 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851026
虛擬路由器:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Virtual Router - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
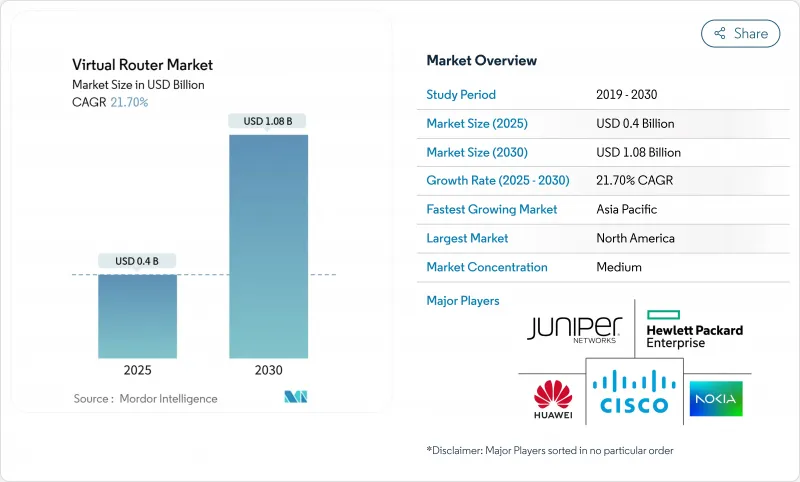
預計到 2025 年,虛擬路由器市場規模將達到 4 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 10.8 億美元,在預測期(2025-2030 年)內,複合年成長率為 21.70%。
這種成長反映了雲端原生應用的激增、私有5G的商業化部署以及在提高網路敏捷性的同時降低資本支出的需求。企業青睞基於軟體的路由,因為它能夠快速擴展、與編配工具整合並支援服務速度,從而加快產品部署速度並降低營運成本。雖然許多超大規模資料中心都在使用開放原始碼路由協定棧,但雲端供應商正在將虛擬路由功能直接整合到其基礎設施即服務(IaaS)中,從而降低了准入門檻。圍繞HPE-Juniper等大型併購案的監管審查表明,市場格局正在日趨成熟,規模和產品組合深度正日益決定著企業的成敗。
全球虛擬路由器市場趨勢與洞察
SDN 和 NFV 架構的日益普及
服務供應商和企業正在整合基礎設施,並將路由工作負載遷移到軟體,以降低營運成本。交換器加速了服務部署,使網路功能能夠在幾分鐘內而非幾週內啟動。像義大利 EOLO 這樣的營運商已經利用 MANO 部署的虛擬路由器擴展了數千個基地台鏈路,證明了這種模式在全國範圍內的可行性。 SDN 控制器還使提供者能夠為需要按延遲或頻寬設定檔進行隔離的 5G 服務引入網路切片。因此,企業正在投資編配平台,增加軟體工程團隊的人員,並將網路營運轉型為敏捷的軟體管線。
對網路敏捷性和可擴展容量的需求日益成長
混合辦公、視訊會議和雲端工作負載給傳統的廣域網路架構帶來了巨大壓力,這些架構將流量路由到資料中心,導致延遲和成本上升。由中央策略引擎控制的虛擬路由器可以將流量直接導向雲端應用,為遠端辦公人員提供一致的使用者體驗。在亞太地區,製造商正在部署可在生產輪班期間重新配置的軟體定義路由,因為智慧工廠依賴低延遲鏈路來運行機器人和物聯網感測器。這些部署凸顯了虛擬路由器市場如何支援無需現場部署的動態重配置,從而與數位轉型專案的速度相符。
多租戶虛擬網路功能中的安全漏洞
多租戶託管增加了攻擊面,因為虛擬路由器共用計算層和虛擬機器管理程式。康考迪亞大學的調查團隊發現了可以繞過租戶隔離的跨層攻擊。為此,ETSI 更新了其 NFV 安全框架,納入了更強大的能力斷言和加密的管理通道。金融服務和政府機構已要求進行額外的滲透測試和審核日誌記錄,這將延緩部署速度,但最終將增強平台的安全性。
細分市場分析
到2024年,解決方案產品將佔虛擬路由器市場收入的60.3%,證實了軟體授權和虛擬設備仍然是企業尋求SD-WAN和NFV功能的主要購買促進因素。這種主導地位源於路由代碼的高價值、對營運商級規模的需求以及這些許可在網路現代化計劃中發揮的關鍵作用。然而,服務才是成長引擎,到2030年將以24.5%的複合年成長率成長,因為企業需要購買設計、遷移和營運方面的專業知識。許多強制執行TIC 3.0的聯邦機構都依賴整合商來確保在向軟體定義路由過渡期間的合規性。
企業缺乏內部NFV(網路功能虛擬化)人才,因此服務供應商正在將諮詢和維運服務打包出售,以確保成功。託管服務擴大納入執行時間和效能的服務等級協議,從而將維運風險從客戶轉移出去。這種趨勢表明,供應商的策略正在轉變,他們不再僅僅依靠技術清單,而是開始注重生命週期服務,這強化了虛擬路由器市場的諮詢式銷售模式。
到2024年,雲端基礎的部署將佔虛擬路由器市場規模的68.7%,複合年成長率將達到25.01%,成為成長最快的模式。企業青睞超大規模雲端提供的即時可用性、計量收費的經濟模式以及內建的高可用性。微軟的虛擬廣域網路中心路由策略表明,軟體路由將成為雲端的原生功能,而非外部設備。雖然在需要本地資料處理的高度監管行業中,本地部署仍然很常見,但隨著安全框架的日趨成熟,其成長速度已落後於雲端模式。
混合模式應運而生,出於延遲方面的考慮,控制平面部署在雲端,而資料平面則保留在本地。供應商透過提供允許實例跨站點免費遷移的授權協議來應對這一趨勢,從而推動了混合模式的普及。隨著頻寬密集型工作負載的激增,雲端爆發仍然是關鍵促進因素,雲端託管路由也逐漸成為新站點的預設選擇。
虛擬路由器市場按元件(解決方案和服務)、部署類型(雲端基礎和本地部署)、最終用戶(服務供應商、企業及其他)、應用程式(SD-WAN 和 WAN 邊緣、VCPE/邊緣路由、VPN 和網路安全及其他)以及地區進行細分。市場預測以美元計價。
區域分析
受雲端運算普及和SD-WAN早期部署的推動,北美地區將在2024年佔據虛擬路由器市場38.1%的佔有率。 AT&T等通訊業者正在將核心流量遷移到白盒路由,這清楚地表明軟體路由已達到營運商層級。美國各地的企業正在將虛擬路由器整合到零信任架構中,而加拿大服務供應商正在部署虛擬路由器以擴展農村寬頻覆蓋範圍。聯邦機構正在推動TIC 3.0合規性,並保持持續的支出動能。
亞太地區將以23.8%的複合年成長率(CAGR)實現最快成長,到2030年,這主要得益於日本、韓國和印度等國政府大力推進的5G網路建設。製造業和採礦業的專用5G網路需要在局部路由來控制自主機器,這為邊緣虛擬路由器的發展創造了有利條件。 GSMA預計該地區的專用5G投資將大幅成長,並強調數位轉型將推動這一成長。
歐洲持續保持穩定成長,資料主權法律推動了國內雲端區域的發展,而這些區域需要軟體定義互連。通訊業者正在採用NFV技術以在價格監管下降低成本,歐盟的Gaia-X舉措正在推廣開放式數位基礎設施和虛擬路由。中東和非洲正在投資智慧城市計劃,並鼓勵全球供應商試行用於公共網路的邊緣路由。拉丁美洲也取得了一些進展,尤其是在尋求可靠雲端連接以支持金融科技應用的金融中心。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- SDN 和 NFV 架構的日益普及
- 對網路敏捷性和可擴展容量的需求日益成長
- 與硬體路由器相比,整體擁有成本更低
- 雲端運算和邊緣運算工作負載的爆炸性成長
- 超大規模資料中心業者所使用的開放原始碼虛擬路由協定棧
- 虛擬路由器支援私有的 5G 企業網路
- 市場限制
- 多租戶虛擬網路功能中的安全漏洞
- 與傳統路由設備整合的挑戰
- 虛擬化中不可預測的效能
- 專有許可和供應商鎖定
- 產業價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 產業吸引力:波特五力分析
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 宏觀經濟因素如何影響市場
第5章 市場規模與成長預測數據
- 按組件
- 解決方案
- 服務
- 依部署類型
- 雲端基礎的
- 本地部署
- 最終用戶
- 服務供應商
- 公司
- 資料中心/雲端供應商
- 政府/公共部門
- 透過使用
- SD-WAN 和 WAN 邊緣
- vCPE/邊緣路由
- VPN和網路安全
- 資料中心互連
- 其他(物聯網閘道器、智慧家庭)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 韓國
- 新加坡
- 馬來西亞
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Nokia Corporation
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company
- Broadcom Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- ZTE Corporation
- Arista Networks, Inc.
- VMware, Inc.
- 6WIND SAS
- VyOS(Sentrium SL)
- Netgate(Rubicon Communications)
- Arrcus, Inc.
- netElastic Systems, Inc.
- F5, Inc.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Versa Networks, Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Telco Systems(BATM)
- Kaloom, Inc.
- Radisys Corporation
- Altiostar(Rakuten Symphony)
- Pluribus Networks, Inc.
- Mavenir Systems, Inc.
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
- 閒置頻段與未滿足需求評估
The Virtual Router Market size is estimated at USD 0.4 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.08 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.70% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Growth reflects the surge of cloud-native applications, the commercial rollout of private 5G, and the drive to trim capital outlays while boosting network agility. Enterprises prefer software-based routing because it scales rapidly, integrates with orchestration tools, and supports service velocity, enabling faster product rollouts and lower operating expenses. Competitive dynamics also favor the technology: open-source routing stacks now power many hyperscale data centers, while cloud providers embed virtual routing functions directly into infrastructure-as-a-service offerings, flattening barriers to entry. Regulatory scrutiny of large mergers, such as the contested HPE-Juniper deal, signals a maturing landscape where scale and portfolio depth increasingly decide winners.
Global Virtual Router Market Trends and Insights
Rising adoption of SDN and NFV architectures
Service providers and enterprises are shifting routing workloads onto software to consolidate infrastructure and cut operating expenses, achieving up to 60% savings when NFV replaces fixed hardware. The switch accelerates service rollouts because network functions spin up in minutes rather than weeks. Operators such as EOLO in Italy scaled thousands of base-station links with MANO-deployed virtual routers, proving the model works at a nationwide scale. SDN controllers also let providers introduce network slicing for 5G services that need isolation by latency or bandwidth profiles. As a result, companies pour investment into orchestration platforms and staff up software engineering teams, transforming network operations into agile software pipelines.
Growing need for network agility and scalable capacity
Hybrid work, video meetings, and cloud workloads stress legacy WAN architectures that route traffic back to a data center, adding latency and cost. Virtual routers, controlled by central policy engines, steer traffic directly to cloud applications, delivering a consistent user experience for remote staff. In Asia-Pacific, smart factories depend on low-latency links for robotics and IoT sensors, prompting manufacturers to deploy software-defined routing that can be re-provisioned during production shifts. These deployments highlight how the virtual router market supports dynamic reconfiguration without physical truck rolls, matching the speed of digital transformation programs.
Security vulnerabilities in multi-tenant VNFs
Multi-tenant hosting increases attack surfaces because virtual routers share compute layers and hypervisors. Researchers at Concordia University identified cross-layer attacks that can bypass tenant isolation. In response, ETSI updated its NFV security framework to include stronger capability assertions and encrypted management channels. Financial services and government agencies demand additional penetration testing and audit logging, which slows rollouts but ultimately strengthens platform security.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Lower total cost of ownership vs. hardware routers
- Proliferation of cloud and edge-computing workloads
- Integration pain-points with legacy routing gear
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solution offerings generated 60.3% of virtual router market revenue in 2024, confirming that software licenses and virtual appliances remain the core purchase for enterprises seeking SD-WAN and NFV capabilities. This dominance is underpinned by the high value of routing code, the need for carrier-grade scale, and the critical role these licenses play in network modernization projects. Services, however, are the growth engine, rising at 24.5% CAGR through 2030 as organizations purchase design, migration, and managed operations expertise. Many federal agencies pursuing TIC 3.0 mandates rely on integrators to ensure compliance while migrating to software-defined routing.
Enterprises lack in-house NFV talent, so service providers package advisory and run-operate services to guarantee success. Managed offerings increasingly embed service-level agreements for uptime and performance, transferring operational risk away from customers. The pattern indicates a strategic pivot, in which vendors differentiate on lifecycle services instead of technical checklists, reinforcing the virtual router market's consultative sales motion.
Cloud-based deployment captured 68.7% of the virtual router market size in 2024 and also posted the fastest 25.01% CAGR. Enterprises value instant availability, pay-as-you-grow economics, and built-in high availability offered by hyperscale clouds. Microsoft's Virtual WAN Hub routing policies illustrate how software routing becomes a native cloud function rather than an external appliance. On-premise deployments remain common in highly regulated sectors requiring local data processing, but their growth lags cloud models as security frameworks mature.
Hybrid patterns emerge in which control planes reside in the cloud while data planes stay on-premises for latency reasons. Vendors respond with licensing that moves instances across sites without additional fees, reinforcing adoption. As bandwidth-intensive AI workloads proliferate, cloud bursting remains a major driver, positioning cloud-hosted routing as the default for new sites.
Virtual Router Market is Segmented by Component (Solution and Service), Deployment Type (Cloud-Based and On-Premise), End-User (Service Provider, Enterprise, and More), Application (SD-WAN and WAN Edge, VCPE/Edge Routing, VPN and Network Security, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated the largest slice of the virtual router market revenue at 38.1% in 2024, boosted by cloud adoption and early SD-WAN rollouts. Telecom operators such as AT&T migrate core traffic to white-box routing, sending a clear signal that software routing is carrier-grade. Enterprises across the United States integrate virtual routers into zero-trust architectures, while Canadian service providers deploy virtual routers to extend broadband in rural regions. Federal agencies' push for TIC 3.0 compliance maintains spending momentum.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest mover at a 23.8% CAGR to 2030, supported by state-backed 5G build-outs in Japan, South Korea, and India. Private 5G networks in manufacturing and mining require localized routing to control autonomous machines, creating fertile ground for edge-ready virtual routers. The GSMA expects private 5G investment in the region to rise sharply, highlighting how digital transformation fuels this expansion.
Europe maintains steady growth as data-sovereignty laws encourage in-country cloud regions that need software-defined interconnects. Telecom operators deploy NFV to cut costs amid price regulation, and the EU's Gaia-X initiative promotes open digital infrastructure aligned with virtual routing. The Middle East and Africa invest in smart-city projects, inviting global vendors to pilot edge routing for public safety nets. Latin America experiences moderate progress, with adoption centered on financial hubs that demand reliable cloud connectivity for fintech applications.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Nokia Corporation
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company
- Broadcom Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- ZTE Corporation
- Arista Networks, Inc.
- VMware, Inc.
- 6WIND S.A.S.
- VyOS (Sentrium S.L.)
- Netgate (Rubicon Communications)
- Arrcus, Inc.
- netElastic Systems, Inc.
- F5, Inc.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Versa Networks, Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Telco Systems (BATM)
- Kaloom, Inc.
- Radisys Corporation
- Altiostar (Rakuten Symphony)
- Pluribus Networks, Inc.
- Mavenir Systems, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising adoption of SDN and NFV architectures
- 4.2.2 Growing need for network agility and scalable capacity
- 4.2.3 Lower total cost of ownership vs. hardware routers
- 4.2.4 Proliferation of cloud and edge-computing workloads
- 4.2.5 Open-source virtual routing stacks used by hyperscalers
- 4.2.6 Virtual routers enabling private 5G enterprise networks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Security vulnerabilities in multi-tenant VNFs
- 4.3.2 Integration pain-points with legacy routing gear
- 4.3.3 Performance unpredictability under virtualization
- 4.3.4 Proprietary licensing and vendor lock-in
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUES)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Solution
- 5.1.2 Service
- 5.2 By Deployment Type
- 5.2.1 Cloud-based
- 5.2.2 On-Premise
- 5.3 By End-user
- 5.3.1 Service Provider
- 5.3.2 Enterprise
- 5.3.3 Data Center/Cloud Provider
- 5.3.4 Government and Public Sector
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 SD-WAN and WAN Edge
- 5.4.2 vCPE/Edge Routing
- 5.4.3 VPN and Network Security
- 5.4.4 Data Center Interconnect
- 5.4.5 Others (IoT Gateways, Residential)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Chile
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Singapore
- 5.5.4.6 Malaysia
- 5.5.4.7 Australia
- 5.5.4.8 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Juniper Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.5 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company
- 6.4.6 Broadcom Inc.
- 6.4.7 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.8 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.9 Arista Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.10 VMware, Inc.
- 6.4.11 6WIND S.A.S.
- 6.4.12 VyOS (Sentrium S.L.)
- 6.4.13 Netgate (Rubicon Communications)
- 6.4.14 Arrcus, Inc.
- 6.4.15 netElastic Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.16 F5, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Fortinet, Inc.
- 6.4.18 Versa Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.19 Ciena Corporation
- 6.4.20 Telco Systems (BATM)
- 6.4.21 Kaloom, Inc.
- 6.4.22 Radisys Corporation
- 6.4.23 Altiostar (Rakuten Symphony)
- 6.4.24 Pluribus Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.25 Mavenir Systems, Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment









