 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851521
能源領域的物聯網:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Internet Of Things In Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
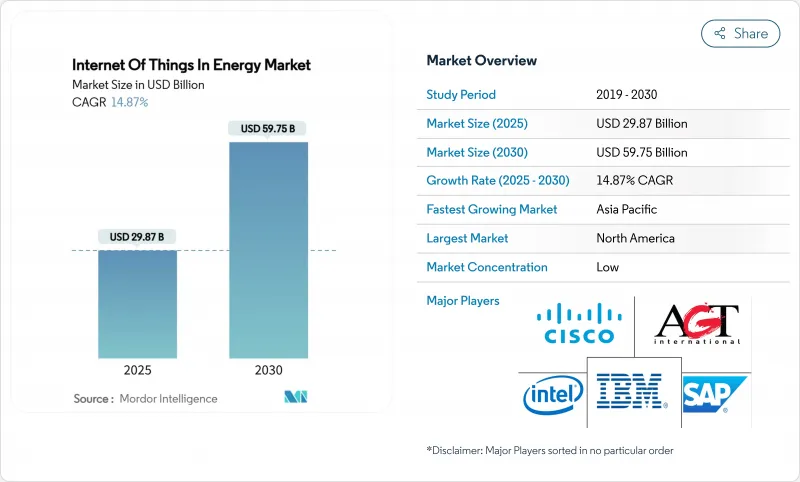
預計到 2025 年,能源物聯網市場規模將達到 298.7 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 597.5 億美元,複合年成長率為 14.87%。
為了實現即時電網最佳化、預測性資產管理和自主能源交易的共存,主要經濟體的公共產業正從集中式指揮控制轉向分散式智慧。由於智慧電錶、智慧變電站維修和邊緣分析技術堆疊的投資能夠減少停電時間和維護預算,因此這些領域的資本投入正在增加。半導體價格的穩定使得低功耗廣域模組的價格降至3美元以下,從而為二級饋線、農村太陽能電站和用戶側設備提供了連接。行動電話營運商、通訊群和私有5G供應商正致力於建構混合網路,以確保保護繼電器訊息的確定性延遲,同時降低簡單感測器流量的頻寬成本。軟體供應商正在將人工智慧套件包整合到資產性能平台中,以幫助能源公司及早預測組件故障,並在批發市場中實現靈活性服務的商業化。
全球能源物聯網市場趨勢與洞察
電力公司強制推行智慧電錶和電網現代化改造
強制性高級計量基礎設施已超越試點階段,監管機構要求提高低壓電網和需求需量反應結果的透明度。Honeywell和威瑞森目前正在將原生5G無線電模組整合到電錶中,從而實現遠端韌體更新、自癒式網狀通訊和自主斷電。挪威已完成全國範圍內的部署,但只有29.5%的家庭擁有即時用電量數據,凸顯了消費者參與度和直覺易用的應用程式將決定難以實現的節能效果能否真正落實。因此,公共產業正在將技術部署與客戶教育、遊戲化儀錶板和電價獎勵相結合。高級電錶將精細的時間間隔數據傳輸到配電管理系統,使其能夠預測屋頂太陽能回饋和電動車(EV)叢集,並在不增加額外容量的情況下實現負載平衡。
降低 5G/LPWAN 模組的成本
隨著晶片供應趨於正常化,窄頻物聯網模組的價格預計將在2023年至2025年間下降28%,從而消除大規模部署感測器的關鍵成本障礙。實驗室測試表明,LTE-M相比許多其他低功耗通訊協定,能夠實現更高的吞吐量和更低的能耗,這在電池更換成本高昂的情況下尤其重要。半導體製造商正在重新設計微控制器,以整合人工智慧加速功能,從而實現邊緣異常檢測。調查團隊證明,將LoRa閘道器轉變為輕量級運算節點,可以在不破壞傳統有效載荷格式的前提下,將回程傳輸流量減少70%。能源公司目前正在為偏遠風電場、區域變電站和閥組配備這些模組,在卡車鮮少涉足的地區部署資產智慧。
網路安全與OT/IT整合風險
隨著運行設備接入公共網路,攻擊面不斷擴大。歐盟《網路彈性法案》將於2025年8月生效,該法案將要求設備製造商記錄軟體元件並及時發布修補程式。許多變電站仍然使用未經身份驗證的傳統通訊協定,入侵研究表明,薄弱的網路分段機制使得惡意軟體能夠在幾分鐘內從收費伺服器轉移到斷路器控制系統。空中升級管道、硬體信任根和零信任網路分段正成為新採購框架的強制性要求。有效的管治依賴於資訊技術團隊和操作技術團隊之間的密切合作。
細分市場分析
到2024年,智慧電錶、智慧感測器、閘道器和邊緣控制器將佔據能源物聯網市場41%的佔有率。大量硬體正在支援公用事業公司的數位雙胞胎,將細粒度的現場數據推送至分析雲端。隨著監管機構要求供應商對從晶片到雲端的設備完整性進行認證,安全硬體模組和可信任執行環境正日益受到關注。預計2030年,物聯網安全平台將成長17.89%,是系統平均成長速度的兩倍。基於堅固耐用的ARM或x86主機板建構的邊緣伺服器配備了人工智慧加速器,可在毫秒內偵測故障。東芝最近發布了一款金鑰管理晶片組,可在韌體對其進行簽名,從而縮短合規負責人的審核時間。
軟體和服務的發展速度僅次於硬體。公用事業公司正在為全端式解決方案付費,供應商會將設備、連接和訂閱儀錶板捆綁在一起。在資料科學人才短缺的地區,託管服務合約極具吸引力,因為它們將整合風險轉移給了供應商。因此,服務收入在能源市場物聯網擴張中所佔的佔有率越來越大。同時,零件供應商正在將製造地轉移到更靠近需求中心的地方,以緩衝地緣政治衝擊對半導體流通的影響。
即時電網監控在2024年佔總收入的38.5%,這得益於變壓器、饋線和電壓調節器進行計量的程序。人工智慧技術能夠動態調整設定點,幫助電網在屋頂太陽能發電高峰期避免過電壓。互聯電動車基礎設施將以15.35%的複合年成長率實現最快成長,因為充電樁既是負載又是儲能設備。公共產業將充電樁視為靈活的節點,可提供無功功率並在白天吸收多餘的能量。政府正在補貼雙向充電樁,並要求採用開放通訊協定的遠端檢測。
隨著可再生能源業主追求更高的發電容量,預測性維護也緊跟著。離岸風力發電目前正在整合軟體定義網路環,即使在惡劣的海洋環境中也能與機艙感測器保持確定性的連接。商業建築的需量反應計畫可在關鍵時段將峰值功率降低高達 86%。工業用戶正在部署邊緣分析技術,以降低單位輸出的能耗,這項指標可直接用於 ESG 評分卡和投資者篩檢。
區域分析
到2024年,北美將佔能源領域物聯網收入的38%。聯邦政府對電網韌性的投資、各州清潔能源標準的製定以及成熟的行動電話網路覆蓋,正在推動物聯網的快速普及。Schneider Electric警告稱,資料中心負載的成長速度超過了變電站的擴容速度,迫使電力公司部署物聯網感測器,以最大限度地利用現有輸電線路的電力。由於在永凍土帶鋪設光纖成本高昂,加拿大的偏遠微電網率先採用了衛星物聯網技術。墨西哥的能源改革吸引了許多分散式太陽能投資者,他們希望從一開始就能運用預測分析技術。
亞太地區將成為成長最快的地區,到2030年複合年成長率將達到17%。日本的超級太陽能計劃採用鈣鈦礦電池,理論效率超過30%,目標是2030年達到20吉瓦的裝置容量。中國的「十四五」智慧電網部署計畫包括多能源微電網和嵌入輸電塔的5G基地台。印度大力發展再生能源,將物聯網感測器與政府補貼的雲端託管服務結合;韓國的工業則為工廠配備人工智慧邊緣運算設備,以節省用電高峰時段的電力。
在嚴格的碳排放法規和跨境平衡市場的推動下,歐洲正經歷穩定成長。歐盟的網路安全法將安全支出硬性納入所有物聯網預算。德國的工業4.0舉措意味著工廠正在將電能品質計量表整合到生產計畫中,使單位能耗(瓦時/單位)與節拍時間一樣成為重要的關鍵績效指標。英國一項公共部門節能計劃在建築管理人員獲得精確到分鐘的能源數據後,已實現了兩位數的節能效果。法國正在為核能發電廠冷卻泵加裝振動感測器,以延長其運作許可證的有效期;北歐電網營運商正在測試一個用於實現即時靈活性的市場平台。中東和非洲雖然起步較早,但大規模太陽能發電廠和儲能計劃以及綠氫能工廠正在為未來的需求提供保障。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 電力公司強制推行智慧電錶和電網現代化改造
- 5G/LPWAN模組成本下降
- 對分散式可再生編配的需求
- 基於人工智慧的預測性維護的投資報酬率案例研究
- 將彈性貨幣化(V2G、P2P能源)
- 碳計量資料法規
- 市場限制
- 網路安全與OT/IT整合風險
- 傳統系統與SCADA系統互通性差距
- 邊緣運算人才短缺
- 半導體供應波動
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭的激烈程度
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按組件
- 硬體
- 智慧型恆溫器
- 智慧電錶
- 電動車充電站
- 其他硬體
- 軟體與分析
- 物聯網平台
- 物聯網安全
- 物聯網服務
- 硬體
- 透過使用
- 智慧電網監測
- 能源管理系統
- 預測性維護
- 互聯電動車基礎設施
- 分散式可再生能源併網
- 需量反應和靈活性
- 透過連接技術
- 蜂窩網路(2G-5G)
- LPWAN(NB-IoT、LoRaWAN、Sigfox)
- 衛星物聯網
- Wi-Fi/BLE
- PLC 和其他
- 按部署模式
- 雲
- 邊緣
- 本地部署
- 最終用戶
- 電力和天然氣業務
- 石油和天然氣上游/中游/下游
- 商業和工業設施
- 住宅和專業用戶用途
- 可再生能源發電發電廠
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- ASEAN
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 非洲
- 南非
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- AGT International
- Davra Networks
- Flutura Business Solutions
- Wind River Systems
- Silver Spring Networks
- Verizon Business
- Vodafone IoT
- GE Digital
- Emerson Electric
- Siemens Gamesa(renewable IoT)
- Landis+Gyr
- Kamstrup
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Internet of Things in the energy market stood at USD 29.87 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 59.75 billion by 2030, reflecting a 14.87% CAGR.

Utilities across major economies are moving from centralized command-and-control to distributed intelligence so that real-time grid optimization, predictive asset care, and autonomous energy trading can co-exist. Capital spending on smart meters, intelligent substation retrofits, and edge analytics stacks has risen because these investments cut outage minutes and lower maintenance budgets. Semiconductor pricing has stabilized, allowing low-power wide-area modules to fall below the USD 3 threshold, which brings connectivity to secondary feeders, rural solar farms, and behind-the-meter devices. Cellular operators, satellite fleets, and private 5G providers are converging on hybrid network offers that guarantee deterministic latency for protection relay messages while squeezing bandwidth costs for simple sensor traffic. Software vendors have responded by embedding AI toolkits inside asset performance platforms so that energy firms can predict component failures early and monetize flexibility services in wholesale markets.
Global Internet Of Things In Energy Market Trends and Insights
Utility Smart-Meter Roll-Outs and Grid-Modernization Mandates
Mandated advanced metering infrastructure has moved beyond the pilot stage as regulators demand visibility of low-voltage networks and demand response outcomes. Honeywell and Verizon now embed native 5G radios into meters, enabling remote firmware updates, self-healing mesh communication, and autonomous service disconnects. Norway completed nationwide roll-outs yet only 29.5% of households checked live consumption data, underscoring that consumer engagement and intuitive apps decide whether hard savings materialize. Utilities therefore pair technical deployment with customer education, gamified dashboards, and tariff incentives. Advanced meters feed granular interval data to distribution management systems so that rooftop solar back-feed and electric vehicle (EV) clustering can be forecast and balanced without over-building capacity.
Falling 5G/LPWAN Module Cost
Chip supply normalization pushed narrow-band IoT module prices down by 28% between 2023 and 2025, removing a key cost barrier for high-volume sensor roll-outs. Laboratory tests show LTE-M offers higher throughput and lower energy consumption than many alternative low-power protocols, which is important where battery swaps are costly. Semiconductor makers are redesigning micro-controllers with integrated AI acceleration so that anomaly detection can occur at the edge. Research teams have proved that turning LoRa gateways into lightweight compute nodes trims backhaul traffic by 70% without breaking legacy payload formats. Energy firms now equip remote wind farms, rural substations, and valve arrays with these modules, placing asset intelligence where trucks rarely visit.
Cyber-Security and OT/IT Convergence Risk
As operational equipment becomes routable on public networks, attack surfaces multiply. The EU Cyber Resilience Act will come into force in August 2025, obliging device makers to document software components and issue timely patches. Many substations still run legacy protocols that lack authentication, and intrusion studies show malware can pivot from billing servers to breaker controls in minutes if segmentation is weak. Over-the-air update pipelines, hardware root-of-trust, and zero-trust segmentation are becoming mandatory across new procurement frameworks. Effective governance hinges on closer collaboration between information-technology and operational-technology teams.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Distributed-Renewable Orchestration Needs
- AI-Driven Predictive-Maintenance ROI Cases
- Legacy-SCADA Interoperability Gap
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Smart meters, intelligent sensors, gateways, and edge controllers collectively secured 41% of the Internet of Things in the energy market share in 2024. The hardware wave anchors utility digital twins and pushes granular field data into analytics clouds. Security hardware modules and trusted execution environments gain notice because regulators now ask vendors to prove device integrity from chip to cloud. IoT security platforms are forecast to compound at 17.89% through 2030, twice the system average, as the cost of a single operational breach can erase multi-year efficiency savings. Edge servers built on ruggedised ARM or x86 boards are shipping with AI accelerators that handle fault detection in milliseconds. Toshiba recently unveiled a key-management chipset that signs firmware blobs before they touch the field device, trimming audit times for compliance reviewers.
Software and services follow hardware's beachhead. Utilities are paying for full-stack offerings where the vendor bundles devices, connectivity, and a subscription dashboard. Managed service contracts appeal in regions short of data-science talent because they shift integration risk to the supplier. As a result, services revenue is taking a larger slice of the expanding Internet of Things in the energy market. Meanwhile, component suppliers are moving manufacturing closer to demand centres to buffer any geopolitical shock to semiconductor flows.
Real-time distribution grid monitoring accounted for 38.5% of 2024 revenue thanks to programs that instrument transformers, feeders, and voltage regulators. AI overlays adapt set-points on the fly so that networks avoid over-voltage when rooftop solar spikes midday. Connected EV infrastructure shows the fastest 15.35% CAGR because chargers double as both load and storage assets. Utilities view them as flexible nodes that can supply reactive power and soak up midday excess. Governments are subsidising bidirectional chargers and demanding open-protocol telemetry, which funnels more devices into the Internet of Things in the energy market.
Predictive maintenance sits close behind as renewable owners chase higher capacity factors. Offshore wind farms now integrate software-defined networking rings that maintain deterministic links to nacelle sensors despite harsh marine environments. Demand-response programs inside commercial buildings have trimmed peak kW draw by up to 86% during critical intervals. Industrial users deploy edge analytics to lower electricity per unit of output, a metric that directly feeds ESG scorecards and investor screens.
The Internet of Things in the Energy Market Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Software and Analytics, Iot Platforms, and More), Application (Smart Grid Monitoring, Energy Management Systems, Predictive Maintenance, and More), Connectivity Technology (Cellular (2G-5G), Satellite IoT, and More), Deployment Model (Cloud, Edge, and More), End-User (Electric and Gas Utilities, Residential and Prosumer, and More), and Geography
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 38% of 2024 revenue for the Internet of Things in the energy market. Federal investment in grid resilience, state-level clean-energy standards, and a mature cellular footprint enable rapid adoption. Schneider Electric warns that data-centre load is climbing faster than substation build-outs, forcing utilities to deploy IoT sensors to squeeze every amp from existing lines. Canada's remote microgrids are early satellite IoT adopters because fibre drops are expensive in permafrost. Mexico's energy reform is attracting distributed solar investors who demand predictive analytics from day one.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region at a 17% CAGR through 2030. Japan's super-solar project targets 20 GW by 2030 using perovskite cells with a theoretical efficiency beyond 30%. China's smart-grid rollout under the 14th Five-Year Plan includes multi-energy microgrids and 5G base stations embedded in transmission pylons. India's renewables push blends IoT sensors with government-subsidised cloud hosting, while South Korean industrial parks equip factories with AI edge boxes to shave power peaks.
Europe shows steady expansion on the back of stringent carbon laws and cross-border balancing markets. The EU Cyber Resilience Act hard-codes security spending into every IoT budget. Germany's Industry 4.0 initiatives mean factories integrate power-quality meters with production scheduling so that watt-hours per unit become a KPI as important as takt time. The United Kingdom's public-sector energy efficiency program has already logged double-digit savings after building managers gained minute-level insights. France upgrades nuclear station cooling pumps with vibration sensors to extend operating licenses, and Nordic grid operators test market platforms for real-time flexibility. The Middle East and Africa are earlier in the curve but mega solar-and-storage projects linked to green-hydrogen plants guarantee future demand.
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- AGT International
- Davra Networks
- Flutura Business Solutions
- Wind River Systems
- Silver Spring Networks
- Verizon Business
- Vodafone IoT
- GE Digital
- Emerson Electric
- Siemens Gamesa (renewable IoT)
- Landis+Gyr
- Kamstrup
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Utility smart-meter roll-outs and grid-modernization mandates
- 4.2.2 Falling 5G/LPWAN module costs
- 4.2.3 Distributed-renewable orchestration needs
- 4.2.4 AI-driven predictive-maintenance ROI cases
- 4.2.5 Flexibility monetisation (V2G, P2P energy)
- 4.2.6 Carbon-accounting data regulations
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cyber-security and OT/IT convergence risk
- 4.3.2 Legacy-SCADA interoperability gaps
- 4.3.3 Edge-compute talent scarcity
- 4.3.4 Semiconductor-supply volatility
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 Smart Thermostats
- 5.1.1.2 Smart Meters
- 5.1.1.3 EV Charging Stations
- 5.1.1.4 Other Hardware
- 5.1.2 Software and Analytics
- 5.1.3 IoT Platforms
- 5.1.4 IoT Security
- 5.1.5 IoT Services
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Smart Grid Monitoring
- 5.2.2 Energy Management Systems
- 5.2.3 Predictive Maintenance
- 5.2.4 Connected EV Infrastructure
- 5.2.5 Distributed-Renewable Integration
- 5.2.6 Demand Response and Flexibility
- 5.3 By Connectivity Technology
- 5.3.1 Cellular (2G-5G)
- 5.3.2 LPWAN (NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, Sigfox)
- 5.3.3 Satellite IoT
- 5.3.4 Wi-Fi/BLE
- 5.3.5 PLC and Other
- 5.4 By Deployment Model
- 5.4.1 Cloud
- 5.4.2 Edge
- 5.4.3 On-premise
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Electric and Gas Utilities
- 5.5.2 Oil and Gas Up/Mid/Down-stream
- 5.5.3 Commercial and Industrial Facilities
- 5.5.4 Residential and Prosumer
- 5.5.5 Renewable Power Plants
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Russia
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 Turkey
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.3 Siemens AG
- 6.4.4 Schneider Electric
- 6.4.5 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.6 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.7 SAP SE
- 6.4.8 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.9 AGT International
- 6.4.10 Davra Networks
- 6.4.11 Flutura Business Solutions
- 6.4.12 Wind River Systems
- 6.4.13 Silver Spring Networks
- 6.4.14 Verizon Business
- 6.4.15 Vodafone IoT
- 6.4.16 GE Digital
- 6.4.17 Emerson Electric
- 6.4.18 Siemens Gamesa (renewable IoT)
- 6.4.19 Landis+Gyr
- 6.4.20 Kamstrup
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment












