 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851292
亞太網路安全:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)APAC Cybersecurity - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
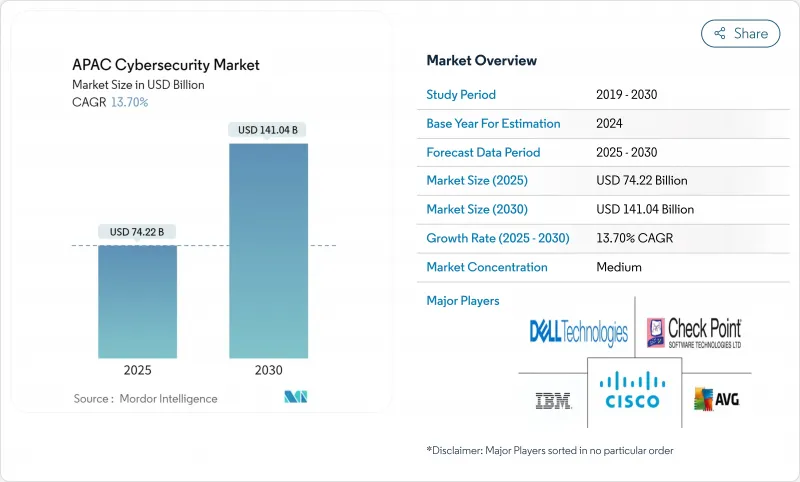
亞太地區網路安全市場預計到 2025 年將達到 742.2 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 1,410.4 億美元,年複合成長率為 13.7%。
這反映了各國政府對數位主權的推動以及企業向主動網路防禦模式的轉變。
國家級網路攻擊日益增多、5G網路部署加速、數位支付詐騙激增以及人才長期短缺,正在改變預算優先事項。如今,競爭不再僅僅取決於產品功能,而是更取決於能否在法規環境分散的情況下,提供自主雲架構、人工智慧主導的託管檢測以及整合的IT和OT安全解決方案。對於那些能夠將本地化威脅情報與可擴展的託管服務相結合的供應商而言,尤其是在缺乏內部安全專家的中端市場領域,機會比比皆是。
亞太網路安全市場趨勢與洞察
亞太地區各國政府的資料主權要求推動了國內網路安全支出。
中國將於2025年生效的《網路資料安全管理條例》將要求資料處理必須在中國境內進行,並要求在中國營運的跨國公司實施獨立的安全架構。新加坡的「網路安全基礎認證」(Cyber Essentials)計畫將政府合約與供應商認證掛鉤,刺激了對本地供應商的需求。澳洲的REDSPICE舉措撥款20億澳元用於為情報機構建立主權雲,顯示相關政策正在直接轉化為網路安全方面的支出。為了維持市場准入,供應商正在將研發中心和安全營運中心(SOC)在地化,而本土專家則獲得了合規方面的優勢。
5G的推出為日本、韓國和印度的通訊業者帶來了新的潛在網路威脅。
高吞吐量的5G架構引入了微切片和邊緣運算節點,這些節點無法透過傳統的邊界防護工具進行保護。日本的《主動網路防禦法》允許對針對通訊網路的網路威脅進行先發制人的干擾。韓國記錄顯示,2024年公共網路遭受了156萬次駭客試驗,其中80%的目標是5G和物聯網終端。印度通訊業者報告稱,57%的攻擊導致服務降級,凸顯了零信任和人工智慧主導分析的迫切需求。因此,市場對安全存取服務邊際(SASE)平台和針對營運商環境最佳化的虛擬化防火牆的需求日益成長。
亞太新興經濟體網路安全人才嚴重短缺,推高服務成本。
該地區網路安全負責人缺口高達280萬,限制了託管服務的擴充性,並導致薪資水平超出中小企業的預算。菲律賓僅有200名認證專家,而新加坡則有3000名,加劇了計劃延誤。越南已累計1億美元用於人才發展計劃,目標是在2025年前培養1000名專家和5000名工程師。 OT安全和雲端架構領域的人才短缺最為嚴重,迫使企業外包相關功能或延遲部署,從而減少了可滿足的需求。
細分市場分析
到2024年,解決方案收入將佔總收入的57.6%,到2030年將以21.4%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於企業面臨人才短缺,導致託管安全服務不斷擴張。亞太網路安全市場青睞那些將全天候安全營運中心 (SOC) 監控、威脅調查和事件回應整合到基於結果的服務等級協定 (SLA) 中的供應商。 Ensign InfoSecurity 將成為2024年唯一躋身全球十大託管安全服務供應商 (MSSP) 行列的亞太地區公司,這標誌著該地區託管服務成熟度的提升。
內部分析師薪資的上漲,加上董事會層級對安全漏洞的課責,正促使大型企業與外部安全營運中心 (SOC) 共同管理其安全工具。人工智慧驅動的故障排查和自動化功能使託管安全服務提供者 (MSSP) 能夠盈利服務中端市場客戶,從而推動了此類服務的普及。因此,對基於平台的服務產品的投資正在加速成長,服務供應商正透過整合擴展災難復原 (XDR)、安全營運自動化與回應 (SOAR) 和機器學習分析等技術來提升自身競爭力。
至2024年,本地部署的網路安全將佔亞太地區網路安全市場佔有率的62.5%。同時,受遠端辦公政策和多重雲端部署的推動,雲端原生安全將以23.5%的複合年成長率成長。 HashiCorp的一項調查顯示,70%的區域企業透過多重雲端實現業務目標,90%的企業將安全視為關鍵成功因素。
為了保護跨雲端服務供應商 (CSP) 和邊緣節點的工作負載,各組織正在採用零信任網路和容器安全。儘管技能短缺仍然是一大挑戰(31% 的組織表示其雲端專業知識有限),但供應商正透過低程式碼策略編配和託管 SASE 來應對這項挑戰。因此,雲端採用在綠地計畫越來越受歡迎,而混合架構也正在成為傳統系統遷移的途徑。
亞太網路安全市場報告按解決方案、服務、部署類型(本地部署、雲端部署)、最終用戶垂直產業(銀行、金融服務和保險、醫療保健、IT 和通訊、工業和國防、製造業、零售和電子商務、能源和公共產業、製造業、其他)、最終用戶公司規模(中小企業、大型企業)和國家/地區對產業進行分類。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 政府資料主權要求推動亞太地區各國加大國內網路安全投資。
- 5G的推出為日本、韓國和印度的通訊業者帶來了新的潛在網路威脅。
- 數位支付和電子商務詐騙激增推動東南亞安全投資
- 亞太地區主導對關鍵基礎設施的攻擊日益增多,推動了OT安全技術的普及應用。
- 中國和東協地區正經歷一波中小企業遷移到雲端的浪潮,因此需要保護其雲端工作負載。
- 國家網路安全激勵計劃(例如,SG Cyber Safe、REDSPICE)正在推動市場成長
- 市場限制
- 亞太新興經濟體網路安全人才嚴重短缺,推高服務成本。
- 分散的區域合規體系阻礙了解決方案的標準化。
- 亞太地區中小企業對價格的高度敏感限制了先進解決方案的採用。
- 由於對安全硬體組件的出口限制,供應鏈中斷
- 關鍵法規結構評估
- 價值鏈分析
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 主要用例和案例研究
- 宏觀經濟因素對市場的影響
- 投資分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 報價
- 解決方案
- 應用程式安全
- 雲端安全
- 資料安全
- 身分和存取管理
- 基礎設施保護
- 綜合風險管理
- 網路安全設備
- 端點安全
- 其他服務
- 服務
- 專業服務
- 託管服務
- 解決方案
- 透過部署模式
- 本地部署
- 雲
- 按最終用戶行業分類
- BFSI
- 衛生保健
- 資訊科技和電訊
- 工業與國防
- 製造業
- 零售與電子商務
- 能源與公共產業
- 製造業
- 其他
- 按最終用戶公司規模分類
- 中小企業
- 主要企業
- 按國家/地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 澳洲和紐西蘭
- 新加坡
- 亞太其他地區
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Kaspersky Lab
- Broadcom, Inc.(Symantec Enterprise Division)
- BAE Systems plc
- NEC Corporation
- Infosys Limited
- Tata Consultancy Services Limited
- Darktrace plc
- Zscaler, Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- F5, Inc.
- Sophos Ltd.
- Okta, Inc.
- SentinelOne, Inc.
- Rapid7, Inc.
- Imperva, Inc
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The APAC cybersecurity market size reached USD 74.22 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand at a 13.7% CAGR to USD 141.04 billion by 2030, reflecting governments' push for digital sovereignty and enterprises' shift toward proactive cyber-defense models.

Heightened state-sponsored attacks, accelerating 5G roll-outs, surging digital-payment fraud, and chronic talent shortages are reshaping budget priorities, while local data-protection rules are recasting procurement in favor of regionally domiciled vendors. Competition now hinges less on product features and more on the ability to deliver sovereign-cloud architectures, AI-driven managed detection, and integrated IT-OT security across fragmented regulatory environments. Opportunities abound for providers that combine localized threat intelligence with scalable managed services, especially in mid-market segments underserved by in-house security expertise.
APAC Cybersecurity Market Trends and Insights
Government Data-Sovereignty Mandates Accelerating Domestic Cybersecurity Spend Across APAC
China's Network Data Security Management Regulations taking effect in 2025 require in-country data processing and create separate security stacks for multinationals operating inside China. Singapore's refreshed Cyber Essentials program ties government contracts to vendor certification, driving local provider demand. Australia's REDSPICE initiative allocates AUD 2 billion to a sovereign cloud for the intelligence community, illustrating how policy translates directly into cybersecurity outlays. Vendors now localize R&D centers and SOCs to preserve market access, while homegrown specialists gain a compliance-driven edge.
5G Roll-Outs Creating New Network Threat Surfaces for Telcos in Japan, South Korea and India
High-throughput 5G architectures introduce micro-slicing and edge-compute nodes that traditional perimeter tools cannot secure. Japan's Active Cyber Defense law authorizes pre-emptive disruption of cyber threats targeting telecom networks. South Korea logged 1.56 million hacking attempts on public networks in 2024, 80% aimed at 5G and IoT endpoints. India's operators report that 57% of breaches result in service slowdowns, highlighting the urgency for zero-trust and AI-driven analytics. Consequently, demand is rising for secure access service edge (SASE) platforms and virtualized firewalls optimized for carrier environments.
Acute Cybersecurity Talent Shortage Inflating Service Costs in Emerging APAC Economies
The region accounts for 2.8 million unfilled cyber roles, restricting managed-service scalability and pushing salaries beyond SME budgets. The Philippines counts only 200 certified specialists versus Singapore's 3,000, amplifying project delays. Vietnam earmarked USD 100 million for workforce programs to train 1,000 experts and 5,000 engineers by 2025. Scarcity is most severe in OT security and cloud architecture, forcing enterprises to outsource functions or postpone deployments, dampening addressable demand.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in Digital-Payment and E-Commerce Fraud Driving Security Investments in Southeast Asia
- Escalating State-Sponsored Attacks on APAC Critical Infrastructure Stimulating OT Security Adoption
- Fragmented Regional Compliance Regimes Complicating Solution Standardization
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solutions retained 57.6% revenue in 2024, yet managed security services are projected to expand 21.4% CAGR through 2030 as enterprises confront staffing gaps. The APAC cybersecurity market favors providers that bundle 24X7 SOC monitoring, threat hunting, and incident response under outcome-based SLAs. Ensign InfoSecurity became the only APAC firm to reach the global top-10 MSSP list in 2024, signaling the region's ascent in managed-service maturity.
Rising wages for in-house analysts, coupled with board-level accountability for breaches, push even large enterprises to co-manage security tools with external SOCs. AI-assisted triage and automation enable MSSPs to serve mid-market clients profitably, widening adoption. As a result, investment in platform-based service delivery is accelerating, with providers embedding XDR, SOAR, and machine-learning analytics to differentiate.
On-premise installations held 62.5% of APAC cybersecurity market share in 2024 because regulated sectors still favor physical control over data. Cloud-native security, however, is growing at 23.5% CAGR, propelled by remote-work mandates and multi-cloud adoption. A HashiCorp survey showed 70% of regional firms hit business targets via multi-cloud, with 90% rating security the defining success factor.
Organizations are embracing zero-trust networking and container security to protect workloads that span CSPs and edge nodes. Skills shortages remain a headwind-31% cite limited cloud expertise-but vendors counter with low-code policy orchestration and managed SASE offerings. Consequently, cloud deployments increasingly win green-field projects, while hybrid architectures emerge as a transition path for legacy systems.
The APAC Cybersecurity Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Offering (Solutions, and Services), Deployment Mode (On-Premise, and Cloud), End-User Vertical (BFSI, Healthcare, IT and Telecom, Industrial and Defense, Manufacturing, Retail and E-Commerce, Energy and Utilities, Manufacturing, and Others), and End-User Enterprise Size (Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), and Large Enterprises), and Country.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Kaspersky Lab
- Broadcom, Inc. (Symantec Enterprise Division)
- BAE Systems plc
- NEC Corporation
- Infosys Limited
- Tata Consultancy Services Limited
- Darktrace plc
- Zscaler, Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- F5, Inc.
- Sophos Ltd.
- Okta, Inc.
- SentinelOne, Inc.
- Rapid7, Inc.
- Imperva, Inc
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government Data-Sovereignty Mandates Accelerating Domestic Cybersecurity Spend Across APAC
- 4.2.2 5G Roll-Outs Creating New Network Threat Surfaces for Telcos in Japan, South Korea and India
- 4.2.3 Surge in Digital Payments and E-commerce Fraud Driving Security Investments in Southeast Asia
- 4.2.4 Escalating State-Sponsored Attacks on APAC Critical Infrastructure Stimulating OT Security Adoption
- 4.2.5 SME Cloud Migration Wave Necessitating Cloud Workload Protection in China and ASEAN
- 4.2.6 National Cybersecurity Incentive Programs (e.g., SG Cyber Safe, REDSPICE) Catalyzing Market Growth
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Acute Cybersecurity Talent Shortage Inflating Service Costs in Emerging APAC Economies
- 4.3.2 Fragmented Regional Compliance Regimes Complicating Solution Standardization
- 4.3.3 High Price Sensitivity Among APAC SMEs Limiting Adoption of Advanced Solutions
- 4.3.4 Supply-Chain Disruptions from Export Controls on Security Hardware Components
- 4.4 Evaluation of Critical Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Key Use Cases and Case Studies
- 4.9 Impact on Macroeconomic Factors of the Market
- 4.10 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Offering
- 5.1.1 Solutions
- 5.1.1.1 Application Security
- 5.1.1.2 Cloud Security
- 5.1.1.3 Data Security
- 5.1.1.4 Identity and Access Management
- 5.1.1.5 Infrastructure Protection
- 5.1.1.6 Integrated Risk Management
- 5.1.1.7 Network Security Equipment
- 5.1.1.8 Endpoint Security
- 5.1.1.9 Other Services
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.1.2.1 Professional Services
- 5.1.2.2 Managed Services
- 5.1.1 Solutions
- 5.2 By Deployment Mode
- 5.2.1 On-Premise
- 5.2.2 Cloud
- 5.3 By End-User Vertical
- 5.3.1 BFSI
- 5.3.2 Healthcare
- 5.3.3 IT and Telecom
- 5.3.4 Industrial and Defense
- 5.3.5 Manufacturing
- 5.3.6 Retail and E-commerce
- 5.3.7 Energy and Utilities
- 5.3.8 Manufacturing
- 5.3.9 Others
- 5.4 By End-User Enterprise Size
- 5.4.1 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 5.4.2 Large Enterprises
- 5.5 By Country
- 5.5.1 China
- 5.5.2 Japan
- 5.5.3 India
- 5.5.4 South Korea
- 5.5.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.5.6 Singapore
- 5.5.7 Rest of Asia Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Fortinet, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Kaspersky Lab
- 6.4.8 Broadcom, Inc. (Symantec Enterprise Division)
- 6.4.9 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.10 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.11 Infosys Limited
- 6.4.12 Tata Consultancy Services Limited
- 6.4.13 Darktrace plc
- 6.4.14 Zscaler, Inc.
- 6.4.15 CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.16 F5, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Sophos Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Okta, Inc.
- 6.4.19 SentinelOne, Inc.
- 6.4.20 Rapid7, Inc.
- 6.4.21 Imperva, Inc
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment





