 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850970
衛星天線:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Satellite Antenna - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
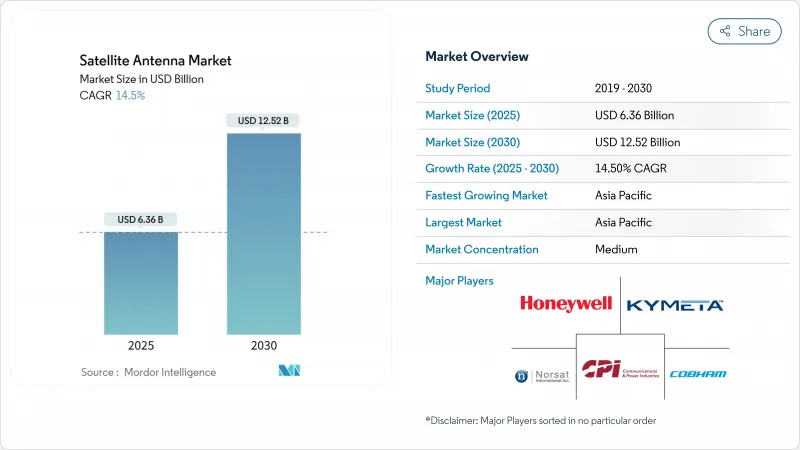
預計到 2025 年,衛星天線市場規模將達到 63.6 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 125.2 億美元,複合年成長率將達到 14.5%。
對高吞吐量連接的強勁需求、多軌道衛星群的部署以及天線製造成本的下降,正在加速衛星天線在商業和國防領域的應用。軟體定義的波束控制、輕質複合材料和高度整合的晶片組在提升性能的同時,也降低了營運商的生命週期擁有成本。戰略併購拓展了產品系列,各國政府將太空基礎設施視為其數位主權的重要支柱,這些因素也推動了衛星天線市場的成長。儘管供應商需要應對監管和軌道碎片等複雜問題,但這些因素共同推動了衛星天線市場持續兩位數的成長。
全球衛星天線市場趨勢與洞察
低地球軌道寬頻衛星星座的激增
星鏈(Starlink)和OneWeb等低地球軌道計劃正在重新定義鏈路預算,促使營運商部署能夠每分鐘追蹤數十顆高速移動衛星的電子控制陣列。截至2024年9月,已註冊的衛星群達到411個,但僅有5%完成發射,這為天線供應商留下了巨大的發展空間。緊湊相位陣列將GNSS接收器與邊緣運算整合,使終端能夠在低地球軌道(LEO)、中地球軌道(MEO)和地球同步軌道(GEO)層之間自動切換波束。偏遠社區、海上航道和災害應變團隊已初步受益。相控相位陣列無需機械零件,降低了全生命週期維護成本,並增強了大規模部署的經濟效益。隨著衛星天線市場規模擴大到類似手機的水平,能夠以家用電子電器價格分佈大規模生產雙軌道終端的供應商將獲得巨大的市場價值。
太空快速軍事化(MilSATCOM)
國防部官員將可靠且抗干擾的連結視為任務關鍵。美國2025會計年度預算撥款252億美元用於天基系統,將推動採購能夠在複雜電磁環境下運作的多頻段定向天線。經實戰驗證的要求包括旁瓣抑制、抗欺騙和動態波束跳變以減輕干擾。歐洲和亞太地區的平行計畫進一步擴大了需求。軍方也在推動研發更輕的終端,以便小型無人機和士兵使用,促進了氮化鎵功率放大器和共形複合材料技術的突破。雖然從長遠來看,安全的光纖交聯將與射頻技術形成互補,但近期支出重點在於先進的相位陣列射頻複合材料,以保持衛星天線市場的良好發展勢頭。
赤道Ku/ Ka波段雨衰
強降雨會使Ku波段和Ka波段訊號衰減高達20dB,迫使業者增加鏈路餘裕或切換到較低頻率。印尼和巴西的熱帶微暴流會導致不可預測的訊號衰落,從而影響企業和回程傳輸客戶的服務等級協定(SLA)。緩解措施包括自我調整編碼、站點分集和在暴風雨期間回落至C波段的雙頻終端,但這些措施會增加服務提供者的資本支出和營運支出(OPEX)。儘管Ka波段網路具有容量優勢,但由於對未來氣候變遷的不確定性,通訊業者仍不願部署以Ka波段為中心的網路。因此,赤道地區的Ka波段網路採用趨勢可能落後於全球衛星天線市場。
細分市場分析
憑藉成熟的地面基礎設施和均衡的抗雨致衰減能力, Ku波段將在2024年佔據衛星天線市場29%的佔有率。該波段仍將是廣播和VSAT服務的核心,尤其是在已獲得監管批准的地區。相較之下,Ka頻寬正以15.2%的複合年成長率快速成長,吸引尋求更低每位元成本和靈活點波束架構的寬頻營運商。這一成長趨勢,加上NASA為地球觀測衛星群提出的每日26Tb的路由需求,將推動配備Ka終端的衛星天線市場規模的擴大。 C波段在易受颶風影響的地區仍將發揮重要作用,而X波段由於其抗干擾能力,將繼續在國防領域佔據一席之地。新興的多波段天線打破了傳統的頻段壁壘,實現了即時頻率切換。這種能力提高了系統的整體可用性,並拓寬了衛星天線市場供應商的潛在收入來源。
多波束平板天線設計可同時支援Ku波段和Ka波段的連接,並可在雨衰期間反轉通訊方向。整合可程式射頻前端的供應商能夠根據需要動態分配功率,從而提高頻譜效率。這些進步顯著提升了行動VSAT、郵輪、油氣平台等提案的價值。因此,預計到2030年,高頻率終端衛星天線市場規模將翻倍,供應商必須融入天氣自適應智慧技術,才能充分滿足熱帶地區的需求。
2024年,拋物面天線將佔衛星天線市場規模的38%,由於其具成本效益,常用於固定式衛星閘道。機械萬向節對於大型郵輪和衛星地面站而言仍然經濟高效。然而,以18.4%的複合年成長率快速成長的平板電子控制陣列正在重新定義行動應用場景。採用Anokiwave技術的面板現已完成工廠校準,縮短了安裝時間,並支援安裝在窄體飛機的保形機身上。一種原型充氣式碟形天線有望實現20:1的封裝效率,以適應對發射品質敏感的小型衛星。
混合架構將緊湊型拋物面天線段與變速器子陣列結合,兼具碟形天線的高增益優勢和ESA天線的靈活性。研發軟性介電材料的供應商使天線能夠彎曲貼合車輛車頂,從而消除空氣阻力帶來的不利影響。因此,可尋址衛星天線市場擴展到私家車、火車和城市無人計程車等領域,這些應用都需要超薄終端。反射器廠商將透過整合自動指向和健康監測韌體來保護已安裝的設備,這表明到2030年,雙方將採取共存而非徹底替換的策略。
衛星天線市場報告按頻段(C 波段、 X波段、 Ku波段、其他)、天線類型(碟形天線、喇叭天線、FRP 天線罩天線、其他)、應用(星載、機載、其他)、最終用戶(民用和政府、國防)和地區進行細分。
區域分析
亞太地區將以14.6%的複合年成長率實現最快成長,直至2030年,這主要得益於中國、印度、日本和韓國擴大多軌道系統規模和提升國內製造業水準。中國第五個南極衛星站將於2024年2月啟用,屆時將展示用於科學和國防領域的衛星天線。印度「印度製造」政策下的與生產連結獎勵計畫將鼓勵饋源喇叭、雷達罩和射頻積體電路子系統的在地化生產,從而降低該地區營運商的成本。日本汽車產業正準備利用非地面電波回程傳輸實現聯網汽車服務,這促使供應商將天線小型化,以便整合到車頂上。
由於深厚的航太供應鏈、巨額國防開支和蓬勃發展的太空企業,北美仍然是最大的衛星天線市場。美國太空軍維護一個衛星控制網路,目前運作19個天線,運轉率75%,並計畫從2025年開始部署12個新的高容量天線。加拿大的極地通訊專案也增加了對耐低溫天線的需求。墨西哥和其他拉丁美洲國家正在利用地球同步軌道(GEO)閘道器提供網路社群Wi-Fi服務,但資本支出壓力將限制其短期內的規模。
歐洲保持著強勁的市場佔有率,這得益於歐洲太空總署(ESA)的技術演示,例如AMPER計劃用於支援軍事和氣候監測任務的異形網狀反射器。德國和英國正在資助建造主權衛星地面站,以確保資料自主性;行動網路營運商正在蘇格蘭和巴伐利亞的鄉村地區測試基於衛星的回程傳輸。東歐通訊業者正在採用租賃購買模式來應對外匯波動,這種策略有助於天線供應商平穩訂單。在中東,海灣合作理事會(GCC)的主權財富基金正在支持地球同步軌道甚高通量衛星(GEO VHTS)計劃,沙烏地阿拉伯的藍圖要求到2030年將該國的航太收入提高兩倍。南美洲發展落後,但巴西出現了成長跡象,該國強制要求海上油氣連接使用雙冗餘天線。總而言之,這些動態維持了衛星天線市場的區域需求多元化,從而保護了全球收入免受宏觀衝擊的影響。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場動態
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 低地球軌道寬頻衛星星座的擴展
- 太空快速軍事化(MilSATCOM)
- 高通量衛星(HTS)有效載荷採用
- 商用機上互聯(IFC)的蓬勃發展
- 基於ESA的平板成本曲線通貨緊縮(未公開)
- 月球和近月任務的通訊需求(UNDER-RADAR)
- 市場限制
- 赤道地區 Ku/ Ka波段降雨衰減
- 相位陣列晶片組的出口管製瓶頸
- 軌道碎片保險成本不斷上漲(未公開通報)
- 新興市場通訊業者資本支出危機(不受重視)
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按頻寬
- C波段
- X波段
- Ku波段
- Ka波段
- L/S波段
- VHF/UHF頻段
- 依天線類型
- 拋物面反射器
- 平面顯示器(ESA/RSA)
- 喇叭
- 介質共振器
- 玻璃纖維雷達罩
- 金屬印章
- 透過使用
- 太空船
- 空中
- 海上
- 陸地(移動和固定)
- 最終用戶
- 商業的
- 政府和國防部
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 海灣合作理事會國家
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Honeywell International Inc.
- CPI International Inc.
- Kymeta Corp.
- Norsat International Inc.
- Cobham SATCOM
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- Maxar Technologies
- Ball Aerospace
- Intellian Technologies
- Isotropic Systems(All.Space)
- Hanwha Phasor
- SES SA(O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- Thales Alenia Space
- MT Mechatronics
- SatixFy Ltd.
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- LEOcloud Inc.
- Hughes Network Systems
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The satellite antenna market size stands at USD 6.36 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 12.52 billion by 2030, reflecting a robust 14.5% CAGR.

Strong demand for high-throughput connectivity, the roll-out of multi-orbit constellations, and falling antenna production costs are accelerating adoption across commercial and defense domains. Software-defined beam steering, lighter composites, and highly integrated chipsets are improving performance while lowering lifetime ownership costs for operators. Growth is also being reinforced by strategic mergers that broaden product portfolios and by governments treating space infrastructure as a pillar of digital sovereignty. These converging factors keep the satellite antenna market on a double-digit growth path even as suppliers navigate regulatory and orbital-debris complexities.
Global Satellite Antenna Market Trends and Insights
Proliferation of LEO broadband constellations
Low Earth Orbit projects such as Starlink and OneWeb are rewriting link-budget assumptions, pushing operators to deploy electronically steered arrays that can track dozens of fast-moving satellites per minute. In September 2024, 411 constellations were registered, yet only 5% were fully launched, leaving extensive runway for antenna suppliers. Compact phased arrays now include integrated GNSS receivers and edge computing, letting terminals auto-switch beams across LEO, MEO, and GEO layers. Remote communities, maritime routes, and disaster-response teams are early beneficiaries. Because phased arrays eliminate mechanical parts, lifetime maintenance costs fall, reinforcing the economic case for large-scale roll-outs. Vendors able to mass-produce dual-orbit terminals at consumer-electronics price points will capture outsized value as the satellite antenna market broadens to handset-like volumes.
Rapid militarization of space (MilSATCOM)
Defense authorities see assured, jam-resistant links as mission-critical. The U.S. FY 2025 budget allocates USD 25.2 billion to space-based systems, triggering procurement of multi-band, directive antennas that operate in contested electromagnetic environments. Battle-proven requirements include side-lobe suppression, anti-spoofing, and dynamic beam hopping to mitigate interference. Parallel programs in Europe and Asia-Pacific further widen demand. Militaries also push for lighter terminals to fit small UAVs and dismounted soldiers, encouraging breakthroughs in GaN power amplifiers and conformal composites. Over the long term, secure optical cross-links will complement RF, but near-term spending remains anchored in advanced phased-array RF architectures, sustaining momentum for the satellite antenna market.
Ku/Ka-band rain fade in equatorial regions
Heavy rainfall events attenuate Ku and Ka signals by up to 20 dB, forcing operators to oversize link margins or revert to lower frequencies. Tropical micro-bursts in Indonesia and Brazil create unpredictable fades that undermine SLAs for enterprise and backhaul customers. Mitigation tactics include adaptive coding, site diversity, and dual-band terminals that fall back to C band during storms, yet these solutions raise capex and opex for service providers. Future climate variability adds uncertainty, making some telcos reluctant to commit to Ka-centric networks despite their capacity advantages. Consequently, adoption curves in equatorial belts may lag the global satellite antenna market trend.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- High-throughput satellite (HTS) payload adoption
- Commercial in-flight connectivity (IFC) boom
- Export-control bottlenecks on phased-array chipsets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Ku Band accounted for 29% of the satellite antenna market in 2024, capitalizing on mature ground infrastructure and balanced rain-fade resilience. The segment continues to anchor broadcast and VSAT services, especially where regulatory clearances already exist. In contrast, Ka Band is scaling rapidly at a 15.2% CAGR, attracting broadband operators that seek lower cost per bit and flexible spot-beam architectures. This growth trajectory translates to an expanding satellite antenna market size for Ka terminals, underpinned by NASA's requirement to route 26 Tb/day on its upcoming Earth-observation constellation. C Band maintains relevance in cyclone-prone zones, while X Band remains a defense niche thanks to interference immunity. Emerging multi-band antennas blur traditional silos, permitting real-time frequency switching, a capability that uplifts overall system availability and widens supplier addressable revenue streams within the satellite antenna market.
Multi-beam flat-panel designs now facilitate simultaneous Ku and Ka connectivity, enabling operators to reverse traffic when rain fade hits. Suppliers integrating programmable RF front-ends can dynamically allocate power where needed, lifting spectral efficiency. These advances transform value propositions for mobile VSAT, cruise, and oil-and-gas platforms. As such, the satellite antenna market size for high-frequency terminals is forecast to double by 2030, though suppliers must embed weather-adaptive intelligence to unlock full demand across tropical geographies.
Parabolic reflectors held 38% share of the satellite antenna market size in 2024, favored for static gateways that prize high gain per dollar. Mechanical gimbals remain cost-effective for large cruise ships and teleport hubs. Yet flat-panel electronically steered arrays, expanding at an 18.4% CAGR, are redefining mobility use cases. Anokiwave-powered panels are now factory-calibrated, slashing installation time and supporting conformal fuselage mounting on narrow-body aircraft. Inflatable dishes under prototyping promise 20:1 packing efficiency, catering to launch-mass-sensitive small satellites.
Hybrid architectures blend small parabolic segments with phase-shifter sub-arrays, extracting the high-gain benefits of dishes and the agility of ESAs. Vendors exploring flexible dielectric materials can bend antennas around vehicle roofs, erasing aerodynamic drag penalties. Consequently, the addressable satellite antenna market widens to include personal vehicles, trains, and urban drone taxis, all of which require ultra-low-profile terminals. Reflector incumbents respond by embedding auto-pointing and health-monitoring firmware to protect installed bases, signaling a coexistence rather than outright displacement scenario through 2030.
The Satellite Antenna Market Report is Segmented by Frequency Band (C Band, X Band, Ku Band, and More), Antenna Type (Parabolic Reflector, Horn, FRP-Radome, and More), Application (Spaceborne, Airborne, and More), End-User (Commercial and Government and Defense), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific records the quickest expansion, charting a 14.6% CAGR to 2030 as China, India, Japan, and South Korea scale multi-orbit systems and indigenous manufacturing. China's fifth Antarctic outpost, opened in February 2024, showcases dual-use satellite dishes that serve science and defense agendas. India's production-linked incentives, aligned with its "Make in India" drive, catalyze local fabrication of feed horns, radomes, and RFIC subsystems, lowering costs for regional operators. Japan's auto sector readies connected-car services using non-terrestrial backhaul, prompting suppliers to miniaturize antennas for rooftop integration.
North America remains the largest satellite antenna market thanks to deep aerospace supply chains, heavy defense spending, and entrepreneurial space ventures. The U.S. Space Force maintains the Satellite Control Network, operating 19 dishes at 75% utilization, with plans for 12 new high-capacity antennas starting 2025. Canada's Polar communications programs add demand for low-temperature-tolerant antennas. Mexico and other Latin peers leverage GEO gateways for internet-community Wi-Fi, although capex pressures curb near-term scale.
Europe holds robust share, reinforced by ESA technology demonstrators such as the shaped mesh reflector from the AMPER project that supports military and climate-monitoring missions. Germany and the UK fund sovereign teleports to secure data autonomy, while mobile network operators test backhaul-over-satellite in rural Scotland and Bavaria. Eastern European telcos adopt lease-to-own models to overcome currency volatility, a tactic that smooths order pipelines for antenna suppliers. The Middle East, buoyed by GCC sovereign wealth funds, backs GEO VHTS projects, and Saudi Arabia's roadmap foresees a trebling of national space revenues by 2030. South America trails but shows pockets of growth in Brazil, where oil-and-gas offshore connectivity mandates dual-redundant antennas. Collectively, these dynamics keep regional demand diversified within the satellite antenna market, insulating global revenue from macro shocks.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- CPI International Inc.
- Kymeta Corp.
- Norsat International Inc.
- Cobham SATCOM
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- Maxar Technologies
- Ball Aerospace
- Intellian Technologies
- Isotropic Systems (All.Space)
- Hanwha Phasor
- SES S.A. (O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- Thales Alenia Space
- MT Mechatronics
- SatixFy Ltd.
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- LEOcloud Inc.
- Hughes Network Systems
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Proliferation of LEO broadband constellations
- 4.2.2 Rapid militarization of space (MilSATCOM)
- 4.2.3 High?throughput satellite (HTS) payload adoption
- 4.2.4 Commercial in-flight connectivity (IFC) boom
- 4.2.5 ESA-based flat-panel cost curve deflation (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.2.6 Lunar and cislunar mission communications demand (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ku-/Ka-band rain fade in equatorial regions
- 4.3.2 Export-control bottlenecks on phased-array chipsets
- 4.3.3 Mounting orbital-debris insurance premiums (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.3.4 CAPEX crunch at emerging-market telcos (UNDER-RADAR)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Frequency Band
- 5.1.1 C Band
- 5.1.2 X Band
- 5.1.3 Ku Band
- 5.1.4 Ka Band
- 5.1.5 L/S Band
- 5.1.6 VHF/UHF Band
- 5.2 By Antenna Type
- 5.2.1 Parabolic Reflector
- 5.2.2 Flat-Panel (ESA/RSA)
- 5.2.3 Horn
- 5.2.4 Dielectric-Resonator
- 5.2.5 FRP-Radome
- 5.2.6 Metal-Stamp
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Spaceborne
- 5.3.2 Airborne
- 5.3.3 Maritime
- 5.3.4 Land (Mobile and Fixed)
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Government and Defense
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 APAC
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of APAC
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC Countries
- 5.5.5.2 Turkey
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Rest of MEA
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategy, Market Rank)
- 6.4.1 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.2 CPI International Inc.
- 6.4.3 Kymeta Corp.
- 6.4.4 Norsat International Inc.
- 6.4.5 Cobham SATCOM
- 6.4.6 L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Viasat Inc.
- 6.4.8 Airbus Defence and Space
- 6.4.9 Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Maxar Technologies
- 6.4.11 Ball Aerospace
- 6.4.12 Intellian Technologies
- 6.4.13 Isotropic Systems (All.Space)
- 6.4.14 Hanwha Phasor
- 6.4.15 SES S.A. (O3b mPOWER User Terminals)
- 6.4.16 Thales Alenia Space
- 6.4.17 MT Mechatronics
- 6.4.18 SatixFy Ltd.
- 6.4.19 General Dynamics Mission Systems
- 6.4.20 LEOcloud Inc.
- 6.4.21 Hughes Network Systems
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











