 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850396
5G基礎設施:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030年)5G Infrastructure - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
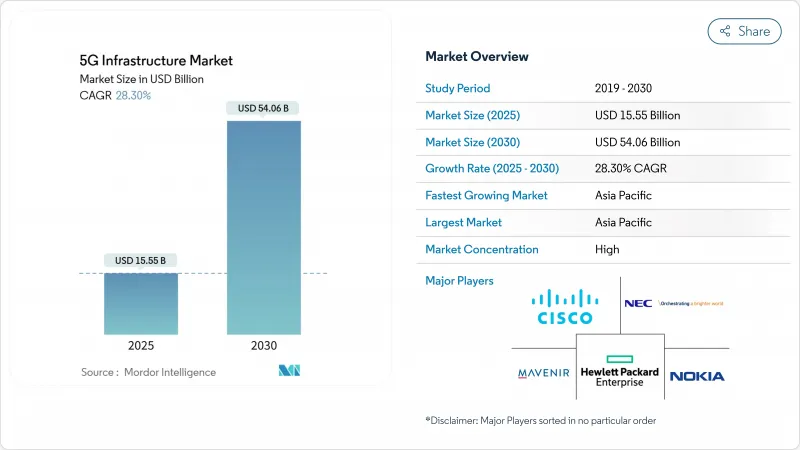
預計到 2025 年,5G 基礎設施市場規模將達到 155.5 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 540.6 億美元。
目前的擴張趨勢主要體現在營運商用完全可程式化的獨立平台取代以往的非獨立組網部署,這些平台支援網路切片、邊緣運算和私有網路建置。資本正從單純的覆蓋轉向軟體定義能力,以縮短服務上線週期、提高自動化程度並降低生命週期營運成本。製造業、行動通訊和能源產業對私人網路的需求,以及將高速寬頻擴展到農村地區的固定無線存取(FWA)部署,都進一步推動了這項需求。同時,頻譜政策正在釋放中頻段頻寬的新容量,供應商的藍圖也朝著雲端原生開放式無線存取網路(Open RAN)設計方向發展,使通訊業者能夠擺脫對單一供應商的依賴,並更快地實現應用程式介面(API)的商業化。
全球5G基礎設施市場趨勢與洞察
不斷提高機器對機器(M2M)和物聯網(IoT)設備密度
獨立組網的5G網路將使每個行動通訊基地台能夠處理多達5萬台連網設備,這是工業4.0生產線和龐大感測器網路的先決條件。現代汽車的RedCap工廠網路已證明,低容量設備可以在不損失網路覆蓋的情況下降低功耗。邊緣運算將運算資源部署到更靠近機器的位置,從而保持機器人和預測性維護方案所需的毫秒延遲。汽車、醫療保健和重工業領域的專用網路演示檢驗了設備密集型環境而非消費級手機帶來的收入成長。這種趨勢將支撐整個預測期內對小型基地台和邊緣資料中心的持續投入。
行動數據消耗量快速成長
隨著雲端遊戲、擴增實境影片和人工智慧串流媒體對穩定多Gigabit連結的需求不斷成長,行動月流量持續攀升至新高。英國電信業者Three已將其骨幹網路吞吐量提升至每秒9太比特,此前其吞吐量在2024年底曾達到每秒2太比特以上的峰值。在中國,監管機構預計到2030年國內流量將成長四倍,這將促使營運商轉向能夠在全天高負載下保持效率的容量架構。醫療保健試點項目,例如即時遠端超音波演示,凸顯了上行鏈路容量對於關鍵成像任務的重要性。隨著固定無線存取(FWA)在印度和美國普及,將流量從智慧型手機重定向到客戶端設備(CPE),營運商正被迫重新設計回程傳輸,以適應用戶以家庭為中心的視訊使用習慣。
無線存取網密集化和高昂的初始回程傳輸成本
小型基地台造價在1萬至5萬美元之間,大型基地台單站造價高達20萬美元,因此,密集型5G網路部署需要大量資金投入,尤其是在毫米波強制部署的情況下。光纖回程傳輸可能使計劃預算增加30%,而郊區走廊挖掘量低導致溝槽開挖進度延誤。預計2023年全球通訊支出將出現自2017年以來的首次下降,這使得財務長在加快網路部署方面更加謹慎。網路共用協議可以節省高達40%的成本,但會降低每個合作夥伴提供優質差異化行銷的能力。每個業者超過10億美元的頻譜授權費進一步加劇了資產負債表的餘量。
細分市場分析
2024年,隨著通訊業者部署密集的大型基地台和小型基地台網路,無線接取網(RAN)設備將佔據5G基礎設施市場的最大佔有率,營收累計37%。雖然首批硬體仍將維持RAN的重要性,但核心網路將以32.36%的複合年成長率超越其他層,因為軟體定義控制將決定未來的獲利模式。隨著能夠虛擬化用戶平面和控制平面功能的獨立雙模分組核心網的部署,5G核心網平台的市場規模將呈指數級成長。沃達豐西班牙和英國Three公司強調,雲端原生核心網路使通訊業者能夠開放用於邊緣運算、安全和按需品質產品的API。
在本世紀後半段,通訊業者將融合核心網路視為專用網路切片、低延遲工業服務和即時分析的引擎。隨著覆蓋目標的逐步實現,無線存取網(RAN)的支出將會減少,而由於產品生命週期更新和功能附加元件,核心網路的成本將持續成長。此外,由於需要分散式單元將線速流量傳輸到資料中心核心網,傳輸和擴展傳輸(xHaul)的預算也將增加。因此,光網路和路由供應商將把自己定位為戰略合作夥伴,而非戰術性合作夥伴。
由於中頻段兼具遠距離傳輸和數百兆赫茲頻寬的優勢,能夠支援大規模MIMO陣列,預計到2024年,中頻段將佔據5G基礎設施市場佔有率的46%。從芝加哥到柏林,通訊業者在使用3.5 GHz無線電覆蓋郊區環網,且基地台成本不高。這一發展趨勢預示著毫米波無線電、中繼器和先進波束成形晶片相關的5G基礎設施市場規模將迅速成長,尤其是在美國、日本和韓國。
低於 1 GHz 的低頻段對於廣域物聯網覆蓋至關重要,但難以滿足Gigabit目標,只能起到輔助作用而非主導作用。監管機構將中頻段和高頻段頻譜資源捆綁在同一輪許可中,將有助於營運商根據不同的服務層級調整其頻率組合。
5G 基礎設施市場按通訊基礎設施(5G 無線接取網路、5G 核心網路、傳輸/XHaul [前傳、中傳、回傳]、其他)、頻譜頻段(低頻段、中頻段、其他)、網路架構(非獨立組網 [NSA]、其他)、核心網路技術(軟體定義網路 [SDN]、其他產業)
區域分析
到2024年,亞太地區將佔據全球5G基礎設施市場佔有率的24%,這主要得益於中國440萬基地台以及印度力爭在2027年前實現3000萬固定無線接入(FWA)用戶的快速成長。該地區將以32.27%的複合年成長率成長,韓國維持97%的人口覆蓋率,而日本則推進郊區高密度化建設。印尼、越南和菲律賓的農村地區將傾向採用共用基地台模式,而澳洲則將轉向混合衛星和5G備援模式,以支援偏遠地區的採礦作業。
在北美,網路覆蓋成熟度已接近80%,預計2023年下滑後,2025年支出將回升。愛立信報告稱,2024年第四季各地區年增54%,這預示著獨立核心網、邊緣區域和大型企業項目的預算將再次成長。美國通訊業者正將固定無線存取(FWA)與光纖捆綁銷售,以涵蓋服務不足的郊區;而加拿大則正在分配新的中頻段頻譜,以加速原住民社區的網路連線。
歐洲在獨立普及率方面落後於其他國家,但計畫透過監管協調,到2030年將其經濟規模擴大1,640億歐元。德國96%的普及率是集體努力的成果,但英國在供應商禁令導致設備更換延遲後,需要重建其普及率。在拉丁美洲,已有29家業者進入商業化階段。隨著頻譜費用下降和雲端服務供應商為中立主機塔提供資金,預計到2030年,該地區的連線數將達到4.25億。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 包含 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 機器間通訊和物聯網設備密度不斷增加
- 行動數據消耗量快速成長
- 政府頻譜競標加速了中頻寬部署
- 通訊業者資本支出轉向雲端原生、開放式無線接取網路架構
- 棕地工業對專用5G的需求日益成長
- 固定無線存取(FWA)作為農村市場光纖的替代方案
- 市場限制
- 無線存取網密集化和高昂的初始光纖回程傳輸成本
- 網路切片貨幣化標準化進程的延遲
- 對中國供應商的國家安全限制
- 毫米波部署所需技術純熟勞工短缺
- 價值鏈分析
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 投資和資金籌措趨勢
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 替代品的威脅
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 透過通訊基礎設施
- 5G無線接取網路(RAN)
- 運輸/跨運輸(去程傳輸、中線運輸、回程傳輸)
- 核心網路(雲端原生 5GC)
- 按頻譜帶
- 低頻寬(低於1GHz)
- 中頻寬(1-6GHz)
- 高頻寬/毫米波(24GHz以上)
- 透過網路架構
- 非獨立式(NSA)
- 獨立版 (SA)
- 透過核心網路技術
- 軟體定義網路 (SDN)
- 網路功能虛擬化(NFV)
- 多接取邊緣運算(MEC)
- 網路切片
- 最終用戶
- 消費性電子產品
- 汽車與出行
- 工業製造
- 醫療保健和生命科學
- 能源與公共產業
- 公共與國防
- 智慧城市和基礎設施
- 其他行業(零售業、媒體業、農業)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 韓國
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東和非洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 土耳其
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亞
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Casa Systems Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Parallel Wireless Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- Ribbon Communications Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The 5G infrastructure market reached USD 15.55 billion in 2025 and is on course to attain USD 54.06 billion by 2030, translating into a 28.30% CAGR.

The current expansion pivots on operators replacing earlier non-standalone rollouts with fully programmable standalone platforms that support network slicing, edge computing and private network creation. Capital is shifting from pure coverage toward software-defined functions that shorten service launch cycles, improve automation and lower lifetime operating costs. Demand is reinforced by private-network interest from manufacturing, mobility and energy, alongside fixed-wireless access (FWA) deployments that extend high-speed broadband into rural zones. Meanwhile, spectrum policy is unlocking fresh mid-band capacity, and vendor road maps are converging around cloud-native Open RAN designs that let carriers avoid single-supplier dependence and monetize APIs more quickly.
Global 5G Infrastructure Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Machine-to-Machine and IoT Device Density
Standalone 5G allows each cell site to handle as many as 50,000 connected devices, a prerequisite for Industry 4.0 production lines and massive sensor grids. Hyundai Motor's RedCap-enabled factory network proved that reduced-capability devices can lower power budgets without losing coverage. Edge computing is moving compute resources closer to machines, keeping latency within millisecond windows that robotics and predictive-maintenance schemes require. Private-network proofs in automotive, healthcare, and heavy industry validate the revenue upside that comes from device-dense environments rather than consumer handsets. This driver underpins sustained spending on small cells and edge data centers over the forecast window.
Surge in Mobile Data Consumption
Monthly mobile traffic continues to set new highs as cloud gaming, extended-reality video, and AI-enhanced streaming demand consistent multi-gigabit links. Three UK boosted backbone throughput to 9 Tbit/s after end-2024 peaks surpassed 2 Tbit/s. In China, regulators expect national traffic to quadruple by 2030, moving operators toward capacity architectures that remain efficient under day-long loads. Healthcare pilots, such as real-time tele-ultrasound demonstrations, underline the value of uplink capacity for mission-critical imagery. FWA uptake in India and the United States is also redirecting traffic from smartphones to CPE units, pushing carriers to redesign backhaul for home-first video habits.
High Upfront RAN Densification and Fiber Back-Haul Costs
Small-cell bills from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 and macro-cell outlays that reach USD 200,000 per site make dense 5G footprints capital heavy, especially where mmWave is mandated. Fiber back-haul can add 30% to project budgets, and scarce digs in suburban corridors slow trenching schedules. Global telecom CAPEX dipped in 2023, the first drop since 2017, making CFOs cautious about accelerated rollouts. Network-sharing deals deliver up to 40% savings but reduce each partner's ability to market premium differentiation. Spectrum licence fees above USD 1 billion per operator further compress balance sheet headroom.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Spectrum Auctions Accelerating Mid-Band Rollouts
- Telco Capex Pivot to Cloud-Native Open RAN Architectures
- Delayed Standardisation for Network-Slicing Monetisation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
RAN equipment generated the largest slice of the 5G infrastructure market, delivering 37% revenue in 2024 as carriers rolled out dense macro and small-cell grids. That initial hardware wave will keep RAN important, yet core networks outpace other layers with a 32.36% CAGR because software-defined control decides future monetisation. The 5G infrastructure market size for core platforms is set to increase sharply as standalone rollouts mandate dual-mode packet cores that virtualise user plane and control plane functions. Vodafone Spain and Three UK highlight how cloud-native cores let operators expose APIs for edge, security and quality-on-demand products
In the second half of the decade, operators view the converged core as the engine for private-network slices, low-latency industrial services, and real-time analytics. RAN spend will taper as coverage milestones are met, whereas lifecycle refresh and feature add-ons keep core invoices growing. Transport and xHaul budgets also rise because distributed units must feed line-rate traffic into data-centre cores. Consequently, the 5G infrastructure market will witness supplier jockeying where optical and routing vendors position themselves as strategic rather than tactical partners.
Mid-band commanded 46% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024 because it blends propagation reach with multi-hundred-MHz bandwidth that supports massive MIMO arrays. Operators from Chicago to Berlin use 3.5 GHz radios to cover suburban rings without overspending on cells. mmWave, however, shows the fastest 33.58% CAGR by serving FWA households and event venues. This trajectory means the 5G infrastructure market size linked to mmWave radios, repeaters and advanced beamforming silicon will climb quickly, especially in the United States, Japan and South Korea.
Low-band below 1 GHz stays vital for wide-area IoT coverage but struggles with gigabit targets, keeping it a supplement, not a star. mmWave deployment faces line-of-sight and foliage loss, yet high-gain antennas and AI-aided beam steering are closing some gaps. Regulators that bundle mid-band and high-band blocks in the same licence round help carriers align the spectrum mix with differentiated service tiers.
The 5G Infrastructure Market is Segmented by Communication Infrastructure (5G Radio Access Networks, 5G Core Networks, Transport / XHaul [Front, Mid, Back-Haul], and More), Spectrum Band (Low-Band, Mid-Band, and More), Network Architecture (Non-Standalone [NSA] and More), Core Network Technology (Software-Defined Networking [SDN] and More), End-User Vertical (Consumer Electronics, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific held 24% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024, driven by China's 4.4 million base stations and India's race to connect 30 million FWA subscribers by 2027. The region will expand at a 32.27% CAGR as South Korea sustains 97% population coverage and Japan adds suburban densification. Rural programmes in Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines will lean on shared-tower models, while Australia advances with hybrid satellite-5G back-ups for remote mining operations.
North America shows coverage maturity above 80% of people yet reinvigorated spending in 2025 after a 2023 dip. Ericsson logged 54% year-over-year regional growth in Q4 2024, signalling that standalone cores, edge zones, and large enterprise deals are moving budgets again. US carriers bundle FWA with fibre to capture underserved suburbs, and Canada allocates fresh mid-band spectrum to accelerate indigenous-community connectivity.
Europe trails on standalone penetration but targets a EUR 164 billion economic boost by 2030 from harmonised regulation. Germany's 96% coverage illustrates what cohesive awards achieve, whereas the United Kingdom must rebuild performance after vendor bans slowed equipment swaps. Latin America steps into commercial phase with 29 operators live; regional connections should reach 425 million by 2030 as spectrum fees fall and cloud players finance neutral-host towers.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Casa Systems Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Parallel Wireless Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- Ribbon Communications Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing machine-to-machine and IoT device density
- 4.2.2 Surge in mobile data consumption
- 4.2.3 Government spectrum auctions accelerating mid-band rollouts
- 4.2.4 Telco capex pivot to cloud-native open RAN architectures
- 4.2.5 Emerging demand for private 5G in brownfield industrial sites
- 4.2.6 Fixed-wireless access (FWA) substituting fiber in rural markets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront RAN densification and fiber back-haul costs
- 4.3.2 Delayed standardization for network-slicing monetization
- 4.3.3 National-security restrictions on Chinese vendors
- 4.3.4 Skilled-labor shortages for mmWave deployment
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Investment and Funding Trends
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8.5 Threat of Substitute Products
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Communication Infrastructure
- 5.1.1 5G Radio Access Network (RAN)
- 5.1.2 Transport / xHaul (Front-, Mid-, Back-haul)
- 5.1.3 Core Network (Cloud-native 5GC)
- 5.2 By Spectrum Band
- 5.2.1 Low-Band (less than 1 GHz)
- 5.2.2 Mid-Band (1-6 GHz)
- 5.2.3 High-Band / mmWave (above 24 GHz)
- 5.3 By Network Architecture
- 5.3.1 Non-Standalone (NSA)
- 5.3.2 Standalone (SA)
- 5.4 By Core Network Technology
- 5.4.1 Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- 5.4.2 Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- 5.4.3 Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC)
- 5.4.4 Network Slicing
- 5.5 By End-user Vertical
- 5.5.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.5.2 Automotive and Mobility
- 5.5.3 Industrial Manufacturing
- 5.5.4 Healthcare and Life Sciences
- 5.5.5 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.6 Public Safety and Defense
- 5.5.7 Smart Cities and Infrastructure
- 5.5.8 Other Verticals (Retail, Media, Agriculture)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 APAC
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of APAC
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airspan Networks Inc.
- 6.4.2 AT&T Inc.
- 6.4.3 Casa Systems Inc.
- 6.4.4 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.5 CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- 6.4.6 Corning Inc.
- 6.4.7 Dell Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.8 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.9 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.4.10 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- 6.4.11 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.13 Juniper Networks Inc.
- 6.4.14 Mavenir Systems Inc.
- 6.4.15 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.16 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.17 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.18 Parallel Wireless Inc.
- 6.4.19 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.20 Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- 6.4.22 Ribbon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.23 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.24 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.25 ZTE Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











