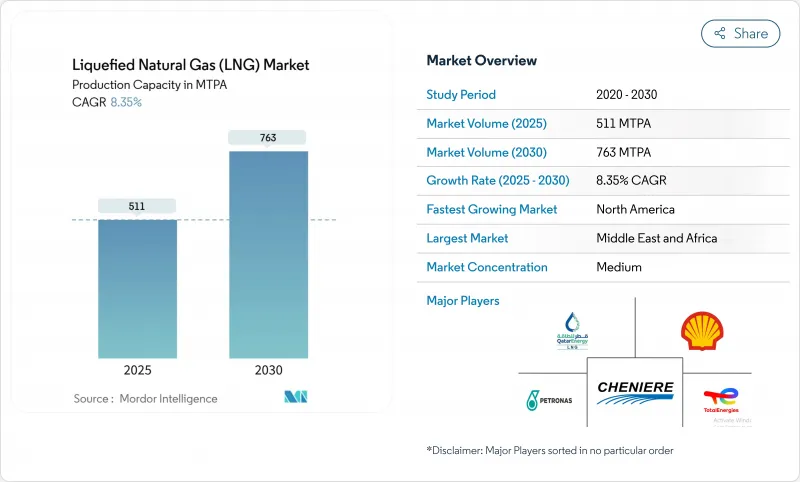
預計液化天然氣 (LNG) 市場產能將從 2025 年的 511 百萬噸/年成長到 2030 年的 763 百萬噸/年,預測期 (2025-2030 年) 的複合年成長率為 8.35%。
能源安全目標和脫碳要求正推動各國政府和公用事業公司將液化天然氣(LNG)作為過渡燃料,而浮體式LNG技術的快速普及正在拓展供應選擇,並釋放先前閒置的近海資源。北美出口終端正受益於來自二疊紀盆地的低成本原料氣,航運業正轉向使用LNG以符合硫含量上限要求,電氣化和碳捕獲升級正在提升營運的永續性。技術主導的成本控制和靈活的合約結構正在重塑交易格局,但持續的工程總承包(EPC)成本上漲和可再生氫的興起仍然是液化天然氣市場的焦點。
全球液化天然氣(LNG)市場趨勢與洞察
亞太地區天然氣發電計劃激增,尋求中游液化天然氣承購協議
亞太電力公司正在新增超過1,000億立方公尺的天然氣再氣化產能,而印度計畫在2030年將其天然氣消費量提高60%。該國的脫碳目標正在加速煤改氣進程,並鼓勵簽訂將液化天然氣供應與購電協議直接掛鉤的整合合約。這種緊密的天然氣連結可以降低資金籌措風險,提高計劃融資可行性,並增強液化天然氣市場的長期需求。
歐洲在國際海事組織2020年實施硫含量上限後,液化天然氣作為船用燃料迅速普及。
預計2024年,全球液化天然氣(LNG)動力船舶數量將增加33%,達到638艘,到2028年將超過1,200艘。貨櫃船佔LNG裝載載重噸的60%,198個港口的加註基礎建設正在加速推進。由於生物LNG計畫的推進,液化天然氣市場正獲得進一步發展動力,這些計畫將有助於更好地遵守未來的排放法規。
EPC成本上漲和模組製造瓶頸導致最終投資決策(FID)延期。
2024年僅有1,480萬噸/年的產能達到最終投資決定(FID),在成本上漲20-30%和勞動力短缺的情況下,產能大幅下降。儘管資本成本不斷上漲,模組化建造方式仍日益普及,但延誤可能會擴大2027年至2029年間的供應缺口,引發液化天然氣市場的波動。
細分市場分析
液化天然氣工廠到2024年將佔總收入的43%,在液化天然氣市場中佔比最高。卡達、美國和澳洲的產能擴張將支撐到2030年預計11.1%的複合年成長率。電動壓縮機和碳捕獲技術將減少排放,並增強大型綜合企業的競爭力。
該領域的生態系統目前包括904艘液化天然氣運輸船,其中許多配備了低甲烷引擎以減少溫室氣體排放。從2021年起,浮式儲存再氣化裝置(FSRU)每年新增7,700萬噸再氣化能力,檢驗了液化天然氣市場模組化部署的可行性,並加速了進口成長,尤其是在歐洲。
到2024年,發電將佔天然氣需求的38%,並且正在亞洲透過一體化液化天然氣發電計劃不斷擴張。這些項目將終端、儲存和發電資產結合在一起,降低了信用風險,並擴大了液化天然氣市場的覆蓋範圍。
在所有應用領域中,船舶燃料庫預計將以14%的複合年成長率實現最快成長。船隊規模的擴大、港口燃料庫網路的完善以及生物液化天然氣試點計畫的開展,都預示著船舶加油業務將持續成長,使其成為液化天然氣市場的重要推動力量。
液化天然氣 (LNG) 市場報告按基礎設施類型(LNG 液化廠、LNG 再氣化設施、LNG 船隊)、最終用途(發電、工業/製造業、其他)、規模(大型、中型、小型)、位置(陸上/海上)和地區(北美、歐洲、亞太地區、南美、中東和非洲)進行細分。
區域分析
2024年,中東和非洲佔全球市場佔有率的28%。卡達北部氣田的產能將於2027年從7,700萬噸/年擴建至1.26億噸/年,將鞏固其區域領先地位,並提升歐亞之間的運輸彈性。阿拉伯聯合大公國和茅利塔尼亞的新項目將進一步拓展液化天然氣市場,但經由霍爾木茲海峽的油輪保險成本仍是營運方面的一個問題。
由於豐富的頁岩氣資源和一條年產能1,330萬噸的出口生產線將於2025年投入營運,北美頁岩氣市場預計到2030年將維持10.5%的複合年成長率。加拿大基蒂馬特的Start-Ups以及與亨利樞紐相關的交易正在推動買家的興趣,但授權的暫時中止削弱了2020年代中期最終投資決策的前景。
亞太地區仍是最大的進口中心,其中中國在2024年的進口量為7,864萬噸。菲律賓和越南作為首次進口國,將擴大其客戶群,而小規模的液化天然氣分銷將推動整個群島的供應。日本和韓國可再生能源和氫能試點計畫的成長,為區域消費帶來了長期的不確定性。
自 2021 年以來,歐洲已部署多艘浮動儲存再氣化裝置 (FSRU) 來取代俄羅斯管道,使再氣供給能力提高了 44%。季節性需求激增將維持高價,而即將推出的歐盟甲烷法規將加強對液化天然氣市場供應鏈的審查。
其他好處
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 亞太地區燃氣發電工程激增,尋求液化天然氣承購協議
- 歐洲在國際海事組織2020年實施硫含量上限後,液化天然氣作為船用燃料迅速普及。
- 二疊紀盆地聯產氣產量為美國墨西哥灣沿岸出口碼頭提供低成本原料
- 浮體式液化天然氣技術釋放非洲海上閒置天然氣田的潛力
- 中國工業鍋爐煤改氣政策將促進現貨液化天然氣進口。
- 經合組織市場能源密集型資料中心對低碳供應的需求日益成長
- 市場限制
- EPC成本上漲和模組製造瓶頸導致最終投資決策(FID)延期。
- 來自可再生氫的競爭抑制了東北亞地區對長期液化天然氣合約的需求。
- 美國和加拿大暫停發放新的液化天然氣出口許可證
- 關鍵咽喉要道(霍爾木茲海峽、蘇伊士運河區)的地緣政治風險將增加液化天然氣運輸船的保險成本。
- 供應鏈分析
- 監理展望
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 依基礎設施類型
- 液化天然氣工廠[陸上液化、浮體式液化天然氣(FLNG)、中型(1-5百萬噸/年)、小型(小於1百萬噸/年)]
- 液化天然氣再氣化設施[陸上進口終端、浮體式儲存再氣化裝置(FSRU)]
- LNG船隊[LNG運輸船類型(Moss、Membrane)、運輸船類型(Q-Max、Q-Flex、Standard)、LNG燃料庫船]
- 按最終用途
- 發電業務
- 工業和製造業
- 住宅及商業地產
- 運輸(船舶燃料庫、重型道路運輸、鐵路運輸)
- 按尺寸
- 大規模(超過500萬噸/年)
- 中等規模(1-5百萬噸/年)
- 小規模(小於1噸/年)
- 按地區
- 陸上
- 海上(FLNG 和 FSRU)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 北歐國家
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 東南亞國協
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 哥倫比亞
- 南美洲其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 卡達
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略性舉措(併購、夥伴關係、購電協議)
- 市場佔有率分析(主要企業的市場排名/佔有率)
- 公司簡介
- QatarEnergy LNG(Qatargas)
- Shell plc
- Cheniere Energy Inc.
- TotalEnergies SE
- Petronas
- Novatek
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Woodside Energy Group
- Equinor ASA
- Sempra Infrastructure
- Venture Global LNG
- ENI SpA
- KOGAS
- Mitsui OSK Lines
- Golar LNG
- BW LNG
- Technip Energies
- Bechtel Corporation
- Fluor Corporation
- KBR Inc.
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Liquefied Natural Gas Market size in terms of production capacity is expected to grow from 511 MTPA in 2025 to 763 MTPA by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.35% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Energy-security goals and decarbonization mandates are steering governments and utilities toward LNG as a transitional fuel, while the rapid adoption of floating LNG technology broadens supply options and unlocks previously stranded offshore resources. North American export terminals enjoy low-cost feedgas from the Permian Basin, marine shipping is pivoting to LNG for sulfur-cap compliance, and electrification plus carbon-capture upgrades are advancing operational sustainability. Technology-driven cost management and flexible contract structures are reshaping trade patterns, yet prolonged EPC inflation and the rise of renewable hydrogen remain watchpoints for the liquefied natural gas market.
Global Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Asia-Pacific Gas-to-Power Projects Seeking Midstream LNG Offtake Agreements
Asia-Pacific utilities are adding over 100 bcm of new regasification capacity, and India plans to lift gas consumption 60% by 2030. National decarbonization targets are accelerating coal-to-gas switching and prompting integrated contracts that link LNG supply directly to power-purchase deals. This tight coupling lowers financing risk, improves project bankability, and reinforces long-run demand for the liquefied natural gas market.
Rapid Uptake of LNG as Marine Bunker Fuel Following IMO-2020 Sulfur Cap in Europe
The global LNG-fueled fleet grew 33% in 2024 to 638 vessels and is expected to exceed 1,200 ships by 2028. Container lines represent 60% of LNG-propelled deadweight tonnage, driving accelerated bunker-infrastructure rollout in 198 ports. The liquefied natural gas market is picking up additional momentum from bio-LNG initiatives that extend compliance into future emissions-control regimes.
Prolonged FID Delays Owing to EPC-Cost Inflation & Module Fabrication Bottlenecks
Just 14.8 MTPA of capacity reached FID in 2024, down sharply amid 20-30% cost jumps and labor shortages. Modular construction is gaining favor despite higher equipment prices, yet delays could open a supply gap in 2027-2029, inducing volatility across the liquefied natural gas market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Permian Basin Associated Gas Output Unlocks Low-Cost Feedgas for U.S. Gulf-Coast Export Terminals
- Floating LNG Technology Unlocking Stranded Offshore Gas Fields in Africa
- Competitiveness of Renewable Hydrogen Eroding Long-Term LNG Contract Appetite in Northeast Asia
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Liquefaction plants held 43% of 2024 revenues, the highest within the liquefied natural gas market. Capacity boosts in Qatar, the United States, and Australia underpin a forecast 11.1% CAGR to 2030. Electrified compressors and carbon capture trim emissions and sharpen competitive edges for integrated majors.
The segment's ecosystem now includes 904 LNG carriers, many fitted with low-methane-slip engines that curb greenhouse-gas intensity. FSRUs are accelerating import growth, especially in Europe, adding 77 MMtpy of regas capacity since 2021 and validating modular deployment for the liquefied natural gas market.
Power generation retained 38% of demand in 2024 and is expanding through integrated LNG-to-power projects in Asia. These setups consolidate terminal, storage, and generation assets, lowering credit risk and deepening the liquefied natural gas market footprint.
Marine bunkering is poised for a 14% CAGR, the fastest among applications. Fleet counts, port bunkering networks, and bio-LNG pilots signal durable growth, positioning shipping as a dynamic contributor to the liquefied natural gas market.
The Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Market Report is Segmented by Infrastructure Type (LNG Liquefaction Plants, LNG Regasification Facilities, and LNG Shipping Fleet), End-Use Application (Power Generation, Industrial and Manufacturing, and Others), Scale (Large-Scale, Mid-Scale, and Small-Scale), Location (Onshore and Offshore), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
The Middle East & Africa held 28% of the 2024 market. Qatar's North Field build-out from 77 MTPA to 126 MTPA by 2027 cements regional leadership and improves routing flexibility between Europe and Asia. New UAE and Mauritanian ventures add depth, though tanker insurance costs through Hormuz remain an operational concern for the liquefied natural gas market.
North America is set for a 10.5% CAGR through 2030 thanks to abundant shale gas and 13.3 MTPA of export trains entering service in 2025. Canada's Kitimat start-up and Henry-Hub-linked contracts amplify buyer interest, although temporary permitting pauses temper mid-decade FID outlooks.
Asia-Pacific remains the largest import center, with China purchasing 78.64 million t in 2024. First-time importers in the Philippines and Vietnam broaden the customer base, while small-scale LNG distribution gains traction for archipelagic supply. Renewable energy growth and hydrogen pilots in Japan and South Korea inject longer-term uncertainty into regional consumption.
Europe expanded regas capacity by 44% since 2021, installing multiple FSRUs to replace Russian pipeline volumes. Seasonal demand spikes sustain premium pricing, and impending EU methane rules will intensify supply-chain monitoring across the liquefied natural gas market.
- QatarEnergy LNG (Qatargas)
- Shell plc
- Cheniere Energy Inc.
- TotalEnergies SE
- Petronas
- Novatek
- Chevron Corporation
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Woodside Energy Group
- Equinor ASA
- Sempra Infrastructure
- Venture Global LNG
- ENI SpA
- KOGAS
- Mitsui O.S.K. Lines
- Golar LNG
- BW LNG
- Technip Energies
- Bechtel Corporation
- Fluor Corporation
- KBR Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in Asia-Pacific Gas-to-Power Projects Seeking Midstream LNG Offtake Agreements
- 4.2.2 Rapid Uptake of LNG as Marine Bunker Fuel Following IMO-2020 Sulfur Cap in Europe
- 4.2.3 Permian Basin Associated Gas Output Unlocks Low-Cost Feed-gas for U.S. Gulf-Coast Export Terminals
- 4.2.4 Floating LNG Technology Unlocking Stranded Offshore Gas Fields in Africa
- 4.2.5 China's Coal-to-Gas Switching Policies for Industrial Boilers Driving Spot LNG Imports
- 4.2.6 Growing Demand from Energy-Intensive Data Centres for Firm Low-Carbon Supply in OECD Markets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Prolonged FID Delays Owing to EPC-Cost Inflation & Module Fabrication Bottlenecks
- 4.3.2 Competitiveness of Renewable Hydrogen Eroding Long-Term LNG Contract Appetite in N.E. Asia
- 4.3.3 Regulatory Moratoria on New LNG Export Permits in U.S. & Canada
- 4.3.4 Geopolitical Risk at Key Chokepoints (Hormuz, Suez) Escalating LNG Shipping Insurance Costs
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Infrastructure Type
- 5.1.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants [Onshore Liquefaction, Floating LNG (FLNG), Mid-Scale (1-5 mtpa), and Small-Scale (<1 mtpa)]
- 5.1.2 LNG Regasification Facilities [Onshore Import Terminals, and Floating Storage & Regasification Units (FSRU)]
- 5.1.3 LNG Shipping Fleet [LNG Carriers by Containment (Moss and Membrane), Carrier Size (Q-Max, Q-Flex and Standard), LNG Bunkering Vessels]
- 5.2 By End-Use Application
- 5.2.1 Power Generation
- 5.2.2 Industrial and Manufacturing
- 5.2.3 Residential and Commercial
- 5.2.4 Transportation (Marine Bunkering, Heavy-Duty Road Transport and Rail)
- 5.3 By Scale
- 5.3.1 Large-Scale (Above 5 mtpa)
- 5.3.2 Mid-Scale (1 to 5 mtpa)
- 5.3.3 Small-Scale (Below 1 mtpa)
- 5.4 By Location
- 5.4.1 Onshore
- 5.4.2 Offshore (FLNG and FSRU)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Nordic Countries
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.5.3.6 Australia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Colombia
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 Qatar
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Egypt
- 5.5.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 QatarEnergy LNG (Qatargas)
- 6.4.2 Shell plc
- 6.4.3 Cheniere Energy Inc.
- 6.4.4 TotalEnergies SE
- 6.4.5 Petronas
- 6.4.6 Novatek
- 6.4.7 Chevron Corporation
- 6.4.8 Exxon Mobil Corporation
- 6.4.9 Woodside Energy Group
- 6.4.10 Equinor ASA
- 6.4.11 Sempra Infrastructure
- 6.4.12 Venture Global LNG
- 6.4.13 ENI SpA
- 6.4.14 KOGAS
- 6.4.15 Mitsui O.S.K. Lines
- 6.4.16 Golar LNG
- 6.4.17 BW LNG
- 6.4.18 Technip Energies
- 6.4.19 Bechtel Corporation
- 6.4.20 Fluor Corporation
- 6.4.21 KBR Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment








