 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850383
農業機器人:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Agricultural Robots - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
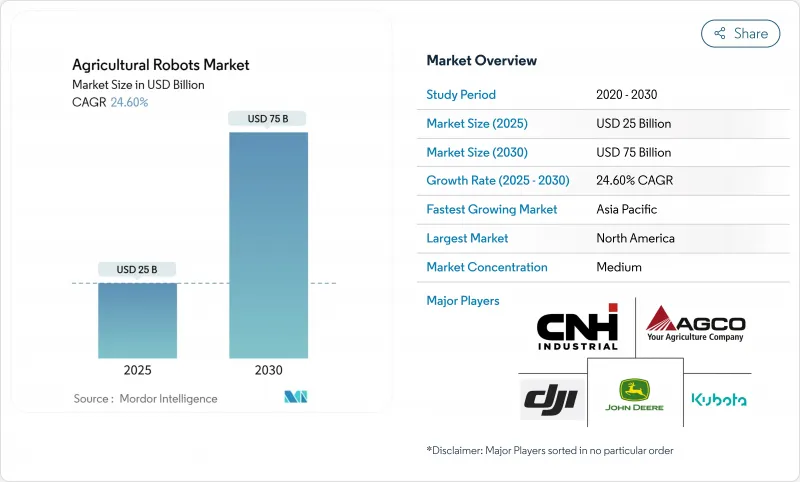
預計到 2025 年,農業機器人市場規模將達到 250 億美元,到 2030 年將成長至 750 億美元,複合年成長率為 24.6%。
這一成長的驅動力源於農民對整合人工智慧、電腦視覺和精準感測器的自主機器的迫切需求,以彌補勞動力短缺、提高產量並減少投入浪費。對能夠在大面積農田和特色作物上晝夜運作的靈活設備的強勁需求,持續推動著對新型田間作業平台的資金流入,同時,零部件價格的下降也使得曾經的高階技術能夠被中型種植戶所接受。儘管硬體仍然是主要的收入來源,但隨著種植者優先考慮整合決策支援、預測性維護和雲端基礎的車隊協調,軟體和服務合約的持續成長正在迅速擴大。創投公司和企業投資者將農業機器人市場視為更廣泛的農業科技生態系統的核心支柱,並持續為解決特定痛點的新興企業提供資金,例如無農藥除草、選擇性收割以及跨不同農業資產的數據融合。最後,政府對永續實踐的補貼將透過承擔部分初始成本和明確自主機器的安全規則來加速其普及。
全球農業機器人市場趨勢與洞察
長期勞動力短缺和農業人口老化
隨著經驗豐富的工人退休,年輕一代轉向非農業領域,勞動力短缺正成為一項結構性挑戰。在美國,由於無法獲得季節性工人,60%的農業相關企業已將計劃延後至2024年,而勞動成本已佔加州高價值農場生產成本的40%。自主機器人能夠提供持續穩定的勞動力,運作且無需加班,從而提高田間作業的連續性並緩解工資上漲壓力。供應商目前優先考慮易於實施性,使農民只需接受極少的培訓即可整合機器人設備,進一步降低了進入門檻。
增加創投和企業對農業機器人領域的投資
儘管農業科技領域的整體資金籌措有所下降,但預計2024年農業機器人領域的投資將成長9%,這印證了投資人對可擴展自動化解決方案的信心。紐荷蘭公司已與Bluewhite公司合作,為果園和葡萄園主提供專業的曳引機改裝服務,預計可降低高達85%的營運成本。 Verdant Robotics、Fieldwork Robotics和其他新興企業已獲得數百萬美元的融資,這將縮短產品開發週期並加速國際市場推廣。由此引發的創新浪潮正使農業機器人市場高度活躍且競爭激烈。
小農戶前期投入成本高,投資報酬率不確定。
一套全自動擠乳設備的成本約為每頭牛1萬美元,一個擁有180頭乳牛的酪農則需要近200萬美元。許多小型農戶缺乏獲得經濟實惠的融資和租賃方案的途徑,而商品價格波動又導致投資回收期過長。模組化設計和合作所有權模式的出現旨在分攤資本負擔,但在價格敏感的地區,其經濟可行性仍然是一大障礙。
細分市場分析
到2024年,無人機將維持農業機器人市場35%的佔有率,因為種植者依賴空中影像、變數噴灑和作物脅迫檢測來提高投入效率。大疆創新(DJI)報告稱,全球已有超過40萬架無人機正在處理5億公頃的農田,證實了無人機作為早期自動化門戶的角色。隨著各國空域管理部門完善允許超視距飛行的規則,與無人機硬體和相關軟體訂閱相關的農業機器人市場規模預計將穩定成長。
由於蔬果種植者面臨嚴重的採摘工人短缺和緊迫的收穫期限,自動收割機將以26%的複合年成長率成為成長最快的領域。 Fieldwork Robotics公司的覆盆子收割機每小時採摘150-300個果實,產量已達到人工水平,並有望實現夜班連續運作。無人駕駛曳引機也正以27%的成長率快速發展,因為原始設備製造商(OEM)正在為現有車輛加裝感知套件,以管理耕作、播種和糧食處理作業。
區域分析
由於農場規模龐大、監管寬鬆以及創業投資充裕,北美地區預計2024年仍將佔據37%的農業機器人市場。 Carbon Robotics公司籌集了7000萬美元用於擴大其第二代雷射除草機的生產,這反映出投資者對無化學除草技術的信心。美國正在修訂無人駕駛曳引機的安全法規,這預示著田間自動駕駛將成為主流。加拿大對穀物和墨西哥對高價值園藝產品的需求成長將擴大這些地區的市場應用。
亞太地區將以25.5%的複合年成長率實現最快增速,這主要得益於中國對國內機器人技術領軍企業的大力扶持以及對糧食安全目標的持續關注。日本政府正在為老齡化農民群體提供果園自動化解決方案的補貼,而澳洲的國家機器人戰略則計劃透過更廣泛的自動化應用,為國內生產總值(GDP)帶來6,000億澳元(約4,200億美元)的收益。印度正在探索低成本的除草和噴灑機器人,以適應小型農民的預算,但網路連接和資金籌措是主要障礙。
在勞動力短缺、永續性法規和高標準的作物保護的推動下,歐洲正穩步推動自動化農業。歐盟的《機械法規》納入了自主移動機械的新條款,為製造商提供了清晰的合規藍圖。德國正在試用芬特e100 Vario全電動式曳引機,該曳引機只需一塊100千瓦時的電池即可實現4至7小時的零排放田間作業。在英國,津貼計畫正在抵銷機器人購買成本;法國和西班牙則正在葡萄園和橄欖園測試多機器人除草機。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 長期勞動力短缺和農業人口老化
- 增加創投和企業對農業機器人的投資
- 政府對智慧農業自動化的獎勵
- 人工智慧、視覺和LiDAR技術的快速發展
- 夜間自動駕駛可避免中暑
- 對不含殺蟲劑的雷射除草解決方案的需求
- 市場限制
- 小農戶面臨前期投入成本高、投資報酬率不確定等問題。
- 農村地區即時控制連接的差距
- 關於動物與機器人互動的倫理問題
- 自主機器的碎片化認證
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 買方/消費者的議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按類型
- 無人駕駛飛行器(無人機)
- 擠乳機器人
- 無人曳引機
- 自動收割系統
- 多用途田間機器人
- 分揀包裝機器人
- 透過使用
- 大面積使用
- 田間測繪
- 播種和種植
- 施肥和灌溉
- 栽培管理工作
- 採摘和收穫
- 酪農
- 擠乳
- 牧羊人與牧民
- 空中數據採集
- 氣象追蹤與預報
- 庫存管理
- 溫室自動化
- 果園管理
- 大面積使用
- 報價
- 硬體
- 自主導航系統
- 感測器和視覺系統
- 機械臂和末端執行器
- 軟體
- 機器人作業系統
- 農場管理平台
- 數據分析與人工智慧演算法
- 服務
- 整合與部署
- 維護和升級
- 資料即服務
- 硬體
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 義大利
- 俄羅斯
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Agrobot
- Harvest Automation Inc.(Tertill)
- AGCO Corporation
- Lely International NV
- Naio Technologies SAS
- Deere & Company
- AgEagle Aerial Systems Inc.
- CNH Industrial NV
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- GEA Group AG
- Kubota Corporation
- SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd.
- BouMatic LLC
- Topcon Corporation
- Yamaha Agriculture Inc.,(Yamaha Motor)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The agricultural robots market is valued at USD 25 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 75 billion by 2030, reflecting a 24.6% CAGR.

This growth stems from farmers' urgent need to offset labor shortages, raise yields, and cut input waste through autonomous machines that integrate artificial intelligence, computer vision, and precision sensors. Strong demand for flexible equipment that can operate day and night across broad-acre and specialty crops keeps capital flowing toward new field-ready platforms while falling component prices make once-premium technologies affordable to mid-sized producers. Hardware remains the revenue anchor today, yet recurring software subscriptions and service agreements expand rapidly as growers prioritize integrated decision support, predictive maintenance, and cloud-based fleet coordination. Venture and corporate investors view the agricultural robots market as a core pillar of the wider AgTech ecosystem and continue financing start-ups that solve specific pain points, such as chemical-free weeding, selective harvesting, and data fusion across disparate farm assets. Finally, government subsidies that reward sustainable practices accelerate adoption by absorbing part of the upfront cost and by clarifying safety rules for autonomous machines.
Global Agricultural Robots Market Trends and Insights
Chronic Labor Shortages and Aging Farmer Population
Labor scarcity has risen to a structural challenge as experienced workers retire and younger generations pursue non-farm careers. In the United States, 60% of agribusinesses postponed projects during 2024 because they could not secure seasonal crews, and labor already accounts for 40% of production costs on high-value California farms. Autonomous robots provide a consistent workforce that operates around the clock without overtime, improving field-work continuity and mitigating wage inflation pressures. Suppliers now emphasize ease of deployment to help growers integrate robotic units with minimal training, further lowering the barrier to entry.
Rising Venture and Corporate Investments in Ag-Robotics
Despite a dip in broader AgTech funding, capital committed to farm robotics rose 9% in 2024, underscoring investor conviction in scalable automation solutions. New Holland partnered with Bluewhite to retrofit specialty tractors, a collaboration expected to trim operating costs by up to 85% for orchard and vineyard owners. Verdant Robotics, Fieldwork Robotics, and other start-ups have secured multi-million-dollar rounds that shorten product-development cycles and accelerate international launches. The resulting innovation wave keeps the agricultural robot market highly dynamic and competitive.
High Upfront Cost and Uncertain ROI for Smallholders
A fully automated milking parlor can cost USD 10,000 per cow, translating into nearly USD 2 million for a 180-cow dairy. Many smallholders cannot access affordable finance or lease programs, and fluctuating commodity prices lengthen the payback horizon. Modular designs and cooperative ownership models have emerged to spread capital burdens, yet economic feasibility remains a hurdle in price-sensitive regions.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Incentives for Smart Farming Automation
- Rapid Advances in AI, Vision, and LIDAR Technologies
- Fragmented Certification for Autonomous Machinery
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
UAVs retained 35% of the agricultural robots market share in 2024 as growers relied on aerial imagery, variable-rate spraying, and crop-stress detection to raise input efficiency. DJI reported more than 400,000 drones treating 500 million hectares worldwide, confirming drones' role as an early-stage automation gateway. The agricultural robots market size tied to UAV hardware and associated software subscriptions is forecast to expand steadily as national airspace authorities refine rules that permit beyond-visual-line-of-sight missions.
Automated harvesters log the fastest 26% CAGR because fruit and vegetable producers confront severe picker shortages and tight harvest windows. Fieldwork Robotics' raspberry unit already matches human throughput at 150 to 300 berries per hour and promises continuous operation through night shifts. Driverless tractors also gain momentum at a 27% growth clip as OEMs retrofit existing fleets with perception kits that manage tillage, seeding, and grain-cart duties.
The Agricultural Robots Market Report is Segmented by Type (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drones), Milking Robots, Driverless Tractors, and More), Application (Broad Acre Applications, Dairy Farm Management, Aerial Data Collection, and More), Offering (Hardware, Software, and Services), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 37% of the agricultural robots market in 2024 due to large farm sizes, supportive regulatory sandboxes, and deep venture capital pools. Carbon Robotics raised USD 70 million to scale its second-generation LaserWeeder, reflecting investor confidence in chemical-free weed control. The United States reviews safety rules for driverless tractors, signaling a path toward mainstream field autonomy. Canada and Mexico add demand through grains and high-value horticulture, respectively, broadening the region's adoption base.
Asia-Pacific posts the fastest 25.5% CAGR as China funds domestic robotics champions and monitors food-security objectives. The Japanese government subsidizes autonomous orchard solutions for an aging farming population, while Australia's National Robotics Strategy targets AUD 600 billion (USD 420 billion) in GDP gains from wider automation. India explores low-cost weeding and spraying robots tailored to smallholder budgets, though connectivity and financing remain obstacles.
Europe advances steadily, spurred by labor shortages, sustainability regulation, and high crop protection standards. The European Union's Machinery Regulation includes new provisions for autonomous mobile machines, giving manufacturers a clearer compliance roadmap. Germany pilots the fully electric Fendt e100 Vario tractor, proving zero-emission field work over four to seven hours of operation on a single 100 kWh battery. The United Kingdom's grant program offsets robotics purchases, and France and Spain test multi-robot weeders in vineyards and olive groves.
- Agrobot
- Harvest Automation Inc. (Tertill)
- AGCO Corporation
- Lely International N.V
- Naio Technologies SAS
- Deere & Company
- AgEagle Aerial Systems Inc.
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- GEA Group AG
- Kubota Corporation
- SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd.
- BouMatic LLC
- Topcon Corporation
- Yamaha Agriculture Inc., (Yamaha Motor)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Chronic labor shortages and an aging farmer population
- 4.2.2 Rising venture and corporate investments in ag-robotics
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for smart farming automation
- 4.2.4 Rapid advances in AI, vision, and LIDAR technologies
- 4.2.5 Night-time autonomous operations to avoid heat stress
- 4.2.6 Demand for pesticide-free laser weeding solutions
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost and uncertain ROI for smallholders
- 4.3.2 Gaps in rural connectivity for real-time control
- 4.3.3 Ethical concerns over animal-robot interaction
- 4.3.4 Fragmented certification for autonomous machinery
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drones)
- 5.1.2 Milking Robots
- 5.1.3 Driverless Tractors
- 5.1.4 Automated Harvesting Systems
- 5.1.5 Multi-purpose Field Robots
- 5.1.6 Sorting and Packaging Robots
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Broad Acre Applications
- 5.2.1.1 Field Mapping
- 5.2.1.2 Seeding and Planting
- 5.2.1.3 Fertilizing and Irrigation
- 5.2.1.4 Intercultural Operations
- 5.2.1.5 Picking and Harvesting
- 5.2.2 Dairy Farm Management
- 5.2.2.1 Milking
- 5.2.2.2 Shepherding and Herding
- 5.2.3 Aerial Data Collection
- 5.2.4 Weather Tracking and Forecasting
- 5.2.5 Inventory Management
- 5.2.6 Greenhouse Automation
- 5.2.7 Fruit Orchard Operations
- 5.2.1 Broad Acre Applications
- 5.3 By Offering
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.1.1 Autonomous Navigation Systems
- 5.3.1.2 Sensors and Vision Systems
- 5.3.1.3 Robotic Arms and End Effectors
- 5.3.2 Software
- 5.3.2.1 Robot Operating Systems
- 5.3.2.2 Farm Management Platforms
- 5.3.2.3 Data Analytics and AI Algorithms
- 5.3.3 Services
- 5.3.3.1 Integration and Deployment
- 5.3.3.2 Maintenance and Upgrades
- 5.3.3.3 Data-as-a-Service
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Spain
- 5.4.3.5 Italy
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 Australia
- 5.4.4.5 South Korea
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.6 Africa
- 5.4.6.1 South Africa
- 5.4.6.2 Egypt
- 5.4.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Agrobot
- 6.4.2 Harvest Automation Inc. (Tertill)
- 6.4.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Lely International N.V
- 6.4.5 Naio Technologies SAS
- 6.4.6 Deere & Company
- 6.4.7 AgEagle Aerial Systems Inc.
- 6.4.8 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.9 Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 GEA Group AG
- 6.4.11 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.12 SZ DJI Technology Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 BouMatic LLC
- 6.4.14 Topcon Corporation
- 6.4.15 Yamaha Agriculture Inc., (Yamaha Motor)












