 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851013
自動駕駛曳引機:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Autonomous Tractors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
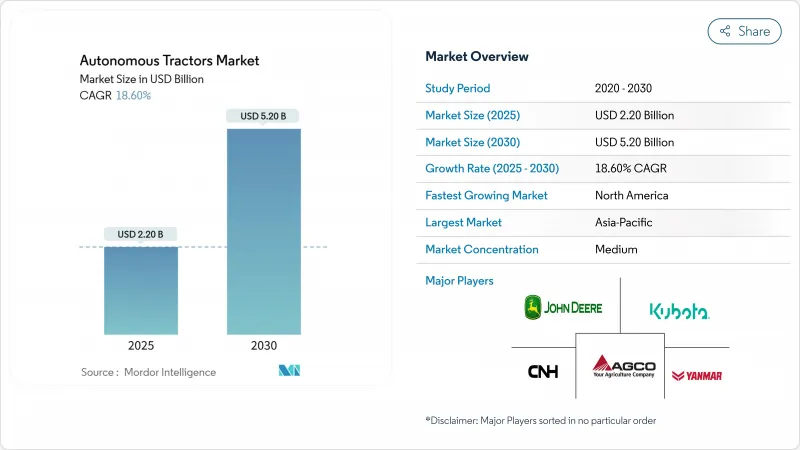
預計到 2025 年,自動駕駛曳引機市場規模將達到 22 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 52 億美元,複合年成長率將達到 18.6%。
這一成長主要受以下因素驅動:嚴峻的農業勞動力危機、精密農業的快速普及,以及政府不斷擴大的獎勵,這些措施縮短了互聯低碳機械的投資回收期。大型商業種植戶已將節省的20%勞動力轉化為更高的利潤率,並透過全天候田間作業提高了季節性產量。以軟體為中心的收入模式、售後套件和電動動力傳動系統進一步擴大了潛在需求,顯示自動駕駛曳引機市場正從利基市場走向主流成長階段。
全球自動駕駛曳引機市場趨勢與洞察
農業勞動力短缺和薪資通膨上升
農村勞動力萎縮與農民平均年齡上升相衝突,導致一半的農業職位空缺無人填補。薪資上漲加劇了農忙尖峰時段的田間作業壓力。尤其是在收割季節,無人駕駛運糧車全天候24小時運作,無需手動操作。種植者報告稱,在關鍵作業時段,生產效率提高了30%至40%,證實了自動駕駛曳引機市場填補了結構性缺口,而非僅增加了可有可無的便利。這種緊迫性使得自動駕駛技術被重新定義為農場長期生存發展所需的核心基礎設施。
加速精密農業和物聯網連接技術的應用
雲端農場管理平台已連接超過一百萬台農機設備,將曳引機變成行動資料中心,向即時決策系統提供土壤、產量和資產資訊。先進的感測器融合、GPS、機器視覺和雷達技術實現了厘米級精度的導航、變數施肥和全田避障。
小農戶面臨前期投入成本高、投資報酬率不確定等問題。
電動自動駕駛曳引機的價格可能超過8.8萬美元,對於面積小於100公頃的農場來說,這是一筆不小的開銷。網路連線升級、本地資料基礎設施建設和服務訂閱等費用進一步加重了負擔。模型顯示,除非有外部補貼抵消資本成本,否則獲利的部署通常需要500公頃或更大的面積,這使得許多家庭農場只能依靠合作所有權或租賃服務,直到價格下降。
細分市場分析
目前市場需求主要集中在31至100馬力以上的曳引機,預計到2024年,該功率區間將佔自動駕駛曳引機市場佔有率的39.5%。 31至100馬力的中等功率範圍,在滿足中等耕作所需的足夠馬力和可控的資金投入之間架起了一座重要的橋樑。模組化附加元件、視覺套件、遠端訊息和自動化裝置的實施,使得自動駕駛功能得以逐步提升。經銷商報告稱,種植者在購買功率更大的200馬力旗艦機型之前,會先嘗試在現有的75馬力曳引機上進行半自動改裝,這表明自動駕駛技術正處於逐步普及的階段。
然而,人們的目光正轉向功率超過100馬力的機械,這類機械的成長速度最快,年複合成長率高達24.0%。這些機械非常適合在大面積土地上耕作和播種,以及在大型農場進行重型耕作。功率不超過30馬力的緊湊型機械正在幫助園藝、酪農和混合種植農場實現割草和噴灑等重複性工作的自動化。採用多台輕型機器人取代單一重型曳引機的作業模式,可以減少土壤壓實,降低農戶進入田間作業的門檻,並使小型農戶也能享受到精準農業技術帶來的便利。
到2024年,半自動配置(操作員留在駕駛座上或遠端監控機器)將佔據68.2%的市場佔有率。農民優先考慮的是立即節省勞力,同時保留人工作業的備用方案。全自動駕駛解決方案將表現更佳,在預測期內將以23.1%的複合年成長率成長。從遠端轉向輔助、特定任務自動駕駛到全車隊編配,這條循序漸進的路徑與汽車產業的演變軌跡相呼應。即時動態GPS、多相機感知和冗餘安全層是目前正進入商業領域的L4級自動駕駛能力的基礎。
在聯合收割機連續12小時無需人工干預即可自主運作的演示之後,種植者的信心日益增強。監管機構正在製定基於性能的指導方針,而不是強制規定技術,這有助於技術的推廣應用。保險公司也開始為那些能夠降低事故風險的成功應用的自主收割系統提供保費折扣。
區域分析
到2024年,亞太地區將繼續保持領先地位,市佔率將達到46.3%。中國承諾投入數兆美元用於農業現代化,將為設備補貼、人工智慧研究中心和農村5G網路部署注入資金。日本正大力發展智慧農業,以因應農業人口快速老化的問題;澳洲則將津貼用於開發適合其廣袤乾旱地區農業作業的自動化解決方案。這些協同政策為全部區域的自動駕駛曳引機市場提供了巨大的發展機會。
北美是成長最快的地區,複合年成長率高達23.2%。高昂的人事費用、充裕的創業投資以及活躍的OEM開發平臺將加速商業化進程。美國在精密農業互聯計劃佔據主導地位,但僅27%的農場採用了這些項目,仍有巨大的成長空間。聯邦政府強制要求每個農場達到最低寬頻速度的計畫將加速建立實現自動化所需的數位化基礎。加拿大將利用潔淨科技補貼,而墨西哥將透過推廣機械化推動自動化向南發展。
在鼓勵數位化、低碳農業發展的通用農業政策改革的支持下,歐洲正穩步發展。德國、法國和西班牙在推廣應用方面處於領先地位,這得益於其成熟的機械製造商和有利於電動驅動的嚴格排放標準。東歐擁有廣闊的發展空間,其大片連片農田適合大規模自動駕駛曳引機的部署。碳權補貼計畫和能源轉型基金降低了融資門檻,鞏固了歐洲作為自動駕駛曳引機市場關鍵組成部分的地位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 農業勞動力短缺和薪資通膨加劇
- 加速精密農業和物聯網連接技術的應用
- 政府對智慧低碳家電的獎勵
- 果園和葡萄園正在轉向使用自動曳引機進行窄行耕作。
- OEM開放API生態系實現改裝自主化
- 電動車自動駕駛單元的碳權貨幣化
- 市場限制
- 小型農場初期投入成本高,投資報酬率不確定。
- 互聯車隊的資料隱私和網路安全問題
- 鄉村地區5G/EDGE連線不穩定
- 無人駕駛機器責任法規的演變
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按馬力
- 小於30馬力
- 31~100HP
- 超過100馬力
- 按自動化級別
- 半自動
- 完全自主
- 按驅動類型
- 柴油引擎
- 混合
- 電池驅動
- 透過使用
- 栽培
- 播種
- 收成
- 果園和葡萄園營運
- 按組件
- GPS/GNSS
- 感測器和視覺系統
- LiDAR和雷達模組
- 控制和導航軟體
- 按農場規模
- 小規模(不足100公頃)
- 中型(100-500公頃)
- 大型(超過500公頃)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation(Fendt, Massey Ferguson)
- CNH Industrial(Case IH, New Holland)
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- Monarch Tractor
- AutoNext Automation
- YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD.
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- TYM Corporation
- SDF Group
- Kioti(daedong)
- ISEKI & Co., Ltd
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The autonomous tractor market touched USD 2.2 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2030, sustaining an 18.6% CAGR.

The upswing stems mainly from an acute farm-labor crisis, rapid precision-agriculture uptake, and a widening set of government incentives that shorten payback periods for connected low-carbon machinery. Large commercial growers are already converting labor savings of 20% into higher margins, while continuous 24-hour field operation raises seasonal output. Software-centric revenue models, retrofit kits, and electric powertrains further expand addressable demand, signaling that the autonomous tractor market is entering a mainstream growth phase that transcends niche adoption.
Global Autonomous Tractors Market Trends and Insights
Rising Farm-Labor Shortages and Wage Inflation
A shrinking rural workforce is colliding with rising average farmer age, leaving half of open agricultural roles unfilled. Wage inflation amplifies the strain during peak field windows, particularly for harvest, where autonomous grain-cart systems now run round-the-clock without operators. Growers report productivity gains of 30-40% during critical windows, confirming that the autonomous tractor market is filling a structural gap rather than adding discretionary convenience. The urgency has reframed autonomy as core infrastructure required for long-term farm viability.
Accelerated adoption of precision agriculture and IoT connectivity
Cloud farm-management platforms already link well over 1 million machines, converting tractors into roaming data hubs that feed soil, yield, and asset information into real-time decision systems. Advanced sensor fusion, GPS, machine vision, and radar enable centimeter-level guidance, variable-rate input placement, and full-field obstacle avoidance.
High upfront cost and uncertain ROI for small farms
A single electric autonomous tractor can exceed USD 88,000, a steep outlay for holdings under 100 hectares. Connectivity upgrades, on-premise data infrastructure, and service subscriptions add further load. Models show that profitable deployment often begins above 500 hectares unless external grants offset capital expense, leaving many family farms to rely on co-operative ownership or hire services until prices fall.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government incentives for smart and low-carbon equipment
- Orchard and vineyard shift to narrow-row autonomous tractors
- Data-privacy and cybersecurity concerns in connected fleets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Current demand centers on tractors above 31-100, which accounted for 39.5% of the autonomous tractor market share in 2024. The mid-range 31-100 HP bracket serves as a pivotal bridge, blending horsepower sufficient for moderate tillage with manageable capital requirements. Modular add-ons, vision kits, telematics, and implementing automation allow progressive autonomy upgrades. Dealers report that growers trial a semi-autonomous retrofit on an existing 75 HP tractor before purchasing a larger 200 HP flagship machine, illustrating a stepped adoption curve.
Yet the spotlight is shifting to more than 100 HP, the fastest-growing slice at 24.0% CAGR. These machines suit broad-acre tillage, seeding, and heavy draft implements on large farms. Compact units up to 30 HP empower horticulture, dairy, and mixed-crop holdings to automate repetitive tasks such as mowing or spraying. Fleet concepts that deploy multiple lightweight robots instead of one heavy tractor lower soil compaction, reduce field entry barriers, and democratize precision technology for smallholders.
Semi-autonomous configurations, where an operator remains in the cab or oversees the machine remotely, commanded 68.2% market share in 2024. Farmers value immediate labor savings yet retain manual fallback. Over the forecast period, fully autonomous solutions will outpace all others, expanding at 23.1% CAGR. The step-wise path of remote steering aids, task-specific autonomy, and then full fleet orchestration mirrors the automotive sector's evolution. Real-time kinematic GPS, multi-camera perception, and redundant safety layers underpin Level 4 capabilities now entering commercial fields.
Confidence builds as growers witness a combine run autonomously for 12 straight hours without intervention. Regulators are drafting performance-based guidelines rather than prescribing technology, easing deployment. Insurance carriers have started to offer premium discounts for validated autonomous systems that reduce accident risk.
The Autonomous Tractors Market is Segmented by Horsepower (Up To 30HP, and More), by Automation Level (Fully Automated and Semi-Automated), by Drive Type (Diesel, and More), by Application (Tillage, and More), by Component (GPS/GNSS, and More), by Farm Size (Small, Medium, and Large) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific preserved its leadership with a 46.3% share in 2024, underpinned by sizable land holdings and robust public funding. China's multi-trillion-dollar pledge to modernize farming injects capital into equipment subsidies, AI research hubs, and rural 5G roll-outs. Japan's smart-farming drive counters a rapidly aging farmer demographic, while Australia directs grants toward autonomous solutions suited to vast dryland operations. These aligned policies sustain a deep opportunity pool for the autonomous tractor market across the region.
North America is the fastest-expanding arena at 23.2% CAGR. High labor costs, abundant venture capital, and active OEM R&D pipelines speed commercialization. The United States dominates precision agriculture connectivity projects, yet only 27% of farms have adopted them, implying sizable headroom. Federal programs that require minimum broadband speeds per farm accelerate digital foundations needed for autonomy. Canada leans on clean-tech subsidies, and Mexico's mechanization push spreads automation southward.
Europe follows a steady growth path, supported by Common Agricultural Policy reforms that reward digital, low-carbon farming. Germany, France, and Spain lead deployments through established machinery makers and strict emission standards that favor electric drive. Eastern Europe offers upside as large tracts of contiguous farmland suit fleet-scale autonomy. Subsidized carbon-credit schemes and energy-transition funds lower the financial hurdle, cementing Europe as a vital segment of the autonomous tractor market.
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation (Fendt, Massey Ferguson)
- CNH Industrial (Case IH, New Holland)
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- Monarch Tractor
- AutoNext Automation
- YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD.
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- TYM Corporation
- SDF Group
- Kioti (daedong)
- ISEKI & Co., Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising farm-labor shortages and wage inflation
- 4.2.2 Accelerated adoption of precision agriculture and IoT connectivity
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for smart and low-carbon equipment
- 4.2.4 Orchard and vineyard shift to narrow-row autonomous tractors
- 4.2.5 OEM open-API ecosystems enabling retro-fit autonomy
- 4.2.6 Carbon-credit monetization for electric autonomous units
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost and uncertain ROI for small farms
- 4.3.2 Data-privacy and cybersecurity concerns in connected fleets
- 4.3.3 Patchy rural 5G/edge connectivity
- 4.3.4 Evolving liability regulations for driver-less machinery
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Horsepower
- 5.1.1 Up to 30 HP
- 5.1.2 31 - 100 HP
- 5.1.3 Above 100 HP
- 5.2 By Automation Level
- 5.2.1 Semi-Autonomous
- 5.2.2 Fully Autonomous
- 5.3 By Drive Type
- 5.3.1 Diesel
- 5.3.2 Hybrid
- 5.3.3 Battery-Electric
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Tillage
- 5.4.2 Sowing
- 5.4.3 Harvesting
- 5.4.4 Orchard and Vineyard Operations
- 5.5 By Component
- 5.5.1 GPS/GNSS
- 5.5.2 Sensors and Vision Systems
- 5.5.3 LiDAR and Radar Modules
- 5.5.4 Control and Navigation Software
- 5.6 By Farm Size
- 5.6.1 Small (Less than 100 ha)
- 5.6.2 Medium (100-500 ha)
- 5.6.3 Large (More than 500 ha)
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Mexico
- 5.7.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.7.2 South America
- 5.7.2.1 Brazil
- 5.7.2.2 Argentina
- 5.7.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Spain
- 5.7.3.5 Russia
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.4.1 China
- 5.7.4.2 India
- 5.7.4.3 Japan
- 5.7.4.4 Australia
- 5.7.4.5 South Korea
- 5.7.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.5 Middle East
- 5.7.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.2 UAE
- 5.7.5.3 Turkey
- 5.7.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.7.6 Africa
- 5.7.6.1 South Africa
- 5.7.6.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Deere & Company
- 6.3.2 AGCO Corporation (Fendt, Massey Ferguson)
- 6.3.3 CNH Industrial (Case IH, New Holland)
- 6.3.4 Kubota Corporation
- 6.3.5 Mahindra & Mahindra
- 6.3.6 Monarch Tractor
- 6.3.7 AutoNext Automation
- 6.3.8 YANMAR HOLDINGS CO., LTD.
- 6.3.9 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.3.10 TYM Corporation
- 6.3.11 SDF Group
- 6.3.12 Kioti (daedong)
- 6.3.13 ISEKI & Co., Ltd












