 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1850314
網路切片:市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Network Slicing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
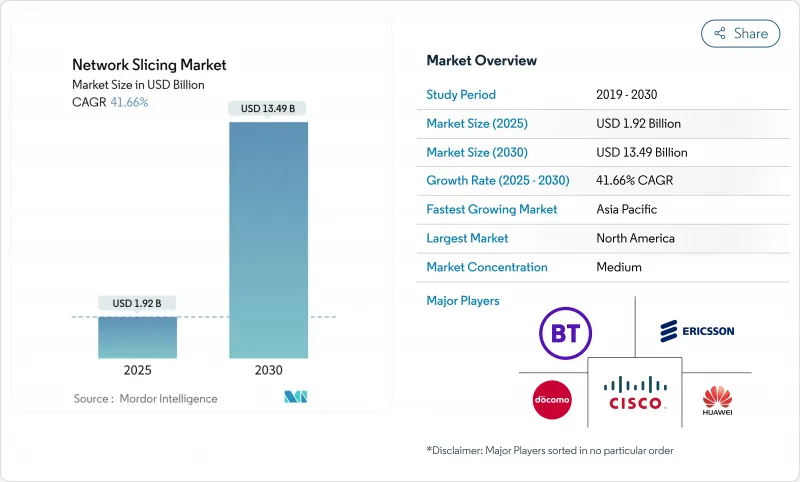
預計到 2025 年,網路切片市場規模將達到 19.2 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 134.9 億美元,預測期(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 41.66%。
從盡力而為的連接模式向可編程、服務差異化網路的轉變是推動通訊服務供應商(CSP) 實現 5G 獨立組網 (SA) 投資收益的關鍵因素,它使 CSP 能夠通過具有服務級別保證的虛擬網路段來實現這一目標。 5G SA 的快速部署、工業 4.0 工廠對超可靠低延遲通訊(URLLC) 的需求以及「切片即服務」模式的吸引力,都在加速這一趨勢的普及。隨著基礎設施供應商、雲端原生軟體專家和超大規模資料中心業者競相提供能夠自動化切片生命週期管理的編配平台,競爭日益激烈。儘管供應鏈限制(例如半導體 56 週的前置作業時間)仍然存在,營運商仍然優先考慮軟體投資,以透過網路即代碼 API 獲取開發者主導的收益源。
全球網路切片市場趨勢與洞察
5G SA部署加速了通訊服務供應商的需求轉變
獨立組網(SA)5G架構充分釋放了網路切片的強大功能,使營運商能夠快速部署隔離的邏輯網路,並提供傳統核心網無法實現的可靠服務水準。到2024年4月,日本的5G基地台覆蓋率將達到98%,這將推動SA升級,並標誌著全球轉型為支援切片的基礎設施。愛立信與12家一級通訊業者合作,目標是在2030年前打造一個價值300億美元的網路API市場,並以切片技術作為可程式化的基礎。 T-Mobile部署混合專用5G+切片技術用於緊急醫療資料傳輸,展現了差異化連接的商業化速度之快。
企業專用網路對URLLC和eMBB切片的需求
工業企業將網路切片視為實現確定性連接的最經濟途徑。在義大利,愛立信、TIM 和 Comau 利用低於 10 毫秒的網路切片技術將數位雙胞胎與機器人同步,在預測性維護和遠端擴增實境 (AR) 支援方面證明了其營運優勢。韓國已於 2024 年 2 月前向 56 個地點分配了私有 5G 頻譜,這表明監管機構支持依賴網路切片隔離的企業級基礎設施。
新興國家 5G 普及率和設備準備度較低
網路切片需要廣泛的獨立組網(SA)覆蓋範圍以及允許用戶選擇切片的設備,但截至2024年底,中國的SA覆蓋率將達到80%,而歐洲僅為2%。印尼5G競標的延遲表明,政策缺口會如何減緩網路部署速度,並降低營運商投資切片平台的意願。
細分分析
到2024年,軟體將佔據網路切片市場45.50%的佔有率,年複合成長率(CAGR)將達到44.25%,營運商將重點放在編配、保障和安全工具上。衍生軟體平台和與無線無關的控制邏輯的網路切片市場預計到2030年將超過60億美元。供應商透過基於意圖的策略引擎來區分彼此,這些引擎可以即時調整切片頻寬。用於隔離租戶流量和檢驗切片完整性的安全模組現在已整合到產品目錄中,而不是作為附加元件出售,這加快了產品上市速度並支援多租戶收益。雖然基礎設施硬體對於5G SA核心網路仍然至關重要,但由於通訊服務供應商(CSP)投資於自動化切片管理,同時消耗了現有的無線接取網路(RAN)資產,其成長正在放緩。傳輸升級的驅動力是需要確保微波、光纖和IP/MPLS連結的確定性延遲。
重視整體擁有成本的營運商傾向於採用具有開放介面的解耦式基礎設施,這種基礎設施允許雲端原生網路功能駐留在通用伺服器上。這種轉變緩解了資本支出高峰,加速了軟體的普及,並強化了自動化在網路切片市場的核心地位。嵌入城域資料中心的多接取邊緣運算(MEC) 節點進一步擴展了軟體的覆蓋範圍,並支援為對延遲敏感的工作負載實例化本地化切片。
到2024年,託管服務將佔據網路切片市場55.45%的佔有率,複合年成長率(CAGR)為42.36%。供應商經營的入口網站可讓IT管理員按需申請網路切片、設定服務品質等級並按使用量收費。隨著通訊服務提供者(CSP)將連接性與安全性和邊緣運算捆綁在一起,作為託管服務一部分的網路切片市場規模到2030年可能超過70億美元。網路即服務(NaaS)模式對缺乏內部頻譜專業知識的中型企業極具吸引力,而政府機構則採用託管網路切片來保障公共影像,並受益於自主資料託管的保障。
專業服務,包括諮詢、整合和測試,為複雜的部署週期提供了便利的入口。系統編配企業級 SD-WAN、ERP 和物聯網平台,進而降低部署風險。概念驗證實驗室在商業化切換前檢驗吞吐量和延遲目標,減少手術機器人和即時品質檢測等關鍵任務應用場景的不確定性。
網路切片市場報告按組件(基礎設施[RAN、核心網、傳輸網]、軟體[MANO、分析、安全])、服務(專業服務[諮詢、整合、測試]、其他)、應用(遠端監督和監控、網路功能虛擬化、雲端RAN、其他)、最終用戶產業(醫療保健、汽車、運輸、其他)和地區進行細分。
區域分析
受早期5G獨立組網(SA)推出和寬鬆頻譜政策的推動,北美將在2024年佔據網路切片市場34.92%的佔有率。像T-Mobile這樣的通訊服務提供者(CSP)正在全國範圍內開放切片訂購API,允許企業將私人網路覆蓋整合到其公共網路中。 Verizon向洛杉磯和芝加哥的緊急應變人員提供的第一線網路切片,正透過高級服務等級協定(SLA)帶來額外收入。創業投資正湧入編配新興企業,強化有利於雲端原生設計的創新循環。半導體短缺導致無線電單元的前置作業時間延長至56週,但由於採用多供應商採購模式,營運商仍能按計畫完成交付。
亞太地區預計將以42.22%的複合年成長率實現最快成長,這主要得益於中國5G基地台數量突破228萬,以及監管機構加速推進企業級網路切片試驗。日本內務部已頒發本地5G牌照,允許工廠自行部署獨立組網(SA)網路,目前已有72個示範計劃,涵蓋智慧港口、物流樞紐和體育場館等領域。韓國已向35家企業集團分配專用頻譜,從而促進了支援網路切片的設備和無線接入網(RAN)自動化設備的供應商生態系統的發展。
歐洲的獨立組網(SA)覆蓋率僅為2%,遠落後於其他國家,這限制了短期內網路切片技術的收益,但相關政策正在改變。已有七個國家開放了26 GHz頻段用於本地5G網路,另有六個國家允許在3.4-3.8 GHz頻段內使用高達100 MHz的頻譜,從而為製造業和科研機構的園區網路提供了支援。沃達豐與英國Three公司價值202.8億美元的合併案承諾,到2035年將投入148.6億美元用於網路升級,這將加速SA和網路切片技術的普及。在中東,歐洲廠商正與當地通訊業者合作試行傳輸網路切片技術,檢驗相關架構,以便在頻寬和投資趨於平衡後,能夠覆蓋歐洲的網路。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 5G SA部署加速了CSP需求的轉變
- 企業專用網路對URLLC和eMBB切片的需求
- 邊緣雲端整合支援動態切片編配
- 在平均每位用戶收入停滯不前的情況下,CSP(通訊服務提供者)的收益是亟待解決的問題。
- 鮮為人知的是:網路即程式碼 API 推動了開發者主導的Slice 採用
- 低調存在:基於權利的遠端廣播套餐(體育、選舉)
- 市場限制
- 新興國家5G普及率及設備準備度低
- 多域編配的複雜性和營運成本負擔
- 未被察覺:碎片化的SLA安全認證標準
- 未被關注的焦點:動態頻譜共用的監管不不確定性
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 監管格局
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 定價分析
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按組件
- 基礎設施(無線存取網、核心網、傳輸網)
- 軟體(MANO、分析、安全)
- 按服務
- 專業(諮詢、整合、測試)
- 託管式(網路即服務、切片即服務)
- 按用途
- 遠端監控與監視
- 網路功能虛擬化與雲端無線存取網
- 行動雲端遊戲和媒體串流
- 遠端工業自動化(IIoT)
- 按最終用戶產業
- 衛生保健
- 汽車和運輸
- 電力和能源
- 航太
- 媒體與娛樂
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- Nokia
- Cisco Systems
- Samsung Electronics
- ZTE
- NEC
- BT Group
- NTT DOCOMO
- Mavenir
- Affirmed Networks
- Argela Technologies
- Aria Networks
- Juniper Networks
- Keysight Technologies
- NetScout
- Verizon Communications
- ATandT
- T-Mobile US
- Deutsche Telekom
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The Network Slicing Market size is estimated at USD 1.92 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 13.49 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 41.66% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The shift from best-effort connections to programmable, service-differentiated networks is the prime catalyst, enabling communication service providers (CSPs) to monetize 5G standalone (SA) investments through virtual network segments with guaranteed service levels. Rapid 5G SA roll-outs, the need for ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in Industry 4.0 plants, and the appeal of slice-as-a-service models are accelerating adoption. Competitive intensity is rising as infrastructure vendors, cloud-native software specialists, and hyperscalers race to deliver orchestration platforms that automate slice life-cycle management. Supply-chain constraints persist, notably 56-week semiconductor lead times, yet operators continue to prioritize software investments to capture developer-led revenue streams through network-as-code APIs.
Global Network Slicing Market Trends and Insights
5G SA Roll-Outs Accelerating CSP Demand Shift
Standalone 5G architecture unlocks full network slicing capabilities, letting operators spin up isolated logical networks with guaranteed service levels that legacy cores cannot provide. Japan reached 98% 5G base-station coverage in designated areas by April 2024, spurring SA upgrades and signaling a global pivot toward slicing-ready infrastructure. Ericsson's alliance with 12 tier-one operators targets a USD 30 billion network-API market by 2030, relying on slicing as the foundation for programmability. T-Mobile's hybrid private-5G-plus-slicing deployment for emergency medical data shows how differentiated connectivity can be commercialized quickly.
Enterprise Private-Network Demand for URLLC & eMBB Slices
Industrial companies view slicing as the most economical route to deterministic connectivity. In Italy, Ericsson, TIM, and Comau synchronized robots with digital twins using sub-10 ms slices, proving operational gains in predictive maintenance and remote AR support. South Korea allocated private 5G spectrum to 56 sites by February 2024, illustrating regulator support for enterprise-run infrastructure that relies on slice isolation.
Low 5G Penetration and Device Readiness in Emerging Economies
Network slicing demands widespread SA coverage plus handsets able to select slices, yet Europe had only 2% SA coverage versus China's 80% at end-2024. Delays in Indonesia's 5G auctions illustrate how policy gaps can slow roll-outs, reducing operator incentive to invest in slice platforms.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Edge-Cloud Convergence Enabling Dynamic Slice Orchestration
- CSP Monetization Urgency Amid ARPU Stagnation
- Multi-Domain Orchestration Complexity and OPEX Burden
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Software held a 45.50% share of the network slicing market in 2024 and is growing at a 44.25% CAGR, thanks to operator focus on orchestration, assurance, and security tooling. The network slicing market size derived from software platforms is projected to exceed USD 6 billion by 2030 alongside radio-agnostic control logic. Vendors differentiate through intent-based policy engines that adjust slice bandwidth in real time. Security modules that isolate tenant traffic and validate slice integrity are now baked into catalogues rather than sold as add-ons, lowering time to market and supporting multitenant monetization. Infrastructure hardware remains essential for 5G SA cores, yet its growth lags as CSPs sweat existing RAN assets while directing new funds to automated slice management. Transport upgrades continue, spurred by the need to guarantee deterministic latency across microwave, fiber, and IP/MPLS links.
Operators evaluating total cost of ownership favor disaggregated infrastructure with open interfaces, allowing cloud-native network functions to reside on commodity servers. This pivot moderates capex peaks and accelerates software uptake, reinforcing the central role of automation in the network slicing market. Multi-access edge computing (MEC) nodes embedded in metro data centers further extend software's reach, enabling localized slice instantiation for latency-sensitive workloads.
Managed services controlled 55.45% of the network slicing market share in 2024 and should post a 42.36% CAGR, reflecting enterprise preference for turnkey slice-as-a-service offerings. Vendor-operated portals now let IT managers request slices on demand, set quality-of-service tiers, and receive usage-based billing. The network slicing market size tied to managed services will likely surpass USD 7 billion by 2030 as CSPs bundle security and edge compute with connectivity. Network-as-a-service (NaaS) variants appeal to mid-market firms lacking in-house spectrum expertise, while government agencies adopt managed slices for public-safety footage, benefiting from sovereign data-hosting guarantees.
Professional services, including consulting, integration, and testing, serve as on-ramps for complex adoption cycles. Systems integrators align slice orchestration with enterprise SD-WAN, ERP, and IoT platforms, de-risking deployment. Proof-of-concept labs validate throughput and latency targets before commercial cut-over, reducing uncertainty for mission-critical use cases such as surgical robotics or real-time quality inspection.
The Network Slicing Market Report is Segmented by Component (Infrastructure [RAN, Core, Transport] and Software [MANO, Analytics, Security]), Service (Professional [Consulting, Integration, Testing] and More), Application (Remote Monitoring & Surveillance, Network Function Virtualization and Cloud RAN, and More), End-User Industry (Healthcare, Automotive and Transportation, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
North America held a 34.92% share of the network slicing market in 2024, anchored by early 5G SA launches and permissive spectrum policies. CSPs such as T-Mobile expose slice order APIs nationwide, letting enterprises stitch private coverage into public footprints. Verizon's Frontline Network Slice caters to first responders in Los Angeles and Chicago, generating incremental revenue via premium SLA tiers. Venture capital flows into orchestration start-ups, reinforcing an innovation loop that favors cloud-native design. Semiconductor shortages have lengthened radio unit lead times to 56 weeks, yet operators remain on schedule thanks to multi-vendor sourcing.
Asia Pacific is projected to deliver a 42.22% CAGR, the fastest regional pace, as China surpasses 2.28 million 5G sites and regulators expedite enterprise slice pilots. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications issues local 5 G licenses that let factories self-deploy SA networks; 72 demonstration projects now span smart ports, logistics hubs, and stadiums. South Korea allocates dedicated spectrum to 35 conglomerates, stimulating a supplier ecosystem around slice-aware devices and RAN automation.
Europe lags on SA coverage at 2%, constraining near-term slice revenues, yet policy is shifting. Seven nations opened the 26 GHz band for local 5G, and six permit up to 100 MHz in the 3.4-3.8 GHz band, enabling campus networks for manufacturing and research. The USD 20.28 billion Vodafone-Three UK merger pledges USD 14.86 billion in network upgrades by 2035, which should accelerate SA and slicing adoption. In the Middle East, European vendors pilot transport-network slicing with regional operators, validating architectures that may backfill Europe once spectrum and investment converge.
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- Nokia
- Cisco Systems
- Samsung Electronics
- ZTE
- NEC
- BT Group
- NTT DOCOMO
- Mavenir
- Affirmed Networks
- Argela Technologies
- Aria Networks
- Juniper Networks
- Keysight Technologies
- NetScout
- Verizon Communications
- ATandT
- T-Mobile US
- Deutsche Telekom
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 5G SA roll-outs accelerating CSP demand shift
- 4.2.2 Enterprise private-network demand for URLLC and eMBB slices
- 4.2.3 Edge-cloud convergence enabling dynamic slice orchestration
- 4.2.4 CSP monetization urgency amid ARPU stagnation
- 4.2.5 Under-the-radar: "Network-as-Code" APIs catalysing developer-led slice uptake
- 4.2.6 Under-the-radar: Rights-based remote broadcasting packages (sports, elections)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Low 5G penetration and device readiness in emerging economies
- 4.3.2 Multi-domain orchestration complexity, OPEX burden
- 4.3.3 Under-the-radar: Fragmented slice-SLA security certification standards
- 4.3.4 Under-the-radar: Regulatory uncertainty over spectrum-sharing for dynamic slices
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Pricing Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Infrastructure (RAN, Core, Transport)
- 5.1.2 Software (MANO, Analytics, Security)
- 5.2 By Service
- 5.2.1 Professional (Consulting, Integration, Testing)
- 5.2.2 Managed (Network-as-a-Service, Slice-as-a-Service)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Remote Monitoring and Surveillance
- 5.3.2 Network Function Virtualization and Cloud RAN
- 5.3.3 Mobile Cloud Gaming and Media Streaming
- 5.3.4 Remote Industrial Automation (IIoT)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Healthcare
- 5.4.2 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.4.3 Power and Energy
- 5.4.4 Aviation and Aerospace
- 5.4.5 Media and Entertainment
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.4.3 South Africa
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Ericsson
- 6.4.2 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.3 Nokia
- 6.4.4 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.5 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.6 ZTE
- 6.4.7 NEC
- 6.4.8 BT Group
- 6.4.9 NTT DOCOMO
- 6.4.10 Mavenir
- 6.4.11 Affirmed Networks
- 6.4.12 Argela Technologies
- 6.4.13 Aria Networks
- 6.4.14 Juniper Networks
- 6.4.15 Keysight Technologies
- 6.4.16 NetScout
- 6.4.17 Verizon Communications
- 6.4.18 ATandT
- 6.4.19 T-Mobile US
- 6.4.20 Deutsche Telekom
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











